ap bio: unit 6 notes
ap biology unit 6: gene expression and regulation
hallo everyone! i’m a current student in ap bio and i’m updating my notes as we go along. so far my class has covered 6.1-6.3!
↪ if u don’t like times new roman… idk i’ll go cry.
⟡ 6.1 - DNA & RNA structure
how heritable information provides for continuity of life
DNA is inherited
monomers of nucleotides in the DNA molecule carry “codes” of info about the organism
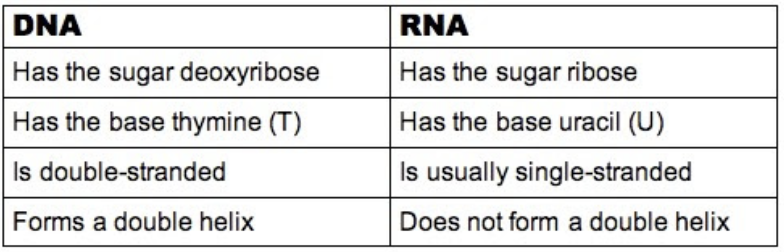
── .✦ DNA vs RNA
DNA
replicates on its own
carries genetic info
RNA
reads DNA to make proteins; mRNA, rRNA, tRNA
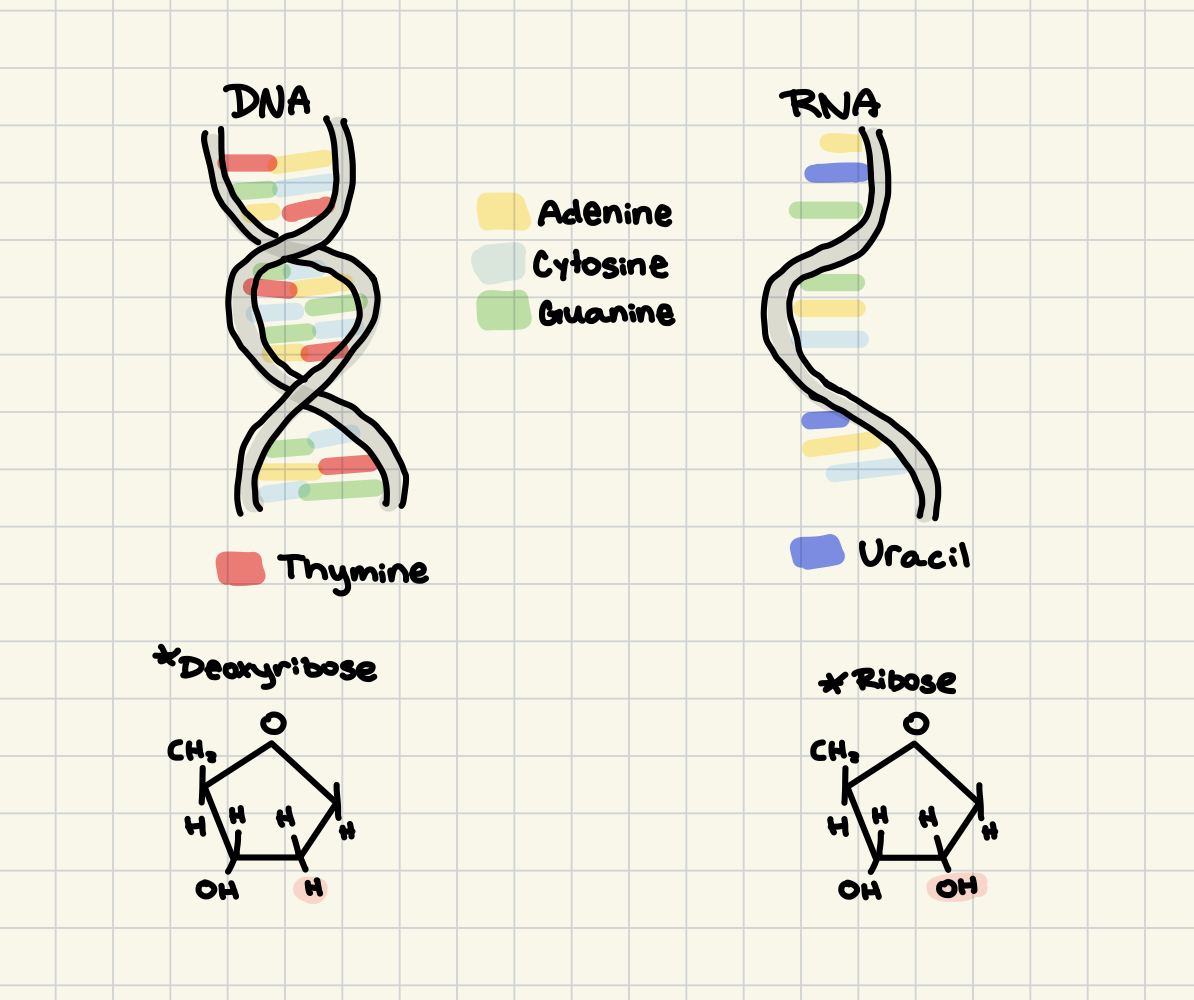
Chargaff’s Rule of Base Pairings in DNA:
A = T
G = C
for RNA:
A = U
G = C
carbons of the deoxyribose sugar are numbered clockwise, DNA bases are “read” in the 5’ to 3’ direction
⟡ 6.2 - replication
replication - DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division in the nucleus of the cell
replication of cells for growth or for reproductive cells to pass to offspring
semi-conservative: two copies of the original DNA molecules are produced, conserving (replicating) the information from one half of the original DNA
topoisomerase:
loosens tension of DNA strand
helicase:
separates DNA strands by breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs
DNA primase:
adds nucleic acid that starts DNA synthesis
primer is the short RNA segment that helps to start the copying of DNA
✰ DNA polymerase:
enzymes that replicate the existing DNA strand to make a complimentary strand
adds DNA bases from 5’ to 3’ on the leading strand
leading strand adds nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction of the NEW strand continuously
one primer needed
on the lagging strand, since DNA cannot be copied in the 3’ to 5’ direction, it is discontinuous and done in fragments called okazaki fragments
multiple primers are needed.
okazaki fragments
DNA cannot be copied in the 3’ to 5’ direction
DNA is copied in fragments
multiple primers are needed
⟡ 6.3 - transcription & RNA processing
gene: DNA segment that codes for one polypeptide
2 steps of protein synthesis:
transcription: genes transcribed from DNA to messenger RNA(mRNA)
translation: mRNA ‘translated’ into proteins by ribosomes and transfer RNA (tRNA)
purpose: Synthesis of RNA using DNA as a template. Where does this occur in the cell?
steps:
initiation: RNA polymerase - binds to promoter; copies DNA sequence to make RNA sequence.
