AP Psychology - Unit 3: Sensation & Perception
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
sensation
the raw data of experience; sensory stimulation. Ex: Our eyes only register light energy and ears only register wave energy

perception
the mental process of sorting, identifying, and arranging raw sensory data into meaningful patterns;

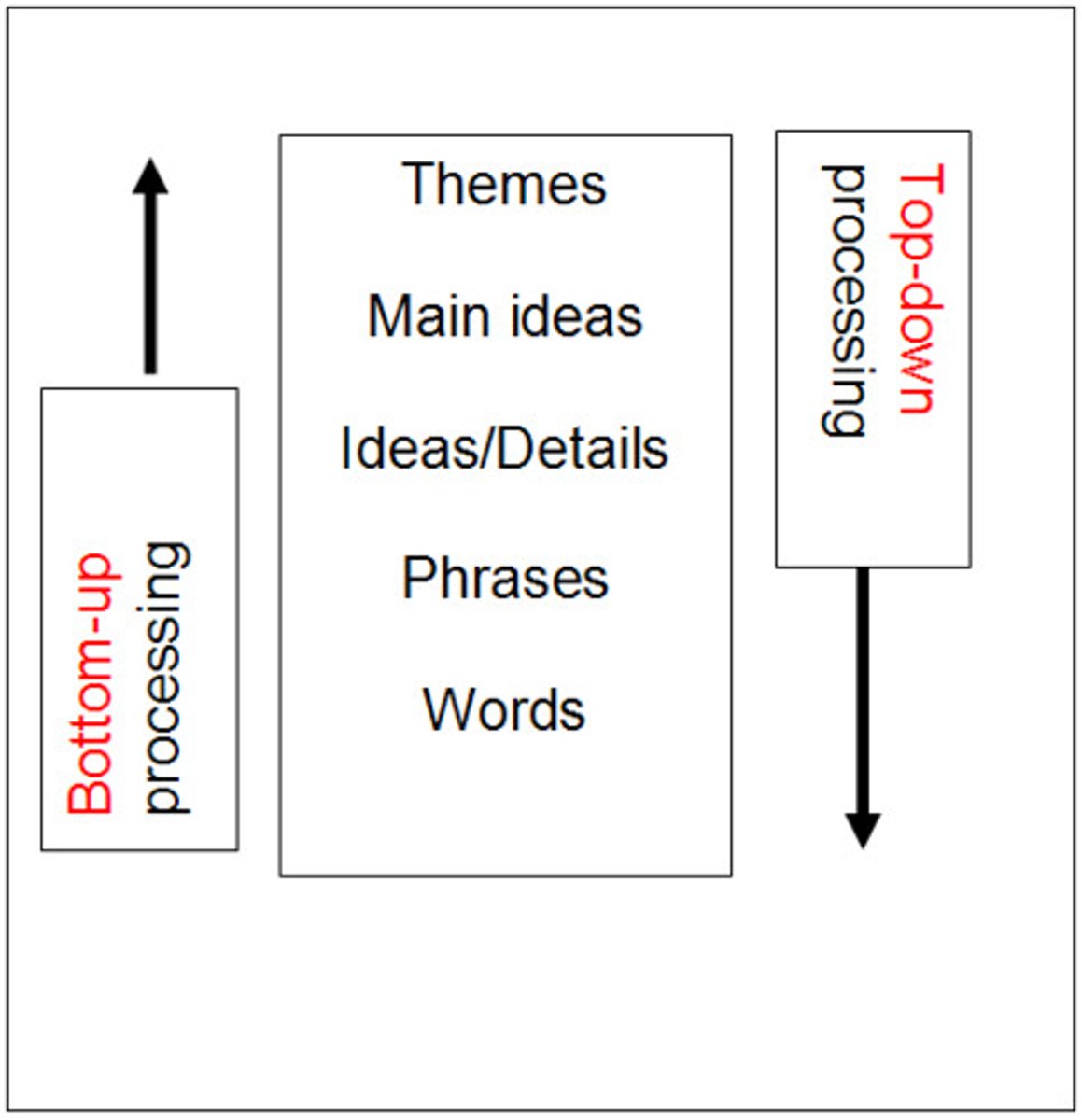
bottom-up processing
Starts with basic sensory information
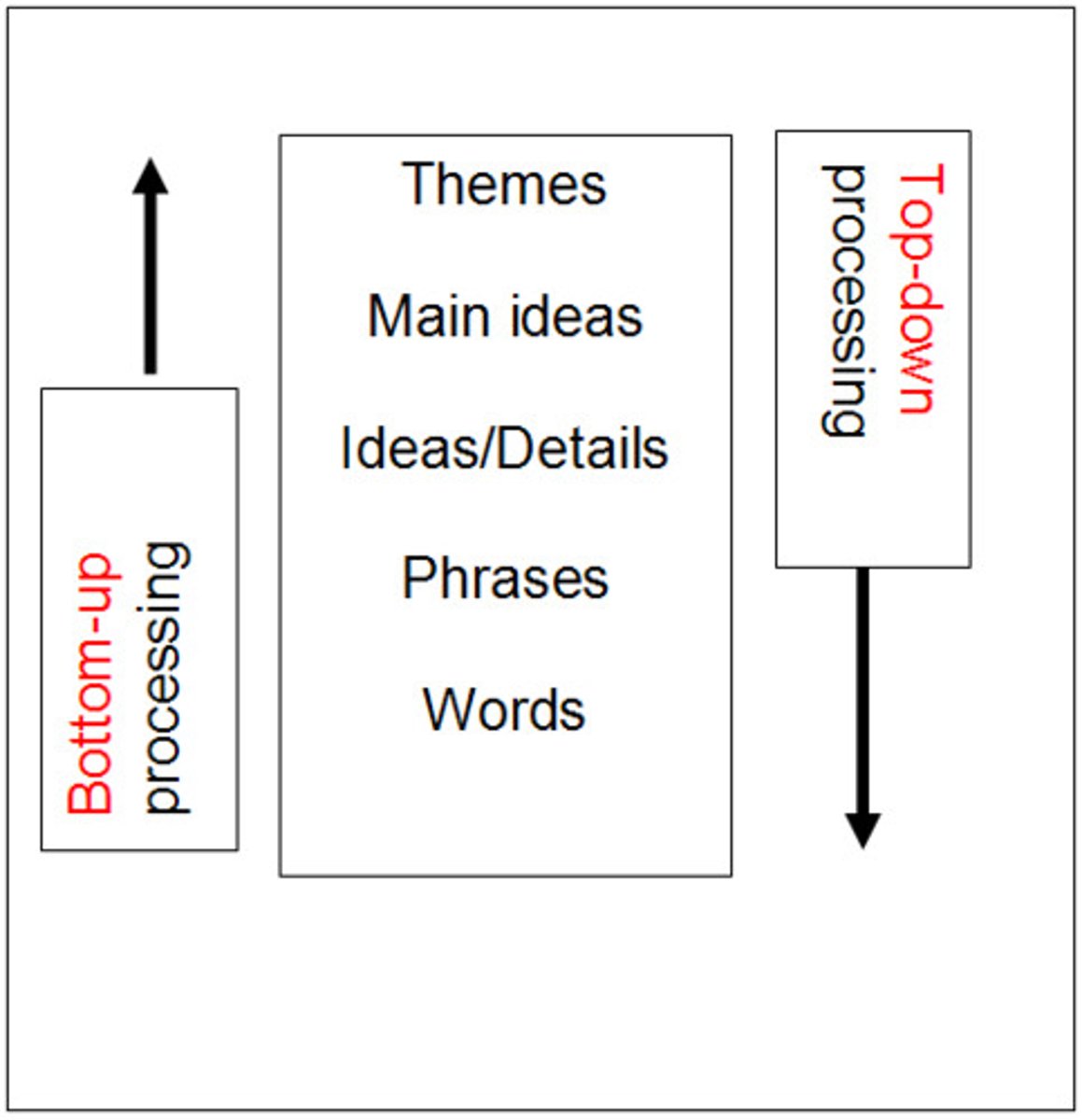
top-down processing
Constructing perceptions based on our experiences and expectations
selective attention
The focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus, like the cocktail effect.

inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere

change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment.

