Molecular and Cellular Biology Exam 1
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Molecular cell biology
The study of processes in and around cells at a molecular level
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells that are small, have no nucleus, have circular DNA, and have a cell wall.
Eukaryotic Cells
Larger cells that have a nucleus and linear DNA
G1 Phase
First phase in a cell life cycle where the cell grows in size, produces proteins, and synthesizes organelles in preparation for DNA replication.
S Phase
The second phase in a cell life cycle where DNA replication occurs and genetic material doubles.
G2 Phase
The third phase in the cell life cycle where the cell continues to grow, DNA replication errors are checked, and the cell prepares for mitosis.
M Phase
The final phase of the cell life cycle where the cell undergoes mitosis.
G1 Checkpoint
At the end of G1 phase before the cell enters S phase, the cell checks it’s size, nutrient availability, growth signals, and DNA integrity.
Proteins that G1 Checkpoint checks
p53, cyclin, and cyclin-kinase
G2 Checkpoint
A checkpoint at the end of G2 phase before entering M phase. The cell checks for proper DNA replication, DNA damage, cell size, and energy levels.
M checkpoint
Checkpoint during metaphase of mitosis. Checks for proper chromosome attachment to spindle fibers and for equal tension on sister chromatids.
Cyclins
Regulatory proteins that control progression through cell cycle by activating CDKs.
CDKs
Enzymes that (when bound to specific cyclins) phosphorylate target proteins to drive cell transitions.
p53s
Proteins that halt the cell cycle if DNA damage is detected. They can also trigger apoptosis if damage is irreparable.
Carbohydrates
Subunits: Monosaccharides
Structure, C, H, and O bonds in 1:2:1 ratio
Features: Rings or linear structures with (-OH) groups
Functions: Primary energy source + structural support
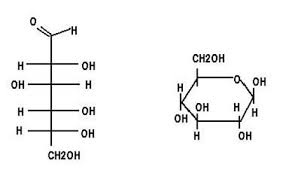
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Subunits: Glycerol + fatty acids, phosphate group, or steroid rings
Structure: Mostly hydrophobic structure comprised of C,H, and O
Identifying Features: Non polar, insoluble in water; Chains can be saturated (no double bonds) or unsaturated
Functions: Long term energy storage, cell membrane structure, hormones, and signalling
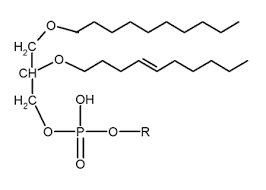
Lipids
Proteins
Subunits: Amino Acids
Structure: Contain C,H,O,N and sometimes S; formed by peptide bonds between amino acids, folded into complex shapes
Identifying features: Amino group (-NH2) + Carboxyl group (-COOH)
Functions: Enzymes, structural support, transport, immune response
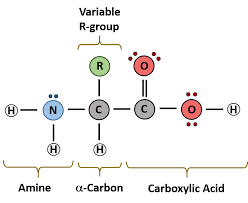
Protein
Nucleic Acids
Subunits: Nucleotides
Structure: C, H, O, N, and P
Identifying Features: Sugar-phosphate, nitrogenous bases
Functions: Store genetic information, protein synthesis, ATP
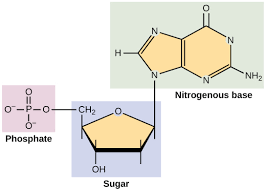
Nucleic Acids
Amino acids consist of:
An amino group (-NH2), carboxyl group (-COOH), R group, and H atom
Basic structure of a nucleotide has three components
A pentose sugar, a phosphate group attached to 5’ carbon on sugar, and a nitrogenous base attached to 1’ carbon on sugar
Purines
are a type of nitrogenous base that includes adenine and guanine, characterized by a two-ring structure.
Pyrimidines
are a type of nitrogenous base that includes cytosine, thymine, and uracil, characterized by a single-ring structure. Think pyrimidine —> cytosine
Nucleotide connections
A phosphodiester bond formed between 3’ -OH of one nucleotide’s sugar and the 5’ phosphate of the next nucleotide.
Catalyst
A substance that speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed in teh process.
Enzyme
Biological catalyst that are mostly proteins. They loewr the activation energy.
Activation sites
Specific regions on an enzyme where the substrate binds and the reaction occurs.
Reaction rate vs. substrate concentration
As substrate concentration increases, the reaction rate also increases. The reaction continuesuntil all enzyme active sites are occupied.
Vmax
The maximum reaction rate achieved by an enzyme when all active sites are saturated with substrate.
