Germs 101 Final Exam
1/303
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
304 Terms
Microbes
anything too small to be seen without a microscope
includes:
-bacteria
-single-celled eukaryotes
-fungi
-viruses
Scientific process
more realistic and useful view of how science works
3 major components:
-scientific method
-peer review & replication
-professional consensus
What is peer review?
when experts decide if a paper is good enough to publish
What is replication
when others try the same methods to get the same results
professional consensus
what the experts on a topic collectively agree is the most likely true/correct
Scientific Method
-A framed explanation of good science
-A foundational tool to generate new knowledge
-generally defined by 5 steps:
1) observations
2)hypothesis
3)prediction
4)data collection
5)hypothesis (supported/refuted)
Observations
describes, measures, records
hypothesis
explains an observation, is testable, is specific
prediction
describes results we should see if hypothesis is true
data collection
can be described as numerical
hypothesis (supported/refuted)
interpretation
Traditionally, 4 characteristics were recognized that defined life:
-reproduction and heredity
-individual growth
-metabolic activity
-response to light and chemical stimuli
REPRODUCTION & HEREDITY
life produces more life, and passes on traits
METABOLIC ACTIVITY
Organisms consume energy sources and excrete waste products
INDIVIDUAL GROWTH
Organisms grow:
-they develop
-they age
RESPONSE TO LIGHT & CHEMICAL STIMULI
Organisms have ways to react to light and environmental chemicals
Traditionally, characteristics were recognized that defined life LATER:
-cellular structure
-cellular transport/ nutrients
What is taxonomy?
The formal study of organizing life according to some notion of similarity or 'relatedness'
What aspects are considered in taxonomy?
Often traits, appearances, and behaviors
Taxonomy organizes life into 7 nested categories:
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, GENUS, SPECIES
BIONOMIAL NOMENCLATURE
A universal system of naming species that reflects their taxonomic organization
Bionomial nomenclature naming rules
-genus is capitalized, species is not
-genus can be abbreviated to one letter, species is never abbreviated
