BIOFOUND 5.3 Osmoregulation pt. 2
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MAKE SURE YOU ARE ANSWERING WITH TERM OR THE IMAGE ONES WONT MAKE SENSE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Kidney
An organ responsible for filtering blood, removing waste, and regulating water and electrolyte balance as part of osmoregulation.
Osmoregulation by the Kidney
Achieved through filtration of blood and reabsorption of water and solutes to maintain internal balance.
Renal Artery
Brings oxygenated, unfiltered blood into the kidney.
Renal Vein
Carries filtered blood away from the kidney.
Ureter
Transports urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
Urinary Bladder
Stores urine until it is excreted from the body
Cortex
One of the three major regions of the kidney, the outer region where filtration begins; contains renal corpuscles and convoluted tubules
Medulla
One of the three major regions of the kidney, the middle region with nephron loops and collecting ducts; key in creating a concentration gradient
Pelvis
One of the three major regions of the kidney, the central cavity where urine collects before draining into the ureter
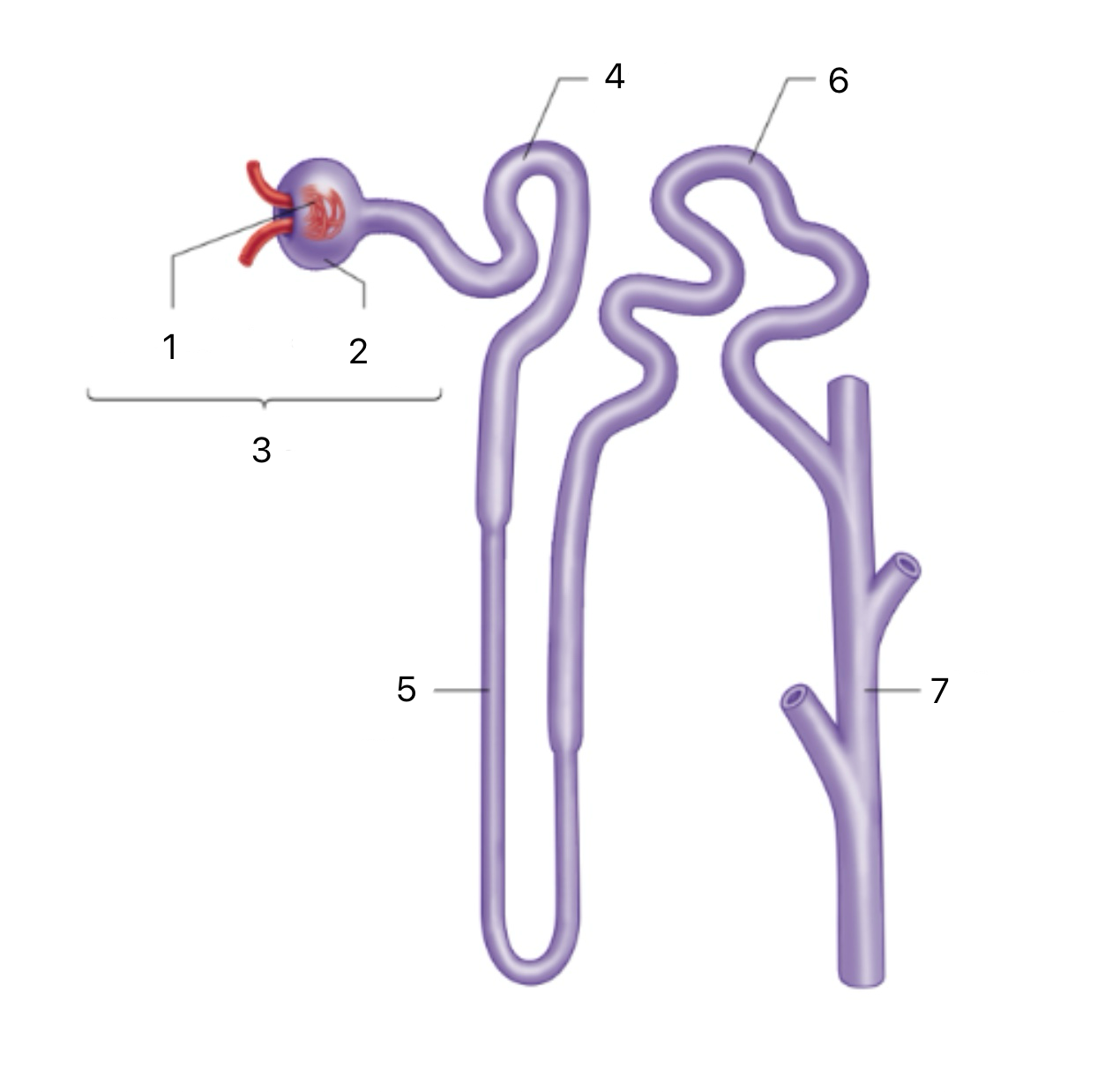
Nephron
The functional unit of the kidney; filters blood, reabsorbs water and solutes, and forms urine.
