General overview (static electricity)
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
How can an insulator be charged by friction?
Electrons are transferred from one material to another. The material gaining electrons becomes negatively charged, while the material losing electrons becomes positively charged
Like forces…
Repel
Opposite forces…
Attract
Explain electric shocks from everyday objects in terms of electrostatic forces
An object can build up electrostatic force if friction acts upon it, causing the transfer of electrons. When we touch the objects, electrons move from/to the ground through us (using human bodies as conductors) to leave the object with no charge. This is because there is a potential difference between the object and the ground so current will flow, causing someone to experience an electric shock
Explain lightning in terms of electrostatic forces
Clouds can build up electrostatic charge. If there is a large potential difference between the clouds and the ground, the air in between begins to become a conductor. Electrons will flow from/to the ground. Some of the electrical energy changes into light energy, producing lightning
Explain how attraction by induction works
When a charged object is placed near a neutral object, there is a separation of charges in the neutral object (as electrons are negatively charged and protons are positively charged). The ‘like’ charges of the neutral object are rearranged to leave a part of the object with an opposite charge. This then means that the objects will stick together
How does earthing remove excess charge?
It provides a path of low resistance for electrons to flow from the object to reduce charge build up
How can static electricity cause danger when fuelling vehicles and how is it resolved?
Static charge can build up due to the friction between the pipe and the fuel. Charge build up may cause a spark, which could start a fire if it reacted with the highly flammable fuel. It is resolved by earthing the vehicle and pump
What is an electric field?
A region where an electric charge experiences a force, such as in electrical wiring
What does the electric field around a positively charged point look like?
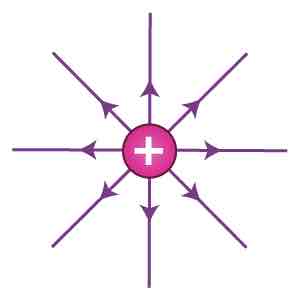
What does the electric field around a negatively charged point look like?
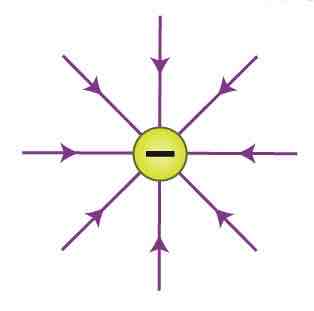
What does the electric field between parallel plates look like?
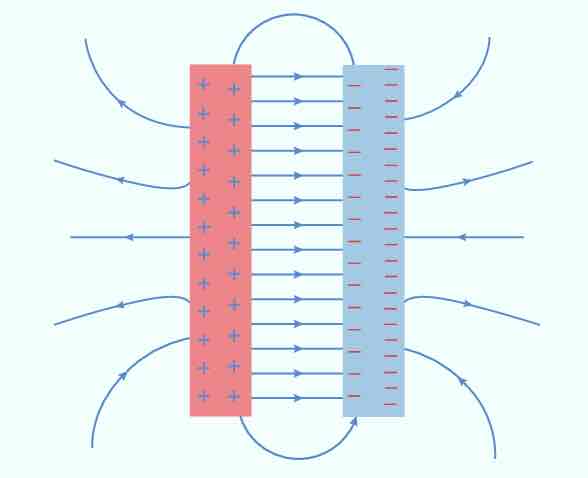
How does the strength of the electric field relate to the concentration of field lines?
A higher concentration/density of field lines means a higher field strength
How can electric fields explain static electricity?
An object that is statically charged will generate an electric field. This field attracts electrons on other objects, causing the flow of charges and a spark