Kd (Dissociation Constant)
A measure of the affinity between an enzyme and its substrate, representing the concentration of substrate at which half of the enzyme's active sites are occupied.
pH
A measure of acidity. A higher pH means lower H+ concentration (basic).
DNA basic structure
The double helix formation of nucleotides, consisting of a sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine) that pair specifically.
DNA 5’ End
Has a phosphate group on DNA
DNA 3’ end
Has a hydroxyl group on DNA
DNA Major Groove
The larger of the two grooves in the DNA double helix, providing access for proteins to bind and interact with the DNA.
DNA Minor Groove
The smaller of the two grooves in the DNA double helix, which is less accessible for protein binding compared to the major groove.
Base content vs. melting temperatures
Higher guanine-cytosine content means a higher melting point due to increased hydrogen bonding.
Exons
Coding sequences that are translated into proteins
Introns
Non-coding sequences that are spliced out during mRNA processing
Promoter
DNA region where RNA polymerase binds to start transcription
UTRs
Regulatory regions before and after coding sequences. They affect mRNA stability, translation, and localization
Chromosomes
Structures that organize and package DNA into a compact form, visible during cell division.
Centromere
Attachment site for spindle fibers during mitosis
Telomeres
Protect chromosome ends from degradation
Origins of Replication (Ori)
Sites where DNA replication begins in chromosomes
Nucleosomes
Structural units of chromatin, consisting of DNA wrapped around histone proteins.
Octameric core
Central protein structure of a nucleosome that consists of 8 histone proteins
H1 Histone
A linker histone that binds to the nucleosome, helping to stabilize the structure and regulate gene expression.
Human genome
Approximately 3 billion base pairs in haploid cells
Euchromatin
A less condensed form of chromatin that is transcriptionally active, allowing for gene expression.
Heterochromatin
A tightly packed form of chromatin that is transcriptionally inactive, often associated with gene silencing.
Repetative DNA
DNA sequences that are repeated multiple times in the genome, often found in non-coding regions and can play roles in structural functions and regulation including centromeres, telomeres, and VNTRs.
Mitochondria
Double membrane bound organelles that generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
Mitochondrial structural features
Smooth outer membrane containing porins to allow passage of small molecules. Inner membrane folded into cristae to increase surface area for ATP production. Between the inner and outer membrane is a space important for proton gradient formation. Also has a matrix containing enzymes for the krebs cycle, mitochondrial DNA, tRNAs, and ribosomes.
Mitochondrial replication
Replication done independently from the cell through binary fission.
Fission
Splitting mitochondrion into two mitochondrion. Increase number in response to high energy demand or stress.
Fusion
Two mitochondria combine to share contents. Helps repair damaged mitochondria by mixing contents.
Helicase
Unwinds DNA helix at replication fork
Single-Stranded Binding Proteins (SSBs)
Prevents reannealing of single-stranded DNA
Topoisomerase
Relieves supercoiling ahead of the replication fork
Primase
Synthesizes new DNA strands
Primase
Synthesizes short RNA primers
DNA Polymerase
Synthesizes new DNA strands
Sliding clamp
Increases processivity of DNA polymerase
Ligase
Seals gaps between okazaki fragments
DNA polymerase I
Removes RNA primer, fills in the DNA, and 3’-5’ exonuclease proofreads
Telomerase
A reverse transcriptase that extends telomeres using an RNA template
TAQ Polymerase
A heat-stable DNA polymerase used in PCR. It has low fidelity and does not proofread.
PCR
A laboratory technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences, making millions of copies from a small initial sample.
Sanger sequencing
A method for determining the nucleotide sequence of DNA using chain-terminating inhibitors.
Glocosylases
Errors: daily mistakes
Recognition: specific glycosylase
Removal: endonuclease
Repair: DNA polymerase fills in, ligase seals
Consequences: breast cancer, colorectal cancer
MMR
Errors: when proofreading is not effective, bases wrong
Recognition: muts
Removal: muts
Repair: DNA polymerase and ligase
Consequences: hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer syndrome
Nucleotide Excision Repair
Errors: T-T bulges
Recognition: XPs
Removal: XP endonucleases
Repair: DNA pol and ligase
Consequences: xeroderma pigmentosum
Homologous Recombination
Errors: DS breaks
Recognition: Rec and Rad
Removal: Complicated
Repair: Strand invasion and strand extension
NHEJ SOS Repair
Errors: DS breaks
Recognition: Ku’s
Removal: Squish ends together
Repair: Trim excess