-Genus and species are always italicized or underlined
Ex:
Genus: Homo sapiens: Species (italicized)
Genus: H.sapiens: species
EVOLUTIONARY TREE
Where taxonomic relationships can be visually studied through
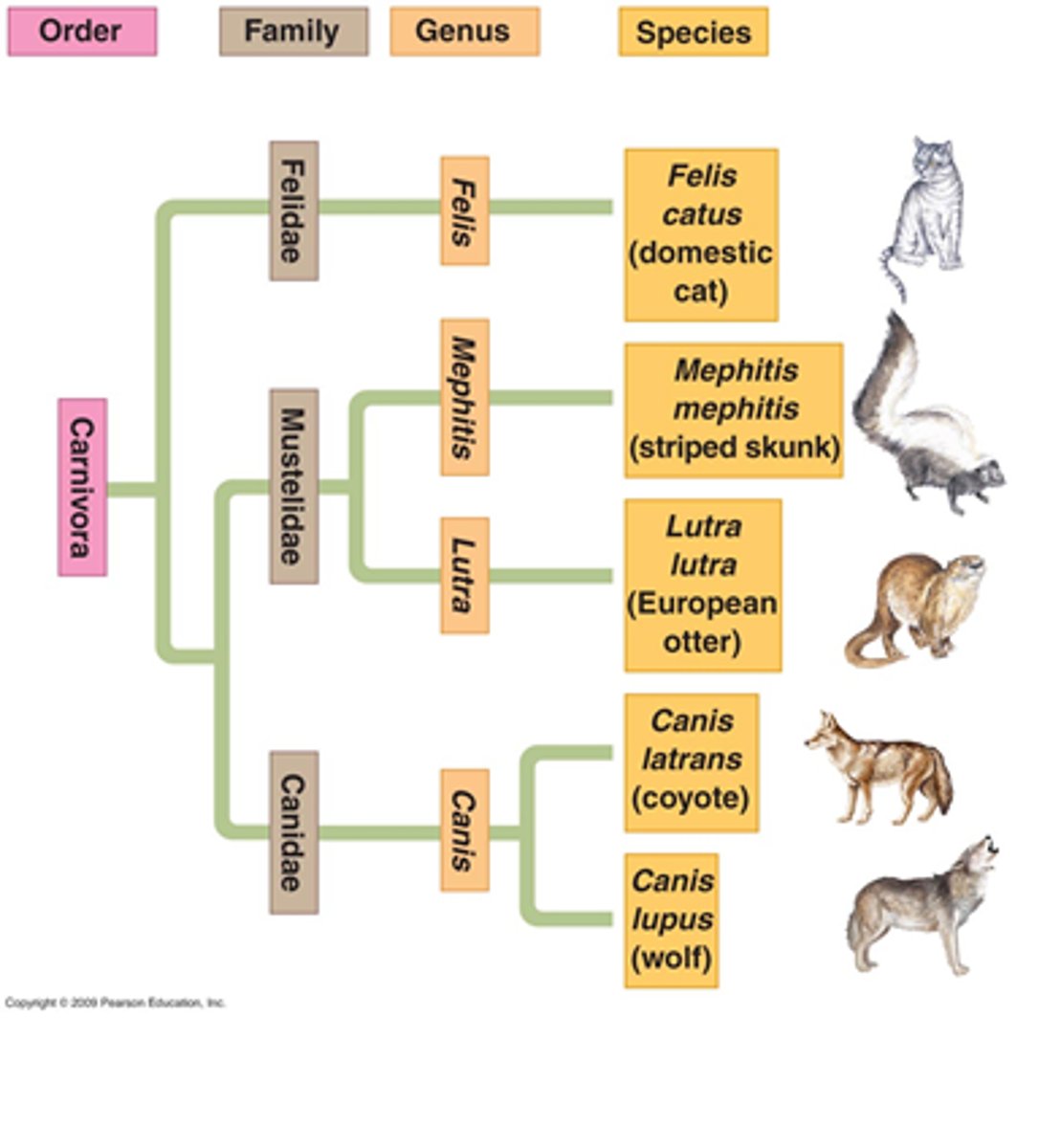
What major kingdoms do we recognize?
Plants and animals
What did ROBERT HOOKE invent and discover?
-helped invented the compound light microscope
-published the first "micrographic" (microscopic picture)
-discovered and named cells
COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE
-passes light through a specimen and 2 lenses
-magnification often 10x-400x, 1,000x-2,000x
-resolution 0.2 micrometers
-most common and affordable microscopes
ANTONY VAN LEEUWEHOEK
-built light microscopes and crafted his own lense
-1674 he discovered single-cell eukaryotes, the first bacteria
-limit of light microscopes is 2000x
WHAT DO CELLS SHARE IN COMMON?
-Some organic molecules
-Cell membrane
-Uses DNA to store genetic information
ORGANIC MOLECULES
-lipids/fats->energy and membranes
-carbohydrates/sugars->energy and structure
-nucleic acid->store information(make up DNA)
CELL MEMBRANE
-contains liquid cytoplasm
-protects cells from environment
-made of lipid bilayer
-site of metabolic reactions
-regulates transport
WHAT ARE DISTINCT DIFFERENCES OF CELLS?
-Eukaryotes
-Prokaryotes
EUKARYOTES
-Fungi cell, animal and plant cell, paramecium (single cell)
-has a nucleus to store DNA
-larger in size
-Have many organelles
PROKARYOTES
-Bacterium Cell
-DNA scattered (loose) in cytoplasm
-much smaller
-No organelles
ARCHAEA
-Bizarre group of cells called "a subset of prokaryotes" in 1977
-known to cause disease
-hottest (hydrothermal vents)
-Often lives in extreme environments
-Saltiest (grows on salt piles)
-Depths of ocean (intense pressure)
-Frozen environments (found in ice core)
EXTREMOPHILES
Cells that often live in extreme environments
What did Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden do in 1838?
They created the cell theory
CELL THEORY
1) All living things are made of cells
2)All cells come from other cells
3)Cells are the fundamental unit of life
Three most known microbes
Animals, plants and fungi
Can you see virus's with light microscopes?
No
what did DMITRY I. IVANOVSKY & MARTINUS W. BEIJERINCK do?