template strand: only ONE strand of DNA is transcribed it codes for a polypeptide/tRNA/rRNA
elongation: pre mRNA, RNA polymerase, rRNA, nucleotides, uracil.
termination: RNA polymerase, terminator (mainly be aware of the stages, not the names)
step 1 of transcription - initiation: Only ONE strand of DNA is transcribed. This is called the template strand. Codes for a polypeptide or tRNA or rRNA. The mRNA that is transcribed is complementary to the original DNA strand. What does this mean? RNA polymerase joins RNA nucleotides as they base-pair along the DNA template strand. What enzymes perform this in DNA replication? Which direction is transcription occurring? The DNA sequence at which RNA polymerase attaches is called the promoter. The DNA sequence that signals the end of transcription is called the terminator. Transcription Initiation complex; Important for gene expression.
Step 2 of Transcription - Elongation: RNA polymerase moves along the DNA, synthesizing a new RNA molecule based on the DNA template by matching the current DNA base with the proper RNA. RNA nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the growing chain. With what type of bonds does RNA polymerase join the nucleotides? (Covalent bonds) As the complex moves down the DNA strand, the double helix reforms, with the new RNA molecule straggling away from the DNA template.
Step 3 Transcription - Termination: Scenario B is when transcription ends as expected at the terminator site. After RNA polymerase transcribes a mRNA at this point? Terminator sequence in mRNA moves from the DNA nucleus to cytoplasm. Rough or smooth ER? What is happening in detail in scenario C? Disruption of gene expression, DNA damage, run into collisions with other genes being encoded.
⟡ 6.4 - translation
⟡ 6.5 gene expression & regulation
vocab!
regulatory gene: codes for a regulatory protein that activated or represses expression of a gene
promoter: nucleotide sequence that enables a gene to be transcribed
operator: region of DNA of operon that is the binding site for regulatory protein
structural genes: genes that are co-regulated y the operon
all cell types have the same DNA in their nucleus, but not all DNA is “expressed” in all cells
operon: a genetic regularotry susem in bacteria which codes for proteins.
regulatory gene
promoter
made up of genes that produce an mRNA during transcription
PCR: