Hormonal Coordination
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is the endocrine system and how does it work?
A system made of glands that secrete chemicals called hormones directly into the bloodstream. The bloodstream delivers the hormone to the desired organ, where it produces an effect. The organ’s receptors on the cell membrane pick up the hormone molecules, triggering a response.
How fast are hormones compared to the nervous system?
Hormones work rapidly, but slower than the nervous system, however the effects are more long lasting.
What hormones give a rapid response, and what are their purposes?
Insulin, which controls blood glucose and adrenaline, which prepares the body for fight or flight.
What hormones give a slow response?
Growth hormones and sex hormones.
What gland controls all other endocrine glands in the body?
The pituitary gland.
What hormones produced by the pituitary have a direct effect on the body and what are their purposes?
ADH, which affects the amount of urine produced by the kidney, and growth hormone, which controls the rate of growth in children.
How does the pituitary gland control other endocrine glands?
It produces a hormone that affects specific endocrine glands, stimulating them to release hormones that bring about the required effect on the body.
What hormones does the pituitary gland use to control other endocrine glands, and what are their purposes?
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the ovaries to make the female sex hormone oestrogen, and TSH, which stimulates the thyroid gland to make thyroxine, a hormone that helps control the rate of metabolism.
What do the hormones released by the pancreas do?
They control the levels of glucose in the blood
What do the hormones released by the ovaries do?
They control the development of the female secondary sexual characteristics and is involved in the menstrual cycle.
What do the hormones released by the testes do?
They control the development of the male secondary sexual characteristics and is involved in the production of sperm.
What does the pancreas do?
It monitors and controls blood concentration.
What 2 hormones does the pancreas produce to control glucose levels?
It produces insulin, allows glucose to move from the blood into the cells and to be stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
it also produces glucagon, which allows glycogen to be converted back into glucose and released into the blood.
Glucagon interacts with insulin in a negative feedback cycle to control glucose levels.
Why may blood glucose be higher in a diabetic person?
In type 1 diabetic people, the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin.
In type 2 diabetic people, the body stops responding to its own insulin.
Why is it important to control blood glucose levels?
Without proper control, blood glucose levels get very high after eating. Eventually, kidneys excrete glucose in urine, making you produce lots of urine and feel thirsty all the time. If glucose stays in the blood and doesn’t get transferred to the cells of your body, you lack energy and feel tired. You break down fat and protein instead, so you lose wight. This is what happens in type 1 diabetes.