-Discovered virus's (bacteria)
Found bacterial infections causing disease - Tobacco "Mosaic" disease
-discovered that sap filtered to remove bacteria still caused disease
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
-1931 the electron microscope was invented
-multiple types; all use electron beams to image a target
-magnifications ranges up to 1,000,000x-50,000,000x
What makes up bacteria?
-cell wall
-capsule or slime layer
-pilus/pilli
-flagellum/flagella
CELL WALL
-coveres the cell membrane
-rigid and provide structural support (unlike membrane)
CAPSULE or SLIME LAYER
-covers cell wall
-gel-like and made of sugars
-helps bacteria stick to surfaces
-can protect them from desiccation or predators
What are PILUS/PILLI?
Protein tubes extending out from bacteria
What are short pilli (fimbriae) responsible for?
Covering the capsule of many bacteria
Why are PILUS/PILLI crucial for bacteria?
They are crucial (with capsule/slime layer) for bacteria to stick to surfaces
What is a flagellum?
A long protein tube that rotates for mobility.
Is a flagellum found in all bacteria?
No, it is not found in all bacteria.
How is a flagellum powered?
It is powered by a multi-protein 'motor'.
-Active motor causes a "run and tumble" movement
What activates a flagellum?
A flagellum can be activated by two mechanisms: chemotaxis and phototaxis.