psychophysics
The study of relationships between the physical characteristics of stimuli, such as their intensity, and our psychological experience of them.
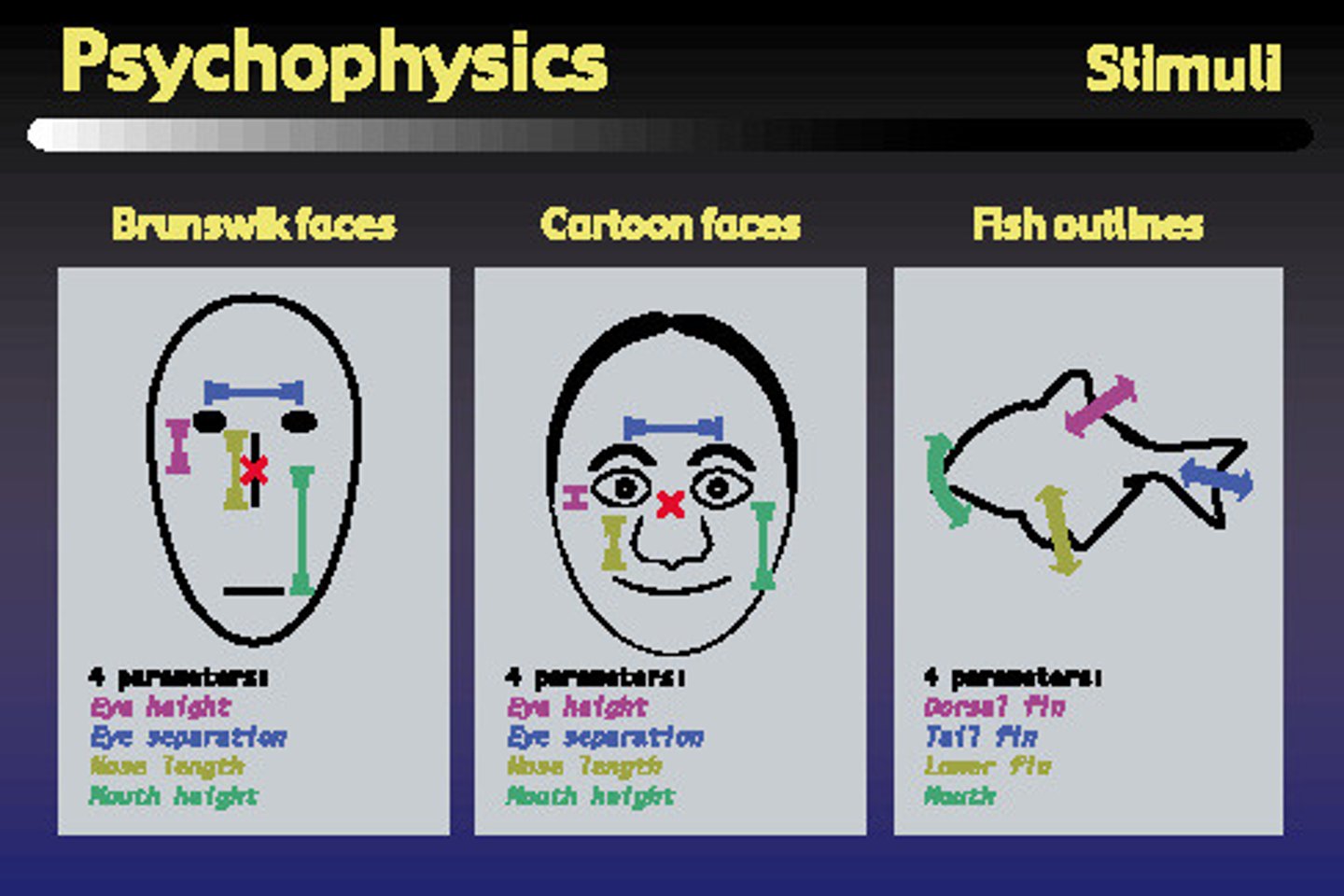
absolute threshold
the minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50 percent of the time.
signal detection theory
States that circumstances, experiences, expectations affect our thresholds
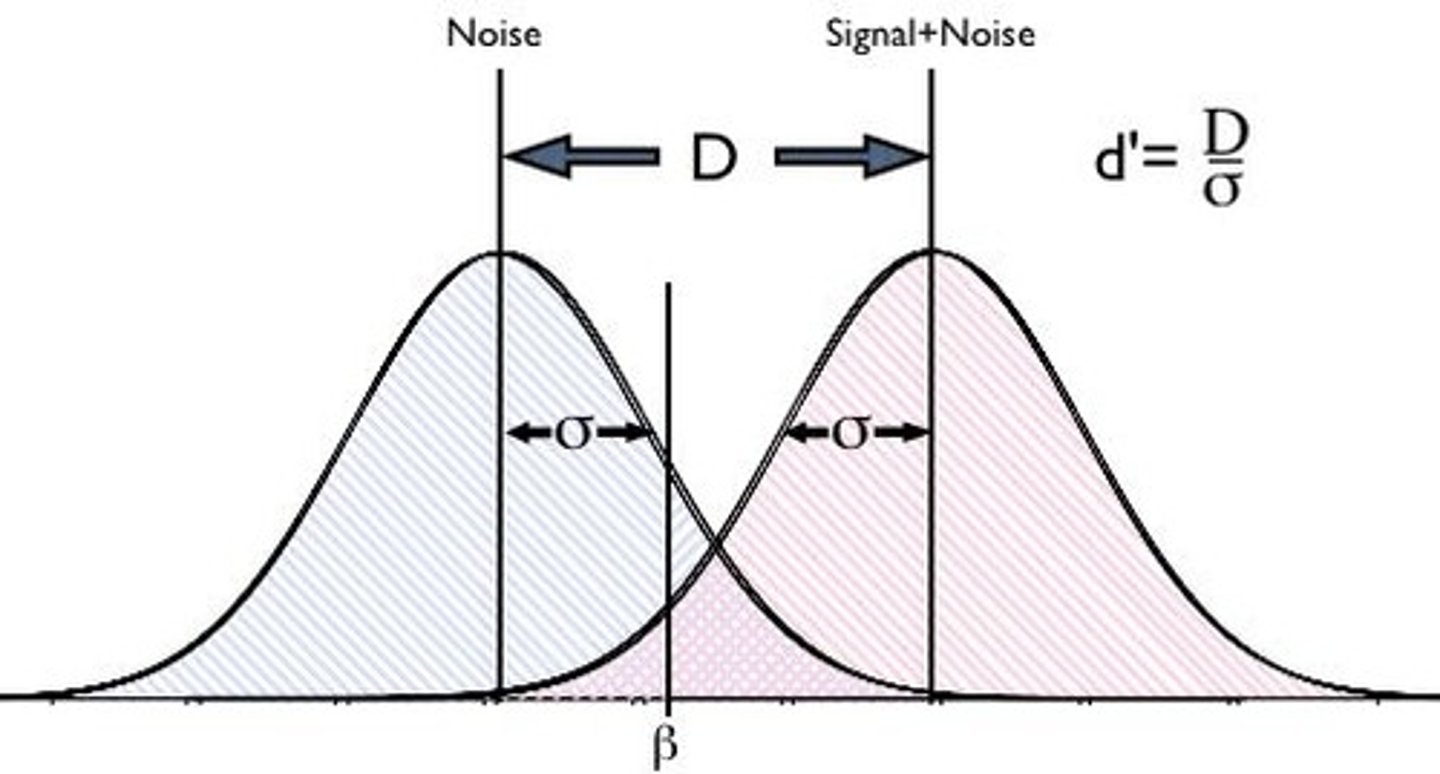
subliminal perception
Sensory information that is detected without our conscious knowledge
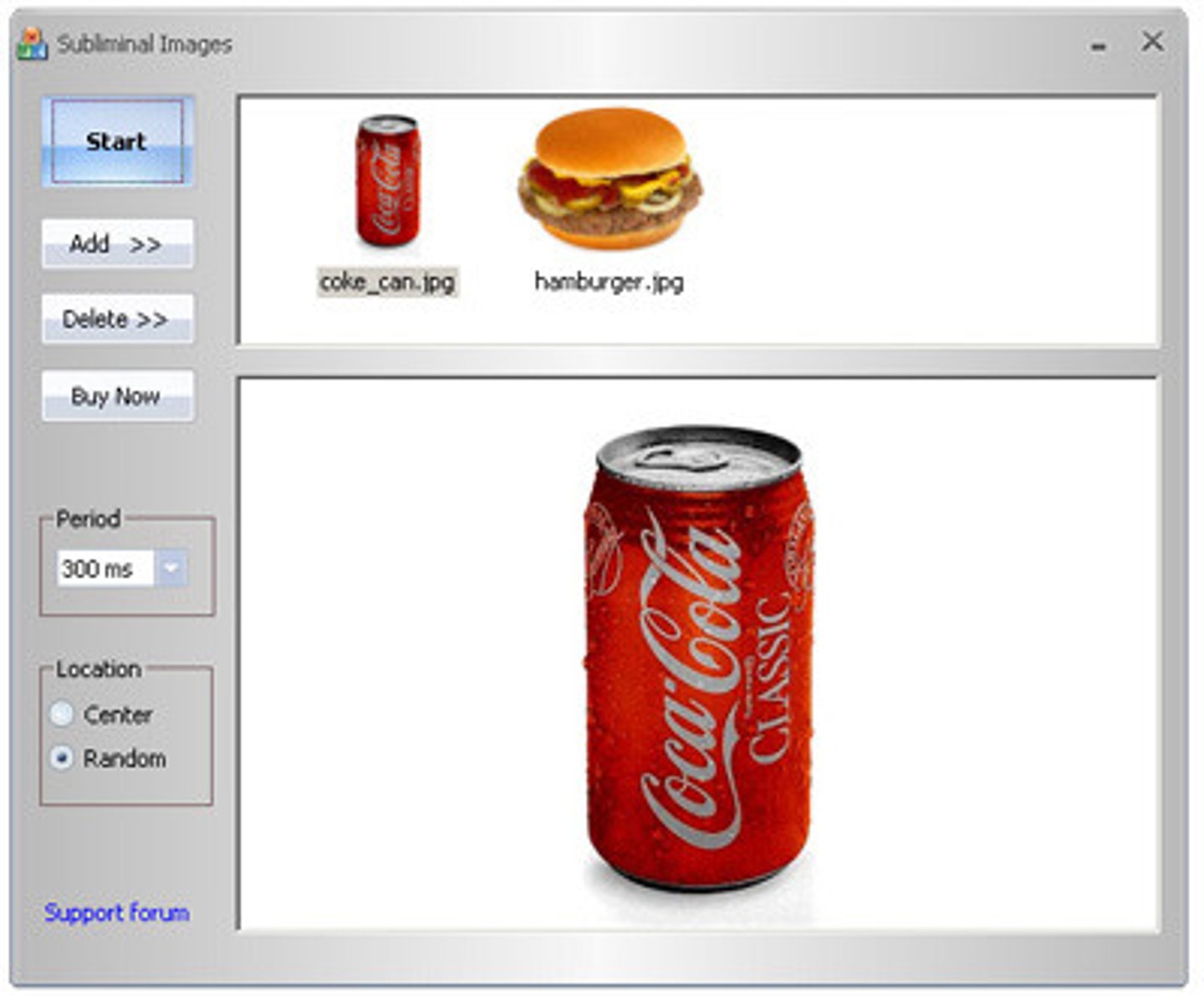
priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing one's perception, memory, or response.

