PE 2 MIDTERM REVIEWER
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
Fitness
is the ability to carry out daily tasks efficiently with enough physical capacity to cope with the physical needs of life.
Physical Fitness
is the primary specific objective in teaching Physical Education. It is the ability to carry out daily tasks with vigor and alertness, without undue fatigue, and with ample energy to enjoy leisure time pursuits and meet unforeseen circumstances.
Health
"a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity."
Food
Rest and Sleep
Exercise or Physical Activities
What are the factors that affect fitness?
Physical Fitness
Social Fitness
Emotional Fitness
Mental Fitness
What are the aspects of fitness?
Physical Fitness
refers to the ability of an individual to perform his daily tasks efficiently without undue fatigue and has some extra "reserves" in case of emergency.
Social Fitness
is the ability to mingle with different types of people with interest and concern for others.
Emotional Fitness
refers to the ability of an individual to control his emotions or feelings.
Mental Fitness
is the ability to cope with common problems of everyday living.
Physical
Under which pillar of physical health do these fall under?
Better health.
Improved quality of life.
Strong bones and muscles.
Fight off illness better.
Weight control.
Improved fitness.
Mental
Under which pillar of physical health do these fall under?
Reduce anxiety and depression.
Reduce and prevent stress.
Increase cognitive functioning.
Feeling more energetic.
Sleep better.
Relaxation
Social
Under which pillar of physical health do these fall under?
Social integration
Build new friendships.
Strengthen relationships.
Increase family time.
Meet new people.
Build social skills.
Emotional
Under which pillar of physical health do these fall under?
Self confidence
Increase feeling of self-worth.
Increase feelings of happiness.
Increase feelings of success.
Positive mood and affect.
Lower tension
Physical Fitness
__________ is the capacity of the body to do activities without undue exhaustion.
components of health-related fitness
components of skill-related fitness.
What are the two distinct categories of physical fitness?
Skill-related fitness
_____________ is the capacity to perform during games and sports. This level of physical fitness is needed to be able to perform the more technical parts of a wide range of sports.
agility
balance
coordination
power
reaction time
speed
What are the six components of skill-related fitness?
Speed
it is the ability to move one's body from one point to another in a shorted possible time. It refers to a person's ability to move fast.
Agility
is the capacity to shift or change the direction of the body quickly, effectively and rapidly from one point to another. A person who competes in track and field exhibits a high level of this.
Balance
is the ability to keep your body in place, whether you're standing still (static balance) or moving (dynamic balance). it involves vision, reflexes, and skeletal muscular system which provides the maintenance of equilibrium.
Coordination
is the ability to move in a way that is smooth, accurate, and under control. It is a difficult skill that also requires good balance, strength, and agility.
Power
is the ability to perform one maximum effort in the shortest possible time. In other words, it is the ability of your muscles to use as much force as possible in as little time as possible, like when you run or swim.
This component of skill-related fitness has to do with cardiovascular endurance. Strength and speed are the two components that combine to create this.
Reaction time
The term "__________" refers to the rate at which an athlete reacts to an external stimulus. Athletes can be exposed to different stimuli when they play sports. So, this is very crucial for any athlete. Whether a player wins or loses in a sport is usually decided in a matter of milliseconds, and it all depends on how fast the player can react.
Strength and speed
What are the two components that combine to create power?
health-related fitness
Exercises that are done with the intention of improving one's physical health and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are included in the concept of __________.
cardiovascular endurance
muscle strength
muscular endurance
flexibility
body composition.
What are the five components of health-related fitness?
Cardiovascular endurance
is the ability of the lungs, heart, and blood vessels to deliver enough oxygen to the cells to meet the needs of long-term physical activity. Getting stronger in your heart and lungs can make it easier for you to carry out the tasks you need to do every day.
Muscular strength
is the capacity of the muscle to produce force during a relatively short period of time. Push-ups, sit-ups, lifting, squats, and lunges promote muscular strength.
