Mircrobio Reagents in media and color outcomes
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Enrichment media
Contains chemicals that enhance the growth of desired bacteria
– Ex) Chocolate agar
*non-selective medium for the primary isolation of fastidious bacteria
Selective media
Suppresses of unwanted microbes; encouraging desired microbes.
-PEA (PhenylEthyl Alcohol), selects and cultivate Gram +
-EMB (Eosin Methylene Blue), selects Gram -
*Mannitol Salt Agar
Differential media
Differentiate colonies of desired microbes from others
– Ex) EMB
Mannitol salt agar
Eosin methylene blue (EMB) of Coli-type colonies
very dark, almost black (green sheen)
-Due to precipitation of methylene blue in the medium from the very high amount of acid produced from fermentation
EMB of Aerogenes type
-colonies are less dark
-Often a dark center is seen surrounded by a wide, light-colored, mucoid rim – resulting in a "fish-eye" type of colony.
-E. aerogenes is able to ferment lactose to produce weak acid end-products

EMB of Non-lactose fermenting colonies
produce no acid from fermentation, so the lighter-colored alkaline reaction is seen
-absence of color in the bacterial growth indicates P. aeruginosa is unable to ferment lactose
Mannitol salt agar (MSA)
-Staphylococcus spp. can grow in high salt concentration
that is inhibitory to most bacteria; MSA is selective
-Bacteria capable of fermenting the mannitol in the medium to acid (Staphylococcus aureus) causes the medium to change color phenol red: (red -> yellow); MSA is differential
Oxygen indicator
Thioglycolate broth/ reducing media with oxygen indicator
-Methylene blue = blue/white
-Resazurin = pink/colorless
OF media
Used to determine whether an organism is oxidative or fermentative
• Semisolid agar deep containing: a high concentration of carbohydrate and
a low concentration of peptone
*Peptone supports the growth non-fermentative bacteria
• 2 tubes: air & no air (seal with mineral oil)
• pH indicator: bromthymol blue
– Turns yellow in acidic environment (carbohydrate is catabolized)
– Turns dark blue color in alkaline condition (peptone is catabolized)
-oxidative catabolism requires presence of O 2
-fermentation of glucose can be done w/out O 2

