psych unit #5
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
harry harlow
experimented with the monkeys and they chose the mother who would hold them, not the one who fed them
Supported the concept of imprinting
Changed the concept of secure and proper attachment
jean piaget
The Theory of Cognitive Development by Jean Piaget, the Swiss psychologist, suggests that children's intelligence undergoes changes as they grow. Cognitive development in children is not only related to acquiring knowledge, children need to build or develop a mental model of their surrounding world
konrad lorenz
A newborn creature bonds to the type of animals it meets at birth
Most obvious examples are ducklings
Proper imprinting leads to children learning to follow and adhere to their parents. A precursor to proper attachment
Demonstrates an innate need to bond
lev vygotsky
Vygotsky's theory (1962) proposes that the child's development is best understood in relation to social and cultural experience. Social interaction, in particular, is seen as a critical force in development.
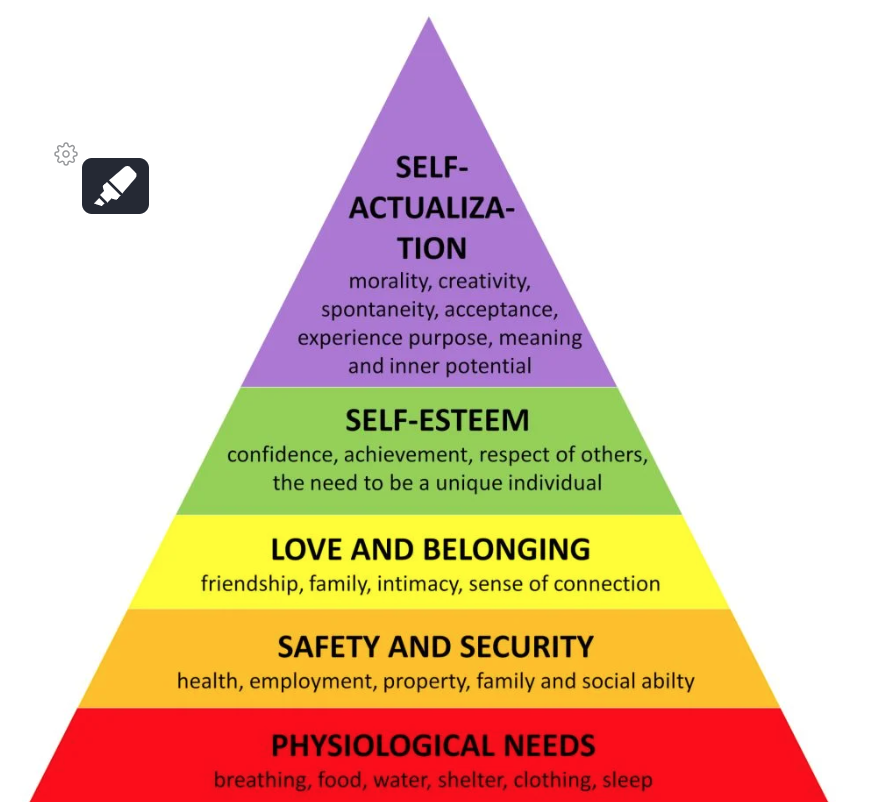
abraham maslow
Abraham Maslow's pyramidal "Hierarchy of Needs" model is a highly-influential way of organizing human needs from the most "basic" to the most advanced. Maslow's argument is that the most basic needs must be met before people can move "up" to the more advanced needs.