Medullary Gradient
A concentration gradient in the medulla that allows water reabsorption from the nephron; key to urine concentration.
Renal Corpuscle
The first section of the Nephron includes the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule; filters blood to form pre-urine.
Glomerulus
A ball of capillaries where high blood pressure pushes plasma and small solutes into Bowman’s capsule.
Filtration Force in Glomerulus
Blood pressure drives filtration of water and solutes from blood into the nephron.
Blood Pressure and Kidney Function
Low blood pressure can reduce filtration rate, impairing waste removal; high pressure can damage glomeruli.
Obligatory Reabsorption
Automatic reabsorption of water and solutes in the nephron, regardless of body need; occurs in the proximal tubule and loop of Henle.
Proximal Tubule
The second section of the Nephron Reabsorbs most of the filtered water, glucose, ions, and amino acids back into the bloodstream.
Descending Limb (Loop of Henle)
Part of the third section of the Nephron, permeable to water, which exits into the medullary gradient; concentrates the filtrate
Ascending Limb (Loop of Henle)
Part of the third section of the Nephron impermeable to water; actively transports ions (Na⁺, Cl⁻) out to dilute the filtrate and maintain the gradient
Regulated Reabsorption
Controlled reabsorption based on the body’s current needs; occurs in the distal tubule and collecting duct.
