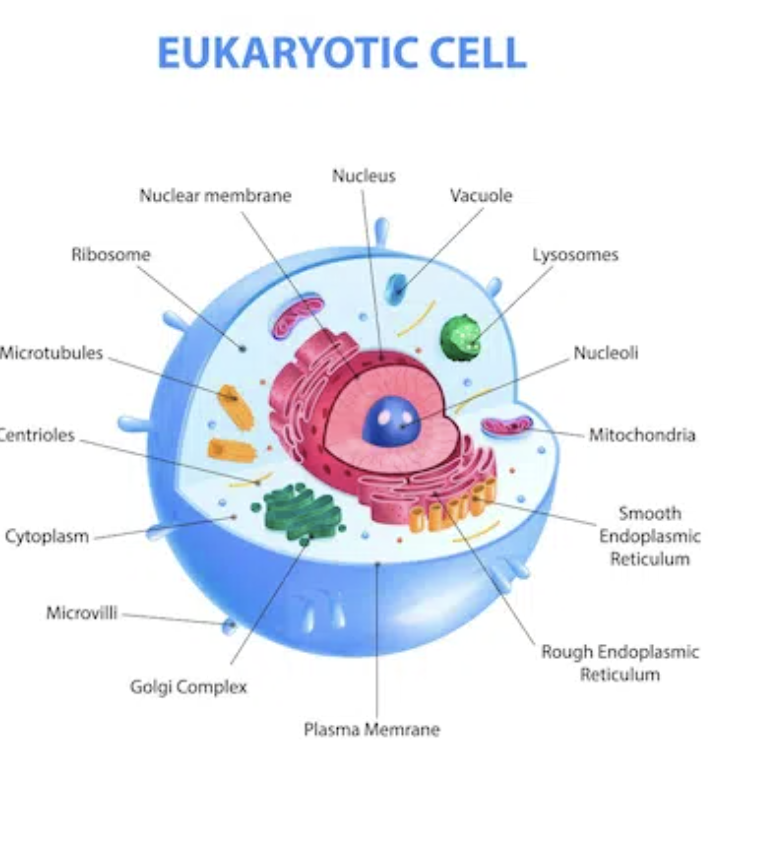
Cells and Organelles
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
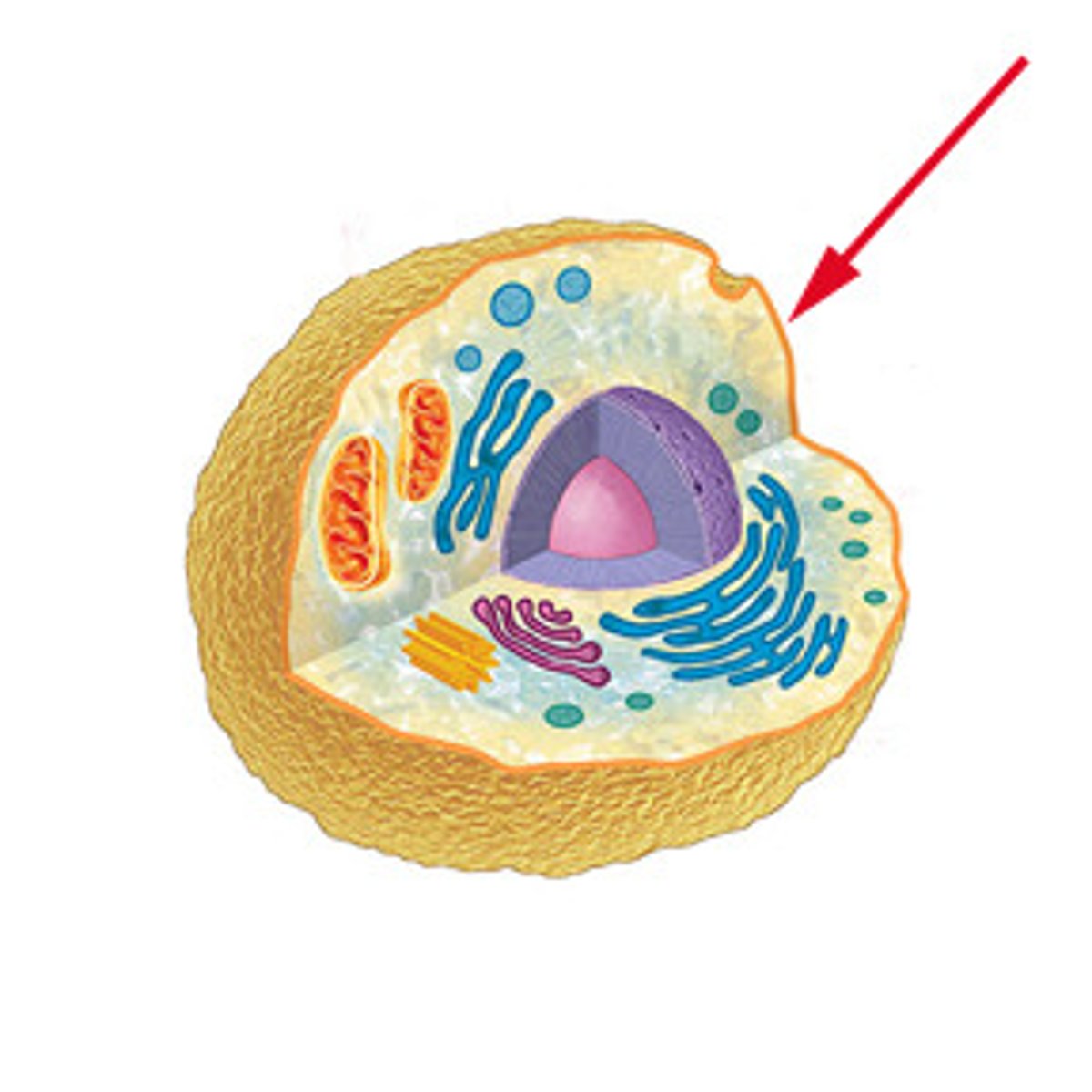
Cell (Plasma) Membrane
This organelle surrounds the cell and encloses all the other organelles within it, acting as a gateway or border that controls and monitors what goes in and out of the cell. This semi-permeable membrane allows a cell to regulate its internal environment by getting the nutrients it needs, getting rid of the waste it doesn’t, as well as protecting the cell from harmful substances.