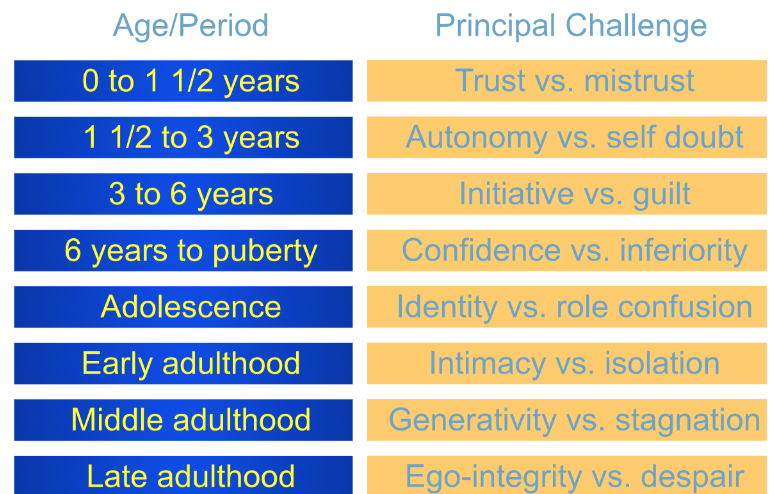
erik erickson
Supported Harlow’s studies on attachment. Attachment at a young age brings trust.
Proper relationships should bring autonomy and initiative to young children.
lawrence kohlberg
Kohlberg (1981,1984) sought to describe the development of moral reasoning by posing moral dilemmas to children and adolescents, such as “Should a person steal medicine to save a loved one’s life?” He found stages of moral development.
mary ainsworth
analyzed attachment to mothers and strangers
The child does not play with stranger and cries when her mother leaves but is calmed down when she comes back
maturation
The development of the brain unfolds based on genetic instructions, causing various bodily and mental functions to occur in sequence
Ex. standing before walking, babbling before talking
habituation
Habituation is a decrease in response to a stimulus after repeated presentations.
roosting reflex
Infants are born with reflexes that aid in survival, including rooting reflex which helps them locate food
assimilate vs. accomodate
While assimilation involves the incorporation of new data into one's existing schemas, accommodation requires a more active and transformative approach, in which learners must modify their current cognitive frameworks to accommodate previously unencountered insights.
attachment
Attachment theory focuses on relationships and bonds (particularly long-term) between people, including those between a parent and child and between romantic partners. It is a psychological explanation for the emotional bonds and relationships between people
imprinting
A newborn creature bonds to the type of animals it meets at birth
Most obvious examples are ducklings
Proper imprinting leads to children learning to follow and adhere to their parents. A precursor to proper attachment
Demonstrates an innate need to bond
object permeance
objects that are out of sight are also out of mind
egocentrism
They cannot perceive things from another’s point of view
ex. think you can see through their eyes, think you already know what happened even if you weren’t there
theory of mind
Preschoolers, although still egocentric, develop the ability to understand another’s mental state when they begin forming a theory of mind.
They think that everyone knows everything
conservation
Conservation psychology is the scientific study of the reciprocal relationships between humans and the rest of nature, with the goal of encouraging conservation of the natural world.
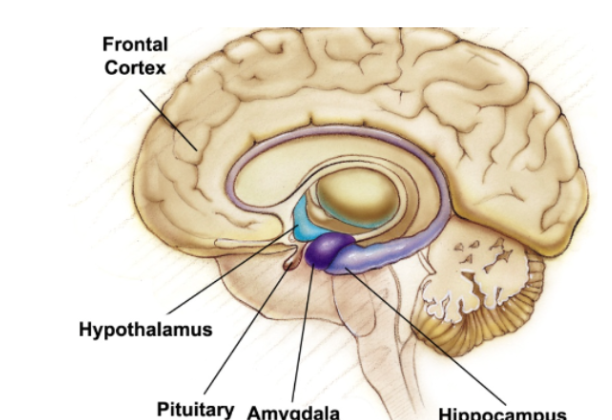
adolescence
Developmental period beginning at puberty and ending at adulthood
During adolescence, neurons in the frontal cortex grow myelin, which speeds up nerve conduction. The frontal cortex lags behind the limbic system’s development. Hormonal surges and the limbic system may explain occasional teen impulsiveness.
attachment
Attachment theory focuses on relationships and bonds (particularly long-term) between people, including those between a parent and child and between romantic partners. It is a psychological explanation for the emotional bonds and relationships between people.
