topic 13 - fermentation
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
in cell. resp. all ATP created in all 3 stages added up to 34 ATP, if 36 ATP is generated according to eq., where did 2 extra ATP come from?
mitochondria makes 2 ATP
what happens w/ respiration when there's no O₂?
• cell resp. = aerobic resp.
• fermentation = anaerobic resp.
• so, fermentation just occurs
fermentation is really ______________.
evolutionarily old
glycolysis does NOT require __________.
oxygen (O₂)
is oxygen terminal e⁻ acceptor in fermentation?
no
wht is terminal e⁻ acceptor in fermentation?
an organic molecule
how many pts. r there in fermentation?
2 pts.
what r the 2 pts. of fermentation?
1. glycolysis
2. recycling NAD⁺
wht happens during glycolysis?
there always has to be enough NAD⁺ to keep it going
wht happens when recycling NAD⁺?
e⁻s/H⁺ given to organic molecule; reducing it rather than oxidizing it
what r 2 basic kinds of fermentation?
1. lactic acid fermentation
2. alcohol fermentation
wht do both kinds of fermentation hv to begin w/?
sugar
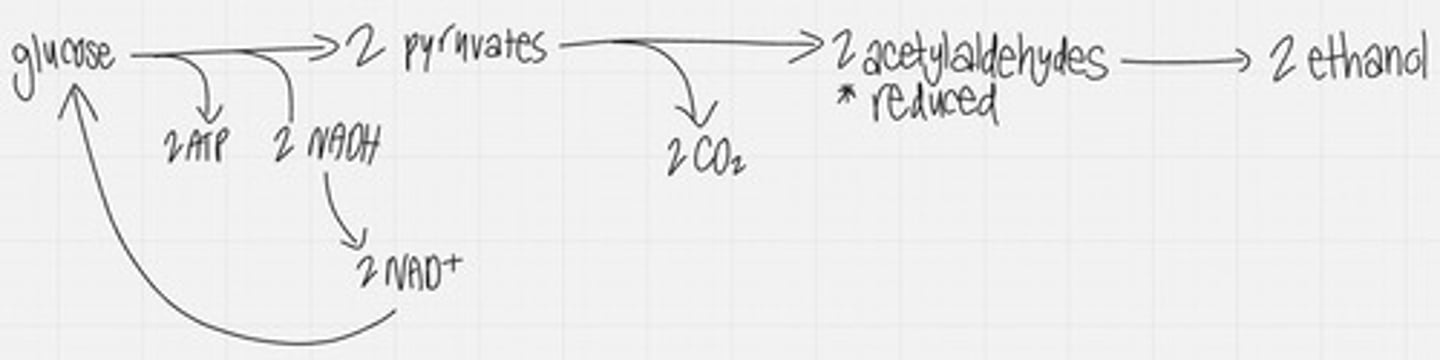
alcohol fermentation
glycolysis followed by the reduction of pyruvate to ethyl alcohol, regenerating NAD+ and releasing carbon dioxide.
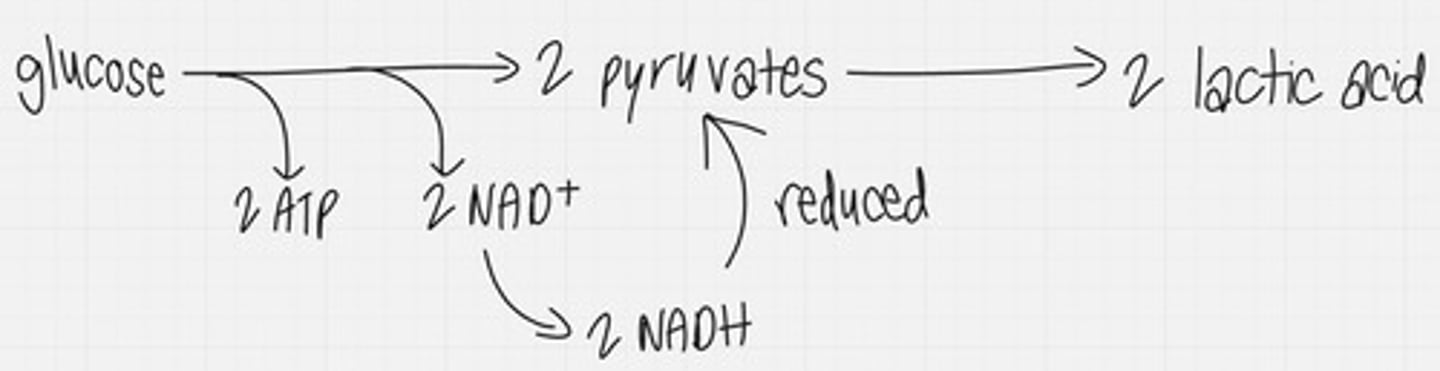
lactic acid fermentation
the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates (sugars) that produces lactic acid as the main end product; produces energy in the form of ATP
glucose is not typically _______________.
fuel used for cell. resp.
how r carbs fuel for cell. resp.?
we eat disaccharides n polysaccharides; broken down into glucose
how r proteins fuel for cell. resp.?
amino acids = intermediates in glycolysis + citric acid cycle
how r lipids fuel for cell. resp.?
glycerol = intermediate in glycolysis; fatty acids can be turned into acetyl-CoA
glycerol
a 3-carbon alcohol to which fatty acids are covalently bonded to make fats and oils
how r nucleic acids fuel for cell. resp.?
related to ATP (phosphate group), NAD⁺, FAD
biosynthesis
kinda like cell. resp. in reverse; cells can make molecules it needs; any extra molecules r reverse engineered into fats (in animals)
how is cell. resp. regulated?
thru inhibition; [ATP] decreases n allows rate of cell. resp. to increase n vice versa