Muscular endurance
__________ is the highest amount of force that a muscle group is able to pull or push in a single contraction. Circuit training, and bodyweight exercises are all good ways to build muscle endurance.
Flexibility
________ is the ability of a joint or group of joints to move through their full range of motion without pain or restriction. Even though it varies a lot from person to person, everyone needs to stay within certain minimum ranges to keep their joints and bodies healthy. Squats, lunges, and stretching can enhance this.
Body composition
________ is how much of your body is made up of fat, bone, and muscle. It is a way for health professionals to figure out if a person is at a healthy weight for their body.
Nutrition and exercise are critical for improving this. Burpees, pushups, squat jumps, lunges, and planking can improve this.
principles of training
The _________ help to guide the trainer in selecting the correct training type and method in creating training sessions that will improve performance. They help the trainer choose the workload for the athlete to ensure they are not levelling out or failing to improve. The trainer uses them in order to ensure their training matches competition and is specific to the adaptations needed.
Specificity
Overload
Progression
Individuality/Individualization
Reversibility
Adaptation
Rest and Recovery
What are the principles of training?
Specificity
This principle of training relates to the type of training that you do. It should be specific to you and your sport. You should train the energy system which you use predominantly (i.e. don’t run 5,000 meters in training if you’re a sprinter!) and the fitness and skill components most important to your sport, for example, agility, balance, or muscular endurance
Physiological adaptations to training are specific to the muscle groups trained, the intensity of the exercise , the metabolic demands of the exercise, and specific movements and activities.
Overload
________ means applying a stimulus that exceeds the current capacity of the muscles, joints, and nervous system. In order to progress and improve our fitness, we have to put our bodies under additional stress. Applying this training principle will cause long-term adaptations, enabling our bodies to work more efficiently to cope with this higher level of performance.
Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type
Overloading can be achieved by following the acronym FITT which means _______.
Frequency
In FITT Principle, this means increasing the number of times you train per week.
Intensity
In FITT Principle, this means increasing the difficulty of the exercise you do. For example, running at 12 km/h instead of 10 or increasing the weight you are squatting with.
Time
In FITT Principle, this means increasing the length of time that you are training for each session. For example, cycling for 45 minutes instead of 30.
Type
In FITT Principle, this means increasing the difficulty of the training you are doing. For example, progress from walking to running.
progression
The principle of __________ is the idea that as your body adapts to your exercise routine, you have to increase the intensity to continue to see enhanced fitness. This can mean gradually increasing the weight, duration, or intensity of your exercise routine.
Individuality/Individualization
People will have unique responses to the same training stimulus, due to individual characteristics such as biological age, training age, gender, body size and shape, past injuries etc. Thus, training should be adjusted to the individual’s characteristics and needs.
reversibility
The effects of training will be lost if training stimulus is removed for an extended period of time.
Adaptation
An individual’s level of training determines how much improvements in performance they achieve due to training. A novice will see huge and relatively, quick gains in performance when they begin training, however, the gains get smaller and come more slowly as they get more experienced.
Rest and recovery
The principle of __________ (or principle of recuperation) suggests that rest and recovery from the stress of exercise must take place in proportionate amounts to avoid too much stress. Both rest and recovery is an equally essential component of an exercise program because it gives the body time to repair, rebuild, and strengthen itself between workouts.
muscle
A ______ is a fibrous tissue attached to the bone that permits body movement.
balance, movement, and strength
Muscles assist with _______, _______, and _______.
shorten, elongates
When a muscle contracts, the fibers _______ (flexing the biceps) while opposing muscles _______ (the triceps stretches).
MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS
___________ elongation allows the muscle to relax and lengthen.
joints
Major muscle groups work together to move ______.