parenting styles
authoritarian (R↓D↑), authoritative (R↑D↑), permissive(R↑D↓), uninvolved (R↓D↓)
association
a connection or relationship between two items (e.g., ideas, events, feelings) with the result that experiencing the first item activates a representation of the second. Associations are fundamental to learning theory and behaviorism
unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
The stimulus that elicits an unconditioned response
unconditioned response (UCR)
The response elicited by an unconditioned stimulus without prior learning
conditioned stimulus (CS)
A previously neutral stimulus that comes to elicit a conditioned response
conditioned response (CR)
A response elicited by a previously neutral stimulus that has become associated with the unconditioned stimulus
acquisition
Initial learning stage in classical conditioning; conditioned response becomes elicited by the conditioned stimulus
extinction
Weakening of a conditioned association in the absence of an unconditioned stimulus stimulus or reinforcer
No longer present UCS
spontaneous recovery
Reappearance of an extinguished conditioned response after a time delay
Re-present the UCS
generalization
involves giving a conditioned response to stimuli that are similar to the CS
Ex. fear of dogs because of dog attack
discrimination
involves responding to one stimulus but not to stimuli that are similar
Ex. specific spider that you are afraid of
trial & error learning
Learner gradually discovers the correct response by attempting many behaviors and noting which ones produce the desired consequences
skinner box
Using Thorndike’s law of effect as a starting point, Skinner developed the operant chamber, or the Skinner box, to study operant conditioning
The Skinner box, comes with a bar or key that an animal manipulates to obtain a reinforcer like food or water. The bar or key is connected to devices that record the animal’s response.
repeated behaviors will happen again
When it would come close to the lever, then it would be rewarded
positive reinforcer
A pleasant event that follows an operant response, increasing the likelihood that the response will recur
negative reinforcer
Strengthens a given response by removing aversive stimuli
Still a reward
Ex. if you have a headache and you take advil, that is a negative reinforcer
Getting rid of the headache
positive punishment
An aversive stimulus which diminishes the strength of the response it follows
omission training (negative punishment)
The removal of a reinforcing stimulus after a response (take away phone, car)
continuous reinforcement
A reinforcement schedule in which all correct responses are reinforced
partial reinforcement
Reinforcement schedule in which some, but not all, correct responses are reinforced
Stronger form of reinforcement
fixed ratio
Rewards appear after a certain set number of responses
Ex. factory workers getting paid after every 10 cases of product are completed
fixed interval
Rewards appear after a certain fixed amount of time, regardless of number of responses
Ex. weekly or monthly paychecks
variable ratio
Variable ratio (VR)
Rewards appear after a certain number of responses, but that number varies from trial to trial
Ex. slot machine payoffs
variable interval
Rewards appear after a certain amount of time, but that amount varies from trial to trial
Ex. random visits from the boss who delivers praise
badura’s bobo doll experiment
Bandura’s Bobo doll study (1961) indicated that individuals (children) learn through imitating others who receive rewards and punishments
First, the child is more likely to attend to and imitate those people it perceives as similar to itself
Second, the people around the child will respond to the behavior it imitates with either reinforcement or punishment
Third, the child will also take into account of what happens to other people when deciding whether or not to copy someone’s actions
mirror neurons
Neuroscientists discovered mirror neurons in the brain of animals and humans that are active during observational learning
long term potentiation
Biological process involving physical changes that strengthen the synapses in groups of nerve cells; believed to be the neural basis of learning
Ex. if a mouse is placed in a pool of murky water, it will swim about until if finds a hidden platform to climb out on. With repetition, the mouse soon learns to locate the platform more quickly
effects of modeled behavior
Modeling may teach a new behavior, influence the frequency of a previously learned behavior, or increase the frequency of a similar behavior.
latent learning
Learning that occurs without any obvious reinforcement of the behavior or associations that are learned
Understanding locations of buildings you walk by each day
Learning a driving route but never showing until you’re asked to drive it
Connected to motivation
Why people learn without rewards/punishments or conditioning
insight learning
Learning that occurs rapidly as a result of understanding all the elements of a problem
“Aha” moments
Solving a riddle