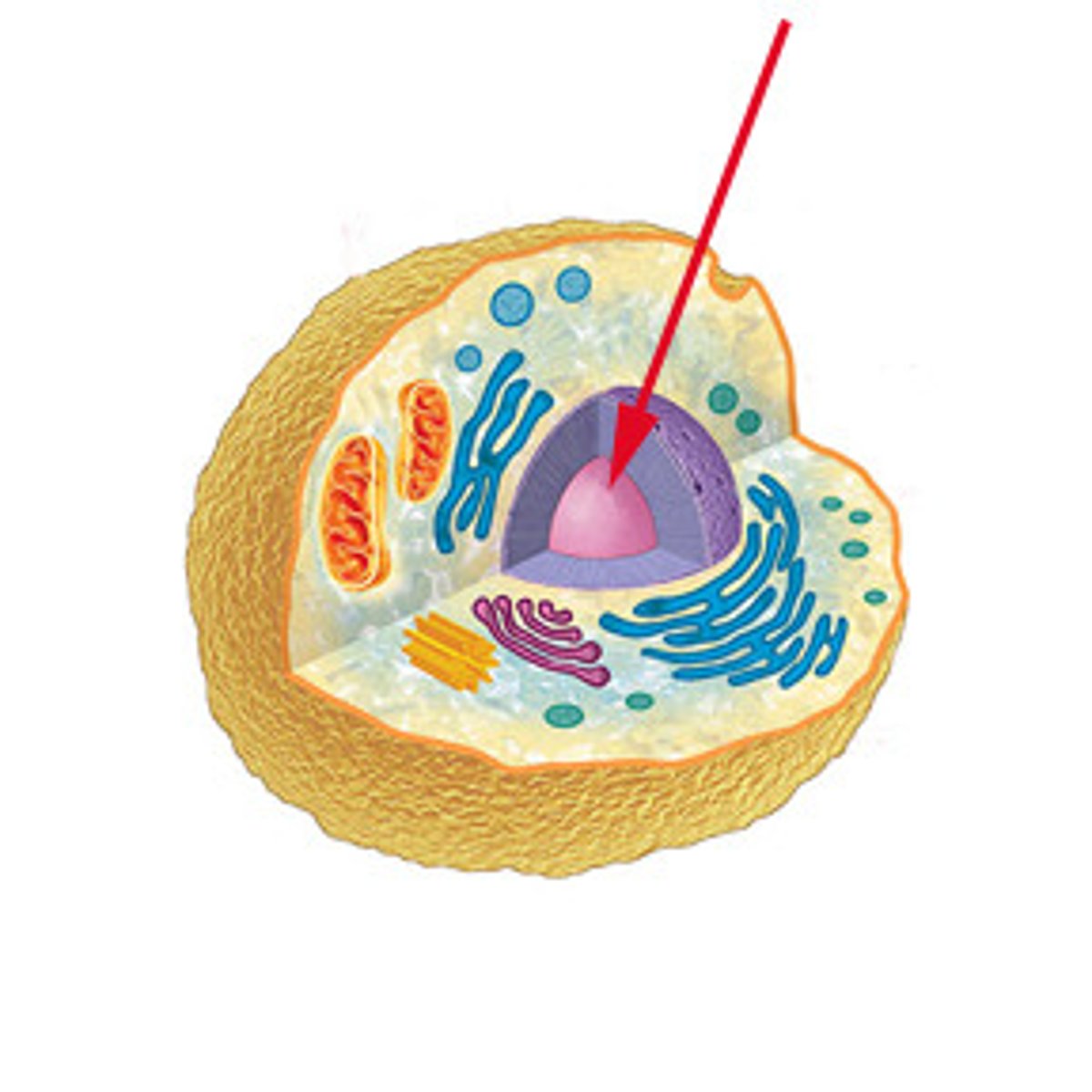
Nucleus
This organelle is the Boss or command center of the cell and stores DNA- the genetic code. This code contains the instructions for life, providing this organelle the information needed to control all cell activities and functions (growth, development, metabolism, reproduction, etc.).
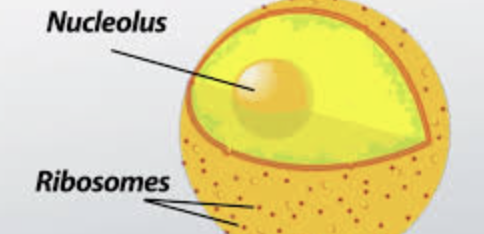
Nucleolus
This structure is found at the center of the Nucleus and its job/function is to create Ribosomes.
Mitochondria
Using a chemical process(reaction) called Cellular Respiration, this organelle breaks down glucose and oxygen