Distal Tubule
The fourth section of the Nephron Reabsorbs sodium and water in response to aldosterone; increases sodium retention and potassium excretion.
Collecting Duct
The fourth section of the Nephron reabsorbs water in response to ADH (antidiuretic hormone); increases water retention and concentrates urine.
Glomerulus
1
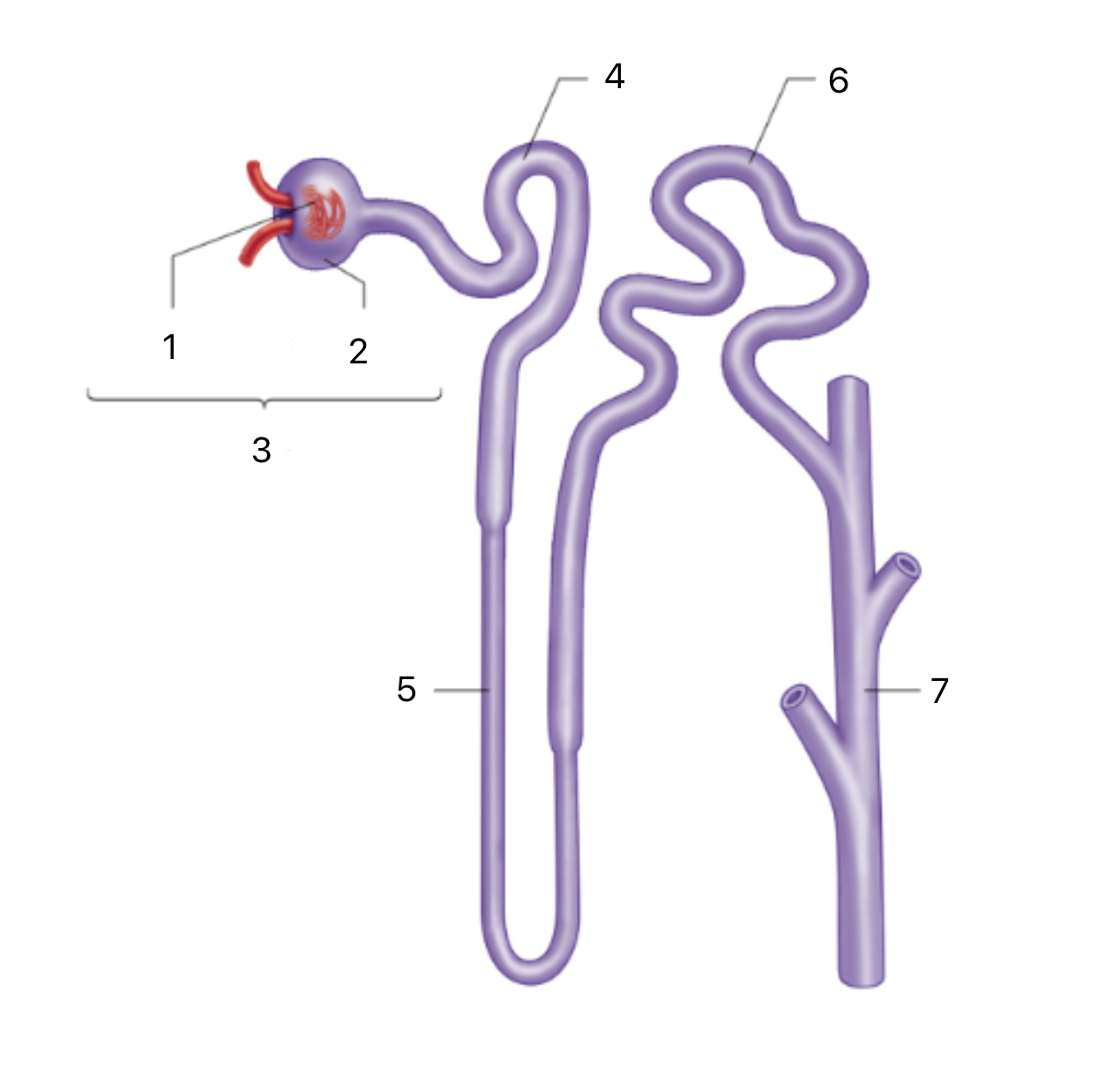
Bowman’s Capsule
2
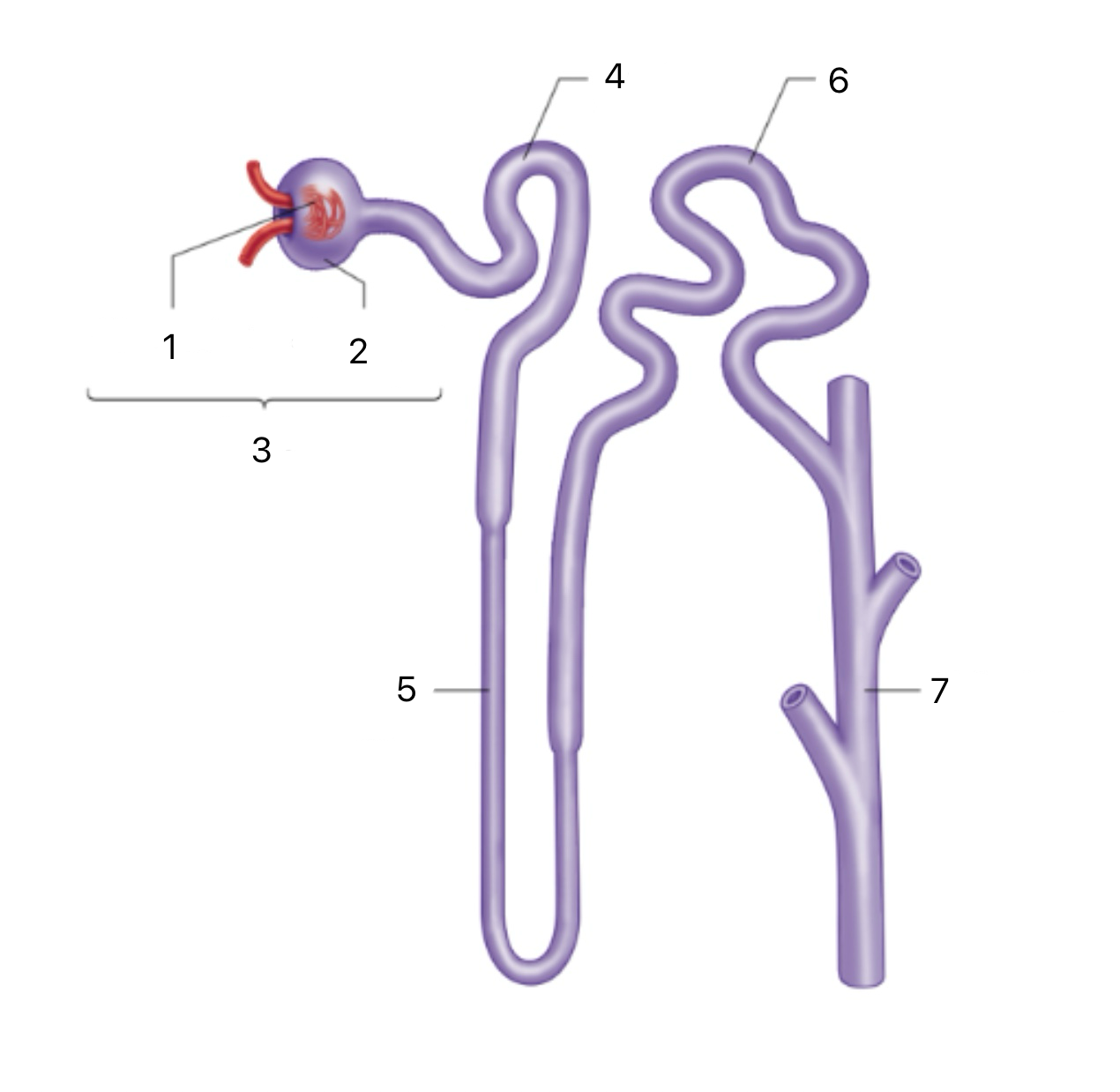
Renal Corpuscle
3
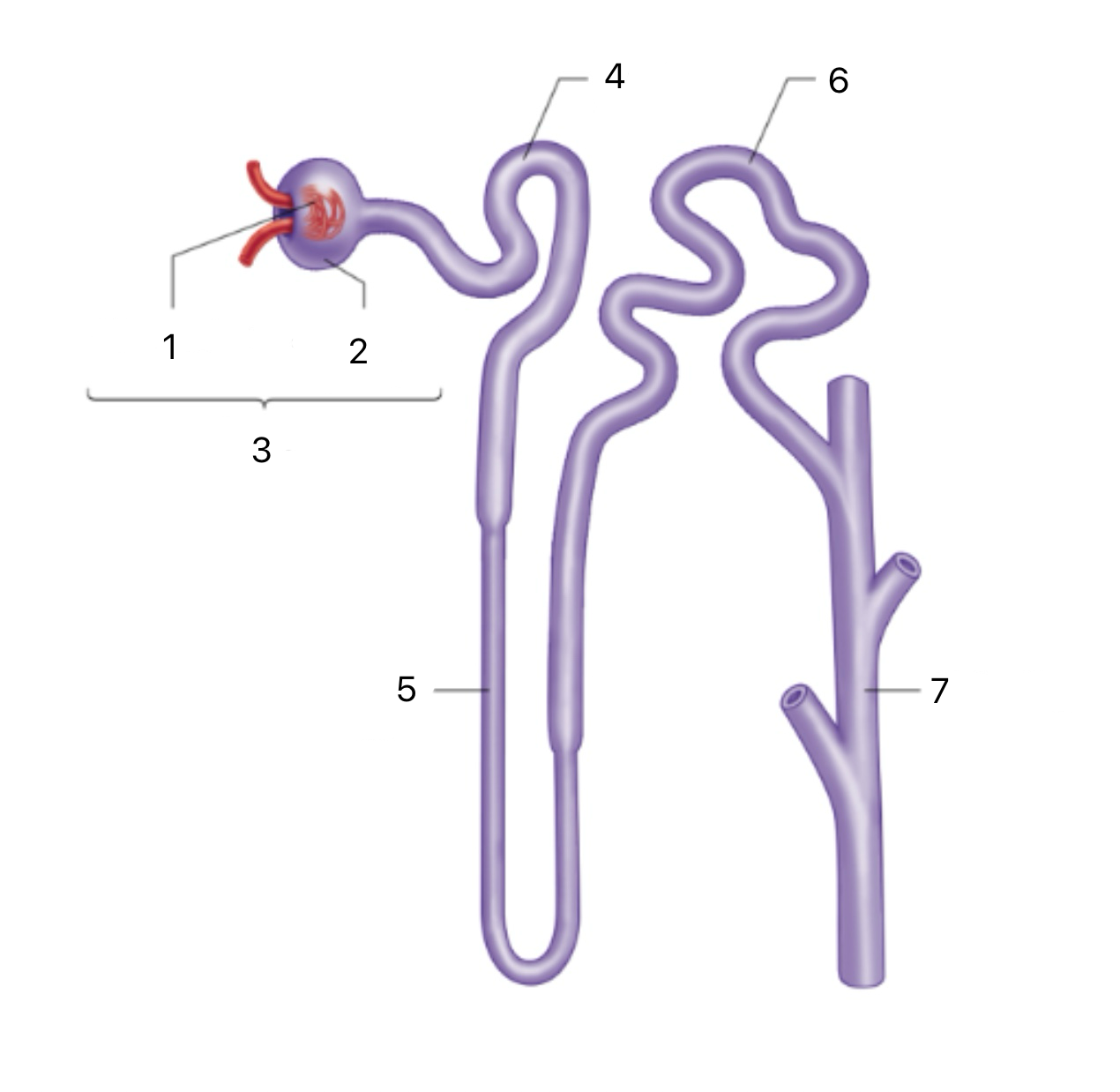
Proximal Tubule
4
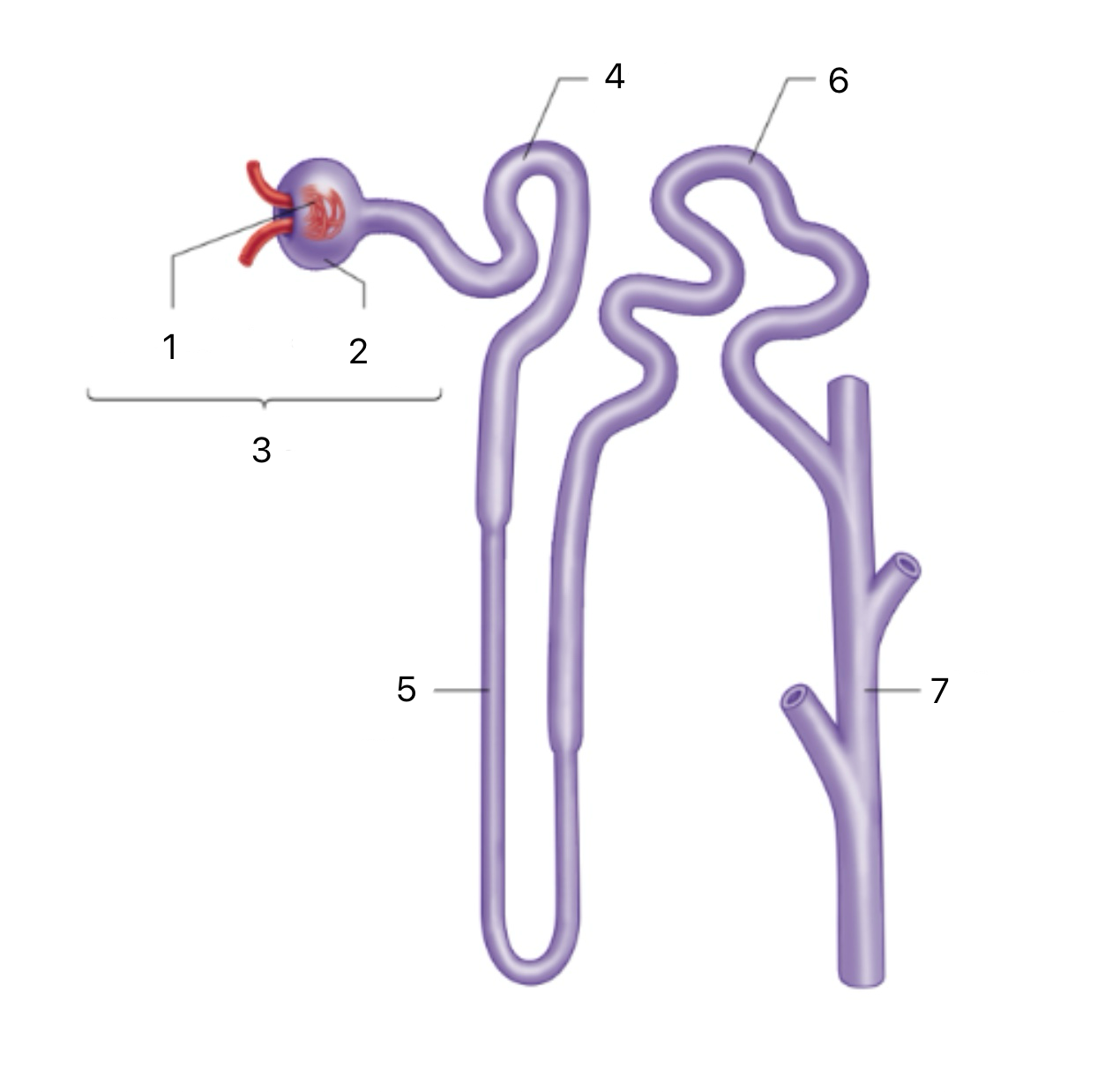
Loop of Henle
5
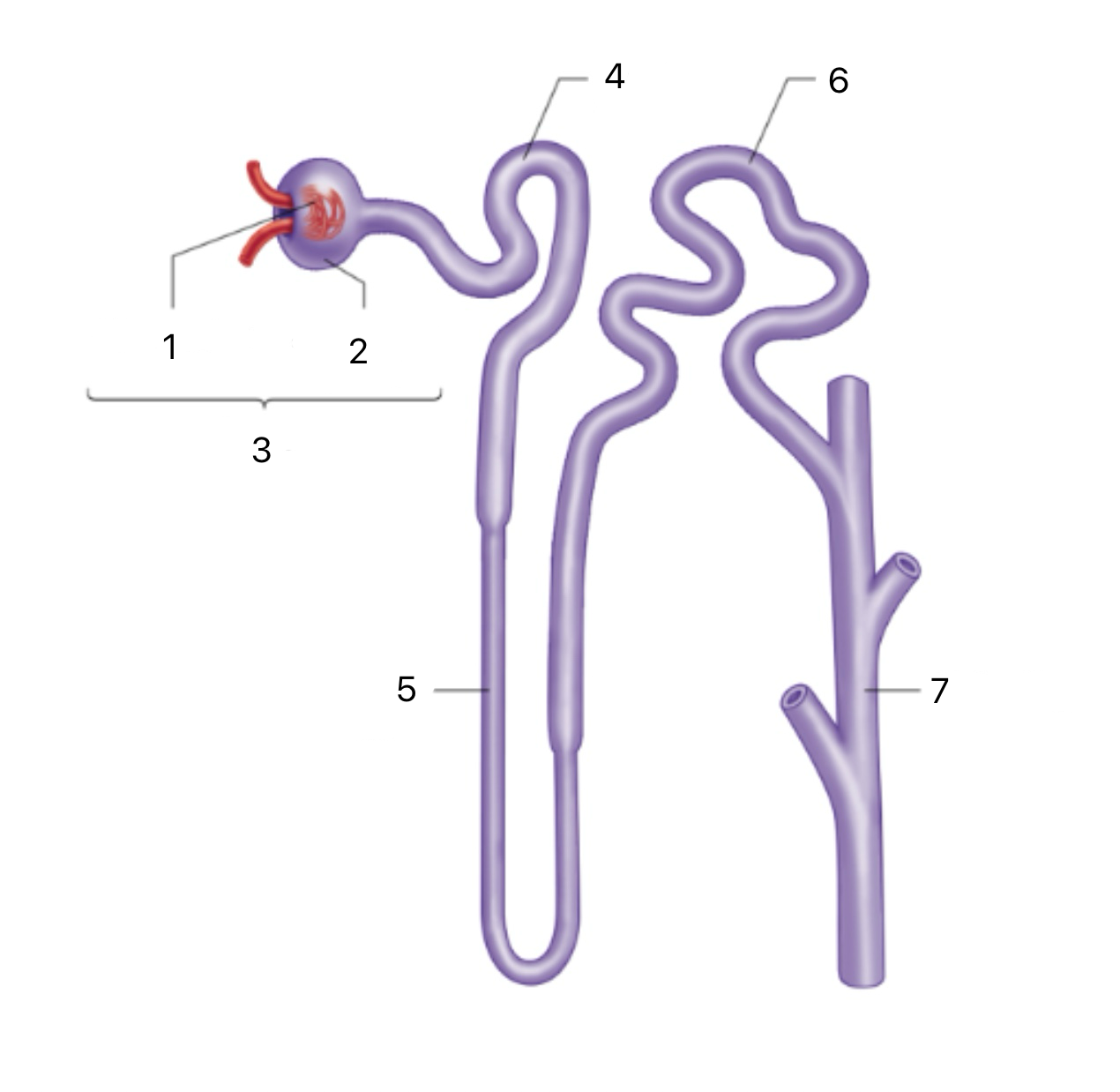
Distal Tubule
6
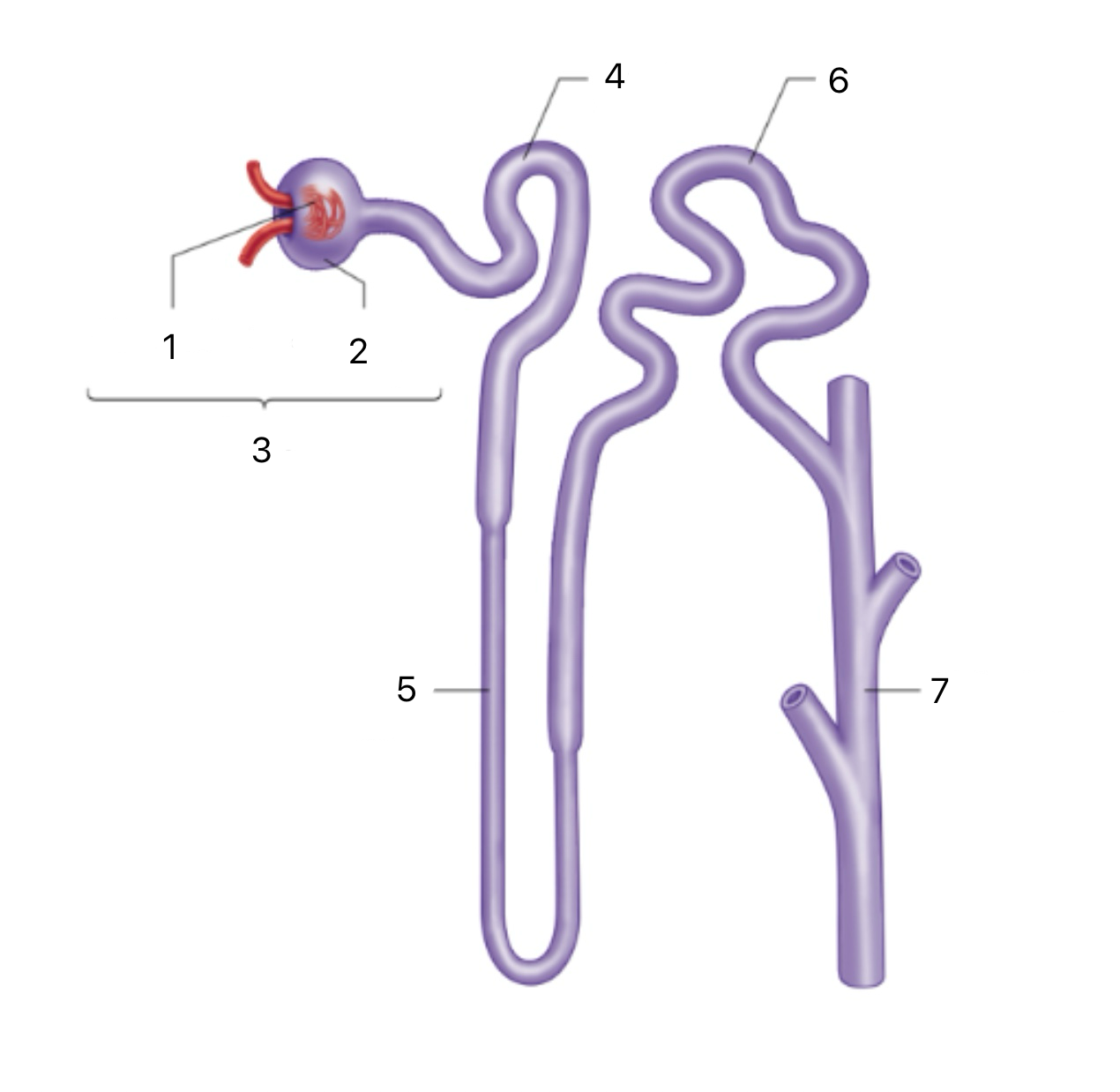
Collecting Duct
7