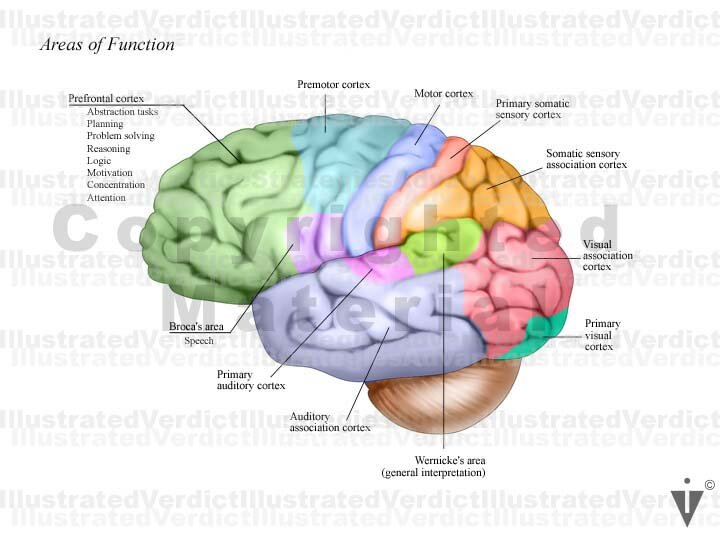
explo psych + neuroscience
eeg
hd-eeg = high density eeg
seeg = stereo eeg
created by hansberger
tms (transcranial magnetic stimulation)
magnetic field stimulate nerve cells in brain
influence electrical activity of brain
the pulse artifact
transient flow of current in the coil with a current peak of several kA
tms-eeg results
unconsciousness - no dreams, asleep
NREM
midazolam
xenon
propofol
anesthetic, but totally unconscious
consciousness- dreams, asleep
awake
REM
locked-in syndrome
no longer able to move, trauma causing disruption in neurons, but conscious
ketamine
anesthetic, conscious, but feel nothing
reaction time = how fast you respond to something
memory
hippocampus - part of brain required for episodic memory and emotion
holds short term memories and transfer to long term memories
emotional processing, including anxiety, avoidance behaviors
to stop his seizures after cracking his skull
lost memory, couldnt form new memories
but still retained memory to form sentences (15 minutes after repeating to himself)
patient known as HM had his hippocampus surgically removed
couldnt form new episodes
declarative memory

hippocampal structure is conserved across species
hippocampus is relatively large in the mouse brain
performs similar functions in all species
forming a declarative (episodic) memory
encode memory
consolidation (can take multiple sleep cycles)
retrieval to long term
memory is continually reconsolidated
elizabeth loftus car accident experiment
people watched a car crash
asked specific question “About how fast were the cars going when they (smashed / collided / bumped / hit / contacted) each other?
people who were asked smashed said the fastest speed
contacted people said slowest speed
how much energy does the human brain use?
electromagnetic induction law
time varying current in coil
time varying magnetic field
induced current in conductor
transcranial magnetic stimulation (influence brain activity, treats depression ocd, etc.)
