VCE Physics - AOS 3, Fields
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
static charge
Imbalance of electric charge on an object. In solids it is due to the transfer of electrons between objects.
Proton charge
1.6 x 10^-19 C
electrostatic force
the force that exists between particles due to their charge. particles of like charge repel, particles of unlike charge attract
permanent magnet
A magnetic material that always has its own magnetic field around it
magnetic flux
the number of magnetic field lines that pass through a surface
Solenoid
A coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying an electric current
inverse-square law
a law that states that an energy field's strength is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the energy field's source
impulse
a force acting at a particular magnitude and time to change an object's momentum
g force
the acceleration of a descending object due to gravity
electromotive force (EMF)
the voltage created or supplied due to energy being transformed into electrical potential energy
electromagnetic induction
the production of an electromotive force (EMF) due to the change in magnetic flux through a conducting loop
faraday’s law
ε = -N x ΔΦB / Δt, calculates EMF
induced current
the current produced in a conductor due to a changing magnetic flux
Lenz’s Law
finds direction of current and induced emf in a loop
generator
a device that transforms kinetic energy into electricity (either AC or DC) by electromagnetic induction
alternator
a device that transforms kinetic energy into AC electricity by electromagnetic induction; an AC generator
alternating current (AC) electricity
electricity with a periodically alternating direction of current and voltage
slip rings
a component used to maintain a constant electrical connection between a stationary external circuit and a rotating coil
amplitude
the distance from the x-axis to the top or bottom of the wave
frequency
the number of cycles completed per second
period
the time taken to complete one cycle
direct current (DC) electricity
electricity with a constant direction of current and voltage
split ring commutator
a component used to reverse the electrical connection between a stationary external circuit and a rotating coil every half rotation
photovoltaic (PV) cell
a device that converts light energy into electrical energy
semiconductor
a material that can be modified to control how it conducts electricity
solar panel
an array of photovoltaic cells connected to produce a desired voltage and current
inverter
a device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC)
voltage
a measure of the difference in electric potential energy between two points, also known as potential difference
current
the rate of flow of electric charge, measured in amperes
resistance
a measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current
resistor
an electrical component that resists the flow of electric current and causes a drop in voltage
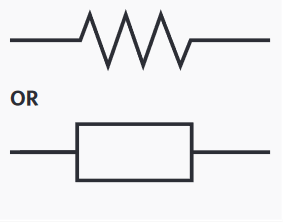
series circuit
an electric circuit where there is only one pathway for current to flow
parallel circuit
an electric circuit where there are multiple pathways for current to flow
ohm’s law
V = IR
root-mean-square (RMS)
the DC voltage or current that would deliver the same average power as an AC source
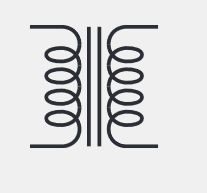
transformer
a device that uses electromagnetic induction to transfer power from one electrical circuit to another
why is the voltage stepped up before being transmitted along the power lines?