Chapter 10 - Motivation and Emotion
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:35 PM on 2/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
what are motives?
needs, wants, interests, and desires that propel people toward a specific behavior
2
New cards
what is motivation?
a set of factors or motives (internal and external) that cause an individual to behave a certain way
or
the psychological feature that arouses us to action toward a desired goal and elicits, controls, and sustains certain goal directed behaviours
or
the psychological feature that arouses us to action toward a desired goal and elicits, controls, and sustains certain goal directed behaviours
3
New cards
what are the four motivational theories? (4)
* drive theories
* incentive theories
* evolutionary theories
* humanistic theories
* incentive theories
* evolutionary theories
* humanistic theories
4
New cards
what is need?
a deprevation that energizes the drive to eliminate or reduce the deprevation
5
New cards
what is drive?
an internal state of tension that occurs because of a physiological need
6
New cards
what is the drive theory of motivation?
physiological need creates an aroused state that drives the organism to satisfy the need
\
__**pushed**__ **by our** __**internal**__ **needs to reduce drive**
\
ex. need (for water) > drive (thirst) > drive-reducing behavior (drinking water)
\
__**pushed**__ **by our** __**internal**__ **needs to reduce drive**
\
ex. need (for water) > drive (thirst) > drive-reducing behavior (drinking water)
7
New cards
what is incentive?
positive or negative stimulus that has the capacity to motivate behaviour
\
ex. A+ on a test, money, food
\
ex. A+ on a test, money, food
8
New cards
what is the incentive theory of motivation?
regulation by external stimuli
\
__**pulled**__ **by** __**external**__ **incentives that lure / repel us**
\
__**pulled**__ **by** __**external**__ **incentives that lure / repel us**
9
New cards
what is the evolutionary theory of motivation?
motivation aimed at promoting survival of the individual’s genes, maximizing reproductive success
10
New cards
what is the humanistic theory of motivation?
people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to other, more advanced needs
11
New cards
what is maslow’s hierarchy of needs? (5)
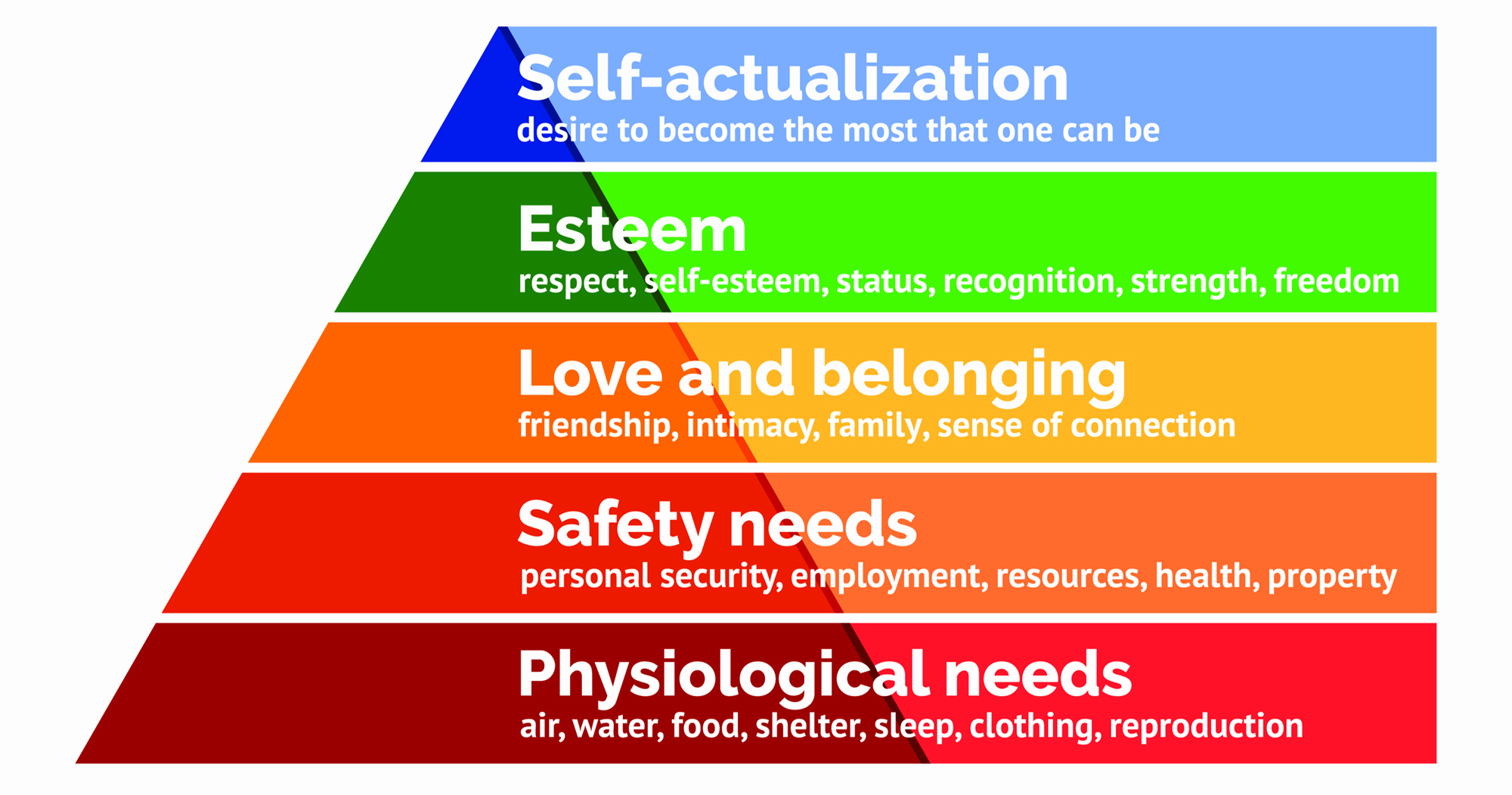
12
New cards
what type of satisfaction matters more in wealthy nations?