difference threshold
Just Noticeable Difference (JND); the smallest change in stimulation that you can detect 50% of the time; differs from one person to the other
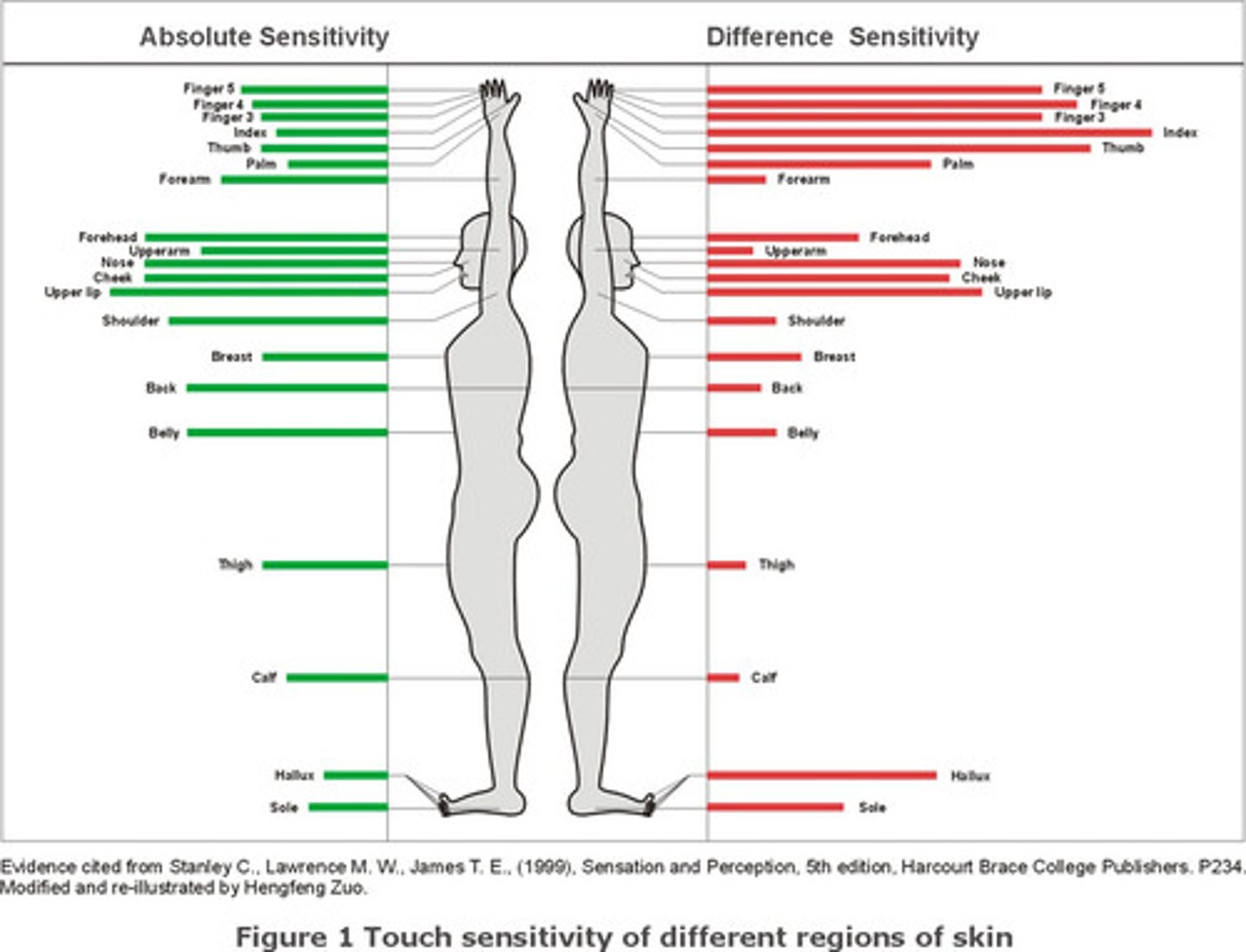
Weber's law
developed the 1930s by Ernst Weber; the principle that accounts for how one notices JND for any sense to be percieved as different , two stimuli must differ by a constant percentage.

sensory adaptation
Diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation.

transduction
Conversion of one form of energy into another. In sensation, the transforming of stimulus energies into neural impulses.
hue
color, or aspects of colors; detemined by the wavelength of light.

intensity
The amount of energy in a light or sound wave, which we perceive as brightness or loudness, as determined by the wave's amplitude.

cornea
The eye's clear, protective outer layer, covering the pupil and iris.
pupil
small opening in the center of the iris; allows light to enter