to create a type of chemical energy called ATP. This energy powers cell and life functions for all living things and is often called the powerhouse of the cell.
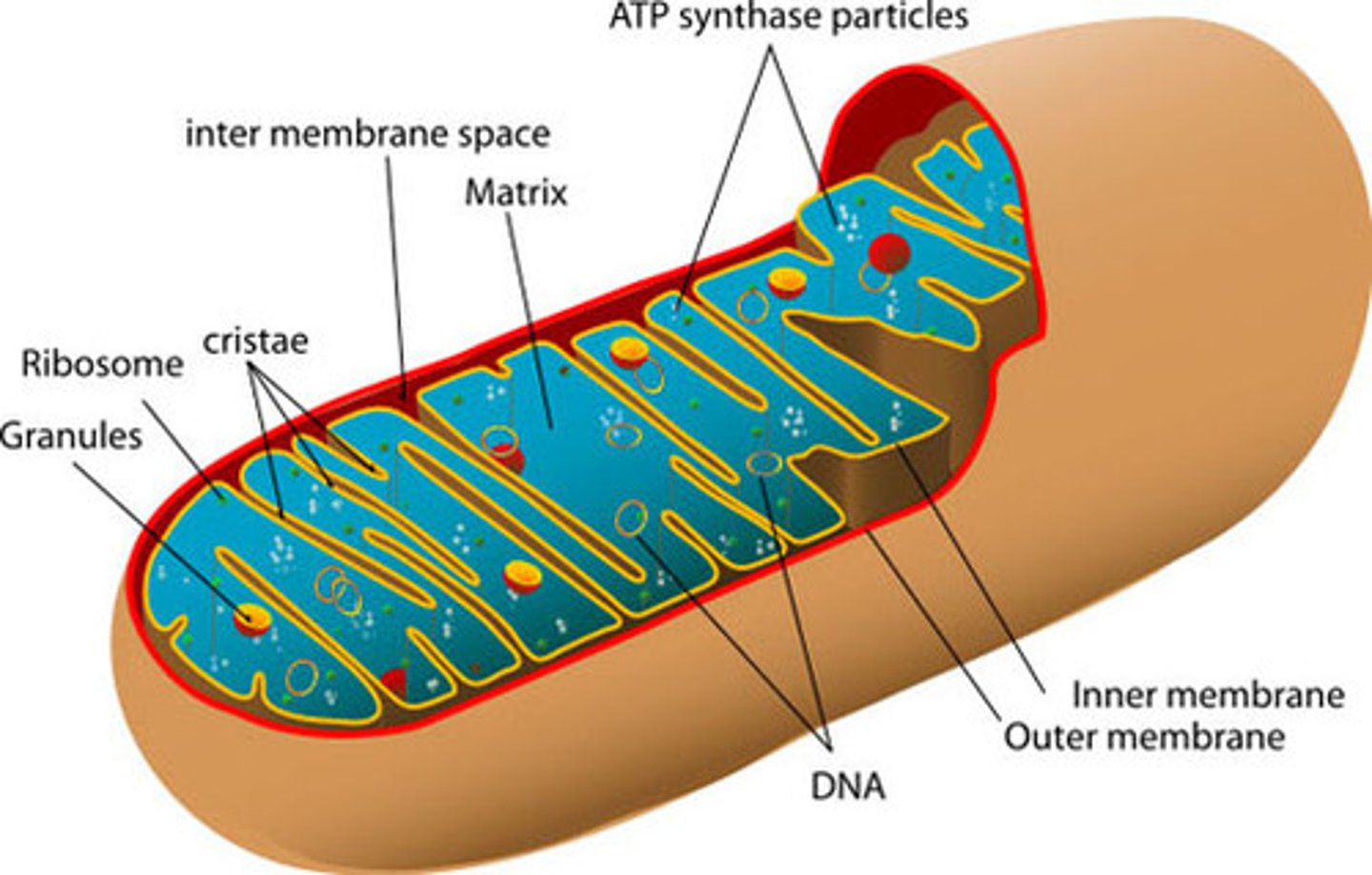
Lysosome
This organelle uses specialized proteins called enzymes to breakdown(digest) old and unnecessary cell parts, playing an important role in eliminating waste and recycling molecules that are not needed
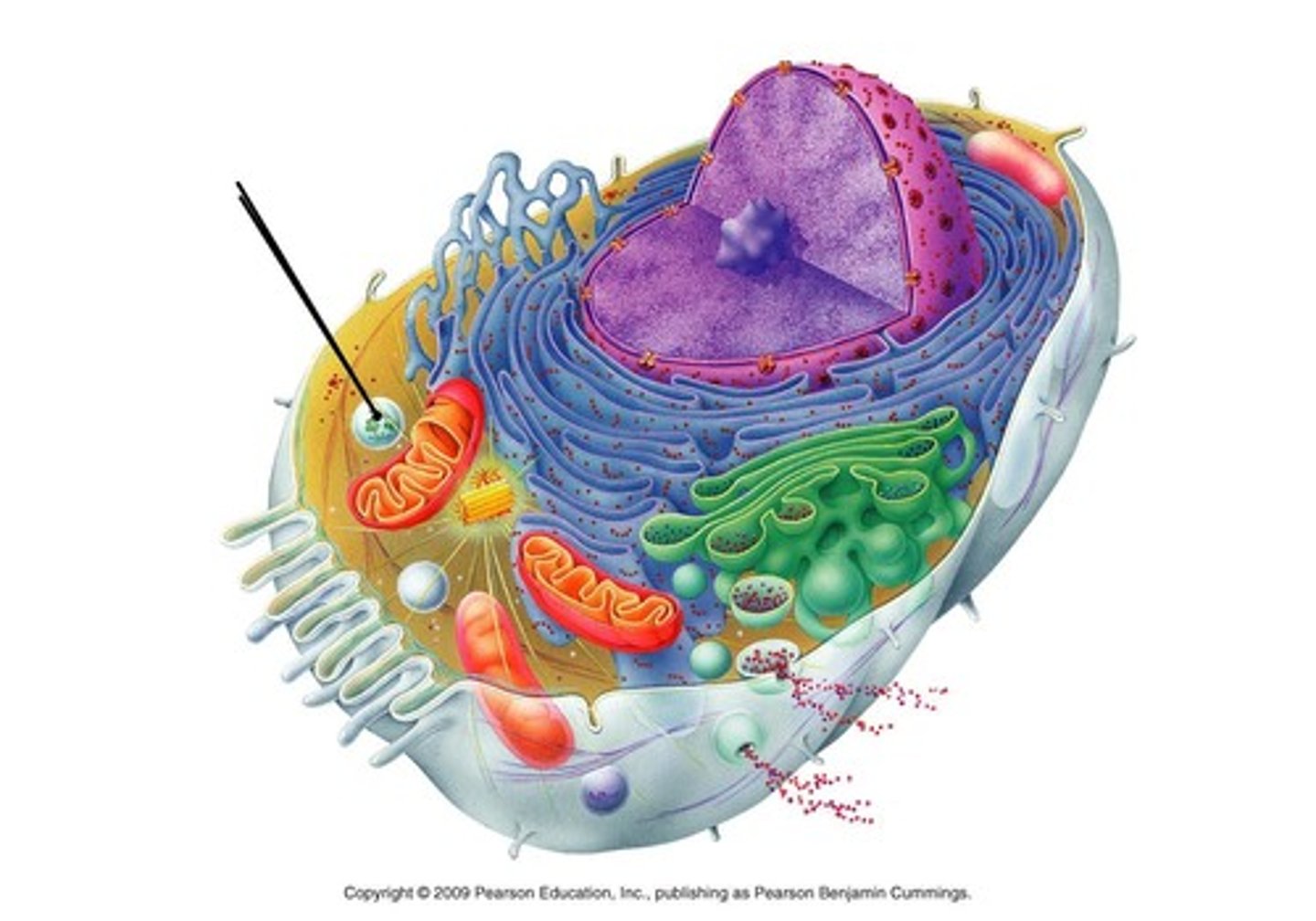
Large Central Vacuole
This organelle is only found in plant cells. It stores water, nutrients and waste, while providing strength, structure and support.