home-life satisfaction
13
New cards
what type of satisfation matters in poorer nations?
financial satisfaction
14
New cards
what is self-determination theory?
a theory concerned with the motivation behind the choices that people make without any external influence and interference
focuses on the degree to which an individual’s behaviour is self-motivated and self-determined
focuses on the degree to which an individual’s behaviour is self-motivated and self-determined
15
New cards
what are the three innate psychological needs proposed in the self-determination theory? (3)
* **need for competence** (succeeding at tasks)
* **need for autonomy** (having a choice)
* **need for relatedness** ( mutual respect and reliance with others)
* **need for autonomy** (having a choice)
* **need for relatedness** ( mutual respect and reliance with others)
16
New cards
what is extrinsic motivation?
when an activity is done to **attain some seperable outcome** (doing an activity because of its instrumental value)
\
ex. getting paid, avoiding punishment
\
ex. getting paid, avoiding punishment
17
New cards
what is intrinsic motivation?
engaging in an activity for it’s inherent satisfaction
\
ex. drawing, sport (for the fun, not the award)
\
ex. drawing, sport (for the fun, not the award)
18
New cards
what is the facial-feedback hypothesis?
our body tells our brain how we are feeling, and our brain tells our body how we are feeling, “bi-directional influence”
19
New cards
what are the 5 theories of emotion? (5)
* common sense theory
* james-lange theory
* cannon-bard theory
* schacter’s two-factor theory
* evolutionary theory
* james-lange theory
* cannon-bard theory
* schacter’s two-factor theory
* evolutionary theory
20
New cards
what is the common sense theory of emotion?
emotion then arousal
“I tremble because I feel afraid”
“I tremble because I feel afraid”
21
New cards
what is the james-lange theory of emotion?
arousal then emotion (stimulus causes emotion)
“I feel afraid because I tremble”
“I feel afraid because I tremble”
22
New cards
what is the cannon-bard theory of emotion?
arousal and emotion at the same time
“The dog makes me tremble and feel afraid”
“The dog makes me tremble and feel afraid”
23
New cards
what is schacter’s two-factor theory of emotion?
arousal then look to external cues to decide what to feel (interpretation of arousal causes emotion)
“I label my trembling as fear because I appraise the situation as dangerous”
“I label my trembling as fear because I appraise the situation as dangerous”
24
New cards
what is the evolutionary theory of emotion?
emotions promote survival, natural reactions, arousal is the emotion
25
New cards
what is arousal spill over?
our arousal response to one event can effect our response to a subsequent event
\
we can experience emotions from one thing, and then attribute that emotion to another thing
\
we can experience emotions from one thing, and then attribute that emotion to another thing
26
New cards
there is a link between ______ __/__ _______ and overeating.
heightened arousal / negative emotion
27
New cards
where in the brain is hunger **regulated**? (2)
the lateral hypothalamus (LH) and ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH)
28
New cards
where in the brain is hunger **controlled**? (2)
arcuate nucleus and paraventricular nucleus
29
New cards
what does the arcutate nucleus in the brain do?
contains a large group of neurons that are sensitive to **incoming hunger signals**, and another group of neurons that respond to **satiety signals**
30
New cards
what two hormones effect hunger signals? (2)
leptin and insulin
31
New cards
what are the three environmental factors that govern eating? (3)
* the availability of food
* learned preferences and habits
* stress
* learned preferences and habits
* stress
32
New cards
what is sensory-specific satiety?
as you eat a specific food, its incentive value declines
33
New cards
what is one of the most important determinants of food intake?
social cues based on the behaviour of others
34
New cards
most of the evidence on biological influences on sexual behaviour come from what?
animal research
35
New cards
as we go up the phylogenetic scale (rats > primates > humans), biological influences are ______.
reduced
36
New cards
what are the four stages of the sexual response cycle? (4)
1. excitement
2. plateau
3. orgasm
4. resolution
37
New cards
what is the gender gap in orgasm consistency?
men seem to reach orgasm more reliably than women
38
New cards
what is the parental investment theory?
theory that states **a species mating patterns depend on what each sex has to invest** - in terms of time, energy, and survival rate - to produce and nuture offspring
39
New cards
what does the parental investment theory predict about men and women?
it predicts that men will show more interest in:
\- casual sexual activity
\- variety in sexual partners
\- willingness to engage in uncommited sex
\- casual sexual activity
\- variety in sexual partners
\- willingness to engage in uncommited sex
40
New cards
what is a criticism of the evolutionary explanation of sexual behaviour?
observed gender differences could be due to social factors
ex. societal suppression of female sexuality, women may value male’s economic and material gains because their own economic potential has been limited
ex. societal suppression of female sexuality, women may value male’s economic and material gains because their own economic potential has been limited
41
New cards
researchers found elevated rates of lesbianism among women exposed to unusually high ______ levels during prenatal development
androgen
42
New cards
what are some biological theories for sexual orientation? (3)
* genetic predisposition
* prenatal hormones
* anatomical differences (anterior hypothalamus)
* prenatal hormones
* anatomical differences (anterior hypothalamus)
43
New cards
what are environmental theories explaining homosexuality? (2)
* freudian theories
* behaviourists
* behaviourists
44
New cards
biological influences on sexual behavior are due to _____ __,__ ___ in men and ______ in women.
hormones ; androgens ; estrogens
45
New cards
female sex drive is the strongest when?
during the ovulation period of the menstrual cycle