Pharm E1- Peds
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What is the gastric pH in full term infants (for the first 1-3 days)?
6-8 due to amniotic fluid
When does acid content for an infant reach the lower limit of adult values?
3 mos
Why is gastric absorption decreased in infants < 6 mos?
faster gastrointestinal emptying time (GIT)
Intramuscular absorption is ______ in neonates compared to adults.
decreased
Percutaneous absorption is _____ in neonates/infants due to thin skin that’s hydrates & inc perfusion.
increased
What term relates the amount of drug in the body to serum concentration?
volume of distribution (Vd)
A child in a critically ill state that is dehydrated would have ____ Vd
decreased
Why do newborns have increased Vd for hydrophilic medications?
greater extracellular water component → more distribution of drugs
Who has the “bigger bucket"“, requiring higher doses to reach the same blood levels?
neonates
What is the most important pathway in phase 1 metabolism reactions?
oxidation - CYP P450
How is CYP450 activity in full term infants?
half of that of adults (some enzymes dont activate until later)
How is GFR & SrCR in term infants for the 1st week of life?
increased
How is GFR in pre-term infants?
decreased
Tubular secretion & reabsorption are significantly ____ in the 1st year of life
decreased
What has a black box warning in children due to altered activity of CYP2D6 pathway (leading to exaggerated or diminished response)?
Codeine
What is a disadvantage of aged based dosing?
assumes maturation of ADME principles is equal in all patients (6 yr olds & 12 yr olds would respond the same to dose)
What is the MC dosing regimen in kids?
body weight (kids have increased med clearance based on wt)
What are disadvantages of bodyweight dosing?
potenital for overdosing or underdosing in overweight children
What are advantages to BSA dosing?
more precise for meds requiring calculations & limits potential for overdose based on weight
What are disadvantages to BSA dosing?
difficult to estimate & numerous calculations
An invasive bacterial infx occurring in the first 90 days of life, most commonly in LBW infants, is _____
neonatal sepsis
Neonatal sepsis- early onset or late onset?
birth - day 6 of life
group B strep, E coli, listeria
manifestations: bacteremia
early onset
Neonatal sepsis- early onset or late onset?
7-89 days of age
group B strep, e coli, staph, candida
manifestations: bacteremia or focal infx
late onset
What is the treatment for early onset neonatal sepsis?
empiric tx: ampicillin + gentamicin x 10 days
What is the treatment for late onset neonatal sepsis?
ampicillin or vancomycin + gentamicin or cefotaxime
(bacteria x 10 days, meningitis x 14-21 days)
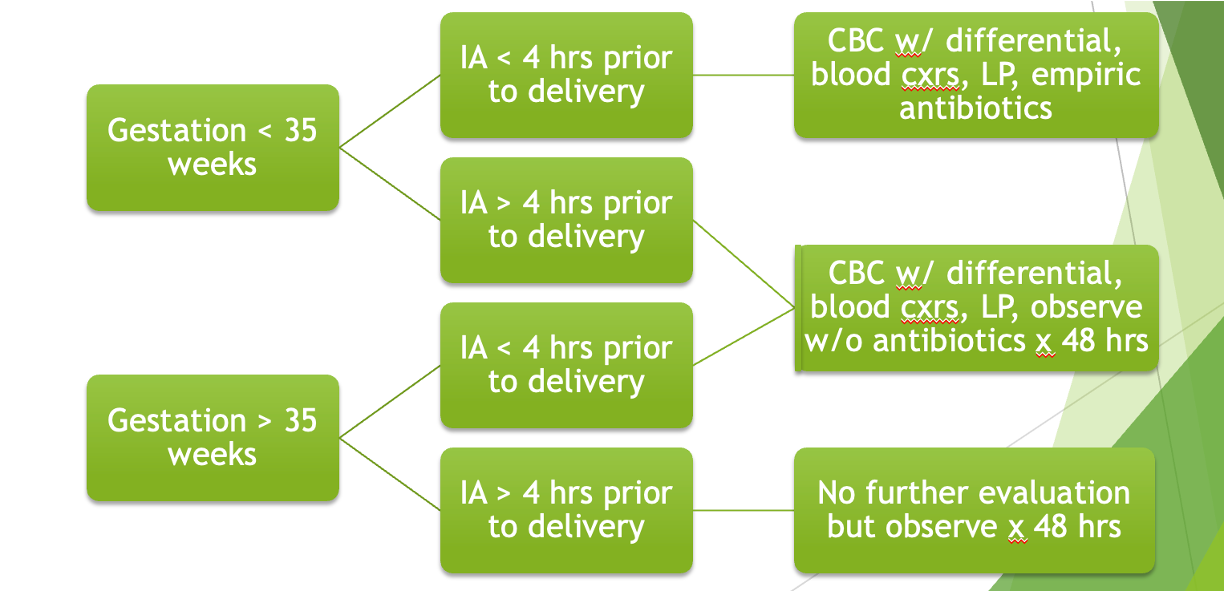
When should intrapartum abx (IA) be given for maternal prevention of GBS sepsis?