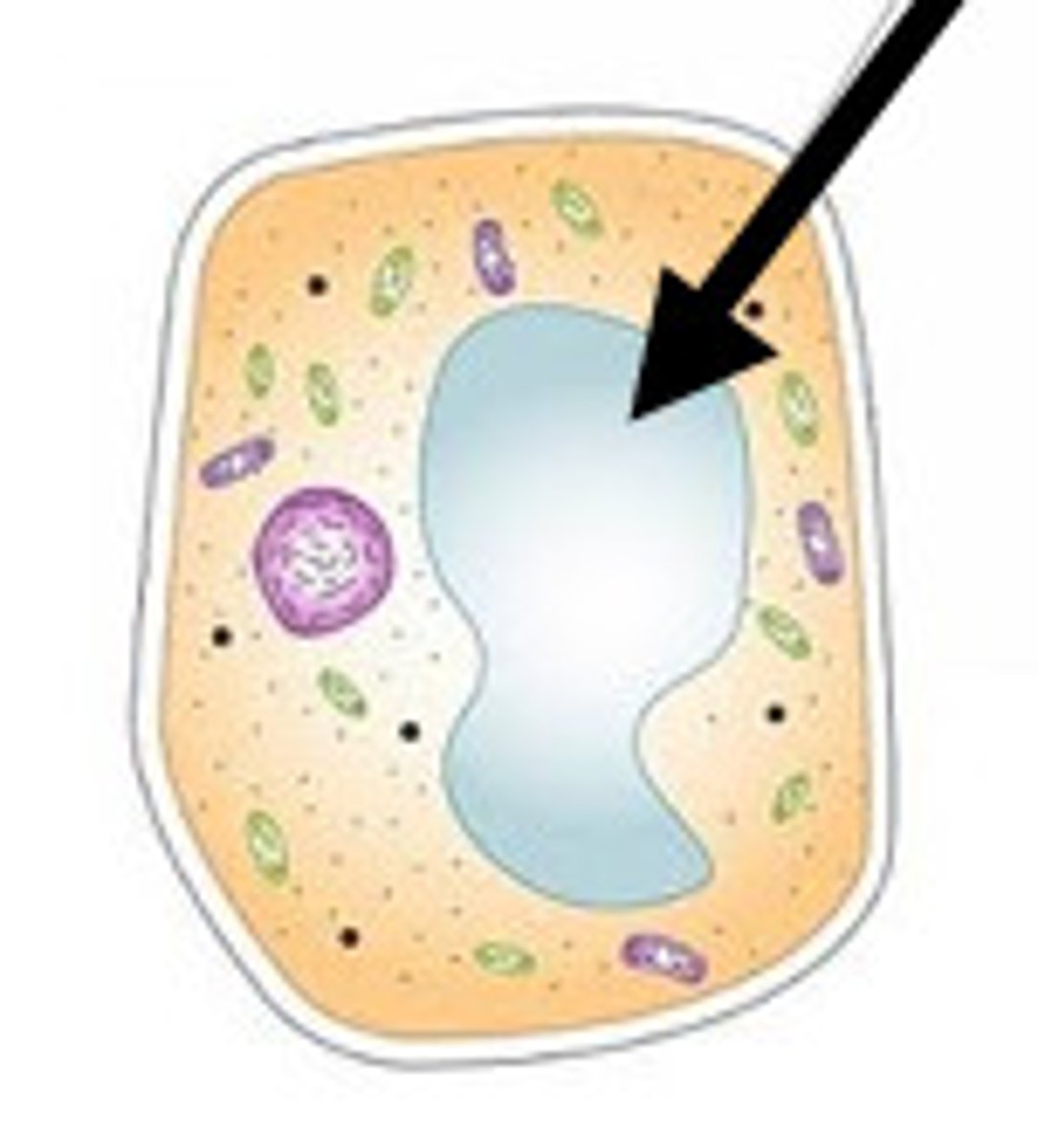
Ribosomes
These tiny organelles are created in the Nucleolus and their function/job is to CREATE PROTEINS by putting Amino Acids together. They can be found attached to the Rough ER or floating in the Cytoplasm
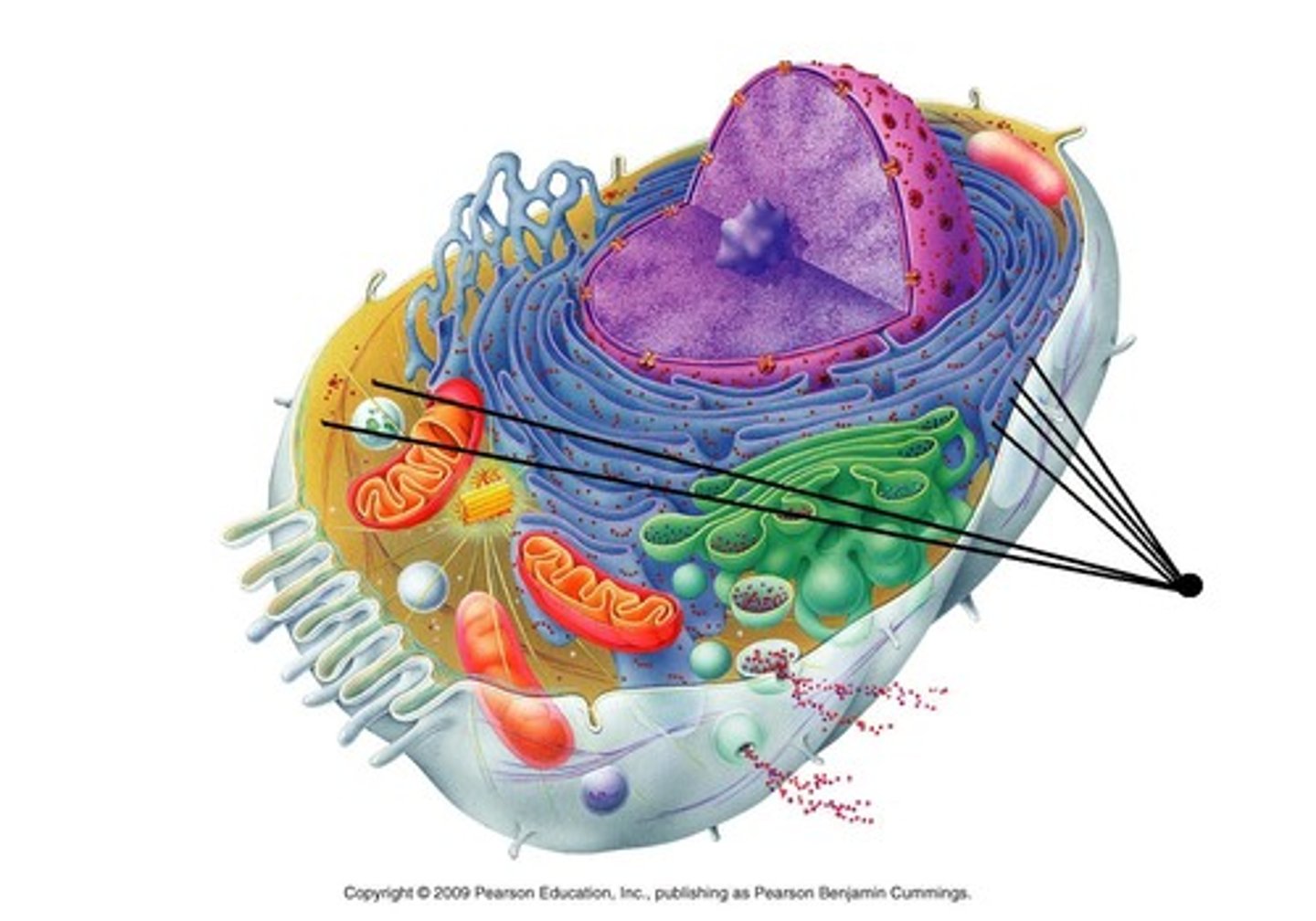
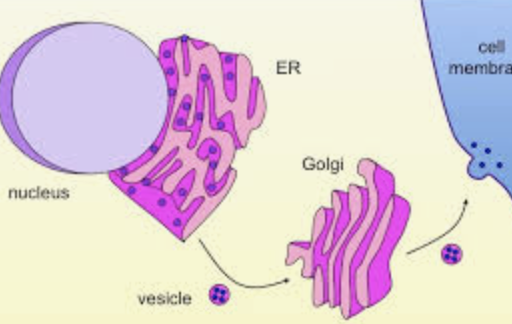
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
This organelle has Ribosomes embedded in (attached to) its outer membrane. Ribosomes deposit new proteins inside the tunnel like structure, where they are packaged and transported to the Golgi Apparatus.
