Radicals and selectivity
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
What is a SOMO
a single occupied molecular orbital.
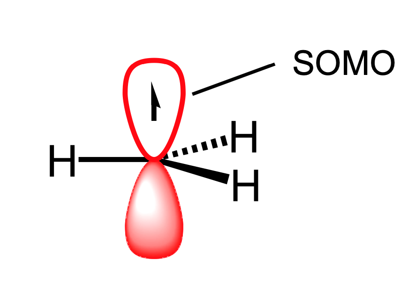
How can a radical be stabilised
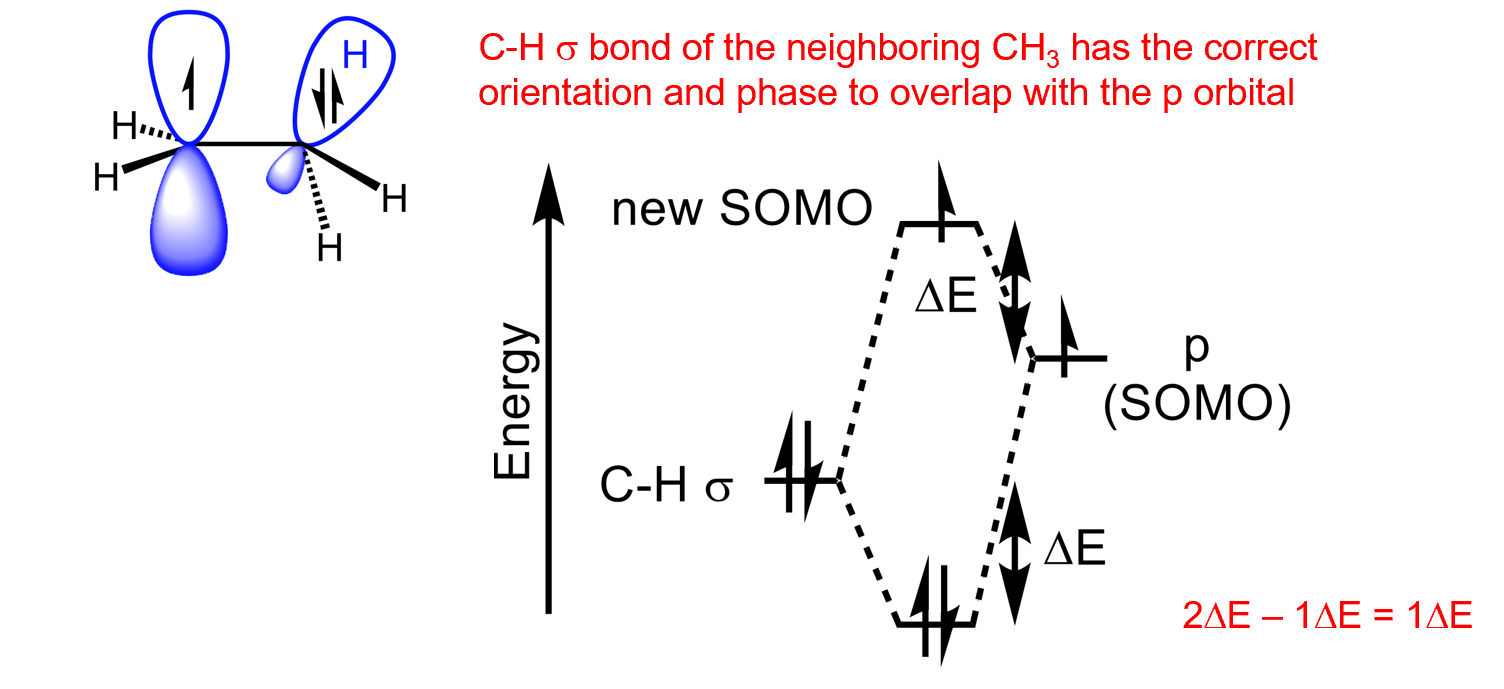
What is a better way to stabilise carbon radicals
Delocalisation of the unpaired electron in conjugation
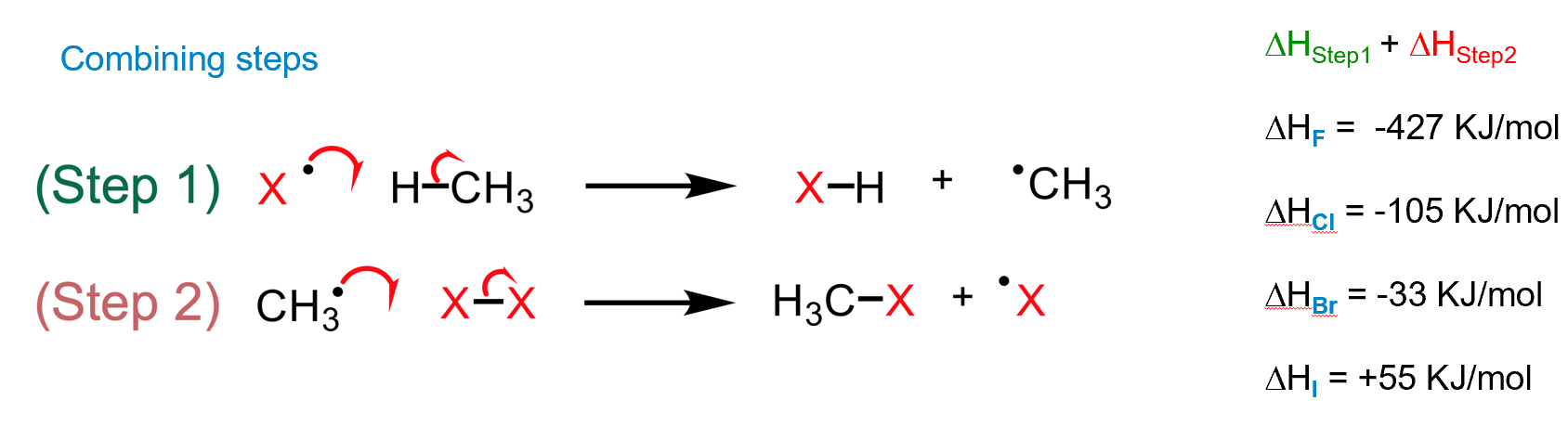
relative rate of reaction of halogen radicals with alkanes
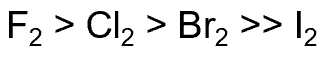
why no reaction with iodine
it is not thermodynamically favourable to undergo the process
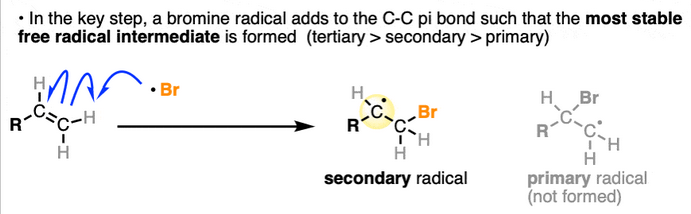
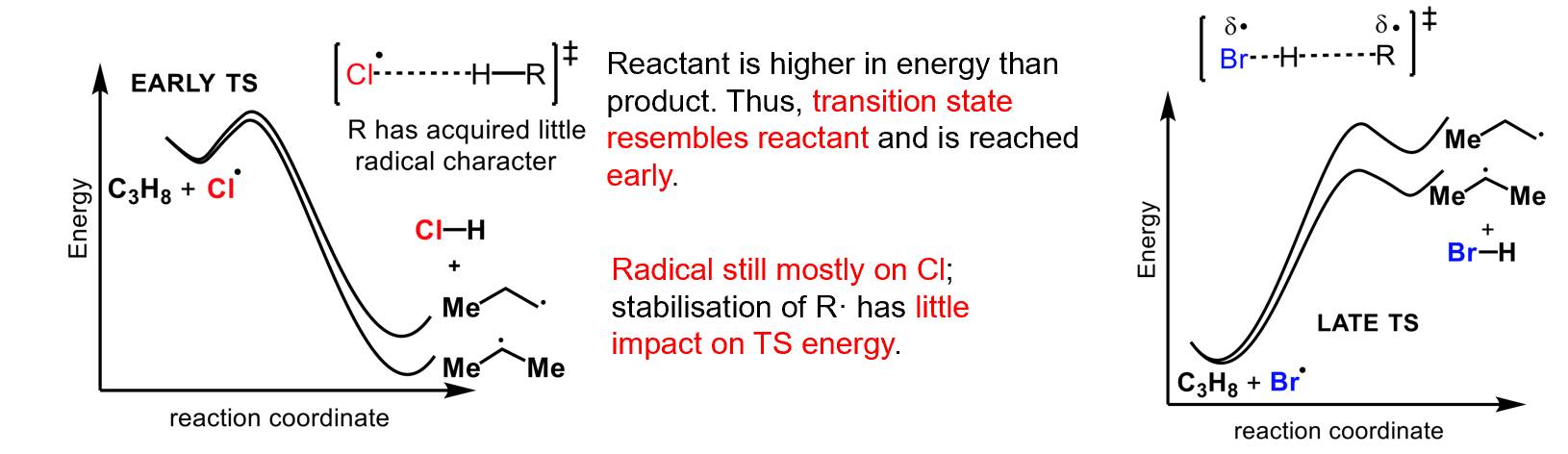
why does bromine favour the more substituted product more than chlorine
The transition state of Cl is reached early so has more alkane character than radical character so the probability of attacking a particular hydrogen matters more.
In contrast, bromine has a transition state with more radical character so overwhelmingly favours the more substituted radical.
Does radical substitution of HBr produce the Markovnikov product
No, the hydrogen adds to the most substituted position as this is where the radical is most stable