iris
A ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening.
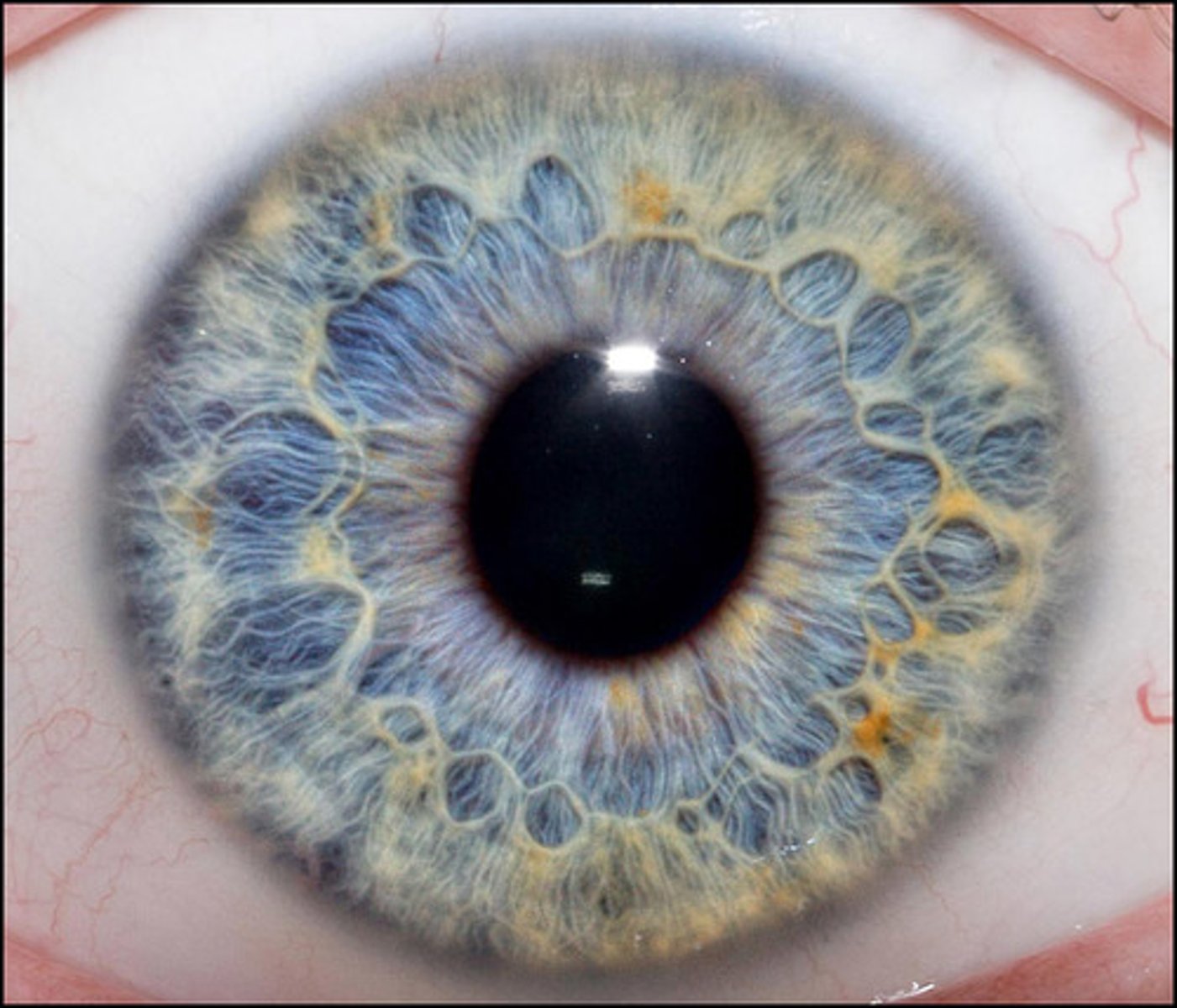
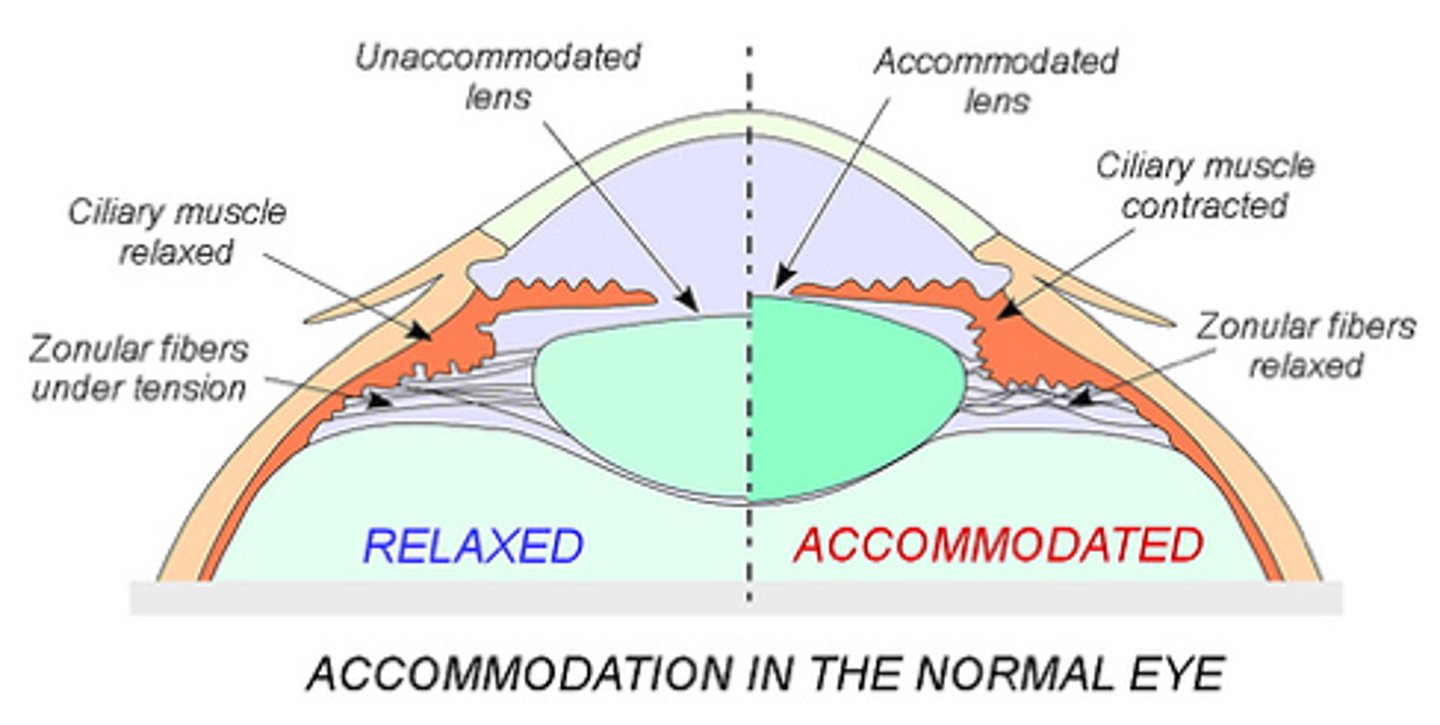
lens
transparent part of the eye behind the iris; focuses light on the retina; change shape to focus on objects;
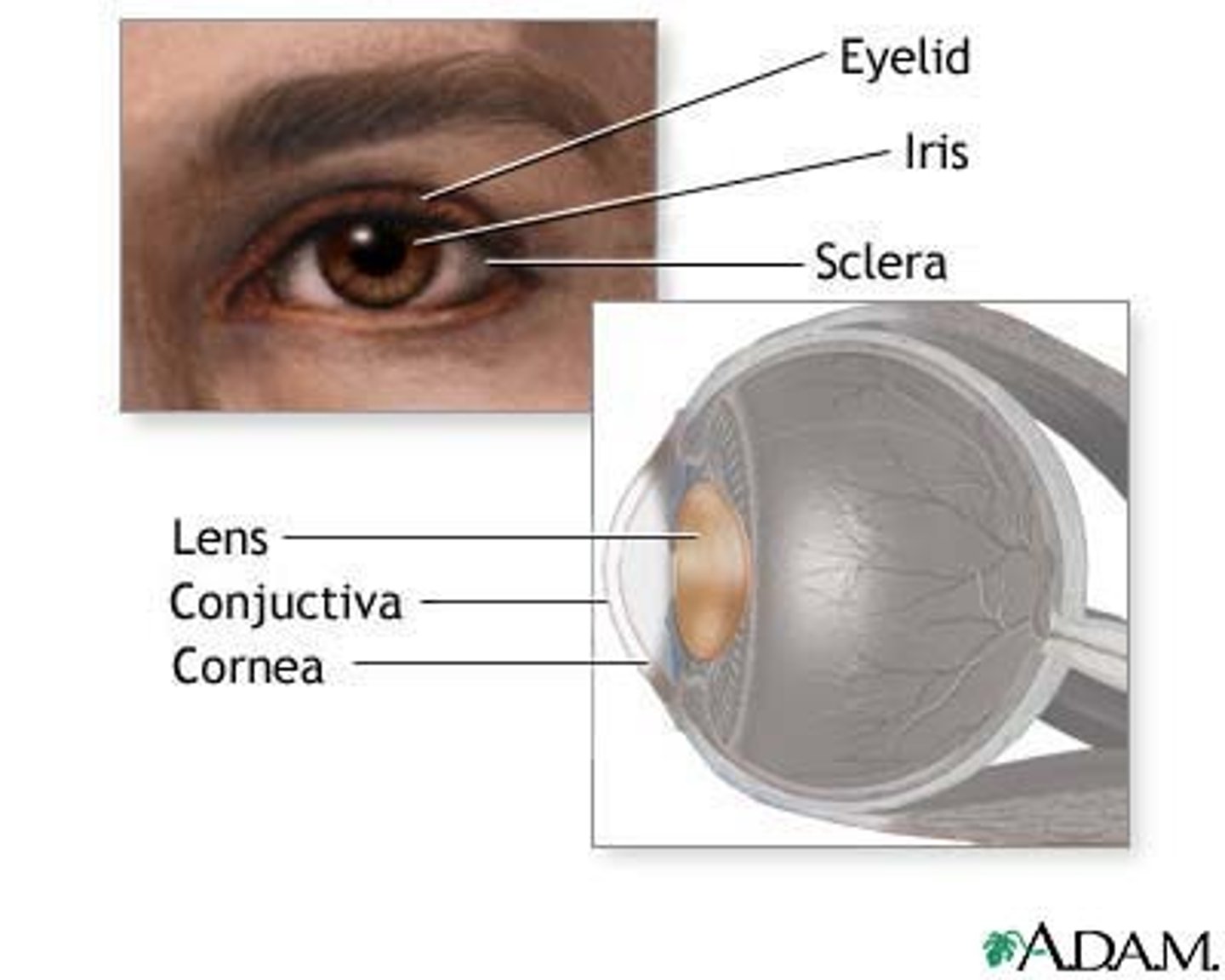
retina
the light-sensitive inner lining of the back of the eyeball; contains receptor cells
accommodation
a process by which the eye adjusts and is able to focus, producing a sharp image at various, changing distances from the object seen.
rods
visual receptor cell; located in retina; 120 million in each eye; respond to varying degrees of light and dark; chiefly responsible for night vision and perception of brightness