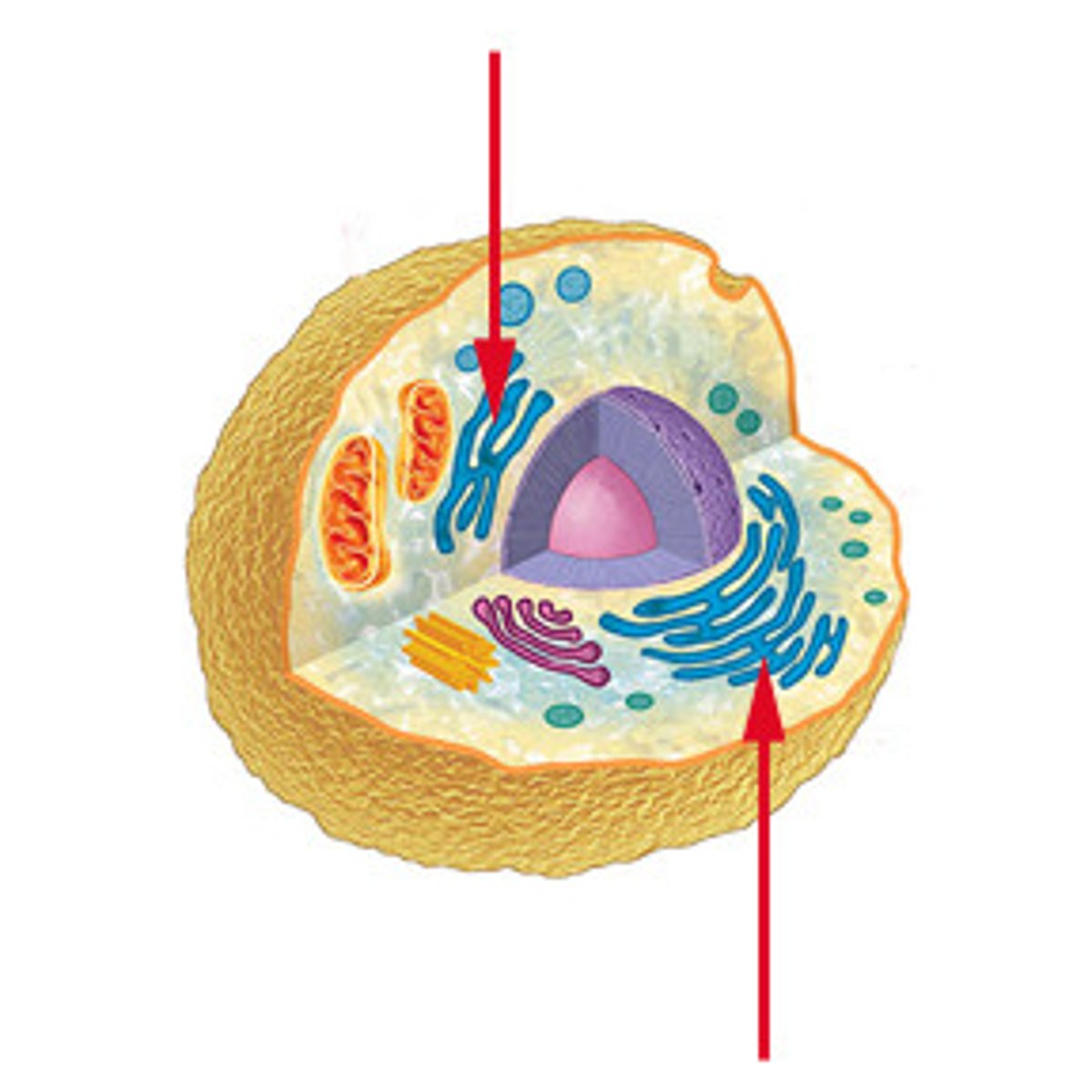
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
This organelle gets its name because it does NOT have Ribosomes attached to it. It has two functions- 1.) make healthy fats(lipids) 2.) Filter and remove toxins that could be harmful
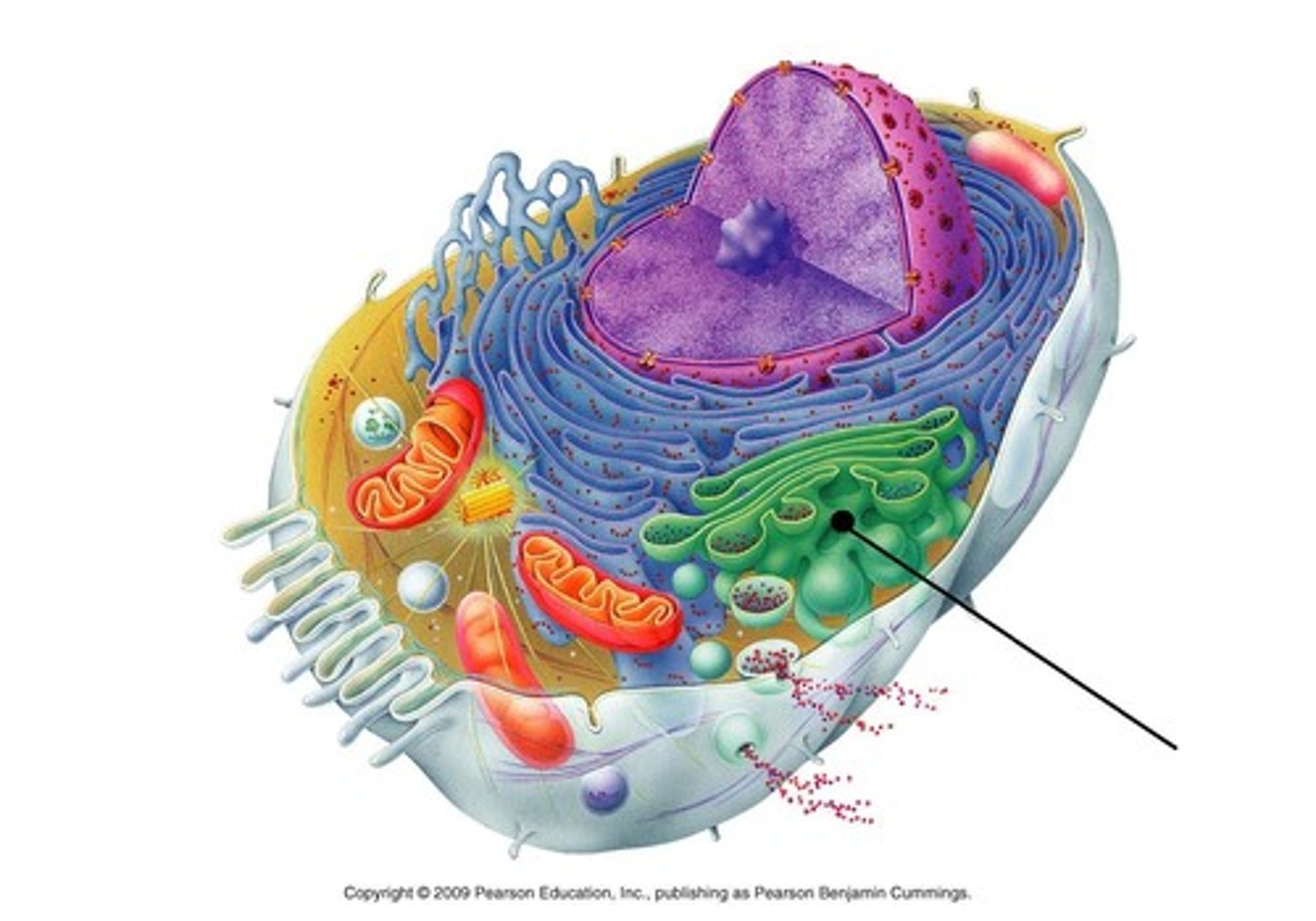
Golgi apparatus
This organelle receives proteins and fats(lipids) from the ER. These molecules are then customized by being folded into a specific shape that allows them to perform important cell functions. They are then packaged and shipped out to where they are needed.