How do we treat type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is normally controlled by injecting insulin to replace the hormone that is not made in the body.
How do we treat type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is normally treated by a carbohydrate-controlled diet and taking more exercise. If this doesn’t work, drugs may be needed.
How can type 1 diabetes be cured?
Pancreas transplants have been successful, however they are dangerous and there are not enough pancreas donors available. Scientists are also looking into ways to use stem cells to make artificial insulin producing cells, or using genetic engineering to fix faulty pancreases and then return it to the patient to avoid rejection issues.
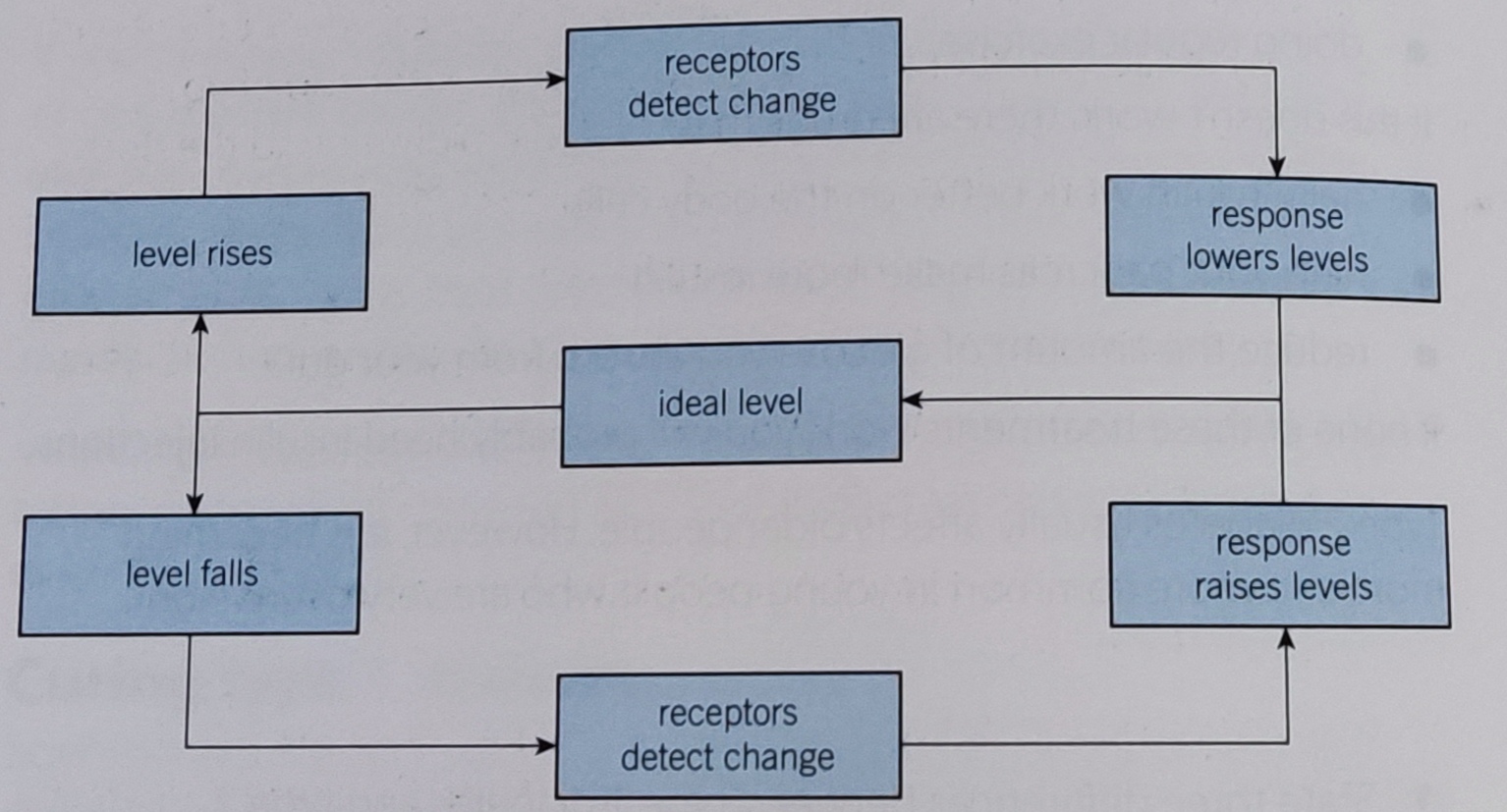
What is negative feedback?
Negative feedback systems work to maintain a steady state. If something in the internal environment increases, changes take place to reduce them to the normal level, and vice versa for if they decrease.
Where is the Thyroid gland, and what does it do?
It is in the neck and it uses iodine from your diet to produce the hormone thyroxine, which controls the basal metabolic rate of the body.
What is the basal metabolic rate?
How quickly substances are broken down and built up, how much oxygen your tissues use, and how the brain of a growing child develops.
How are thyroxine levels controled?
They are controlled by a negative feedback system to make sure the levels are always stable.
Where are the adrenal glands, and what do they do?
They are at the top of the kidneys, and they secrete adrenaline into the bloodstream.
What does adrenaline do?
It affects many organs:
It causes the heart rate to rise, the stored glycogen in the liver is converted into glucose for respiration, the pupils dilate to let in more light, mental awareness increases, blood is diverted away form digestive system to the big muscles of the limbs. It also boosts the delivery of oxygen and glucose to the brain and muscles, preparing the body for fight or flight.
What happens once the danger is over?
The raised levels of awareness are no longer needed, so the adrenal glands stop secreting adrenaline and your systems return to their normal levels.
Does adrenaline use a negative feedback system?
No.
What happens during puberty in males and when does it happen?
The main male reproductive hormone is testosterone, produced by the testes. Boys go into puberty at 9 to 15 years old. They get a growth spurt, pubic hair, underarm and facial hair, larynx grows and voice breaks, external genitalia and skin darkens, testes grow and start producing sperm, and the shoulders and chest broaden as muscle develops. The brain also matures.
What happens during puberty in females, and when does it happen?
The main female reproductive hormone is oestrogen, produced by the ovaries. Females begin puberty at 8 to 14 years old. They get a growth spurt, armpit and pubic hair, breasts develop, external genitals grow and skin darkens, a female pattern of fat is deposited on the hips, buttocks and thighs, the brain matures, mature ova start forming every month in the ovaries, and the uterus grows and becomes active and menstruation begins.
What happens during the menstrual cycle and when does it happen?