circuit from brain to muscles
with each tms pulse
apply a large transcient (not permanent) current to a coil of wire
electrical current induces a magnetic field
magnetic field passes through skull with little force
transcient magnetic field induces a transient electric field in the brain
induced electric field can be sufficient to stimulate cortical neurons
repeat many pulses in sequence for repetitive tms to produce longer lasting changes in excitability (stimulus)
macroscopic response (visible to naked eye)
evoked neural activity (eeg)
changes in blood flow and metabolism
pet = evaluate cerebral metabolism and blood flow
fmri = shows activity in specific parts of brain (mri is different and only for organs)
spect = a type of imaging test that uses a radioactive substance and a special camera to create 3D pictures
muscle twitch
emg = asses health of muscles and nerve cells that control them
gamma <25 Hz = awareness
beta 13-25 Hz = alertness
alpha 8-12 Hz = relaxed
theta 4-7 Hz = tired
delta 1-3 Hz = sleep
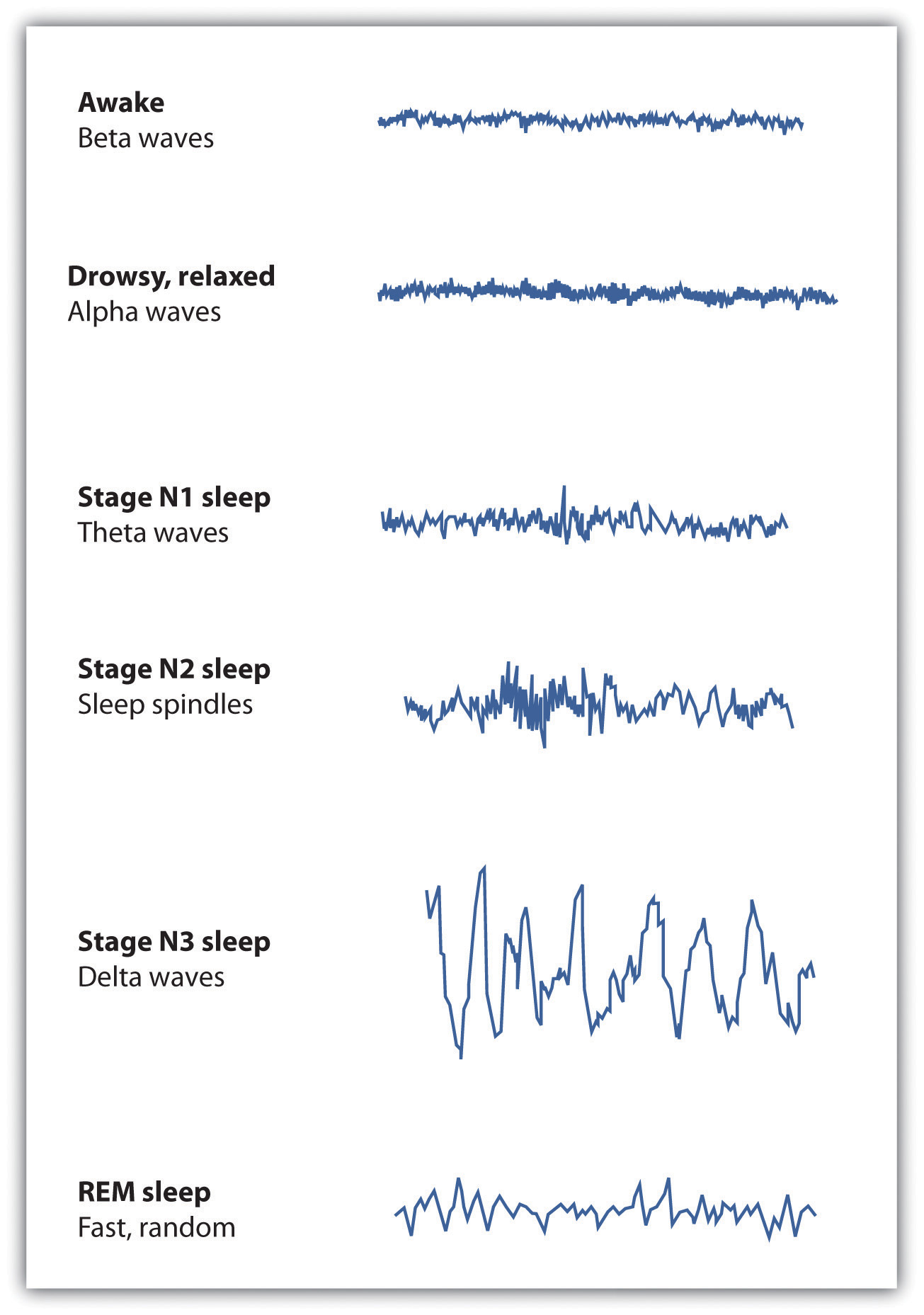
cycle repeats 4-5 times per night
rem = rapid eye movement
dreaming in rem with eye movement
hemispatial neglect
= completely neglect half of their world
usually from strokes
cant do anything on neglected side
music and the brain
auditory motor synchronization = predictive brain process that uses movement networks
auditory noise increase stability (when standing)
music triggers emotional responses by activating the limbic system , controlling motivation and pleasure
quantitative research vs qualitative
quantitative = numerical/measurable data
qualitative = personal accounts that illustrate how people respond within society
nurture vs nature
= nature refers to how genetics influence an individual's personality, whereas nurture refers to how their environment (including relationships and experiences) impacts their development.
