4979 exam 2
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
precocial definition
born self sufficient
altricial definition
need mom’s help, can’t stand up
what is a clutch
the number of days in a row a hen lays an egg in succession
amount of time between laying of each egg
26 hours
what percent of chicks will die in the first week
<1%
two parts of the female repro tract
ovary and oviduct
what side of the ovary usually develops
left side
what is the stigma
lack of vasculature on yolk where it will burst out to become an egg
how long is the repro tract
24-27 inches
what occurs in the infundibulum, how long is it, and how long does the egg spend here
site of fertilization, 3-4 inches, 15-17 minutes
what occurs in the magnum, how long is it, and how long does the egg spend here
largest part, thick albumin deposited around the yolk. 13 inches, 3 hours
what occurs in the isthmus, how long is it, and how long does the egg spend here
inner and outer shell membrane develops, 4 inches, 75 minutes
what occurs in the shell gland/uterus, how long is it, and how long does the egg spend here
makes the shell, uses a lot of calcium. 4 inches, 20 hours
how much of calcium stores is used per egg and where does this calcium come from
8-10%, half from body (medullary bones) and half from diet
what occurs in the vagina, how long is it, and how long does the egg spend here
cutile is applied, 4 inches, idk how long
what occurs in the sperm host glands
store sperm for 1 week
where is the egg developed
down the whole oviduct
where does fertilization occur
infundibulum
what is the cuticle/bloom
covering of the shell, protects the shell from environmental contaminants
how is the egg able to stay shelf stable for so long
the cuticle/bloom protects it from bacteria and moisture loss.
4 parts of the male reproductive tract
testes, vas deferens, cloaca, vent and accessory glands
what does the vas deferens do
carries sperm from testes to outside
what is caponization
essentially castration. bird grows at a slower rate, and has a juicier and softer product.
what helps sperm get up the repro tract
contractions
what kind of breeders are poultry
long day
what does HPG stand for
hypopituitary gonadal axis
what does the HPG axis do
brain stimulated, pituitary, then gonads
photoreceptors in the birds brain
when light is present: GnRH —> FSH + LH —> ovary —> follicle —> ovulation
creates a 24 hour estrous cycle
what is special about roosters in the summer
rooster has increased testes size and testosterone
why do we use AI in turkeys
can’t physically do it, breast size is too large, skeletal structure, and mannerisms
when do we AI turkeys
after 3pm
5 factors that affect fertility
mating frequency, age, diet and body weight, environment (temperature), and semen handling & processing
describe semen handling and processing
do not freeze it, keep it fresh. can be good for 30 minutes at room temperature, and 24 hours with a semen extender
describe the mating dance
drops one wing and walks around hen. hen squats and rooster sits on her back. cloaca contact
when is most mating done naturally
during daylight because they want to see predators
how many hens per rooster
10
what is the chalaza
keeps the yolk center in the egg
what occurs in phase 1 of embryonic development
in the hen
chalaza holds the blastoderm
division and growth of cells
isthmus - 2 cell stage - then 4 cell 20 minutes later
uterus —> 16 cell stage
after 4 hours is a 256 cell stage
gastrulation
segregation of cells for specialized functions
what is physiological zero
point at which something starts to happen
what temperature and humidity do we store eggs
55-67 degrees and 75-80% humidity
what are the five extraembryonic membranes
amnion, yolk sac, allantois, chorion, and air cell
what occurs on day 1 of chick development
alimentary tract, vertebral column, nervous system, head and eye
what occurs on day 2 of chick development
beginning of heart, ear forming, and heartbeat
what occurs on day 3 of chick development
nose, wings, and legs
what occurs in the second half of week 1 chick development
tongue, repro organs, beak forming
what occurs in the second week of chick development
feathers, hardening of beak, scales and claws, positioning for hatching
what occurs in the third week of chick development
scales, claws, beak hardening; beak turns toward air cell; yolk sac absorption begins; yolk sac absorbed
what does SPIDES stand for
short period incubation during egg storage
what is the purpose of SPIDES
increase hatchability in eggs, increase chick quality, and decrease hatch window
what does SPIDES involve
exposing birds to 90˚ F for 4 hours at a time
what does the amnion prevent
dehydration
what depicts feathering
incubation temperature
what day do we move the eggs from the incubator to the hatcher
day 19
chick development in days of chickens, turkeys, quails, ducks, and ostriches
21, 28, 18, 28, 42
what is the temperature and relative humidity of the incubator