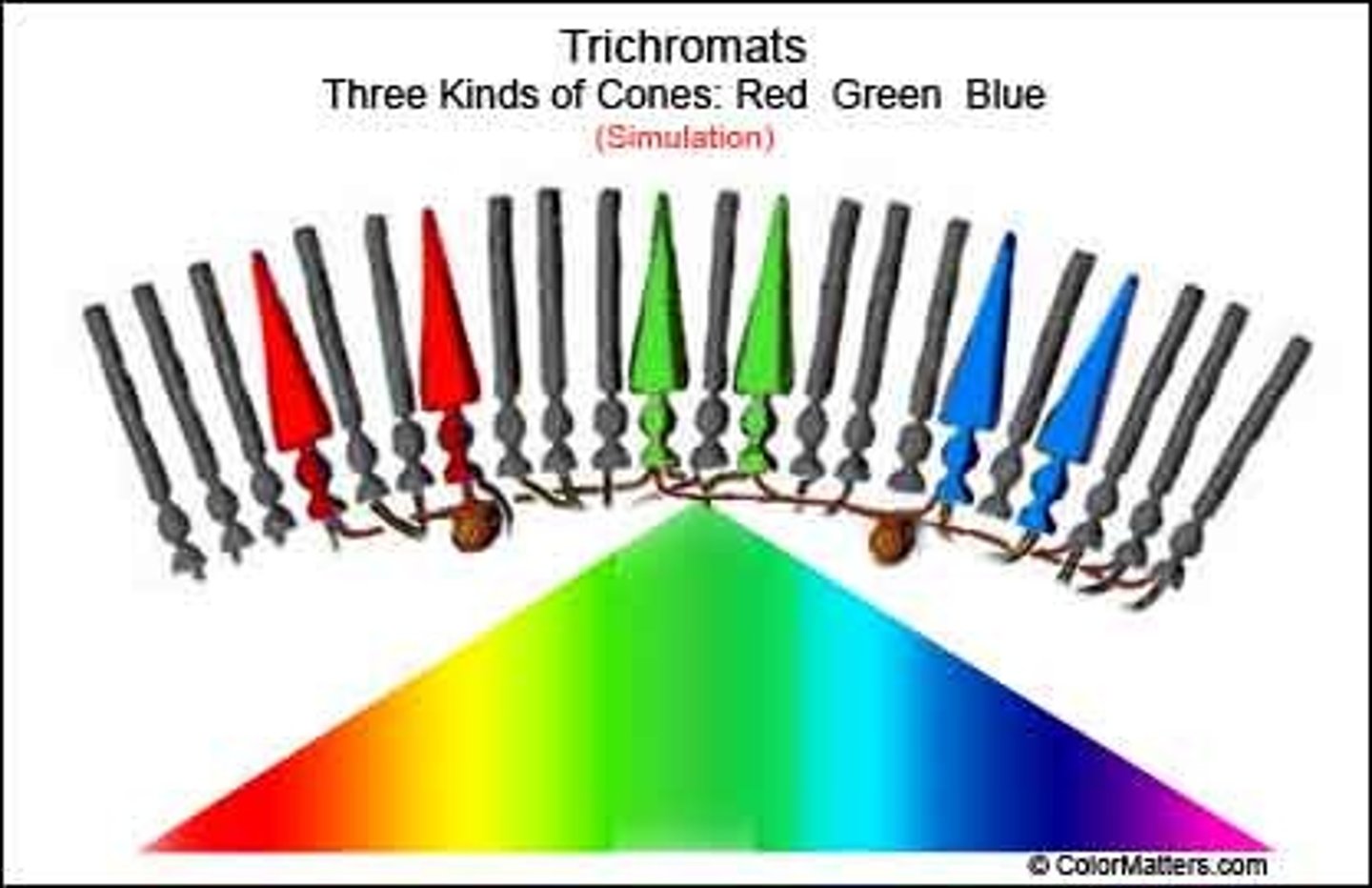
cones
visual receptor cells; located in retina; 8 million in each eye; works best in bright light; chiefly responsible for viewing color; greatest density in the fovea
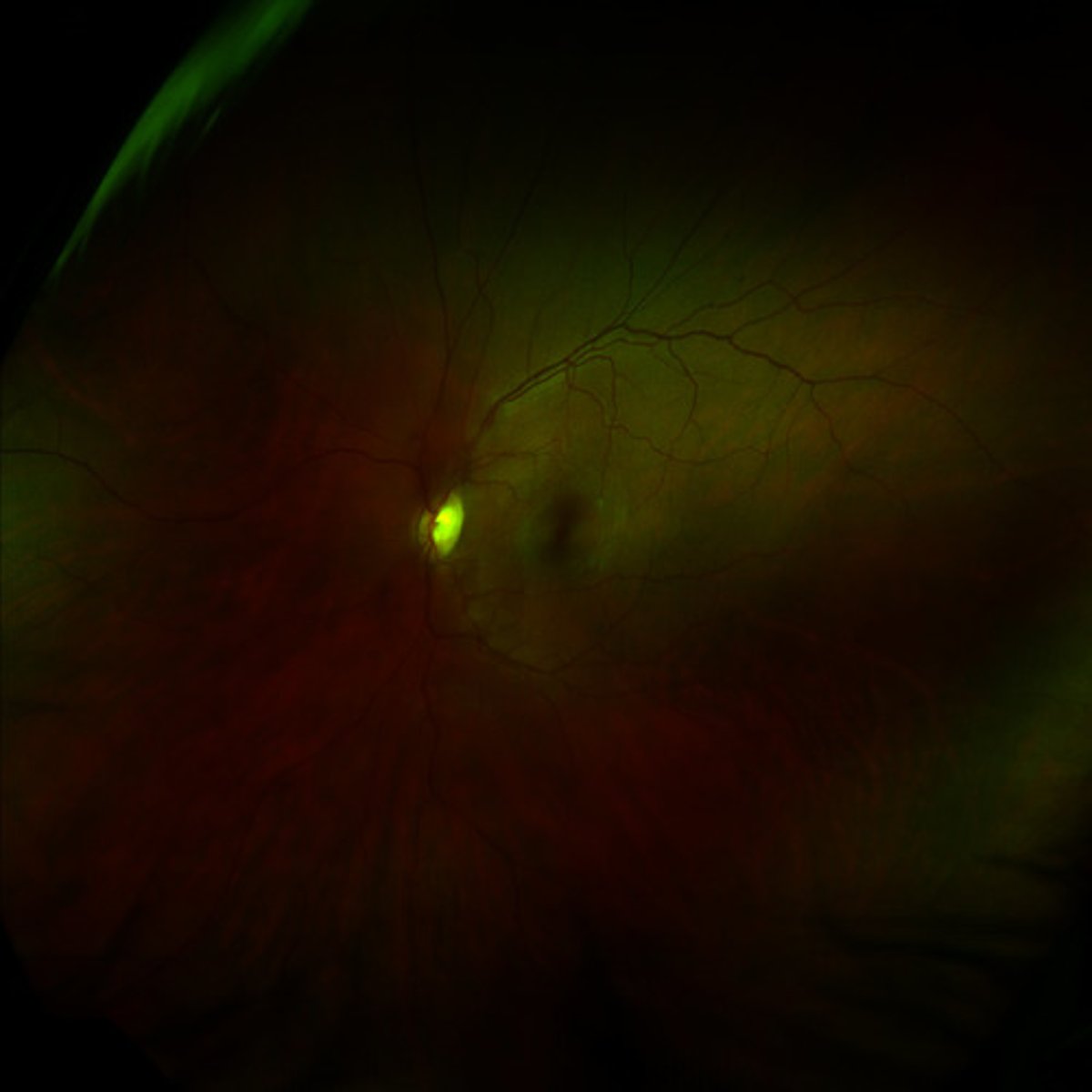
blind spot