Cell Wall
This organelle is the outer layer of a plant cell. This thick rigid barrier It is made of cellulose(fiber) and provides protection, strength and structure for plant cells.
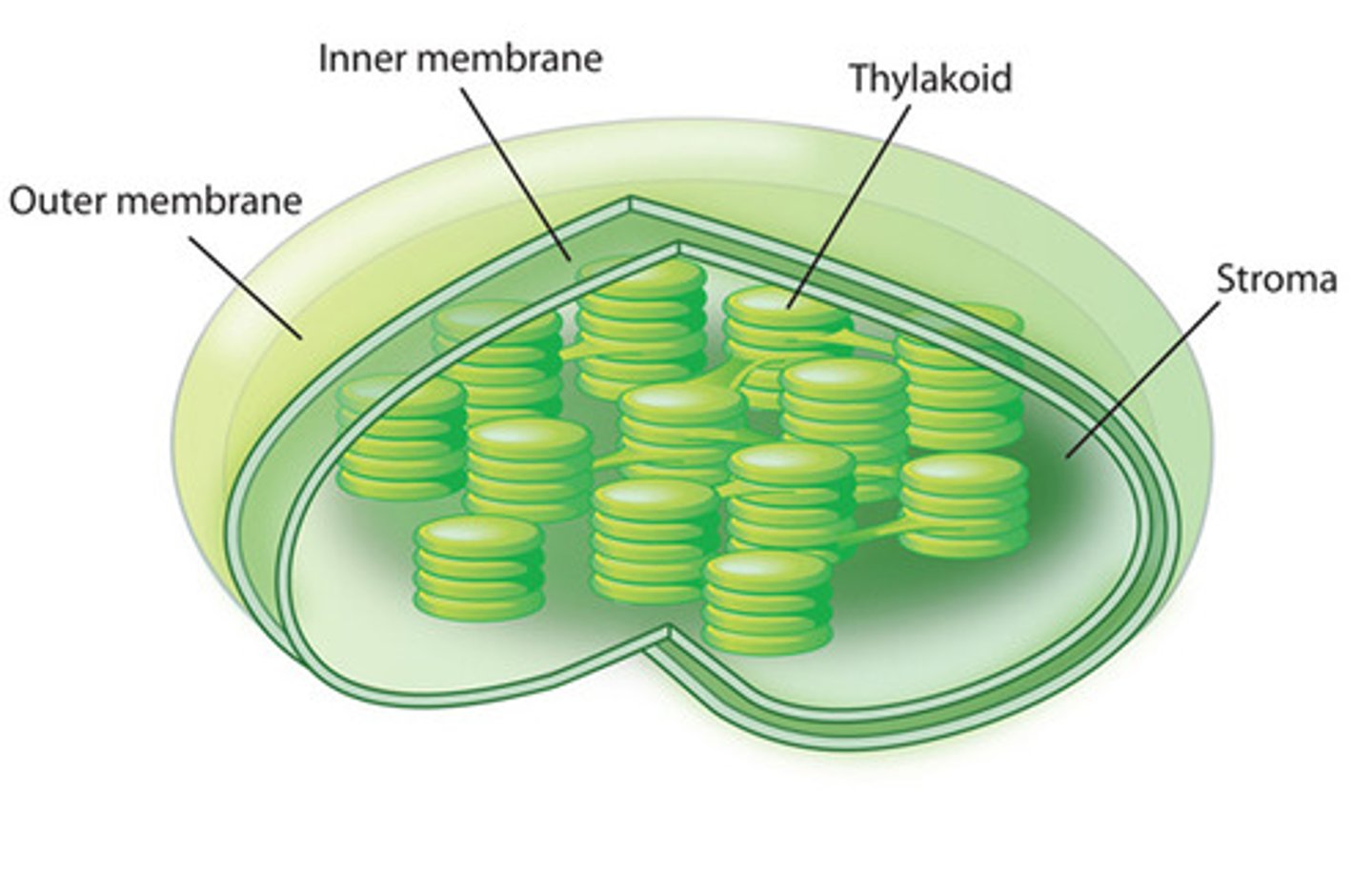
Chloroplast
This organelle is the food producer for the plant cell. It uses the solar energy of the sun to make glucose through a process called Photosynthesis.
Cytoplasm
The jelly-like liquid fills the cell, supporting the organelles and allowing for movement and chemical reactions within the cell.
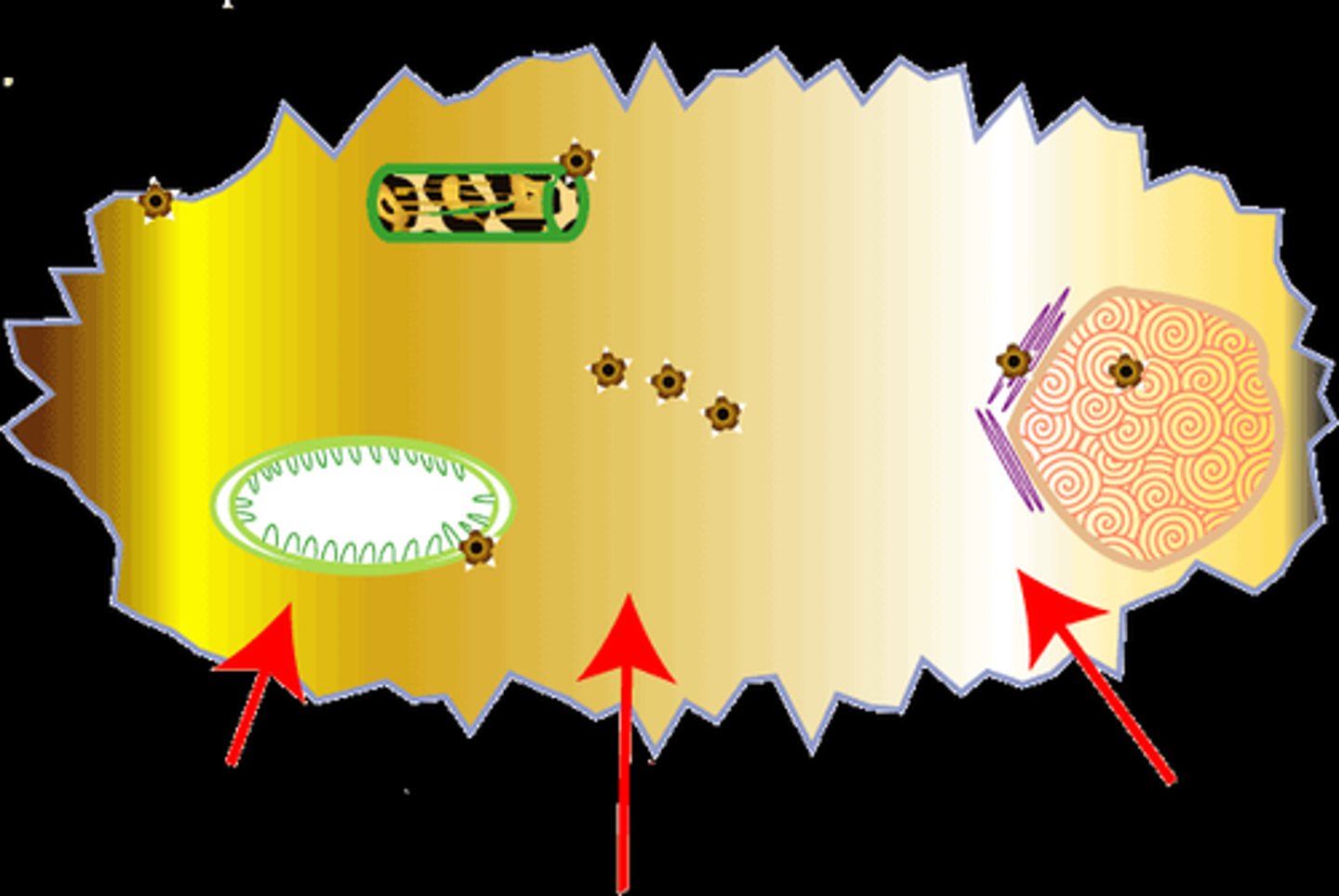
Cytoskeleton
These structures are made of protein and are located throughout the cell. They provide cells with structure, organization, strength, and allow for movement.