narcissistic personality disorder
sense of self + lack of empathy
affect a person’s very nature + distort understanding of themselves
decreased ability to connect and form healthy bonds with others
hunger, satiation and obesity
developmental psychology
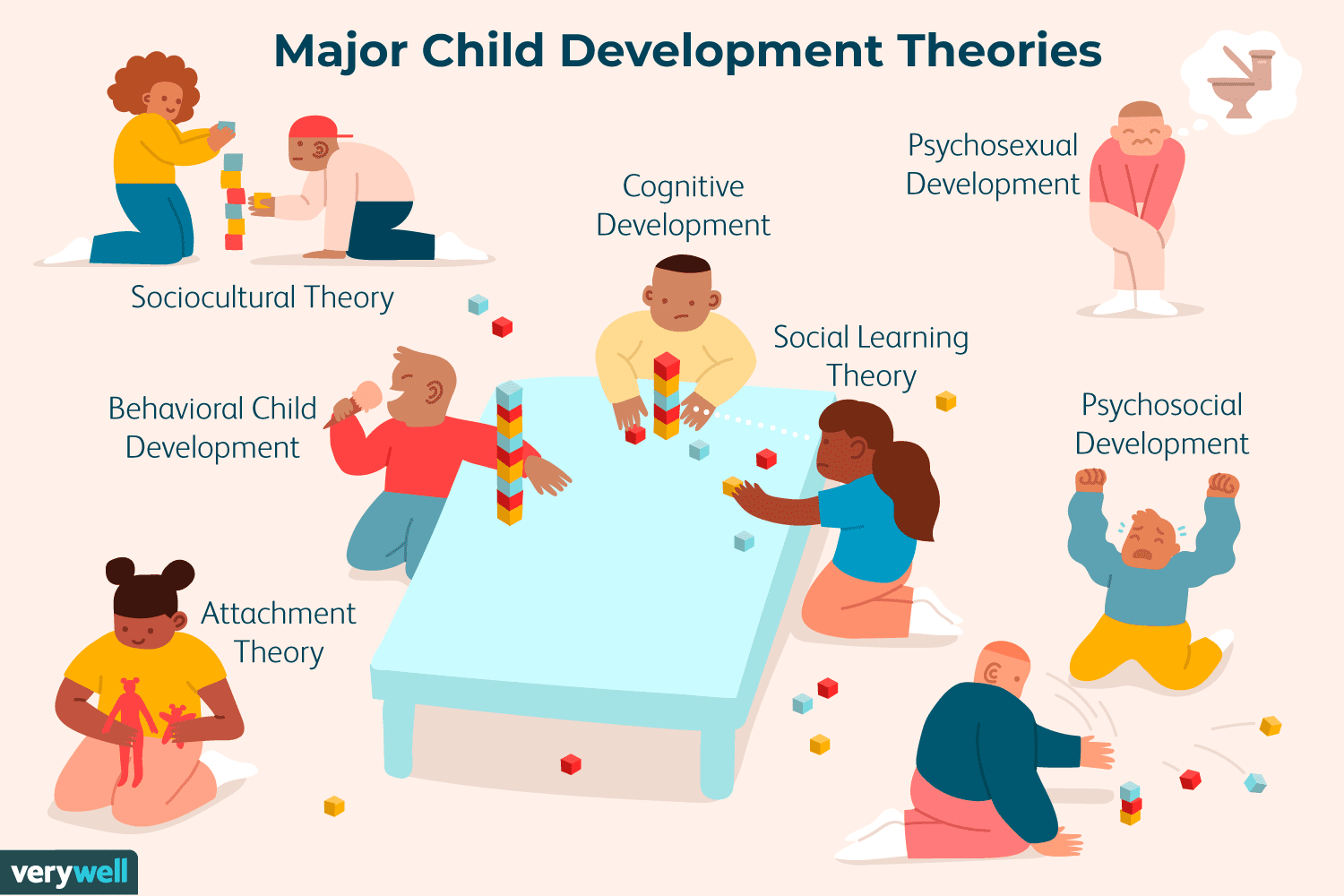
social development theories
= social interaction is fundamental to cognitive devlopment. these theories emphasize the role of culture, language, and social interactions in shaping the learning process. they suggest that learning occurs through social processes before it becomes an individual, internalized process
attachment theory (bowlby and ainsworth)
psychosocial theory (erikson)
stages of moral development (kohlberg)
social development theory (bandura)
ecological systems theory (bronfenbrenner
child development
toddlers, 24-35 months
cognitive
language explosion (girls typically ahead of boys)
curiosity
colors
concept of print
sense of world extends to family and neighborhood
physical
potty training
self feeding
handedness preference
motor skills
daily routines
increased balanced and coordination
social emotional
concept of self
parallel play (not cooperative)
increased independence
bond with family
big emotions, limited vocab
play patterns + toys
synbolic play (items that represent smth else)
roleplay
preschool/prek, 3+4 years
cognitive
recognizing letters + numbers
shapes
life science (matching baby animals to parents, observing plants)
write names
sense of world extends to immediate community (library, school, park, grocery store)
sequencing (order, steps)
curious and not afraid to ask questions
physical
potty trained night + day
self feeding using utensils
fairly established handedness preference
improved fine motor skills (ability to pick up small items)
dressing self including zippers, buttons
social emotional
beginning of cooperative play (playing beside and with others)