CHEMOTAXIS
flagella drives cell toward or away from a chemical stimulis
PHOTOTAXIS
Flagella drives cell towards or away from light
In acceptable environments, growth can proceed on two levels
-cell synthesizes new cell components and increase in size
-the number of cells in the population increases
BINARY FISSION
The basis of bacterial growth
How do bacteria divide?
Through binary fission
SEPTUM
Fission occurs by forming septum
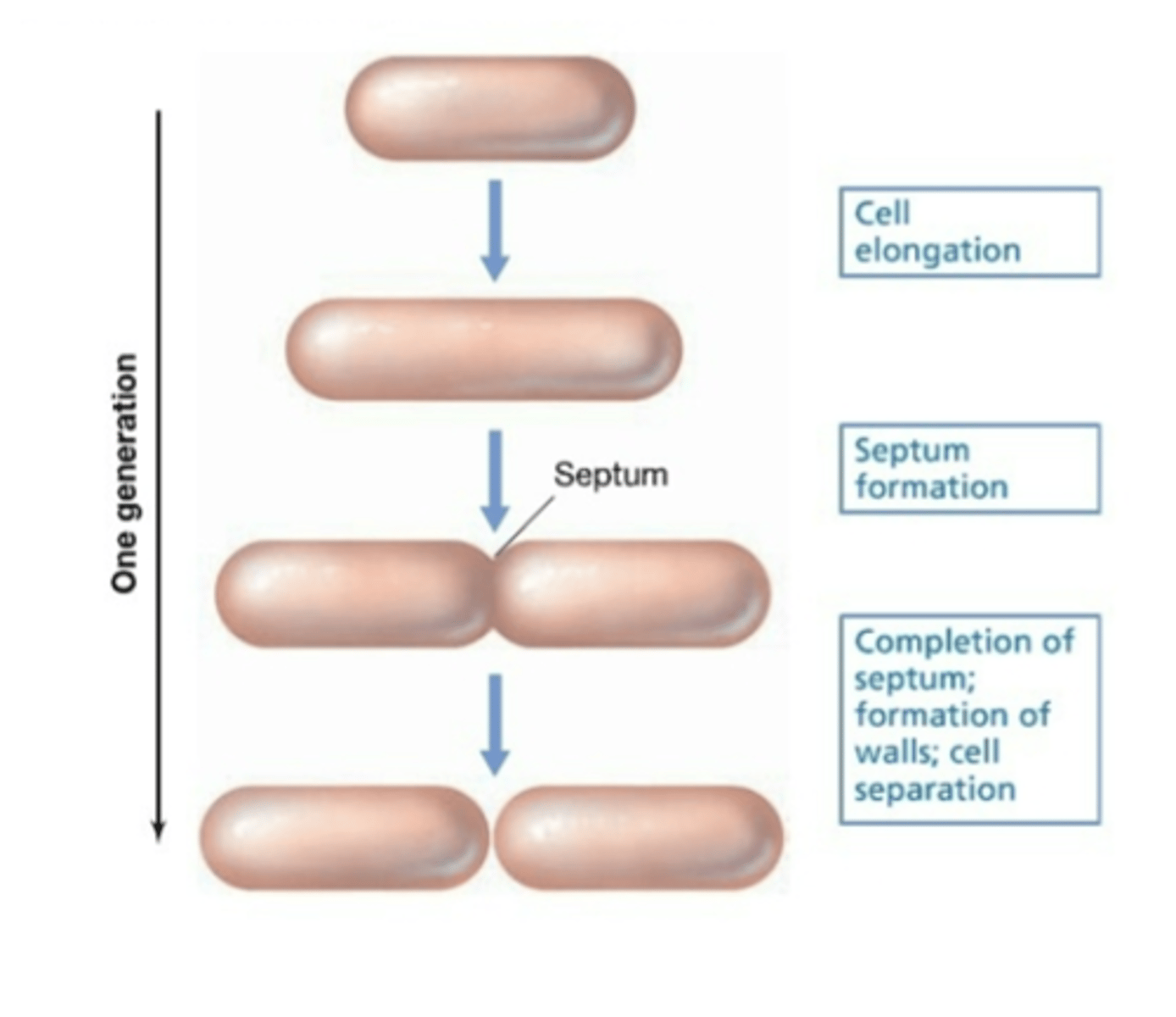
What happens as the septum gets bigger during bacterial division?
The cell splits apart
COLONY
-A visible cluster of bacteria derived from 1 cell
-Take on different appearances based on the species