98.6-100 ˚F and 60% RH
difference between single stage or multistage incubation
single stage: all move together
multi stage: push eggs forward as they get added. air flow is important. larger birds will produce more heat and can be used to keep the smaller birds warm
what happens when eggs are moved to the hatcher
candle to remove infertile eggs
vaccinate eggs
pull basket when most of the chicks hatch to avoid dehydration
what factors influence the hatching time of the egg
parent flock age
storage time
egg size
hatching conditions
stress signals chick to start pipping
what does it mean when a egg has a straight crack vs is badly pipped
straight crack = chick had enough energy to continually pip
badly pipped = chick had to work a lot harder, has no energy left, could be dead
what factors influence hatchability
age of breeders, egg size, fertility, eggshell
hatchability calculation
hatched/total eggs
what is chick yield and what is the ideal number
chick weight as the percentage of initial egg weight; 66-68%
what occurs in the separator room
separate chicks from eggshells via vacuum
shells rendered
unhatched eggs and cull chicks euthanized via mincing
hatching trays cleaned
inspected by hand
cull
counted into groups of 100
spray vaccines
chick processing
what are reasons for culling chicks
unhealed navels
poor down
nutritional disorders
malformations
what occurs at the chick processing table
beak trimming
toe trimming
vaccines - spray and in ovo in the USA
split sex
how are spray vaccines effective
the chicks will ingest the vaccines via preening
how long does it take consumers to see genetic improvements
4-5 years
what are things done in R&D
diet selection, feeding studies, sibling testing, lifetime FCR
how do they look at genetic traits
CT, ultrasound, lithography to look at bone density, genomics, and gut health checks
what are the 3 classes
mediterranean, english, and american
what is nicking
poultry term for hybrid vigor. measure of how much better the offspring do than the average of the parents
number of chromosomes in chickens and turkeys
39 pairs, 40 pairs
chromosome letters for females
ZW
chromosome letters for males
ZZ
what are white leghorns used for
eggs
what are rhode island reds used for
eggs + meat
what are white plymouth rocks used for
eggs + meat
what are barred plymouth rocks used for
eggs + meat
what are new hampshires used for
eggs + meat
what are cornishs used for
meat
who is credited with starting the broiler industry
cecile steele
describe the cornish x white plymouth rock cross
cornish = english class, known for fat growth and muscular style
plymouth = american class, larger, good egg production
by crossing the two, we have birds that are larger, grow faster, have food muscling, and can also lay eggs well
describe the single comb white leghorn
mediterranean class, very light, petite, low maintenance, high egg production
describe the single comb rhode island red
american breed. dual purpose, does well in cage-free aviary-type systems
describe the broad breasted bronze
heritage breed, grow slower, larger lifespan, ability to mate naturally
what are examples of simple inheritance
colors - one gene
patterns and feather types - multiple genes
comb types
skin color
what are examples of sex-linked inheritance
patterns/coloring
feather growth rate
dwarfism
what are polygenic traits
Traits influenced by multiple genes, resulting in a continuous range of phenotypes
what are the four major things focused on in terms of genetics
welfare - how well developed its immune system is, support of skeletal system, cardiac fitness
breeder qualities - egg production + fertility
broiler qualities - F:G, growth, overall weight
processing qualities - quality grade, yield of product
what is heritability
the likelihood a trait is passed down from parent to offspring
what traits are lowly heritable (KNOW THIS)
breast fleshing, fertility, and blood spots
what traits are moderately heritable (KNOW THIS)
none of them hehe
what traits are highly heritable traits in BROILERS (KNOW THIS)
8-week broiler weight, total feed consumption, and fat deposition
what traits are highly heritable traits in LAYERS (KNOW THIS)
adult body weight, egg weight, and egg shape
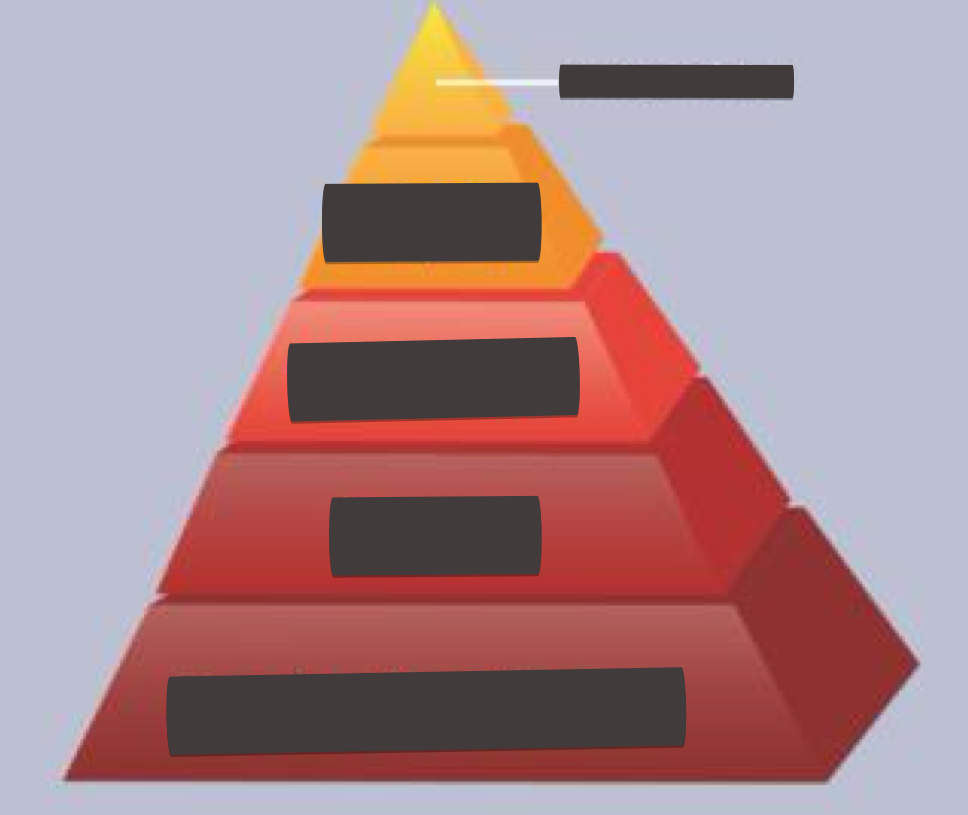
what belongs in the pyramid from bottom to top
production farms; parent; grandparent; great grandparent; pedigree/elite
what is the goal of the health of a bird
promote wealth, health, and productivity
what are some ways to maintain/improve health
sanitation, biosecuriy, vaccination, medication, vector control, and management
two types of immunity and describe them
innate - immediate, non-specific
adaptive - slower, targeted, memory-based
what do macrophages do
find pathogens, attack them, produce cytokines, and inflammation
what are examples of the immune organs
bursa, spleen, thymus, bone marrow, cecal tonsils, and peyer’s patches
3 types of vaccinations
live, live attenuated, and killed