Unit 4 - Attribution Theory and Person Perception
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Attribution Theory
the theory that we explain people's behavior by crediting either the situation or the person's disposition
"That man is yelling because he's a bad person”
Dispositional Attributions
Internal Characteristics (Personal Traits) such as personality and intelligence
Situational Attributions
Environmental Factors
Explanatory Style
a psychological attribute that describes how people explain the causes and impact of events in their lives, whether positive or negative
Actor-Observer Bias
when an individual blames another person unjustly as being the sole cause of their behavior, but then commits the same error and blames outside forces
Fundamental Attribution Error
we attribute the behavior of others to internal factors rather than external
I believe that the man is yelling because he is a bad person, not because he's under a lot of stress.
False Consensus Effect
the belief that a lot of people think the way we do
Self-Serving Bias
we attribute causes of behavior to external causes if we fail & internal causes if we succeed.
I passed my test because I am smart or I failed my test, because my teacher doesn’t teach me well
Internal locus of control
think they control and are responsible for what happens to them
External locus of control
Believe what happens is due to fate, luck, or others
Outgroup homogeneity
The out-group homogeneity effect is the perception of out-group members as more similar to one another than are in-group members
e.g. "they are alike; we are diverse".
allows for all types of bias, prejudice and discrimination (dispositional attribution)
Social Control vs Personal Control
the power of the situation vs the power of the individual
Other-race Effect
the tendency to recall faces of one’s own race more accurately than faces of other races
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
a belief that leads to its own fulfillment
Social Comparison Theory
is the idea that people compare themselves to others to evaluate their abilities, opinions, and attitudes, and to gain a better understanding of themselves
Relative Deprivation
is the idea that someone feels deprived or entitled to something based on a comparison to others
Optimistic explanatory style
attributes negative events to external, temporary, and specific factors, leading to resilience and a positive outlook.
Pessimistic explanatory style
attributes negative events to internal, stable, and global factors, often resulting in feelings of helplessness and low self-esteem.
Upward social comparison
this can motivate individuals to improve but may also lead to feelings of inadequacy or envy
Downward social comparison
this often boosts self-esteem by making individuals feel better about their own situation
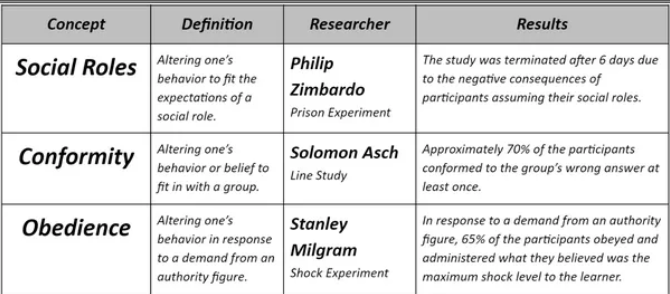
Experiments to know