Transport Vesicle
a temporary structure that buds from the membranes of organelles, allowing materials and molecules to travel throughout the cell. It’s like and uber/taxi to transport materials
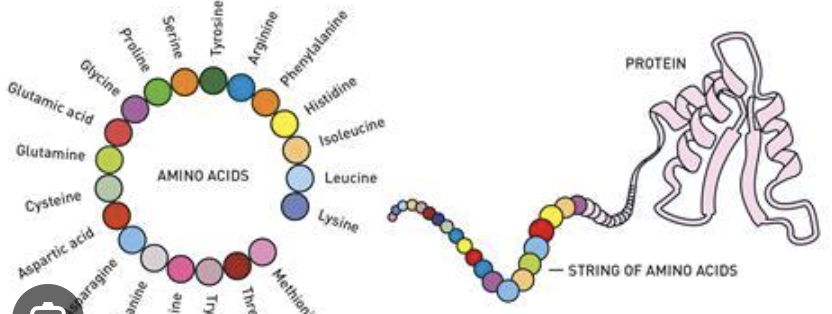
Protein
Molecules built from building blocks called amino acids. This essential nutrient does most of the work within cells and is responsible for the structure, function, and regulation of the body cells, tissues and organs.
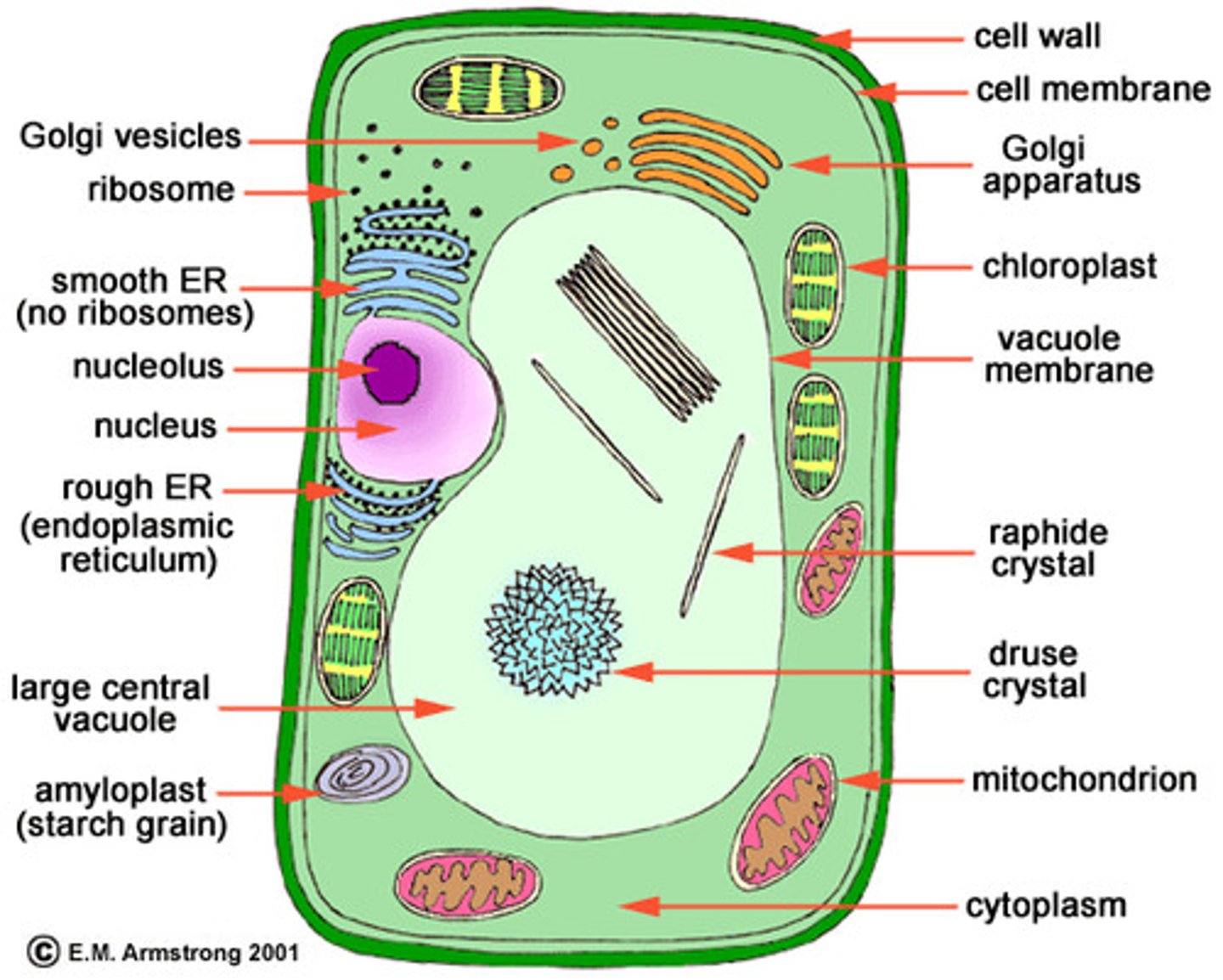
Plant cells
Eukaryotic Cells that have a large central vacuole, a cell wall, and chloroplast.