positive culture or risk factors (gestation < 37 wks, ROM ≥18 hrs, temp ≥100.4)
What is given for prevention of GBS sepsis?
PCN G q4 hours until delivery
alt: ampicillin
PCN allergy: cefazolin, clindamycin, vancomycin
When do you initiate GBS sepsis treatment in an infant?
ill appearing - start empiric tx
healthy appearing - look at chart
What are indications for tx of HSV in neonates?
first sign of disease or exposure to an active lesion
What is the treatment for neonatal HSV?
acyclovir (*monitor kidney function & BM suppression)
What is the disease of immature lungs caused by a deficiency of pulmonary surfactant?
RDS
When does surfactant production begin?
32 weeks GA (matures by 36 wks)
What factors increase surfactant?
antenatal steroids (betamethasone, dexamethasone), PROM, maternal HTN
What drugs are given for RDS?
Survanta (Beractant), Curosurf (Poractant Alfa), Infasurf (Calfactant), Surafaxin (Lucinactant)
How is RDS treatment administered?
via ET tube divided into 2-4 aliquots in different positions
** do not filter or shake (causes foaming → less effective)
What is the treatment for apnea of prematurity?
caffeine
What is the MC life shortening genetic dz in caucasians in the US that results in defective Cl- channels and abnormal epithelial electrolyte permeability?
cystic fibrosis (CF)
What accounts for 95% of morbidity & mortality in CF?
lung disease
After 6 mos of age, what becomes a repeated process for CF patients?
chronic & recurrent infectious bronchitis
What are the typical organisms associated with lung infections in CF patients?
staph, h. influenzae, pseudo
What organisms are late emerging in CF and indicate an advanced disease?
burkholderia cepacia, strenotrophomonas maltophilia, alcaligenes xylosoxidans, aspergillus
Which phenotype of pseudomonas is associated with a ccellerated decline of pulmonary function?
mucoid
Acute chest infx / “exacerbations” in CF patients are associated with/ high rate of morbidity & mortality and require what?
2-3 wks of intensive therapy
What do 90% of CF patients suffer from?
progressive pancreatic disease (can cause CF related diabetes)
Ketoacidosis is ____ in CF patients with hyperglycemia
rare
How would a CF patient with hypochloremic alkalosis present?
salt “frosting” & salty tasting skin
What is important for young CF patients during warm weather or acute gastroenteritis?
oral/IV hydration (excessive loss of salt in sweat → salt depletion episodes)
What treatment clears mucus from airways using percussion/vibrations and postural drainage?
chest physiotherapy (CPT)
What treatment approach for CF lung infections allows greater concentrations to reach the lungs and has less systemic SEs?
aerosolized abx
What drug?
protein based drug - nebulized once every day
reduces viscosity of CF sputum specimens
shown to decrease number of exacerbations in mild-mod lung dz
Pulmozyme (Dornase Alfa)
What drug can treat pulmonary infx in CF patients, improving rheologic properties (flow), mucus transport, airway hydration, mucociliary clearance, and lung function?
