particle model of matter, topic 3
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sep-november
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
solids
distance between particles
bond between particles
motion of particles
particle diagram
very close
very strong
vivrate
liquids
distance between particles
bond between particles
motion of particles
particke diagram
very close
strong
slide past slowly
gases
distance between particles
bond between particles
motion of particles
particle diagram
far apart
none
very fast, random directions
movement of partciles
what particles have the same and which one js different
simmilar
liquid and gases- can move from place to place
different
soldi- only vibrate
closeness of particles
what particles have the same and which one is diff
simmilar
solids+liquids-as particles are very close
differnet
gasses-particles are very far apart
bonds between particles
what particles have the same and which one is diff
simmilar
solids+liquids-particles are very strong
different
gasses-particles have no bonds holding them together
explain why can gasses be compressed but liquids and solids can’t (5)
-solids liquid particles are close together
-when compressing a solid or a liquid there is no space
-gas particles are far apart
-when compressing a gas there is space to be compressed together
-you cannot compress liquids or solids
explain why gases fill their containers but their liquids and solids cannot have a fixed volume (5)
-a gas bond between particles is none
-so a gas spreads out to fill the container
-a solid or a liquid’s bond between particles is strong
-so when a solid or liquid is in a container the particles stay together
-liquids and solids don’t fill their container/ change their volume
whats a solid turning into a liquid called
whats a liquid turning into a gas called
whats a solid turning into a gas called
melting
boiling
sublimation
whats a gas turning into a liquid called
whats a liquid turning into a solid called
whats a gas turning into a solid called
condensing
freezing
deposition
true or false
temperature describes the average kinetic energy movement of the particles in a substance
True
why will the particles move slower in a cup of tea left on a table in a cold room
particles average temp will decrease
so the average kinetic energy decrease
so the particles move slower
why will the particles vibrate faster in an ice cube left out in the sun on a hot summers day
temp of the ice cube will increase
so the kinetic energy will increase
therefore the particles will move faster
true or false
when bonds between particles are broken the particles loose potential energy
false
bonds between particles are broken the particles potential energy
so
bonds between are made the particles loose potential energy
what state of matter do particles have
thw most potential energy
the least potential energy
gas
solid
does the substance gain or loose potential energy when
a substance melts/boils
a substance freezes/condenses
bonds are broken so substance gains potential energy
bonds are made so the substance looses potential energy
internal energy equation
internal energy= kinetic energy of particles + potential energy of particles
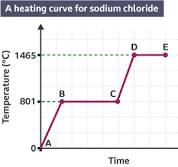
whats A-D
A-solid
B-melting
C-liquid
D-boiling
when the change of state occurs, does the temp change
no it stays the same
when a change of state occurs do the particles loose/gain potential energy
gain
what is specific heat capacity
the amount of energy needed to change the temp by 1C of 1kg of the material
lead will have the biggest change in the movement of particles becaus…
it has the smallest specific heat capacity, biggest temp change so biggest change in kinetic energy
specific heat capacity equation
amount i=of energy=mass of material x specific heat capacity (J/Kg/C)x temp change
what is density
amount of mass a substance has per unit of its volume
measured in (k)g/m3
why are solids more dense than gases
-particles in a solid are closer together
-particles in a gas are far apart
-so solids have a higher density
density equation
density((k)g/m3)= mass((k)g)/volume(m3)
how to measure the density of a regular shape
mass= measure with a balance
volume= measure with ruler→volume= area of cross section x height of shape
how to measure the density of an irregular shape (2 ways)
use a measuring cylinder or displacement can
cylinder
fill a measuring cylinder with 100ml of water and place the object in it, however much the ml went up is the volume
measure object with balance to find the mass
use the density equation to find out density
displacement can
place object on a balance and measure the mass
fill up displacement can with water until level with bottom of the pipe
place a measuring cylinder under the pipe and place the object in the displacement can and wait until no more water comes out the displacent can
measure volume of displaced can
use the density equatoin to work out density
how to find density of a liquid
place empty measuring cylinder on balance, 0 the balance, pour liquid into measuring cylinder
record the mass
divide mass by volume to find density
why is a larger volume more accurate when finding the density
minimises the effects of uncertainty when measuring the measurments
why do gases have the lowest density
In gas state, the particles are spread out, with lots of empty space between them, this gives gases a low density.
what is pressure
an affect of a force on a surface
does a small surface area have a high pressure or low pressure
does a large surface area have a high pressure or low pressure
small surface area-force is more focused/ concentrated- high pressure
large surface area-force is less focused/concentrated (more spread out)-low pressure
what is temperature
the average kinetic energy of the particles
why do gasses cause pressure
when gas particles collide with the surface they exert a force on the surface
so the gases cause on the surface
why would pressure increase if i increase the temperature of the gas
the particles move faster- so there are more collisions so there is more force and pressurw
what happens if you increase the volume of the container
particles collide less often with the internal surface so the force decreases and so does the pressure
why can you squash a gas but not a solid
particles in a gas are far apart, whilst the particles in a solid or liquid are close together . when compressing a solid or liquid there isnt space when compressing a liquid there is space
internal energy
kinetic energy of particles and potential energy of particles
latent heat
amount of energy needed to to COMPLETELY change the state per 1kg of a material
measured in J/kg
latent heat equation
amount of energy (J)= mass of material x latent heat (kg)
what happens to a solid turning into a liquid
In solids, strong attractive forces hold the particles in place, so that they can only vibrate in position.
As the substance is heated the particles gain energy and vibrate faster and faster. Eventually, the particles have so much energy that they can overcome the forces holding them together and the substance melts into a liquid.
when a solid is heated the energy is transfered to the particles _____ energy stores, this casues the particles to vibrate faster
kinetic
melting point
boiling point
melting point - The temperature at which a solid converts into a liquid
boiling point - The temperature at which a liquid converts into a gas
in a fixed container where gas is being heated, what will happen to the volume and pressure
expandable container
fixed container- volume of gas is fixed, pressure inside the container inc
expandable container volume will inc, pressure is fixed
specific latent heat of fusion
specific latent heat of vaporisation
when a substance changes from a solid to a liquid (or vice versa)
when a substance changes from a liquid to a gas (or vice versa)
formular for pressure
pressure= force/area
which 2 factors can increease the pressure of gas
faster moving particles
more collisions with the walls of the container
how does volume affect pressure in a gas
Decreasing the volume of the container, whilst keeping the number of gas particles the same, will increase the concentration.
In this smaller volume, collisions between particles of gas and the walls of the container will be more frequent.
A greater number of collisions per unit area of wall means the pressure increases.
How does temperature and concentration affect a flexible container
An increase in force on the walls of the container would just cause the container to expand.
Therefore, changing temperature or concentration will change the volume of the container, rather than the pressure of the gases inside.
When kept at a constant temperature, the pressure and volume of a gas are
inversely proportional
so when volume inc, pressure decs
so when volume dec, pressure inc
What equation should be used to calculate the energy supplied to the system during the specific heat capacity rp
Q=mcΔT
q=heat(J)
m=mass(g)
c=specific heat capacity(J/kg°C)
ΔT= change in temp (°C)