Chapter 4: Newton's Laws
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
Newton’s First Law
When the net force acting on a body is zero, its acceleration must be zero, meaning that the velocity remains constant.
2
New cards
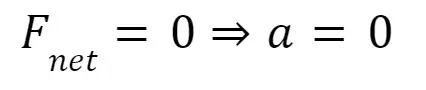
Newton’s First Law
3
New cards
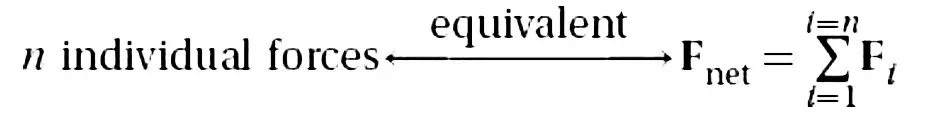
Superposition of Forces
4
New cards
Inertia
It refers to how much an object resists a change in its velocity and is measured by mass.
5
New cards
Newton’s Second Law
This law reveals that force is a vector parallel to the acceleration.
6
New cards
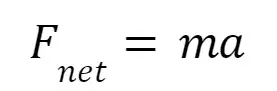
Newton’s Second Law
7
New cards
pounds or newtons
Force is measured in \____________.
8
New cards
Newton’s Third law
For every force exerted by one object on another, there is another force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction that is exerted back by the second object on the first.
9
New cards
Mass
A measure of inertia and is the proportionality constant that relates force to acceleration in Newton’s second law.
10
New cards
Kilograms
SI Unit of Mass
11
New cards
Weight
The magnitude of the force exerted on an object by the closest nearby planet (typically Earth) according to the formula.
12
New cards
Gravitational Force
The most prevalent force in the universe, pulling together on any two objects with mass in the universe.
13
New cards
Normal Force
Denotes FN. Its magnitude is determined by Newton’s second law. Always perpendicular.
14
New cards
Frictional Force
Force that resists the sliding or rolling of one solid object over another.
15
New cards
Static Friction
Objects are not sliding relative to each other.
16
New cards

Static Friction
17
New cards
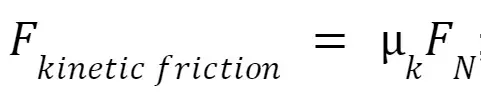
Kinetic Friction
18
New cards
Kinetic Friction
Objects are sliding relative to each other.
19
New cards
Tension Force
A force that develops in a rope, thread, or cable as it is stretched under an applied force.
20
New cards
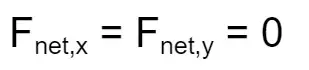
Static equilibrium (object at rest)
21
New cards
centripetal force
The \_________ is the net force required for circular motion . It can be provided by any number of forces such as tension, normal force, gravity, or friction.
22
New cards
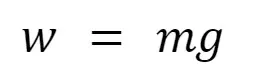
Weight formula