Superficial
_________ muscles are located closer to the surface near the skin.
Appendicular
__________ muscles include the arms and legs
deep
______ muscles are located closer to the bone.
axial
_________ muscles include the torso and head
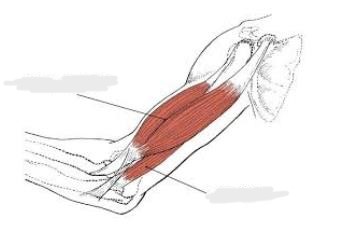
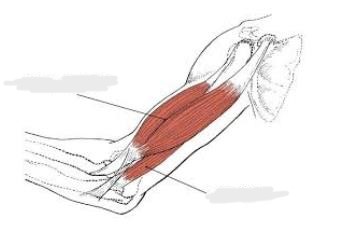
biceps brachii
The __________ runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It is attached to the shoulder blade (the scapula) and extends along the front surface of the upper arm bone (the humerus). When the bicep contracts, the arm bends at the elbow. Notice that the humerus sounds like humor – we call this area of the elbow the funny bone.
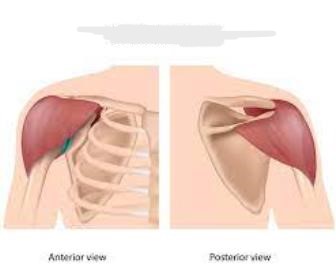
deltoids
The __________ are the triangular muscles of the shoulder. The strongest point is the central section, which raises the arm sideways. The front and back parts of the muscle twist the arm.
deltoids
Deltoid comes from the Greek word _______, meaning shaped like a (river) delta, which is triangular.
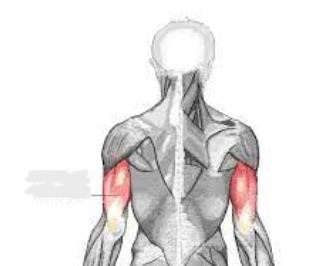
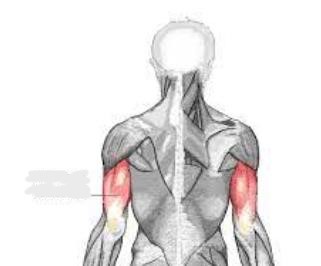
triceps brachii
The __________ is a large, thick muscle on the dorsal part of the upper arm. It often appears as the shape of a horseshoe on the posterior aspect of the arm. The main function of the triceps is the extension of the elbow joint.
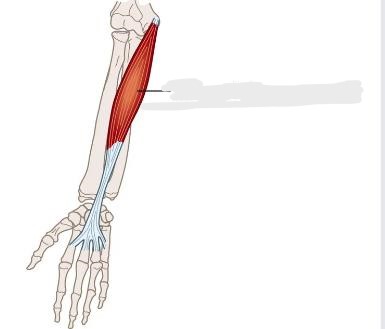
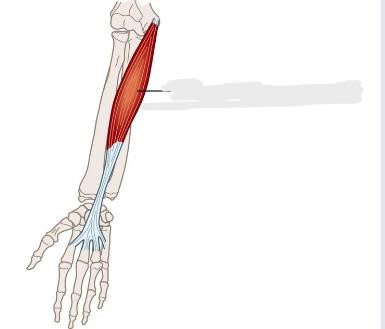
Palmaris Longus
A long muscle of the anterior forearm. It extends from the distal humerus to the root of the hand, although it can be absent in 10% of people. Together with the pronator teres, flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor carpi radialis and flexor digitorum superficialis muscles, __________ belongs to the superficial flexors of the forearm.
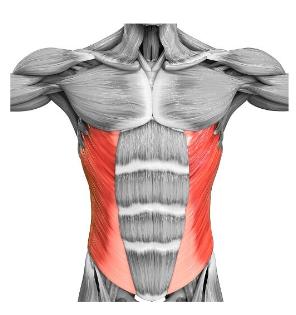
Internal Oblique
The _________ is a muscle found on the lateral side of the abdomen. It is broad and thin. it forms one of the layers of the lateral abdominal wall along with external oblique on the outer side and transverse abdominus on the inner side. Its fibers are obliquely oriented hence the name.
external oblique
The __________ muscle is one of the outermost abdominal muscles, extending from the lower half of the ribs around and down to the pelvis.