Hypertonic Saline 7% INH
What should the sequence of treatment be for pulmonary exacerbations in CF?
mucolytics → CPT → abx
What IV abx should pseudo be treated in CF patients?
minimum 2 abx (aminoglycoside + B lactam)
What are the antipseudomonal beta lactams?
cefepime, ceftazidime, piperacillin//tazobactam, ticarcillin/clavulanate
What IV aminoglycosides cover pseudo?
tobramycin, gentamicin, amikacin
What oral abx can be used to tx staph pulmonary infx in CF pts?
dicloxacillin, cephalexin, clindamycin, augmentin, macrolide
What oral abx can be used to tx h. influenzae pulmonary infx in CF pts?
amoxicillin, augmentin, 2nd or 3rd gen ceph
What oral abx can be used in young CF pts to prevent admission?
cipro; tobramycin or colistin via inhalation
Antibiotic doses are usually ______ in CF treatment.
higher
What anti-inflammatory agents can be used to treat pulmonary infx in CF patients?
corticosteroids, ibuprofen, macrolides (azithromycin on MWF)
What diet is recommended for CF pediatric patients?
high protein, high calorie, normal amounts of fat
What do pancreatic enzyme replacement therapies for CF patients contain?
lipase, protease, amylase
What are common pancrelipase products used in CF patients?
Pancrease, Creon, Zenpep, Ultrase
What should be added to pancreatic enzyme supplement tx if dosing reaches > 3000 units lipase/kg/meal?
PPI or H2RA to increase fat absorption
What can a high dose of pancreatic enzyme supplements (>20,000 units lipase/kg/day) cause?
fibrosing colonopathy and colonic strictures
What vitamins should be included in GI tx of CF patients?
fat soluble vitamins (aquADEK, source CF, vitamin, ABDEK)
What drug?
tx biliary cirrhosis in CF patients
derived from bear bile
dec cholesterol content of bile by reducing cholesterol secretion form liver
ursodeoxycholic acid (ursodiol - aczigall)
What is contraindicated in the treatment of GERD in CF patients?
cholinergic agonists (increases mucus secretion)
What can be used to treat GERD in CF patients?
PPIs
what drugs?
newer agents for CF - homozygous F508del
take w/ fatty foods
improves CFTR channel
SE: fatigue, rash, mentraul irregularities if on OCP, diarrhea/flatulence, dyspnea, chest discomfort, hepatotoxicity rare (usually well tolerated)
Lumacaftor and Ivacaftor (Orkambi)
What lifestyle modifications can be made for children with GERD?
infants: thicken formula (rice cereal) & hypoallergenic formula
children/adolescents: avoid caffeine, chocolate, & spicy foods
What drug?
neutralizes gastric acid
requires frequent administration
episodic tx for GERD; long term regular use NOT recommended
antacids (calcium carbonate & magnesium/aluminum hydroxide)
What mucosal protectants can be used to treat FERD in pediatric patients?
Sodium alginate (Gaviscon) & Sucralfate (Carafate)
what drug?
prokinetic - DA receptor antagonist
enhance motility of esophageal smooth muscle, accelerate gastric emptying, and inc antral contractions
give 30 mins before meals & at bedtime
Metoclopramide (Reglan)
What drug?
prokinetic - macrolide abx
motion receptor agonist
many drug interactions - CYP3A4 & 1A2 inhibitor
Erythromycin (E.E.S.)
What drugs competitively inhibit interaction of histamine with H2 receptors on the gastric parietal cell resulting in decreased acid secretion?
H2RAs (Nizatidine, Famotidine, etc)
What H2RA should not be used because it is a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor?
cimetidine (Tagamet)
What drugs irreversibly bind and deactivate the H+K+ATPase pump and should NOT be crushed or chewed?
PPIs
which type of constipation is MC in children?
functional
What is the treatment for constipation in breast fed infants?
usually only reassurance and close follow up (common occurrence)
What oral medications can be used to treat constipation in children?
mineral oil, polyethylene glycol electrolyte solutions, mag hydroxide/citrate, lactulose, sorbitol, Senna, bisacodyl
What rectal medications can be given to tx constipation in children?
phosphate soda enemas (avoiding < 6 mos), saline enemas, mineral oil enemas followed by phosphate, glycerin suppository, biscodyl suppository
What enemas are not recommended in children due to electrolyte disturbance?
soapsuds, tap water, magnesium
What should be avoided in very young children (< 6 mos) due to risk of fatal hyperphosphatemia?
phosphate soda enemas
What carbohydrates can be used to treat constipation in children?
prunes, pears, apple juice
What laxatives are not recommended in infants?
stimulant laxatives
What tx is usually given first for infants with constipation?
glycerin suppository