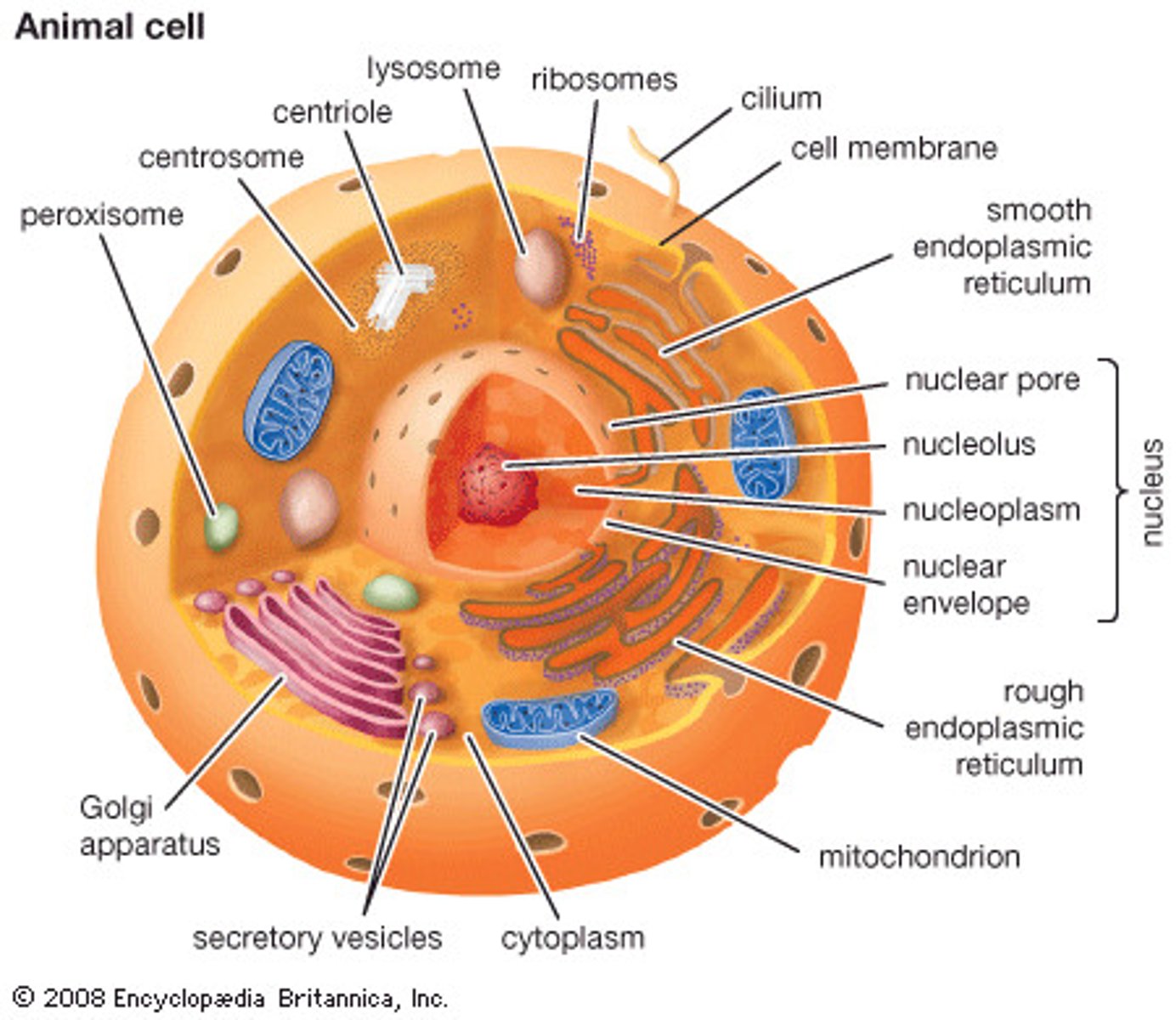
Animal cells
Eukaryotic cells that have no central vacuole, no cell wall and no chloroplast.
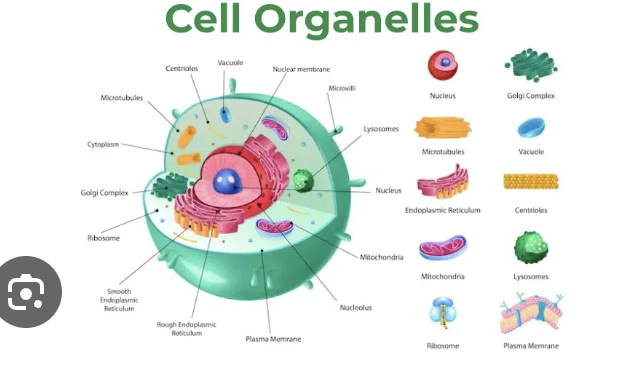
Organelle
The membrane bound structures or "little organs" within a cell that work together to carry out the characteristics of life for each cell
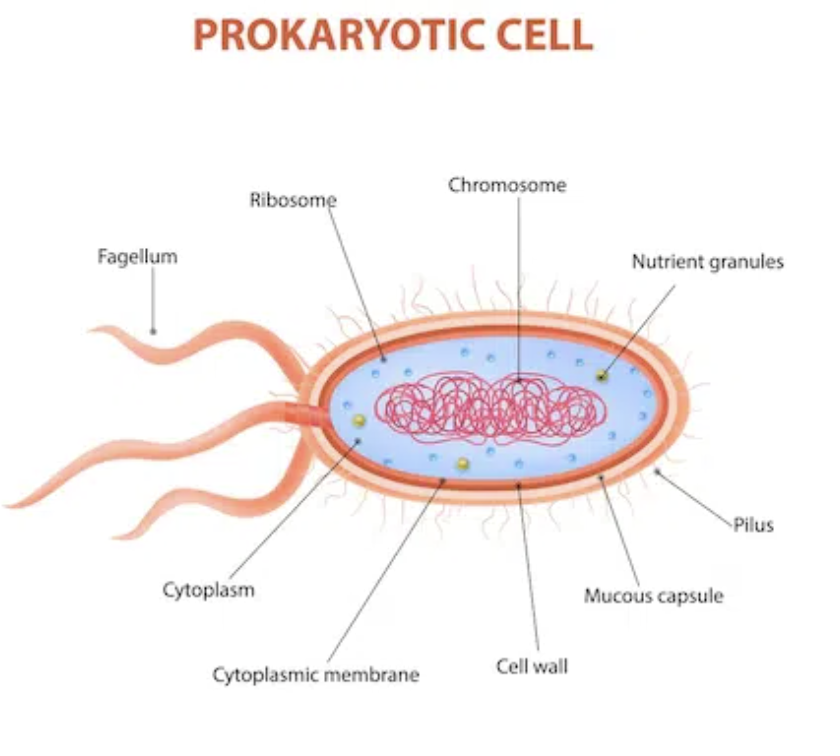
Prokaryote
A small simple cell type that has no Nucleus or membrane-bound organelles and are always single-cell organisms (ex:bacteria) They were the first form of life on Earth, appearing about 3.5 billion years ago.
Eukaryote
A larger, complex cell type that makes up all multi-cellular Organisms (animals, plants, fungi..)They have a nucleus and membrane-bound Organelles and are capable of forming specialized tissues. This complex cell type evolved from Prokaryotes around 2 Billion years ago.