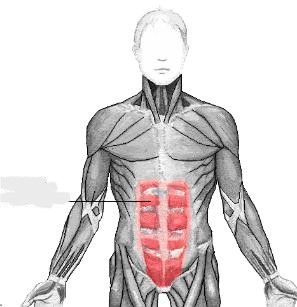
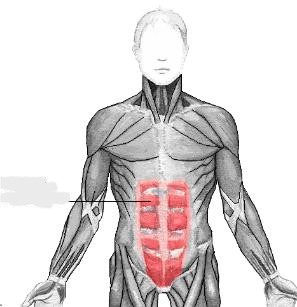
rectus abdominis
The __________ muscles are a pair of long muscles that run vertically up the front of the abdomen, stretching from the pubis to the xiphoid process. They compress the viscera and tense the abdominal wall.
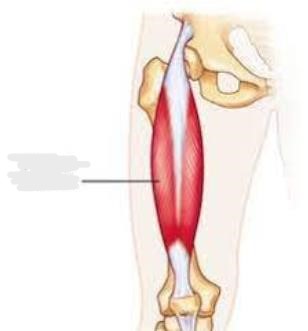
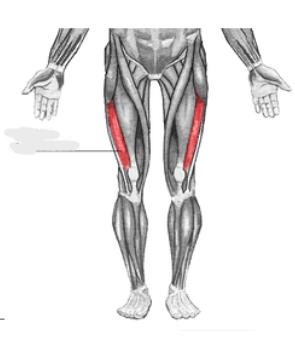
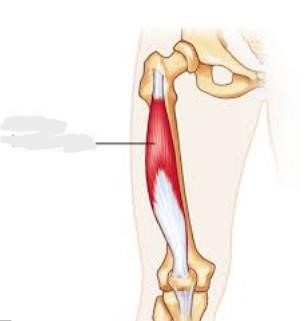
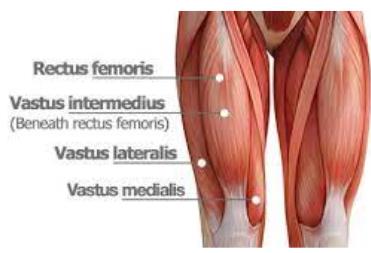
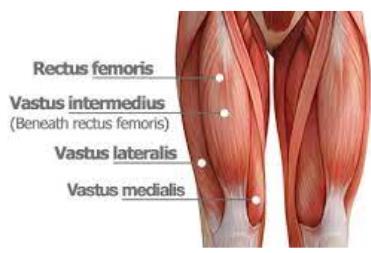
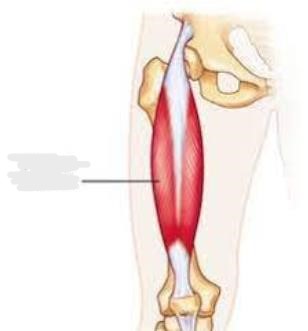
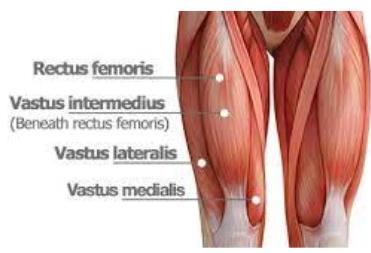
Rectus femoris
__________ is part of the quadriceps group. It is a bulk of muscle located in the superior, anterior middle compartment of the thigh and is the only muscle in the quadriceps group that crosses the hip.