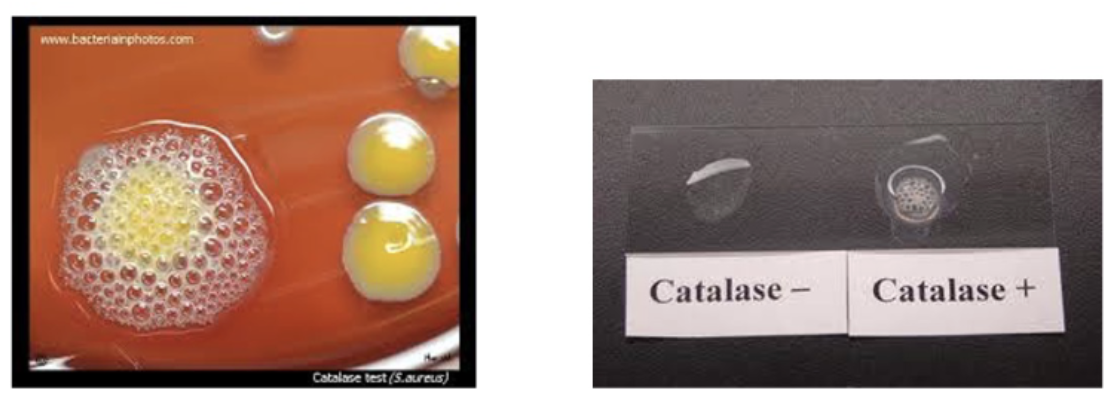
Catalase test
H2O2 produced during normal aerobic respiration
-Toxic and microbes developed enzymes to neutralize it (catalase,peroxidase)
-Agent: 3% of H2O2
*Positive": Milkly color
Reducing media
Contain chemicals (thioglycolate or oxyrase) that combine with O 2
- sodium thioglycolate, that chemically combine with
dissolved oxygen and deplete the oxygen in the culture medium
– Heated to drive off O 2 and/or addition of agar to increase
viscosity -> reduces the diffusion of air into medium
Brewer jar
Palladium (Pd) catalyzes the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen in jar to yield water, which forms as condensation on the inside of the jar.
-Methylene blue is blue only in the presence of oxygen.
*When oxygen is converted to water and condensation forms in the jar, the indicator strip should be clear/white.
*CO 2 and H 2 are given off when pack is exposed to air
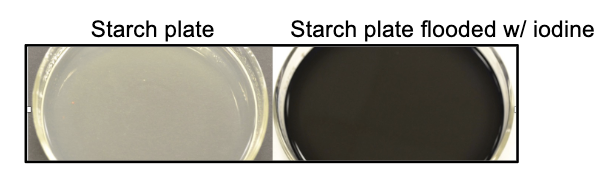
Starch hydrolysis
Starch is polysaccharide and hydrolyzed by exoenzyme amylase into smaller carbohydrates.
• Glucose, a monosaccharide, can be released by hydrolysis,
then enter a cell and can be further catabolized by
endoenzymes.
• Flood starch agar plate with Gram’s iodine: Iodine binds to
starch to form a blue‐black complex covering the agar (this
is negative result for Amylase test)
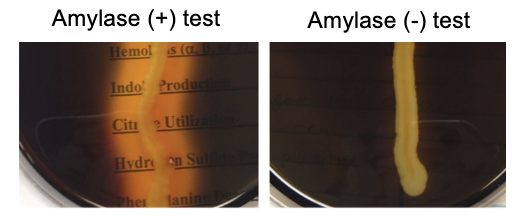
Amylase test
– Areas of starch hydrolysis will appear clear. (+) Amylase test
– Unchanged starch will stain dark blue/black. (-) Amylase test
Obligate aerobes
organisms that grow only in the presence of oxygen
-They obtain their energy through aerobic respiration
*Presence of enzymes catalase and SOD to neutralized toxic forms of oxygen
Ex: Alcaligenes faecalis
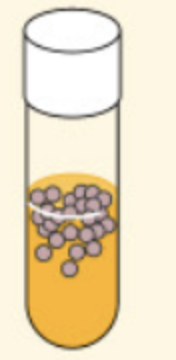
Facultative anaerobes
organisms that grow with or without oxygen but generally better with oxygen
-They obtain their energy through aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but use fermentation or anaerobic respiration if it is absent.
-Most bacteria are facultative anaerobes.
*Presence of enzymes catalase and SOD to neutralized toxic forms of oxygen
Ex: Escherichia coli
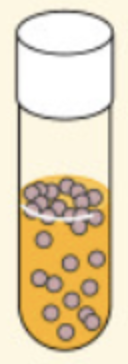
Oligate anaerobes
organisms that grow only in the absence of oxygen and, in fact, are often inhibited or killed by its presence.
-They obtain their energy through anaerobic respiration or fermentation.
*Lacks enzymes to neutralize harmful forms of oxygen
Ex: Clostridium sporogenesy th
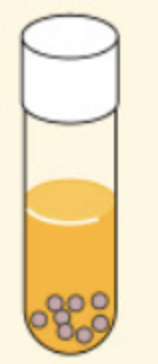
Aerotolerant anaerobes
like obligate anaerobes, cannot use oxygen to transform energy but can grow in its presence.
-They obtain energy only by fermentation and are known as obligate fermenters.
*Presence of SOD that allows partial neutralized form of oxygen
Ex: Lactococcus lactic, Enterococcus faecalis
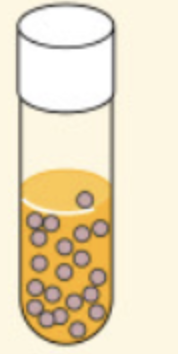
Microaerophiles
organisms that require a low concentration of oxygen (2% to 10%) for growth, but higher concentrations are inhibitory
-obtain their energy through aerobic respiration
*Produce lethal amounts of toxic forms of oxygen if exposed to normal atmospheric oxygen
Ex: Borrelia burgdorferi
Fermentation test
– Used to detect acid and gas production from
carbohydrates
– Contains: peptone, phenol red (pH indicator), 0.5-1% of the desired carbohydrate and an inverted Durham tube to trap gas
Phenol red
– Red in a neutral or alkaline solution (-)
– Turns yellow in the presence of acid (+) below pH 6.8

MRVP broth
Used to distinguish between organisms that produce
large amounts of acid (MR) and those produce neutral
product acetoin (VP).
• MR test: add 4-5 drops of methyl red
– Red (+): acid production below pH 4.4
– Yellow (-): no acid production pH above 6.0
*Orange/red color = 4.4-6
• Voges-Proskauer (VP) test:
add a few drops of 40% KOH & 5% α-napthol
– Red ring (+): acetoin production (Remember: acetoin is a neutral product)
– No color change (-): no acetoin production
Phenylalanine Deanmination
1) Adding 4 or 5 drops of 10% ferric chloride solution to
phenylalanine slant: dark green color indicates a ferric ion
complex with the organic acid.
2) Nessler’s reagent: deep yellow indicates the presence of ammonia.

Decarbroxylation
Ornithine —-Ornithine decarboxylase——> Putrescine (amine) + CO 2
pH indicator: Bromocresol purple
Positive result – lavender-purple above pH 6.8
Negative result – Yellow (acidic conditions) below pH 5.2

Indole Production
can be detected by adding 4-5 drops of Kovac’s reagent to MIO agar medium.
^Rosindole dye
*M=motility I=indole O=ornithine decarboxylase
-Motility will be detectable as diffuse growth radiating from the stab line. Semi-solid agar deep
*formation of a red ring on the surface of the medium indicates (+) result for indole production
