Biology 9 Weeks Exam
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
guys
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
The process in which sunlight energy is used to make glucose from water and carbon dioxide
What are the reactants in photosynthesis?
Water, carbon dioxide, and light.
What are the products of photosynthesis?
Glucose and oxygen.
What is the influence on photosynthesis?
If you change the reactants, it changes the rate of photosynthesis.
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2+6H20 → C6H126O2+6O2
What happens when photosynthesis occurs during hotter weather?
The rate of photosynthesis is higher.
What happens when photosynthesis occurs during colder weather?
The rate of photosynthesis is lower because it will cause photosynthesis to occur slower in plants.
What happens when photosynthesis occurs during too hot or too cold weather?
No photosynthesis occurs because when it’s too hot the stomata closes and when it’s too cold the molecules slow down.
What do more reactants equal?
More products.
What do less reactants equal?
Less products.
What are the two types of reactions in photosynthesis?
Light dependent reactions and the Calvin Cycle.
What do light dependent reactions produce?
ATP & NADPH
How does photosynthesis affect all organisms?
It produces oxygen and glucose which is both important for the survival of all organisms.
What is released when water is broken down?
Oxygen.
What is the equation for the calvin cycle?
Fixed CO2 + ATP + NADPH = glucose
What is glucose?
C6H12O6
How does photosynthesis and cellular respiration relate to each other?
The products of photosynthesis (glucose and oxygen) is used as the starting reactants for cellular respiration.
What is cellular respiration?
The process in which cells use carbohydrates and oxygen to produce chemical energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
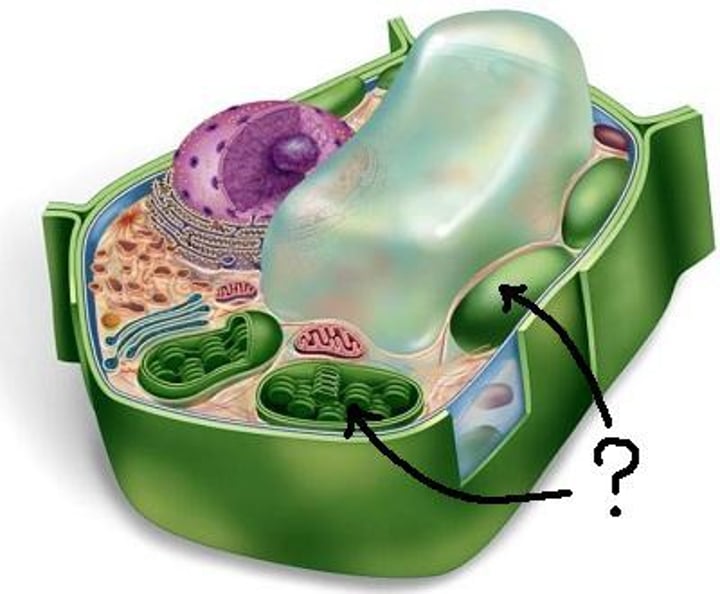
What organelle does photosynthesis occur in?
Chloroplast
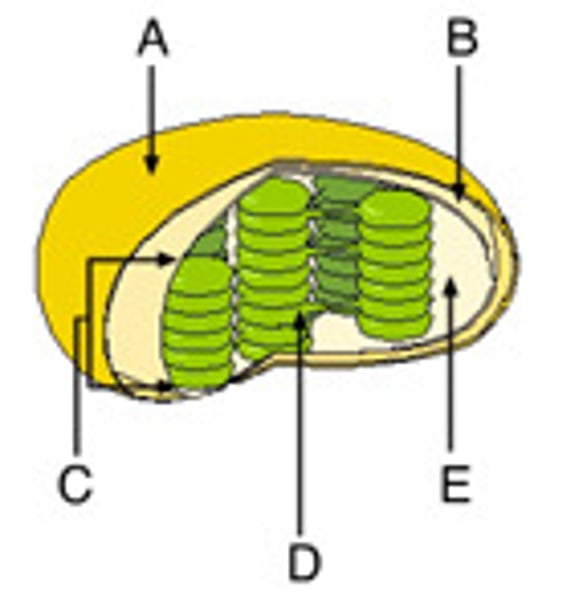
What are the individual sacs in a chloroplast called?
Thylakoids
What is the name of a stack of thylakoids?
Grana
Name two energy molecules made during the light reactions.
ATP and NADPH
What is the purpose of the light dependent reactions?
To trap light energy and convert it to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
What is the Calvin cycle?
To use the chemical energy made in the light reactions to synthesize glucose.
Name the main pigment found in plants.
Chlorophyll
What is the function of chlorophyll?
To absorb light
What is the purpose for plants having many different pigments?