place on the retina out where the ganglion cells axons leaves the eye; no receptors rods/cones) are located here
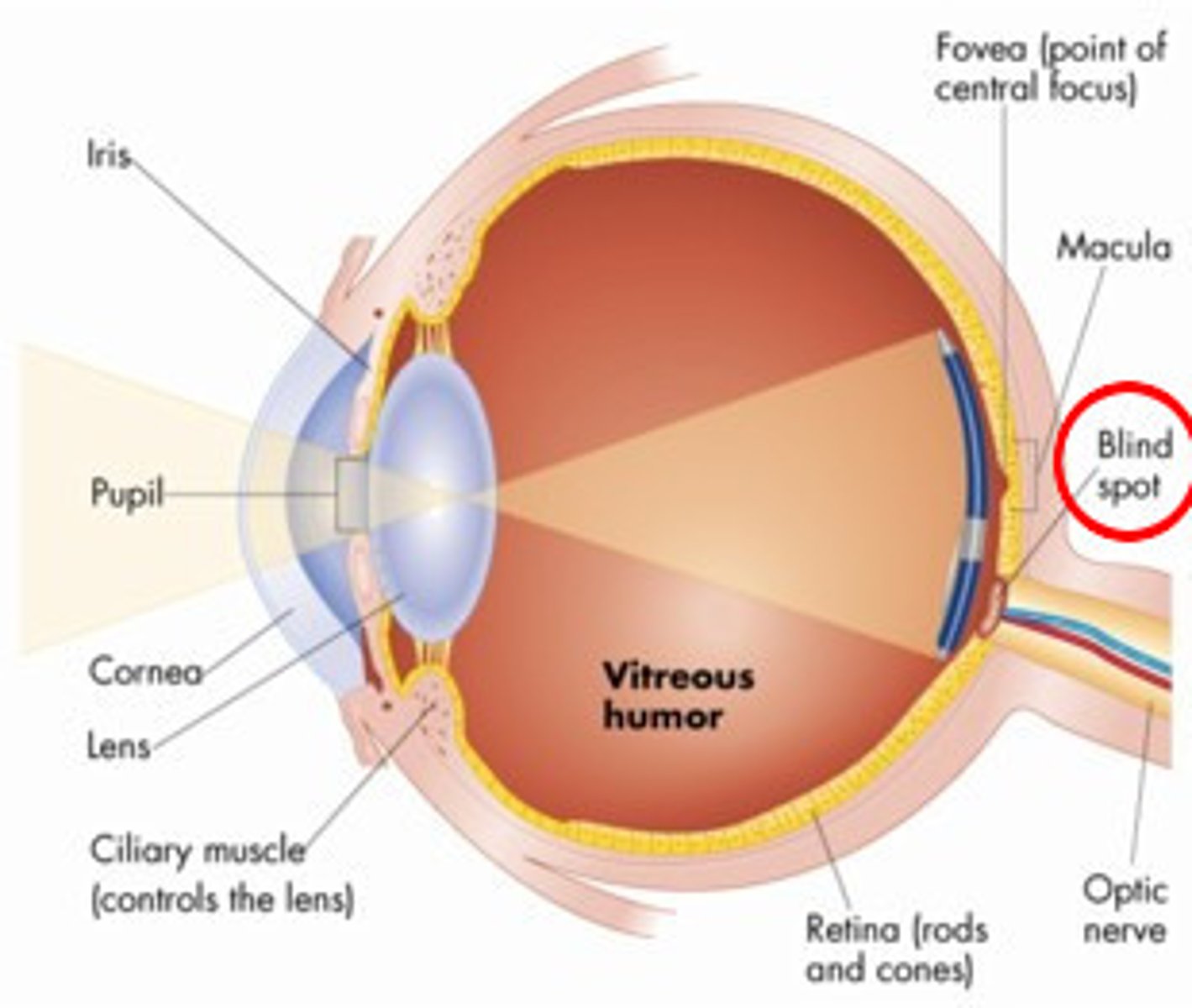
optic nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain.
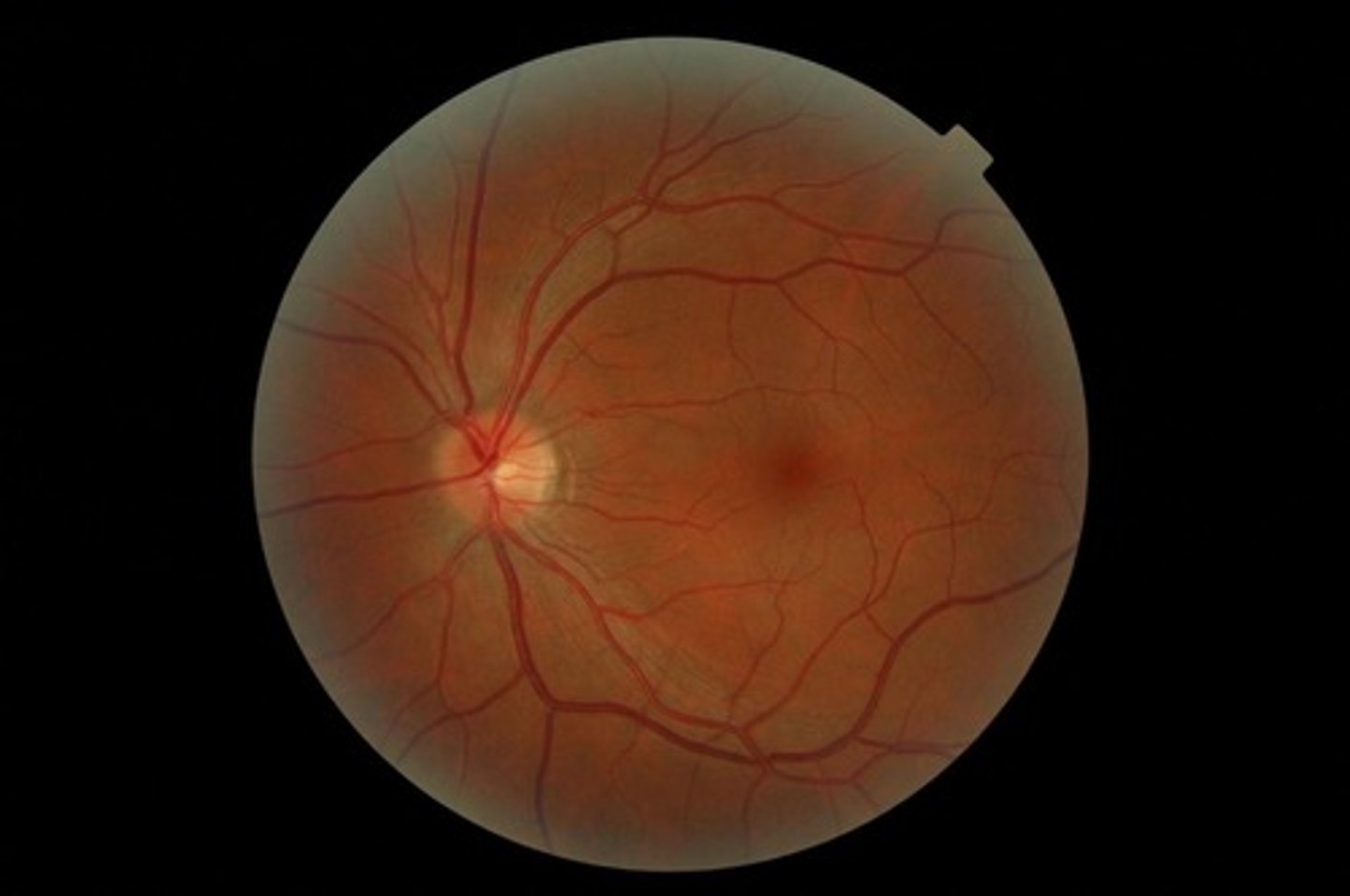
fovea
The central focal point in the retina, around which the eye's cones cluster.