-As the bacterium divides it can form a colony
CULTURE
growing a group of organisms and other cells in the lab to study
-"when scientists culture bacteria in the lab..."
How do we categorize these bacteria?
-genetics
-size
-shape
-metabolism
-cell wall components
Genetic pros
-with taxonomy in animals, genetics is preferred
-only requires a small number of cells
-can accurately ID specific species
Genetic cons
-Sequence machines may not be available
-lots of species' genetics remain unknown
-other ID techniques are established
Size pros
can readily identify species of unsusual size
Size cons
Most bacteria are just "very small", not a very convenient tool
Shape
Gernal bacteria can be sorted into 3 shape groups:
-Coccus (round)
-Bacillus (Rod)
-Curved
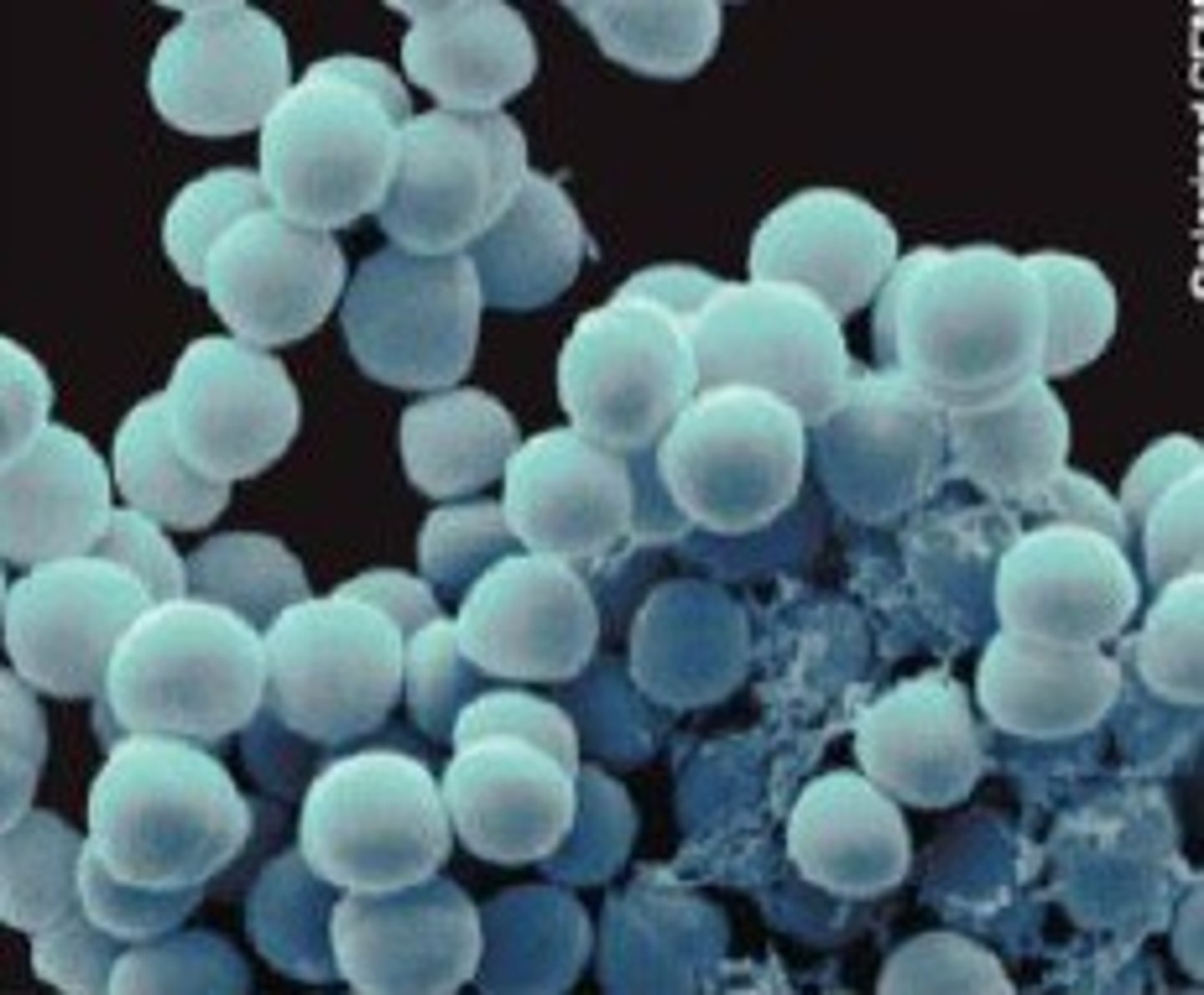
Coccus
-circular form
-often form clusters
-cluster shape determined by how species reproduces
-CLUSTER CAN HELP ID GENERA & SPECIES
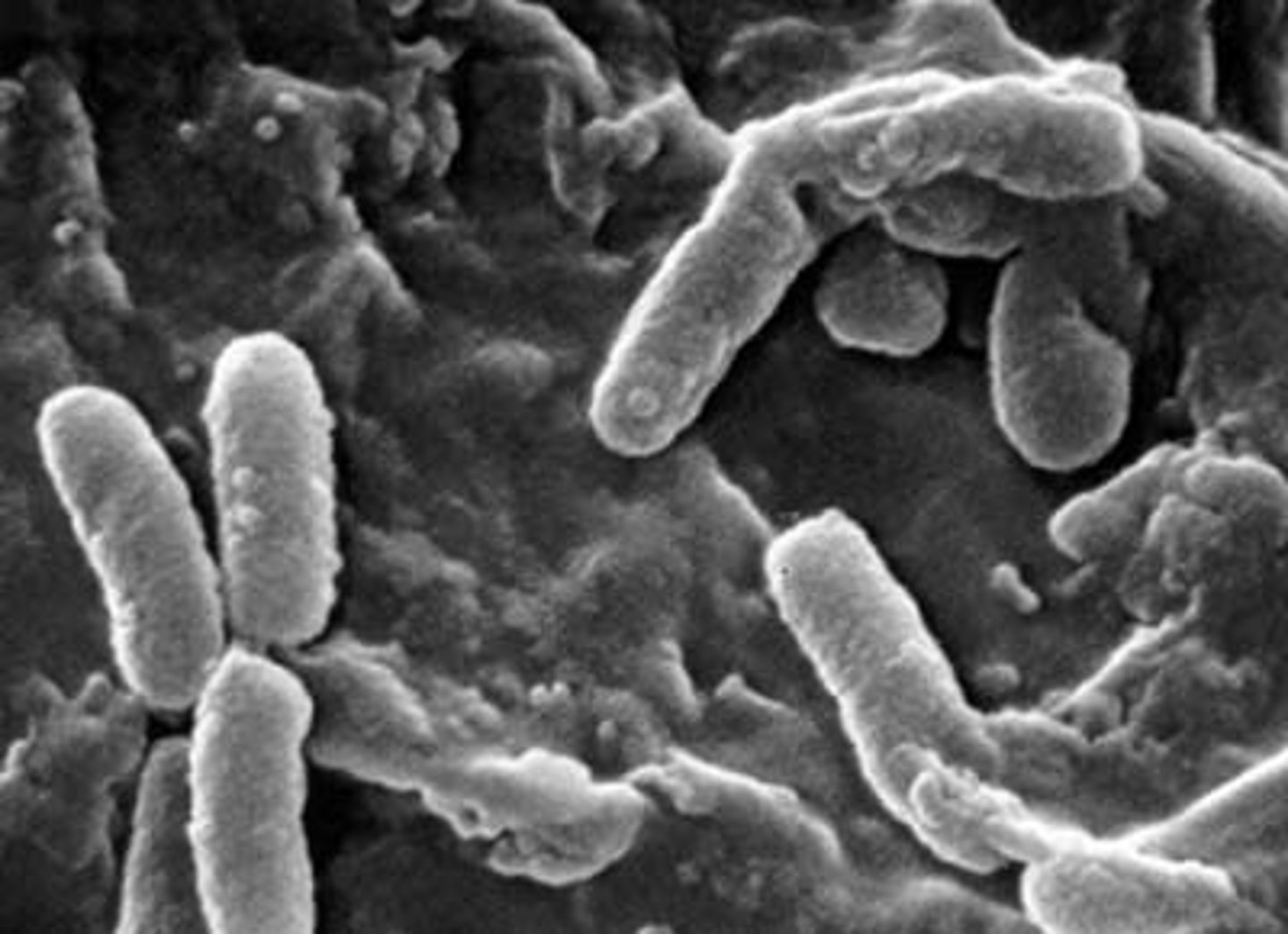
Bacillus
-rod-like form
-can form endospores
-reproduction can result in distinct chains
-CHAINS CAN HELP ID GENERA & SPECIES
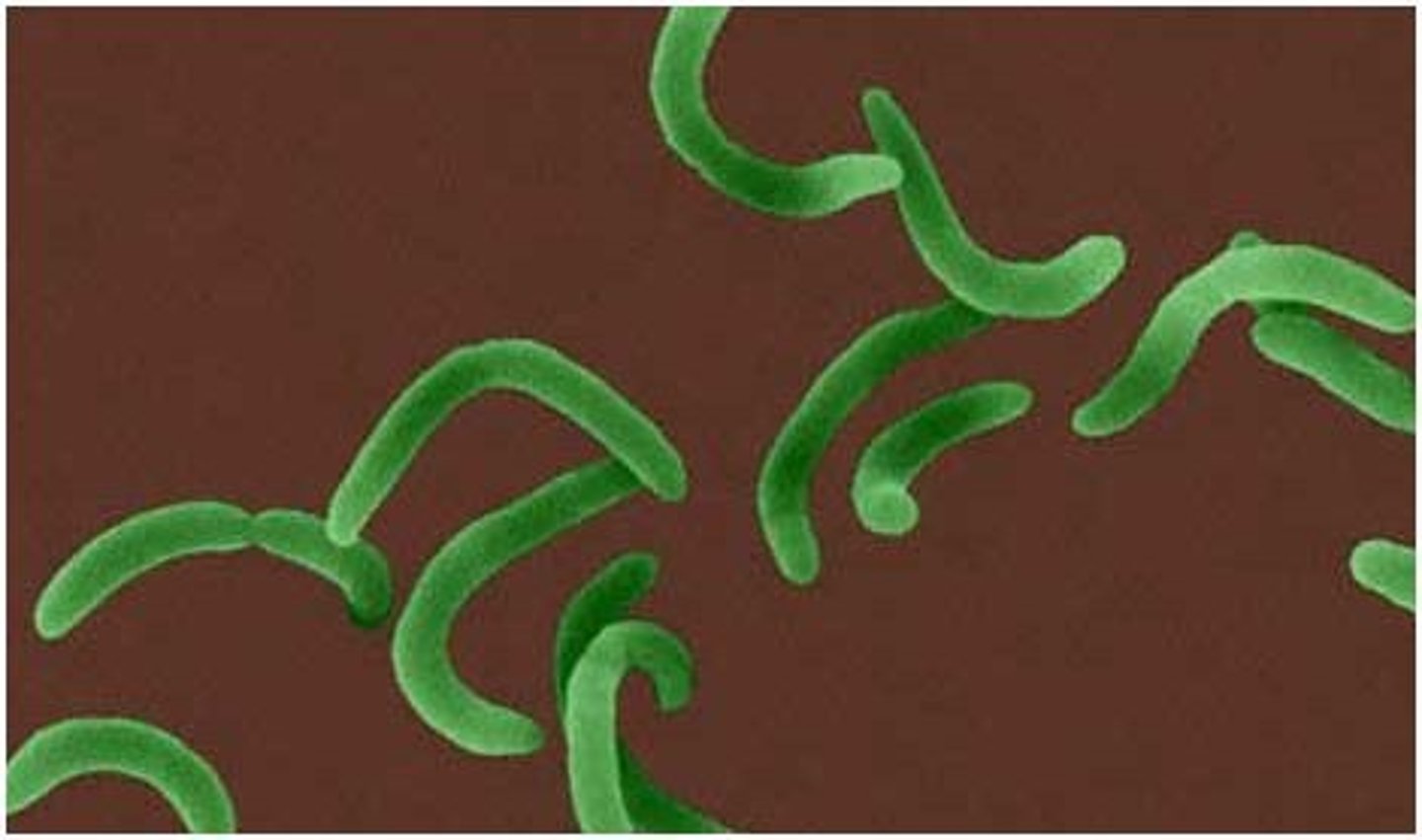
Curved
3 subgroups:
1)Spirilla/spirillum
2)Spirochetes
3)Vibrio
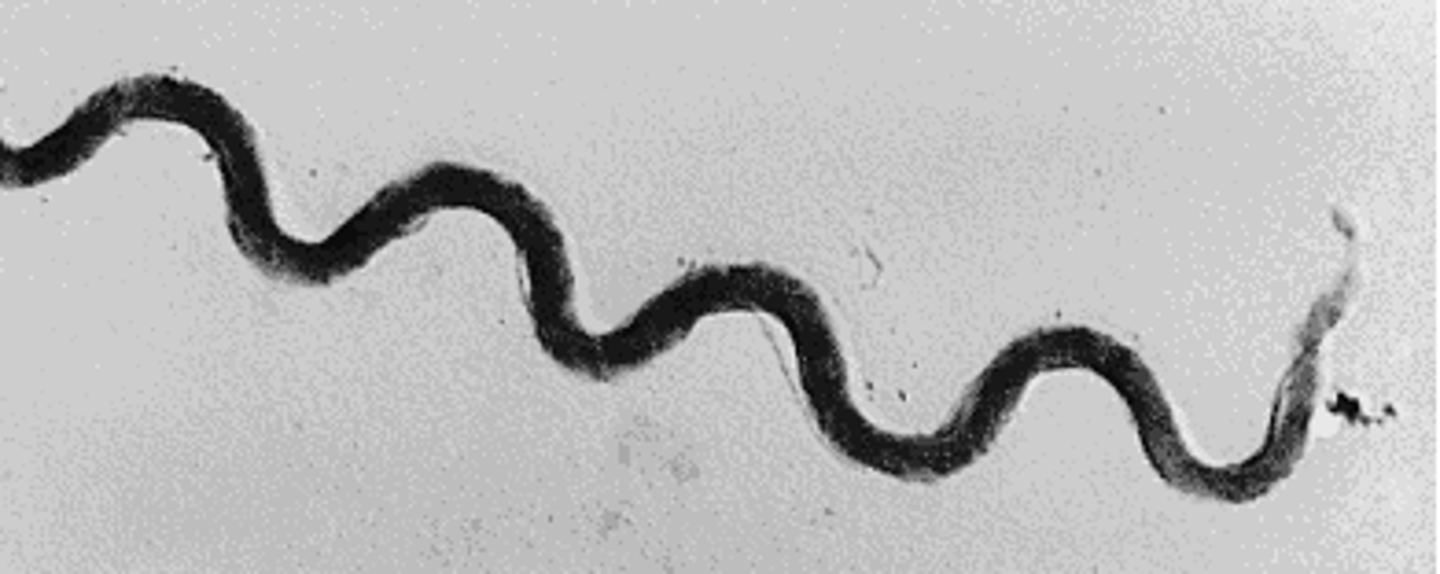
Spirilla/sprillillum
-rigid corkscrew shape
-whip-like flagella at cell ends
