Acids Bases and Salts
==Acid and Base/Alkali Reactions==
Acid + Metal → salt + hydrogen
- Sulphuric acid + iron→ iron sulphate + hydrogen
Base/alkali + acid → salt + water
- Sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid Sodium chloride + water
Acid + metal carbonate → salt + carbon dioxide + water
- Nitric acid + magnesium oxide magnesium nitrate + carbon dioxide + water
Alkali + ammonium salt → salt + ammonia + water
- Sodium hydroxide + ammonium chloride sodium chloride + ammonia + water
==Acid: Proton Donors/ Dissociate into H+ ions==
- Have pH between 1 (strong) and 6 (weak)
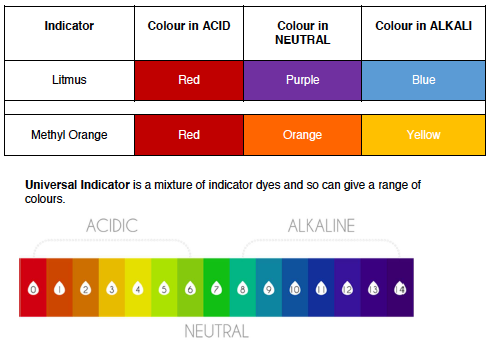
- Turns blue litmus red
- Turns methyl orange indicator red
==Bases: Proton Acceptors/ Dissociate into OH- ions==
- Are the oxides and hydroxides of metals
- Neutralise acids to give a salt and water only
- Are mainly insoluble in water
Alkalis: (are bases that dissolve in water)
- Feel soapy to the skin
- Turn litmus blue
- Gives solutions with a ph greater than 7
- · Give solutions that contain OH – ions
==Neutrality, acidity, alkalinity==
- pH scale runs from 1 – 14
Key facts:
Acids have a ph less than 7
The more acidic a solution, the lower the ph
- Neutral substances, such as pure water have a ph of 7
- Alkalis have ph greater than 7
- Strong acid or base completely ionize in water
- Weak acids partially ionize in water Ways to Measure pH:
Substances that change colour when added to an acid/alkali are called indicators. They are often in solution form but can also be found as paper
==Metal and non-metal oxides==
- Acidic oxides: Non-metal oxides that dissolve in water and form an acidic solution
- Basic oxides: Metal oxides that dissolve in water and form basic solution
- Neutral oxides: Oxides with a pH of 7. Do not react with Acids or Alkalis
- However there some exceptions for this rule, for example carbon monoxide.
- Amphoteric oxides: those that react with both an acid and an alkali to give a salt and water.
eg. zinc and aluminum oxides
Preparing Salts
==Preparing Soluble Salts==
Method A: Neutralization
- Excess insoluble compound (metal/base/carbonate) reacts with acid whilst being heated
- Insoluble base is filtered out
- Solution is heated in an evaporating dish to form soluble salt crystals
Method B: Titration
- Phenolphthalein is added to an alkali (soluble base)
- Add acid to solution using burette; note volume of acid required for solution to change color
- Repeat without indictor using noted acid volume
- Heat in evaporating dish to form soluble salt crystals
==Preparing Insoluble Salts==
Method C: Precipitation
2 soluble salts added to water and mixed
Note: one soluble salt should always be a potassium or sodium solution (eg. potassium sulfate)
Filter out and clean precipitate with distilled water
Dry insoluble salt precipitate in oven

Tests
==Testing Cations==
| Cation | Aqueous NaOH | Aqueous Ammonia |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al3+) | White soluble precipitate, turns colorless in excess | White precipitate, insoluble in excess |
| Ammonium (NH4+) | Pungent ammonium gas produced turns damp red litmus blue | |
| Calcium (Ca2+) | White precipitate, insoluble in excess | Faint or no precipitate |
| Copper (Cu2+) | ^^Blue precipitate, insoluble in excess^^ | ^^Blue precipitate, soluble in excess to give a dark blue solution^^ |
| Iron(II) (Fe2+) | %%green precipitate, insoluble in excess%% | %%green precipitate, soluble in excess%% |
| Iron(III) (Fe3+) | ==Reddish-brown precipitate, insoluble in excess== | ==Reddish-brown precipitate, insoluble in excess== |
| Zinc (Zn2+) | White precipitate, soluble and turns colorless in excess | White precipitate, soluble and turns colorless in excess |
| Chromium (Cr3+) | Grey green precipitate, soluble to give dark green solution in excess | Grey green precipitate, insoluble in excess |
==Testing for Anions:==
Sulfate ions (SO42-):
- Add dilute nitric acid, then add aq. barium nitrate
- White precipitate formed
Sulphite ions (SO32-):
- Add acidified potassium permanganate and heat
- Color changes from pink to colorless
Halide ions:
- Add nitric acid, then aqueous silver nitrate
| Chloride (Cl-) | White precipitate |
|---|---|
| Bromide (Br-) | Cream precipitate |
| Iodide (I-) | Yellow precipitate |
Nitrate ions (NO3-):
- Add aqueous sodium hydroxide then add warm aluminum foil
- Pungent gas produced, turns damp red litmus blue
Carbonate ions (CO32-):
- Add dilute hydrochloric acid
- If bubbles/ gas produced turn limewater cloudy, carbonate ion present
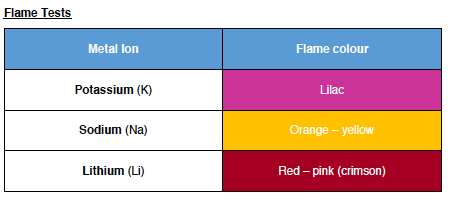
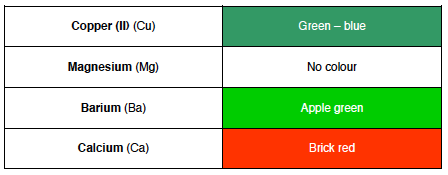
==Flame Tests==
==Test for Gases:==
| Gas | Test result |
|---|---|
| Ammonia (NH3) | Damp red litmus paper turns blue |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | Bubble gas through–from colorless to cloudy |
| Chlorine (Cl2) | Bleaches red/blue litmus paper |
| Hydrogen (H2) | Place lighted splint, squeaky pop |
| Oxygen (O2) | Place glowing splint, splint relights |