feature detectors
nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features of the stimulus, such as shape, angle, or movement.

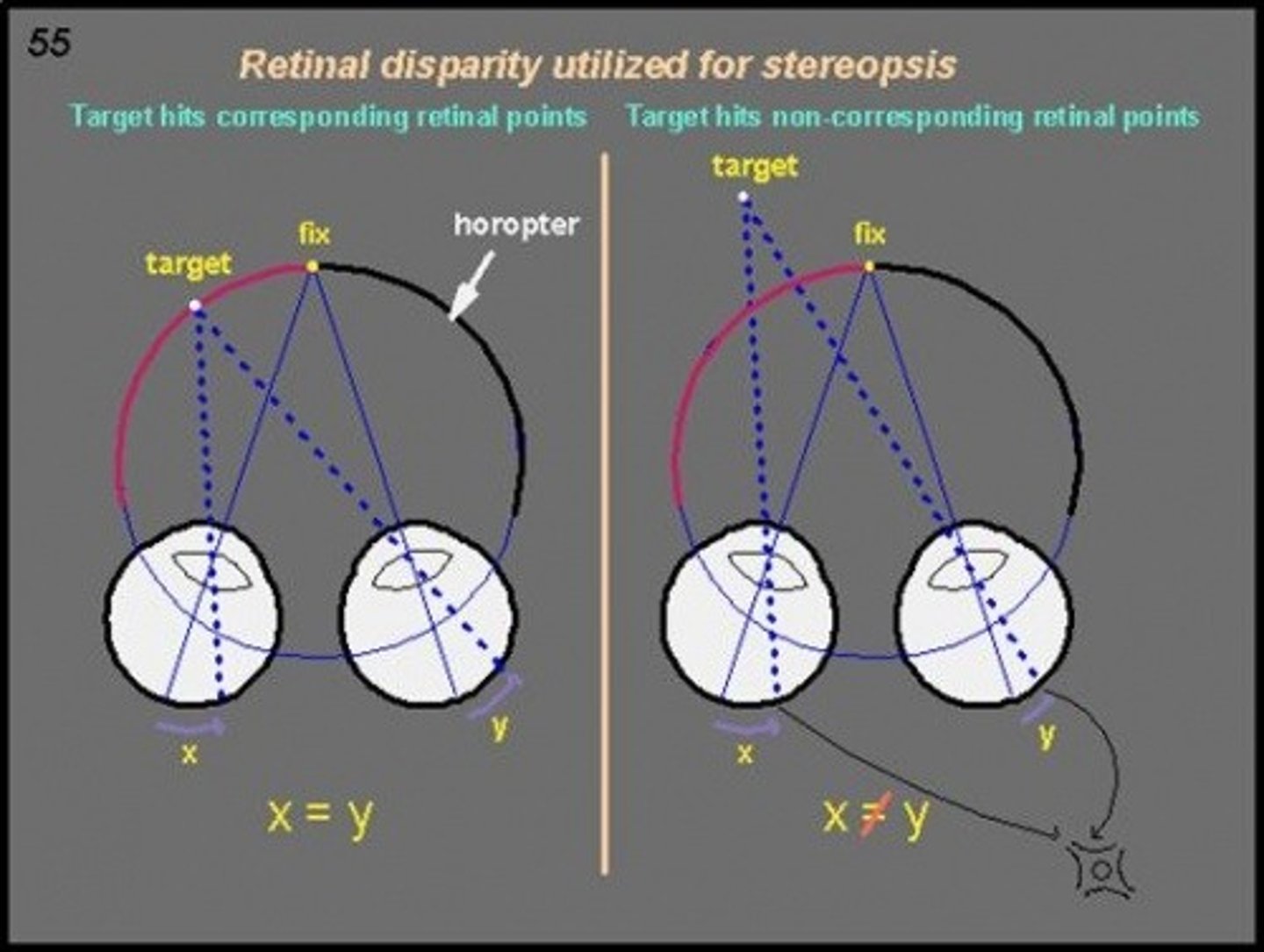
binocular cues
visual messages/cues that require two eyes
Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory
created by Hermann von Helmholtz; theory of color vision suggest that the retina contains three types of color receptors, cones: red, green, blue which can be stimulated in combination to produce the perception of color.

Opponent-Process Theory
created by Edward Hering; alternative theory used to explain after images; suggest that the retina contains three pairs color receptors or cones-yellow-blue, red-green, black-white; pairs work in opposition

audition
the sense or act of hearing
frequency
The number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time (for example, per second).

monocular cues
depth cues, such as interposition and linear perspective, available to either eye alone.

pitch
auditory experience corresponding to the frequency of sound vibrations, resulting in a higher or lower tone; humans respond to 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz

middle ear
The chamber between the eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (Hammer, Anvil, and Stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea's oval window.

cochlea
A coiled, bony, fluid-filled tude in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses.
inner ear
The innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs.

Place Theory
In hearing, the theory that links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea's membrane is stimulated.

Frequency Theory
In hearing, the theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pitch.
conduction hearing loss
Hearing loss caused by damage to the mechanical system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea; usually permanent.

sensorineural hearing loss
Hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea's receptor cells or to the auditory nerves; also called nerve deafness.

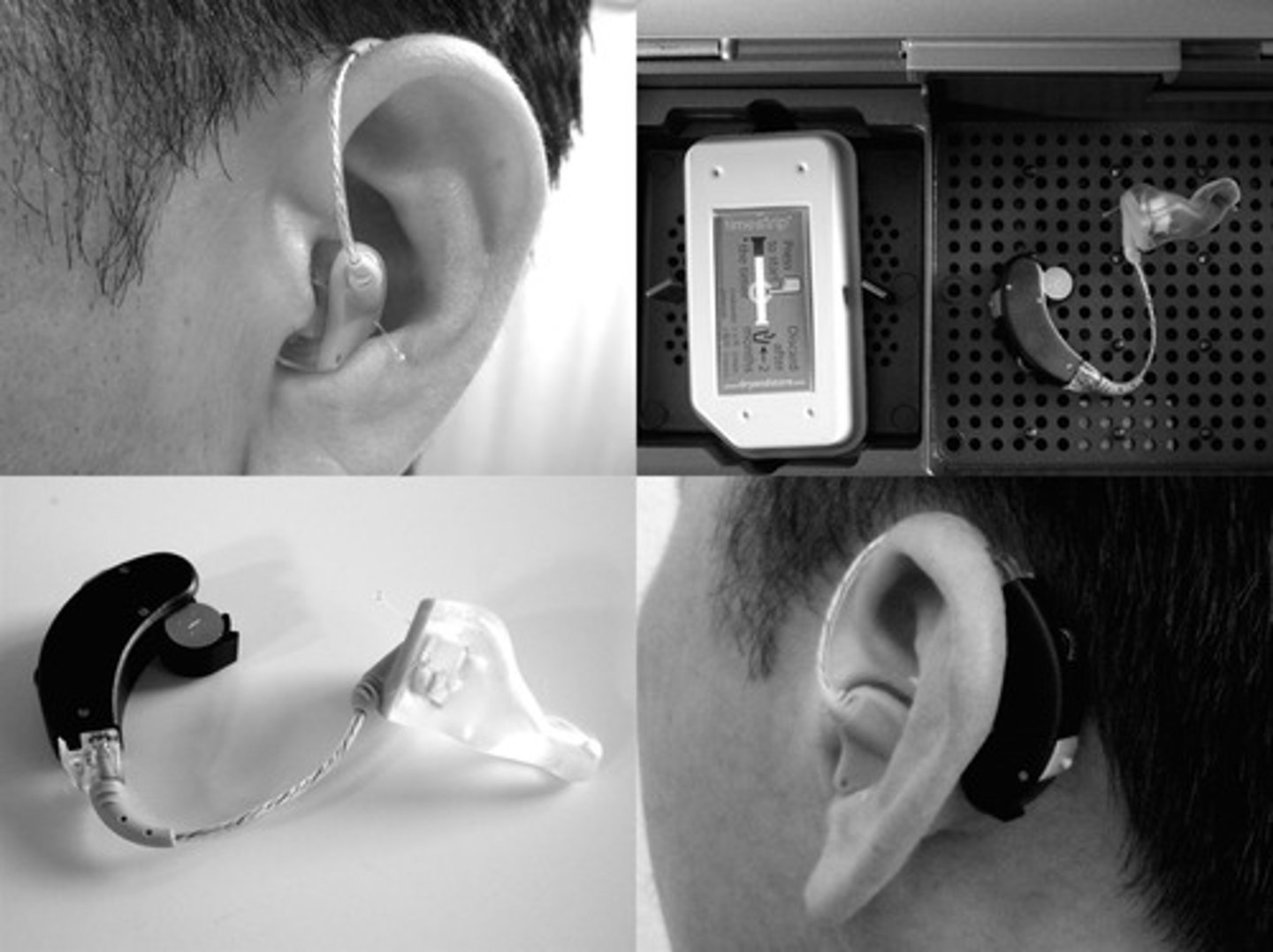
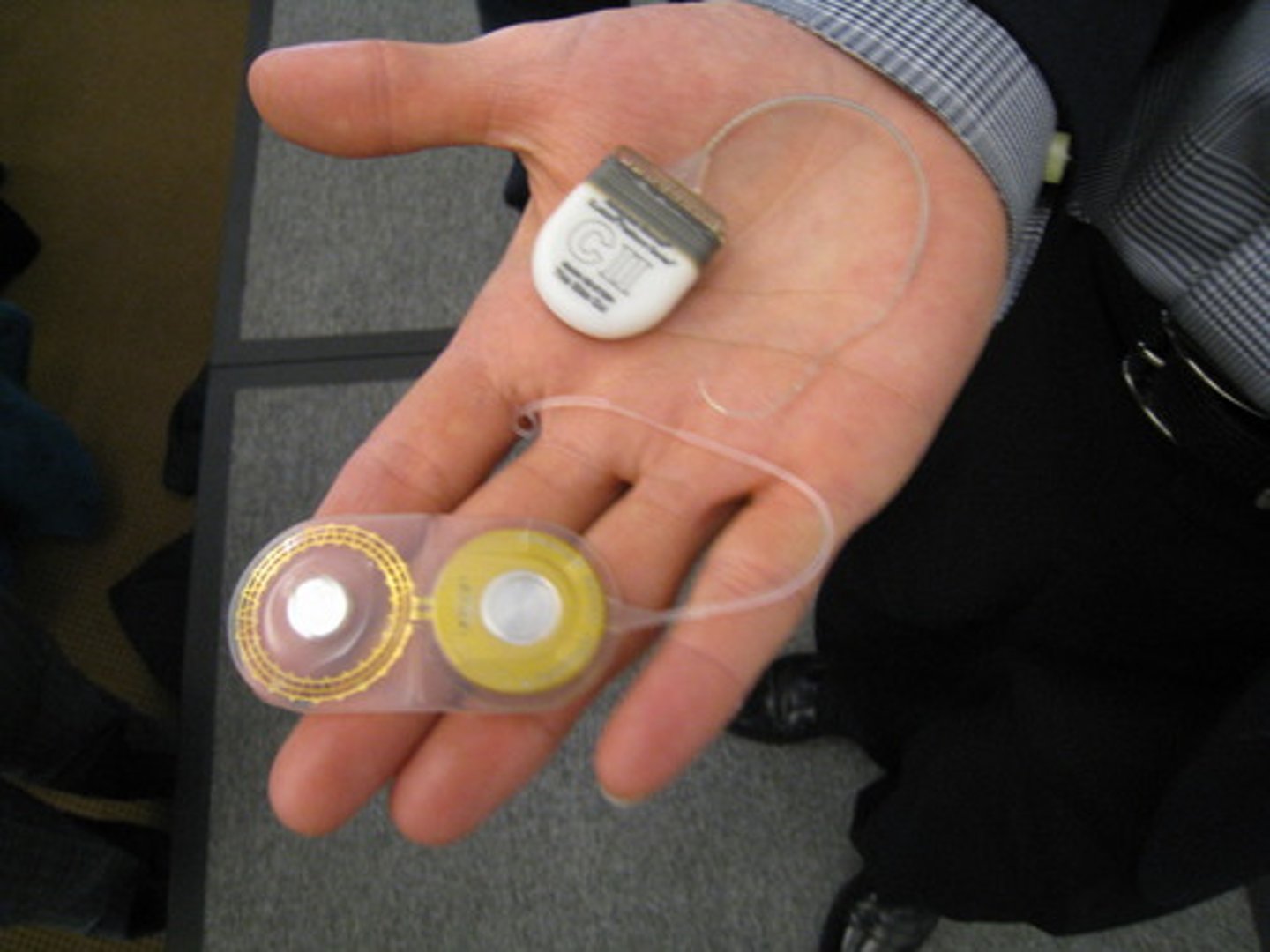
cochlear implant
a device for converting sounds into electrical signals and stimulating the auditory nerve by electrodes threaded into the cochlea