taking turns + sharing
increased empathy
big emotions associated with friends + changing routines
emerging gender preference in terms of friends
interested in how their actions affect others
play patterns + toys
peak of deep conceptual interests
symbolic play with gender specific roles
rough and tumble play
simple crafts
toys with favorite characters
gross motor and outdoor toys
early elementary, 5-7 years
cognitive
reading: sightwords, dhapter books (rapid development)
writing letters, words, sentences
operations (add+subtract)
geometry
patterns
forming hypotheses
sense of world broadens to include town and that there’s a big connected world
sequential thinking
physical
improved gross skills, throwing, kicking
increase coordination for running and balance
improved motor skills (cutting along curved lines)
ability to carry out most daily routines including hygiene
understands safety practices
social emotional
cooperative play
increased empathy
more gender preference in terms of friends
capable of understanding/ creating rule based games
evidence of social constructs, including gender based beliefs
increase in gender intensified roles
play patterns + toys
more play time spent in organized sports
significant drop in unstructured play time
rough and tumble play (play fighting, chase)
construction play
collectibles
cards (trading, comparing)
sensory toys (smelly, sticky, shiny, stretchy)
big kids, 8-10 years
cognitive
multuplication, division
measurement data
follow directions
working memory improvements
avoiding distractions
physical
throwing with speed, running
concept of healthy and less healthy foods
social emotional
solidified friends based on common interests
ability to negotiate common friendship issues (sharing, taking turns)
feels empathy for others and can name emotions
developing sense of self (who they are, what they enjoy)
shifting some attachment from family to friends