To absorb as much light as possible
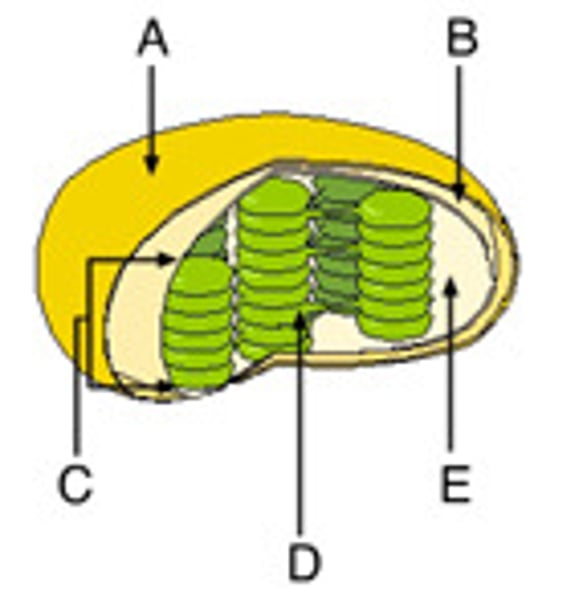
Name the organelle
Chloroplast
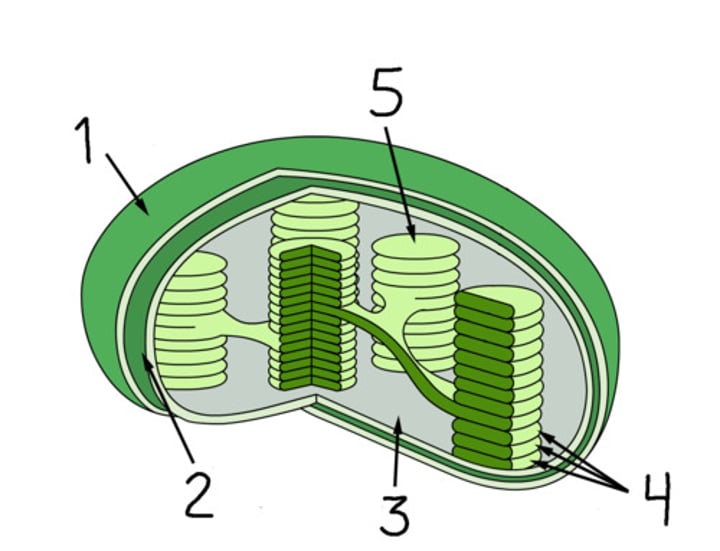
Name structure 4
Thylakoid
Name structure B
Grana
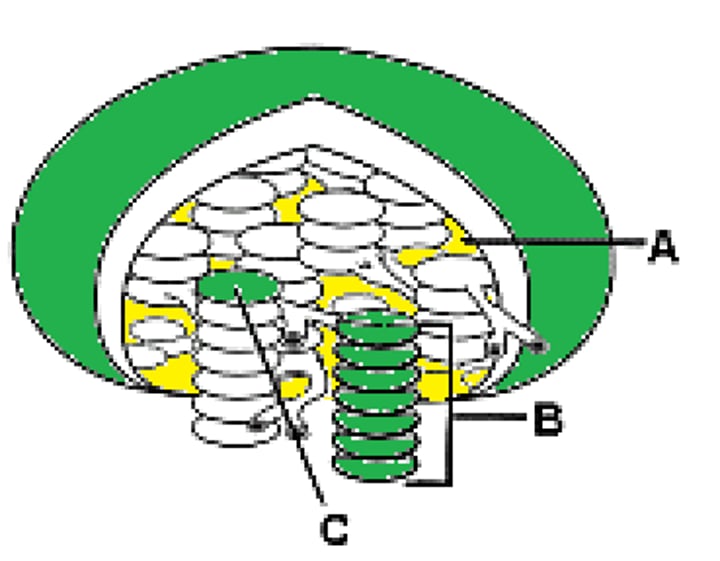
Name structure A
Outer membrane
Name structure B
Inner membrane
What is carbon fixation?
Building low-energy inorganic CO2 into high-energy organic molecules such as glucose.
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6+6O2 → 6CO2+6H20+ATP
Where does cellular respiration occur in?
Inside the mitochandria.
What is the first step of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis.
What is the process of glycolysis?
It turns glucose into useful energy and it requires 2 ATP and makes 4 ATD, 2 NADH, and 2 Pyruvates
Is glycolysis anaerobic or aerobic?
Anaerobic
How much ATP is created in the final stage?
32-38
What is aerobic respiration?
Pyruvic acid is broken down and NADH is used to make lots of ATP
What does pyruvic acid do with no oxygen present?
Fermentation. (Anaerobic respiration)
What is the total number of ATP present at the end of glycolysis?
4 ATP
How many NADH molecules are produced in glycolysis?
2 NADH
How does NAD+ become NADH?
An electron is taking from glycolysis and is attached to NAD+.
Two common fermentation products.
Lactic acid and alcohol.
What happens during the ETC?
Glucose and oxygen break down and turn into ATP and release carbon dioxide.
What is the Krebs cycle?
The second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide.
What is the electron transport chain?
The third stage in which high-energy electrons are used to convert ADP into ATP.
Glycolysis takes place in?
The cytoplasm.
What type of process is cellular respiration?
Aerobic
Where does the krebs cycle take place?
In the mitochondria matrix.
Where does the ETC occur in?
The inner mitochondria membrane.
how does atp turn into adp
it gets used
What does pyruvate oxidation do?
It transport glycolysis products to mitochondria and creates molecules for the Krebs cycle. Co2 is released.
What happens if the cell doesn’t get enough oxygen?
Fermentation (anaerobic respiration) will happen.
What does the Krebs cycle create?
6NADH, 2FADH, and 2ATP
What does the electron transport chain do?
The energy carrying molecules (NADH & FADH) create ATP. This is the final stage.
What is glucose used for?
Energy and growth.
What are the levels of organization? (In order)
Atoms, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome then biosphere.
What is your phenotype?
Physical appearance such as hair and eyes.
What is your genotype?
Genetic makeup such as DNA.
What is common descent?
All living organisms are related to one another.
What stage during cellular respiration creates the most ATP available.
The Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
In what stage does fermentation of ethanol and lactic acid happen?
Anaerobic respiration (pyruvate oxidation)
What is the difference between ethanol and lactic acid?
Ethanol is made by bacteria while our body produces lactic acid.
Where does photosynthesis occur in?
Occurs in the chloroplast.