kinesthesis
sense of muscle movement, posture, and strain on muscles/joints; provides information on speed and direction of movement;
vestibular sense
The sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance. Located in inner ear

Gate-Control Theory
The spinal cord contains a "gate" that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass on to the brain. It's opened by the activity of pain signals traveling up small nerve fibers and is closed by activity in large fibers

sensory interaction
The principle that one sense may influence another, as when the smell of food influences its taste.

Gestalt
an organized whole. Gestalt psychologists emphasized our tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes.
grouping
the perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups.
parallel processing
The processing of several aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain's natural mode of information processing for many functions, including vision, audition etc. Contrasts with the step-by-step (serial) processing.
retinal disparity
binocular distance cue; based on the overlay of two retinal fields when both eyes focus on one object

perceptual accommodation
in perception, the ability to adjust to an idea or mind set

size constancy
the perception of an object as the same size regardless of the distance from which it is viewed; example someone's height

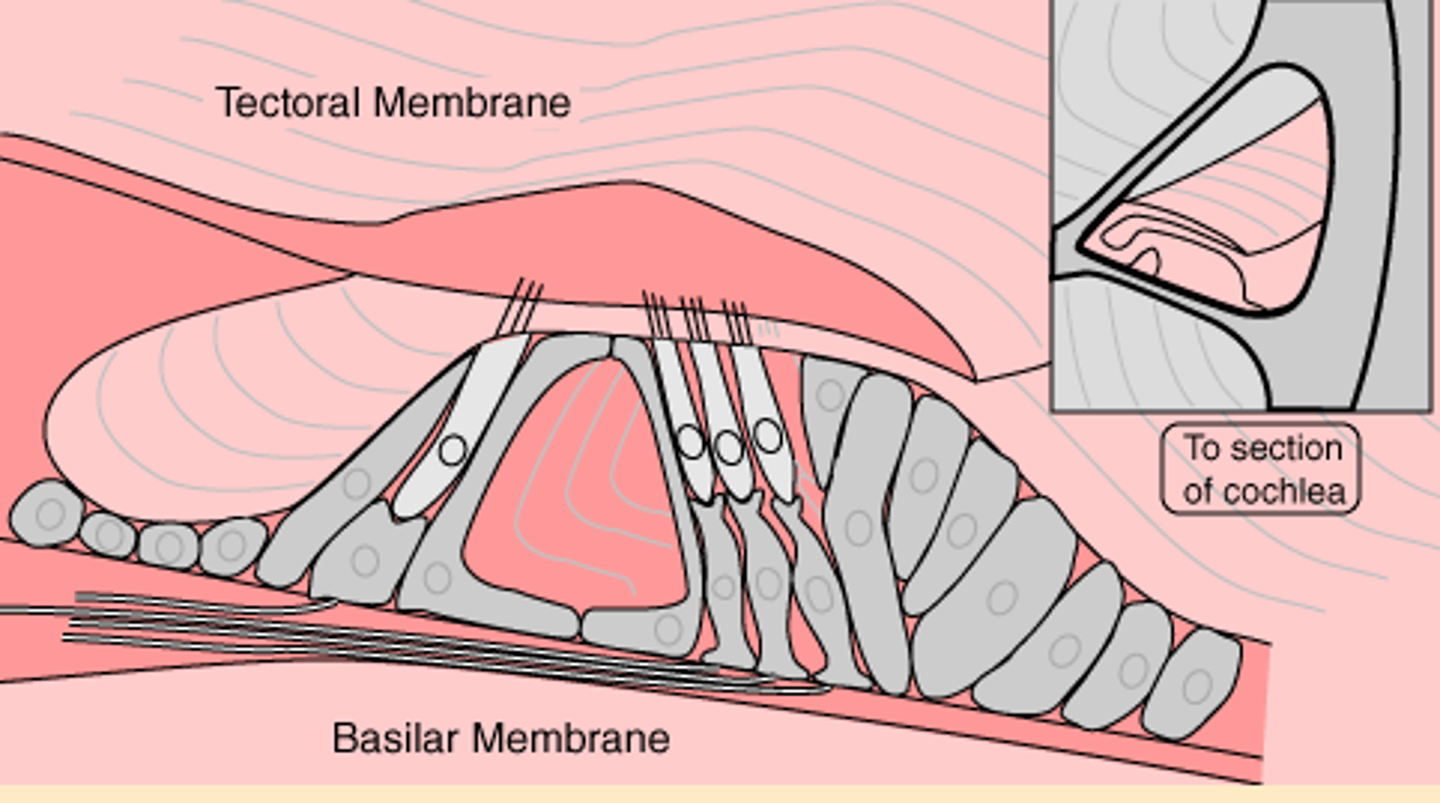
basilar membrane
A membrane inside the cochlea which vibrates in response to sound and whose vibrations lead to activity in the auditory pathways.
olfaction sense
sense of smell

taste buds
groups of cells located on the tongue that enable one to recognize five different tastes (bitter, sweet, salty, sour, umami)

depth perception
ability to see objects in 3-D
perceptual consistancy
perceiving objects as unchanging (having consistent shapes, size, lightness, and color) even as illumination and retinal images change.

Herman von Helmholtz
Theorist who both aided in the development of the trichromatic theory of color perception and Place theory of pitch perception.

Ernst Weber
1795-1878; Field: perception; Contributions: just-noticeable-difference (JND) that eventually becomes Weber's law; Studies: 1st study on JND

habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner
umami
brothy or meaty taste receptors on tongue
synesthesia
stimulation of one sensory pathway leads to involuntary experience of a secondary sense. "Hear colors"
interposition
One object overlaps the other, which causes us to perceive depth.
sensory integration
the idea that one sense influences another. smell and taste
phi phenomenon
Optical illusion of perceiving a series of still images when viewed in rapid succession as continuous motion.
foveal vision
Vision that takes place in the center of the retina. It is responsible for sharp central vision. Necessary for reading.
Gestalt Principle of Closure
Tendency to perceive objects as being whole when they are not complete. When part of the picture is missing they will fill in the gap.
wavelength
the distance from one peak of a wave to another. gives perception of color.
extrasensory perception (ESP)
the controversial claim that perception can occur without perception can occur without sensory input.
parapsychology
The study of paranormal psychic phenonmea including ESP. (Extra sensory perception). Often criticized.
perceptual adaptation
The ability to adjust to changed sensory input, including an artificially displaced or even inverted visual field.
figure-ground
the organization of the visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings .
embodied cognition
the influence of bodily sensations, gestures, and other states on cognitive preferences and judgements
sensory receptors
sensory nerve endings that respond to stimuli
perceptual set
a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another
visual cliff
a laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals
color constancy
perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color, even if changing illumination alters the wavelengths reflected by the object