After puberty, females have a monthly menstrual cycle. Each month, eggs begin to mature in the ovary, and the uterus produces a thickened lining ready for pregnancy. Every 28 days, a mature egg is released - ovulation. If the egg isn’t fertilised within 14 days, the lining of the uterus is shed along with the egg.
What hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle and what do they do?
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), which causes the eggs in the ovary to mature (the eggs grow surrounded by cells called the follicle).
Luteinising hormone (LH), which stimulates the release of the egg at ovulation.
Oestrogen and progesterone, which stimulate the build-up and maintenance of the uterus lining.
How do the levels of the female sex hormones change during the menstrual cycle?
First 5 days, old egg leaves the body. First 12 days, new egg matures in the ovary: LH levels begin to spike, and FSH levels increase. Days 12 - 16, Egg is released, FSH, LH, and oestrogen levels are at their highest. Days 15 - 23, new egg is travelling to the womb and all hormone levels decrease. Days 20 - 28, new egg is in the womb. As the old egg leaves, thickness of the womb lining decreases to its lowest point. It then gradually increases until the new egg leaves the body.
Why does the womb lining thicken?
To provide protection and food for the developing embryo.
How does hormone based contraception work?
The contraceptive pill uses female hormones to prevent pregnancy. The pill contains low doses of oestrogen and progesterone. These hormones prevent the production of FSH by the pituitary gland so no eggs mature, preventing pregnancy.
Why do some contraceptive pills only contain progesterone?
Because they have fewer side effects.
How often should women take the contraceptive pill?
They must take it very regularly, especially the progesterone only one.
What other hormone based contraception methods are there?
Contraceptive injections last about 12 weeks. A contraceptive implant is a tiny tube that is inserted under the skin by a doctor and slowly releases progesterone. It is 99.5% effective and lasts about 3 years. A contraceptive patch is placed under the skin and releases oestrogen and progesterone directly into the bloodstream. It should be replaced every 7 days.
What is a chemical method of contraception?
Chemicals that kill sperm cells are called spermicides. They are readily available, but not as effective at preventing pregnancy.
What is a barrier method of contraception?
They prevent the sperm from reaching the egg. Condoms are readily available, are effective and protect against some STIs.
What are intrauterine devices?
Small structures that are inserted into the uterus by a doctor. They last 3 -5 years, can be removed. Some contain copper and prevent early embryos from implanting in the lining. Others release progesterone to prevent build up of the uterus lining.
What is abstinence?
Not having sex. It is very effective at not getting pregnant, and if you still manage to get pregnant using this method, you have some serous issues.
What are surgical methods of contraception?
If people don’t want any more children, they can be surgically sterilised. Men get a vasectomy, where the sperm ducts (tubes carrying sperm from testes to the peins) are tied or cut. In women, oviducts are cut or tied to prevent the egg form reaching the uterus and the sperm from reaching the egg.
What is the treatment for lack of ovulation in women?
Lack of ovulation is caused by not enough FSH to stimulate the maturation of the eggs in the ovaries. Artificial FSH can be used as a fertility drug. Artificial LH can then be used to trigger ovulation.
What is in vitro fertilisation?
IVF is when the doctors give the mother synthetic FSH to stimulate the maturation of a number of eggs at a time. They collect the eggs and fertilise them with the sperm from the father. One or 2 of the embryos are inserted back into the mother. This is expensive and has a 40% success rate. It can also be traumatising. IVF increases the chance of multiple pregnancies.
What are plants sensitive to?
Light and gravity.
How do plants tilt so they face the light?
They use a hormone called auxin. It is produced at the tip of the shoot and falls down. It uses its photosensitive receptors to always stay on the shaded part of the shoot. Auxin causes cell elongation. Because it elongates the cells on the dark side, the shoot tilts over to the light source. If the light is directly above or coming from all sides, auxin is evenly distributed and the plant grows straight. This is phototropism. Gravitropism is plants responding to gravity. Auxin falls with gravity, so it causes the shoot to grow up if it is sideways, however, in roots, it prevents cell elongation, therefore roots always grow downwards.
How can auxin be used for our benefit?
Overdoes of auxin causes extensive growth of the plant to the point where it can no longer support itself, so it falls over and dies, making it useful as a weedkiller. Rooting powders contain auxin, and it is used to grow roots in cuttings so gardeners can grow more plants.
How can gibberellins be used for our benefit?
They are used in brewing to end seed dormancy. They are used to promote flowering throughout the year. They are used to increase the size of fruit.
How can ethene be used for out benefit?
It is used to control the ripening of fruit. The unripe fruit is harvested and transported, and then ethene is used to ripen it after it has been harvested, allowing for fruit to be imported without being expensive.