SCIENCE SUMMATIVE 1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Hypocenter
- The location below the earth's surface where the earthquake starts.
Epicenter
- The location directly above where the earthquake starts on the surface of the Earth.
Seismic waves
- Vibrations generated by the sudden movement of materials within the Earth, such as slip along a fault during an earthquake.
Seismometer or Seismogram
- Measures and detects seismic waves.
Seismograph
- Record of seismic waves.
P-waves
- First seismic waves to be felt on Earth’s surface; can travel through all states of matter; and speeds reach between 1.5 and 8 km/s.
S-waves
- Second seismic waves to be felt; only travel through solids; and 60-70% slower than primary waves.
Tectonic plates
- The large and small sections the lithosphere is broken into that interact and create tectonic activities on Earth.
Compositional
- meaning materials
Crust, Mantle, Outer core, and Inner core.
- 4 Compositional layers
Crust
- The outermost layer of Earth where life exists
- The thinnest
- Made up of light granitic rocks, made up of mostly aluminum silicates.
- 3.8-4 billion years old
- Coverage is 71% of Earth’s surface
- Composed of dense basaltic rocks made up of magnesium silicates.
- Less than 200 million years old
- 29% of Earth’s surface
Continental crust
- The crust that makes up the continents and is about 40-70km thick.
Oceanic crust
- The crust that underlies the ocean floor and is about 7-10km thick.
Mantle
- Semisolid, rocky and very hot
- 2900 km thick
- Makes up 80% of Earth and most of Earth’s mass.
- Composed of ferro-magnesium silicate rocks. It’s top layer has a temperature of about 900°C
- When you go deeper, the temperature increases from 1000°C to 3700°C.
- Upper & lower
- moves
Outer core
- The only layer that is liquid
- Made up of molten nickel and iron
- 2270 km thick
- Temperature ranges from 3700°C to 4300°C
Inner core
- Composed mostly of solid iron
- Extremely hot
- 1220 km diameter
- Temperature is estimated to be 6000°C
- It is solid because of the amount of pressure
Mechanical
- meaning behavior
- Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, Mesosphere, Outer core, and Inner core.
- Mechanical Layers
Lithosphere
- A rigid layer of Earth that can break under stress.
Asthenosphere
- The layer below the lithosphere, about 180 km thick, containing hot, molten rocks or magma.
Mesosphere
- The layer below the asthenosphere, characterized by high pressure and rigidity.
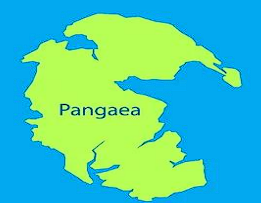
Pangaea
- single landmass or super continent
- comes from the Greek words pan which means “all” and gaea which means “Earth”. - Literally translates to “all of Earth” or “all lands”
Permian period
- 225 million years ago
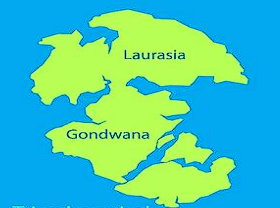
Triassic period
- 200 million years ago
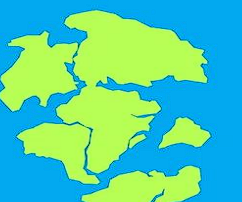
Jurassic period
- 150 million years ago
Cretaceous period
- 65 million years ago
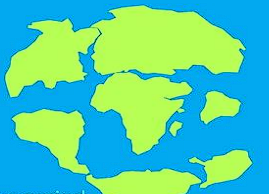
Present days
- Look at the image blablabla
Contraction theory
- Suggests that as Earth cooled after it’s formation, it’s surface contracted and wrinkled, these wrinkles became the mountain ranges on the Earth’s surface.
Theory of Continental drift
- Scientists denied this theory alot, but as time went on, other scientists proved the theory to be right. According to this theory, there was a supercontinent known as Pangaea.
Alfred Wegener
- Proposed the theory continental drift.
1912
- When the theory of continental drift was proposed
1-2 inches
- The amount of inches the lithosphere moves per year
Seafloor spreading theory
- States that the seaflors or ocean, not the continents, move and carry the continents along
Theory of Plate tectonics
- Incorporates the continental drift theory and the seafloor spreading theory. Explains that Earth’s lithosphere is composed of many independent massive slabs of solid rocks called plates. This movement is due to the convection currents beneath the plates.
Convection currents
- Made by the very hot material at the deepest part of the mantle rising, then cooling and sinking again, then cycle repeats.
Plate boundaries
- The regions between tectonic plates.
Convergent boundaries
towards each other
- Makes earthquakes (from pressure), volcanoes (from subduction zone stuffs), and mountain (if pataas, ifykwim)
Himalayas
- Refers to a mountain range in Asia, formed through the collision between the Indo-Australian Plate and the Eurasian Plate.
Mt. Everest
- The tallest mountain, measuring 29,000 ft; grows about an inch every year.
Subduction zone
- Is created with convergent boundaries when there is a denser plate that goes down.
Divergent boundaries
- away from each other
- made the East African Great Rift Valley
- If under the ocean, magma oozes out of the Earth's mantle and fills the space. Seafloor spreading. (Mid-Atlantic Ridge - tallest and longest mountain chain)
Transform boundaries
- slide past each other
- makes fault lines
- Building up of pressure, causes an earthquake
San Andreas Fault
- One of the largest transform boundaries in the world.