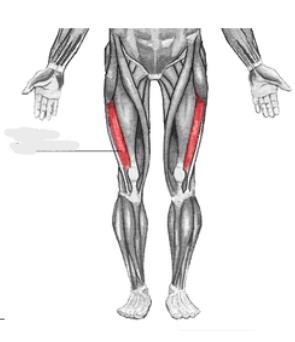
vastus lateralis
The __________ muscle is located on the lateral side of the thigh. This muscle is the largest of the quadriceps which includes: rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, and vastus medialis. Together, the quadriceps act on the knee and hip to promote movement as well as strength and stability.
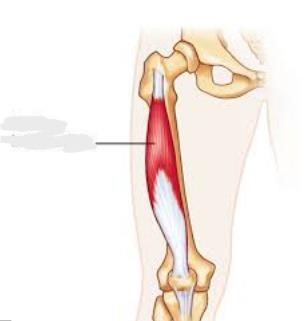
Vastus Intermedius
__________ is located centrally, underneath Rectus femoris in the anterior compartment of the thigh and on each side of it: Vastus medialis and Vastus Lateralis respectively. It is one of the four muscles that form the quadriceps femoris muscle.
vastus medialis
The _________ is a teardrop-shaped muscle that helps move the knee joint and stabilize the kneecap. It is one of the four quadriceps muscles in the front of your upper thigh.
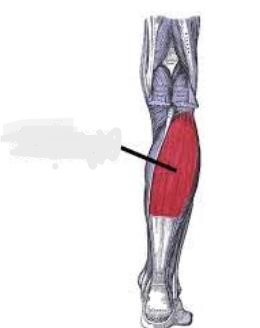
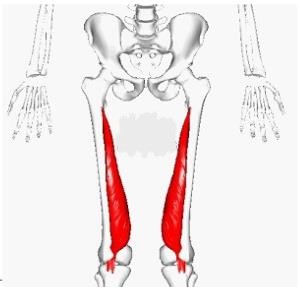
Soleus
Located in the lower leg, the _______ runs from the lower leg bones (the tibia and fibula) to the heel (the calcaneus). This muscle flexes the foot by moving the foot at the ankle. It also helps circulation by pumping blood back up towards the head.
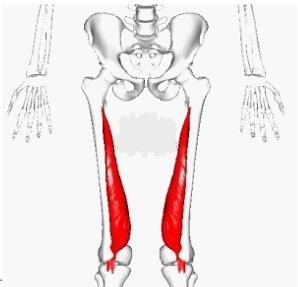
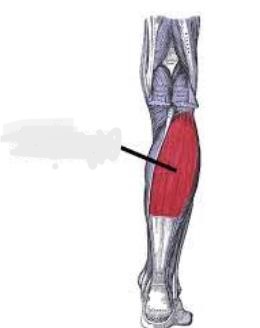
quadriceps femoris
Your quad muscles, or ___________, are a group of muscles at the front of your thigh. Together, they contain more mass than any other muscle group in your body. You use your quads to perform a variety of movements, including kicking, running, jumping and walking
Quadriceps femoris
The ___________ is the most voluminous muscle of the human body. It is a hip flexor and a knee extensor. It consists of four individual muscles; three vastus muscles and the rectus femoris. They form the main bulk of the thigh, and collectively are one of the most powerful muscles in the body It is located in the anterior compartment of the thigh.
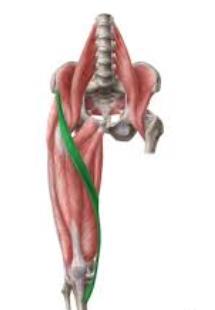
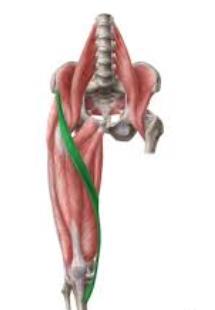
sartorius
The ________ is the longest muscle in the body, spanning both the hip and the knee joints.
sartor
The word sartorius is derived from the Latin word ________, which translates to patcher, or tailor, due to how the individual will position their leg while working.
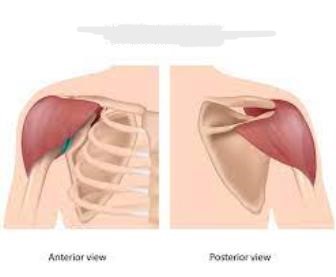
Biceps Brachii
What muscle is this?
Deltoid
What muscle is this?
Triceps brachii
What muscle is this?
Palmaris Longus
What muscle is this?
Internal Oblique
What muscle is this?
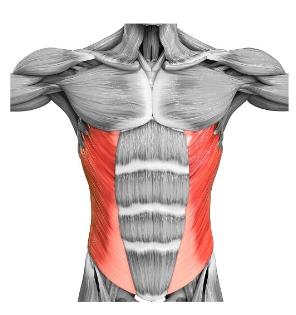
Rectus Abdominis
What muscle is this?
Rectus Femoris
What muscle is this?
Vastus Lateralis
What muscle is this?
Vastus Intermedius
What muscle is this?
Vastus Medialis
What muscle is this?
Soleus
What muscle is this?
Quadriceps Femoris
What muscle is this?
Sartorius
What muscle is this?
joint
A _____ is a point where two bones make contact. They can be classified either histologically on the dominant type of connective tissue functionally based on the amount of movement permitted.
fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial
Histologically the three joints in the body are ______, ______, and _______.
fibrous joint
A _________ is a fixed joint where fibrous tissue comprised primarily of collagen connects bones. They are usually immoveable (synarthroses) and have no joint cavity.
Sutures
are immobile joints in the cranium.
Gomphoses
are the immobile joints between the teeth and their sockets in the mandible and maxillae
Syndesmoses
are slightly movable joints (amphiarthroses). For example, the tibia connects to the fibula
sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses.
Fibrous joints are subdivided into _______, ________, and _______.
cartilaginous joints
In _________, the bones attach by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage.
Primary cartilaginous joints
______________, also known as synchondroses, only involve hyaline cartilage. These joints may be slightly mobile (amphiarthroses) or immobile (synarthroses).
secondary cartilaginous joint
The ________________, also known as symphysis, may involve either hyaline or fibrocartilage. These joints are slightly mobile (amphiarthroses). A classic example is a pubic symphysis.
Synovial joints
__________ are freely mobile (diarthroses) and are considered the main functional joints of the body.
hinge (elbow)
saddle (carpometacarpal joint)
planar (acromioclavicular joint)
pivot (atlantoaxial joint)
condyloid (metacarpophalangeal joint)
ball and socket (hip joint).
Synovial joints are often further classified by the type of movements they permit. There are six such classifications:
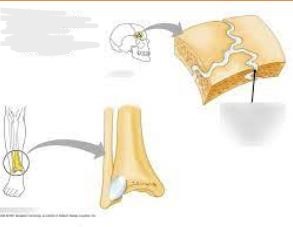
Fibrous Joint
What joint is this?
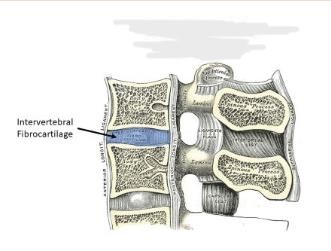
Cartilaginous Joint
What joint is this?
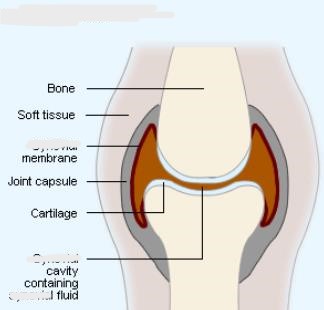
Synovial Joint
What joint is this?
Hinge (elbow)
What joint is this?