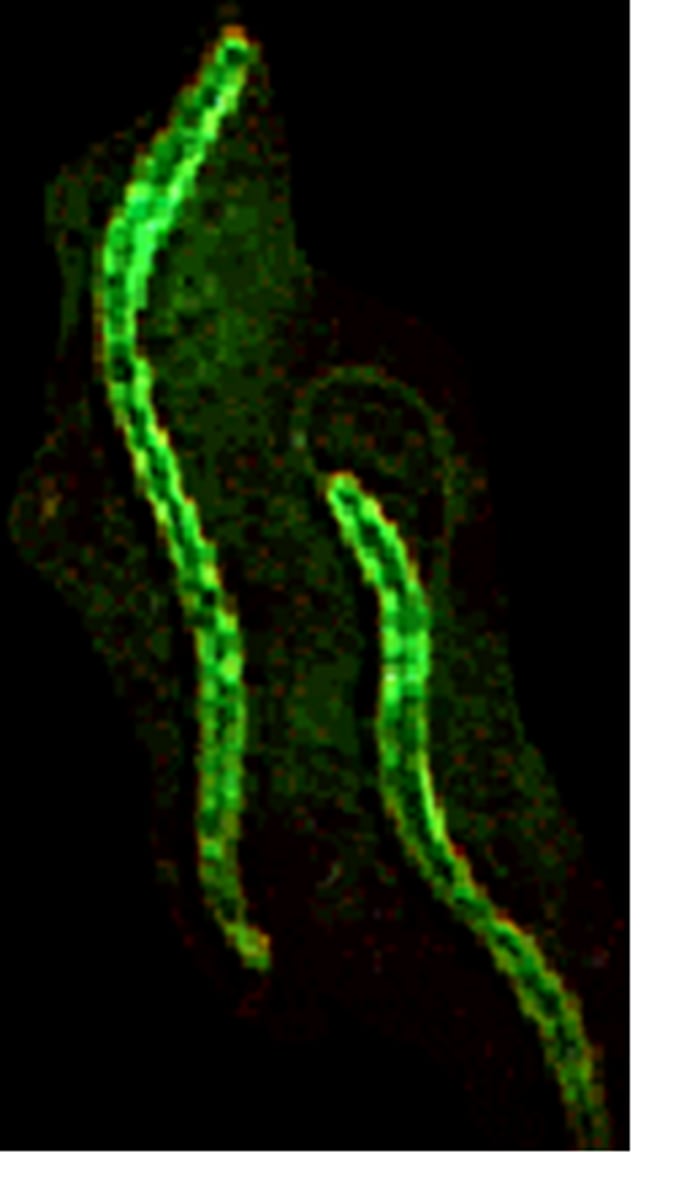
Spirochetes
-flexible spiral shape
-flagella imbedded in capsule
Vibrio
-comma shape
-1-3 flagella at one end
Shape pros
-easy to identify
-shape correlates with evolutionary history, informative
-key diagnostic tool in medical applications
shape cons
-for colony shape, must grow bacteria in the lab
-only a starting point, won't ID specific species
Metabolism
All life metabolizes food for energy in 1 of 2 ways:
1)Aerobic respiration
2)Anaerobic respiration
AEROBIC RESPIRATION
cell uses oxygen to produce energy
ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION
cell produces energy through non-oxygen methods
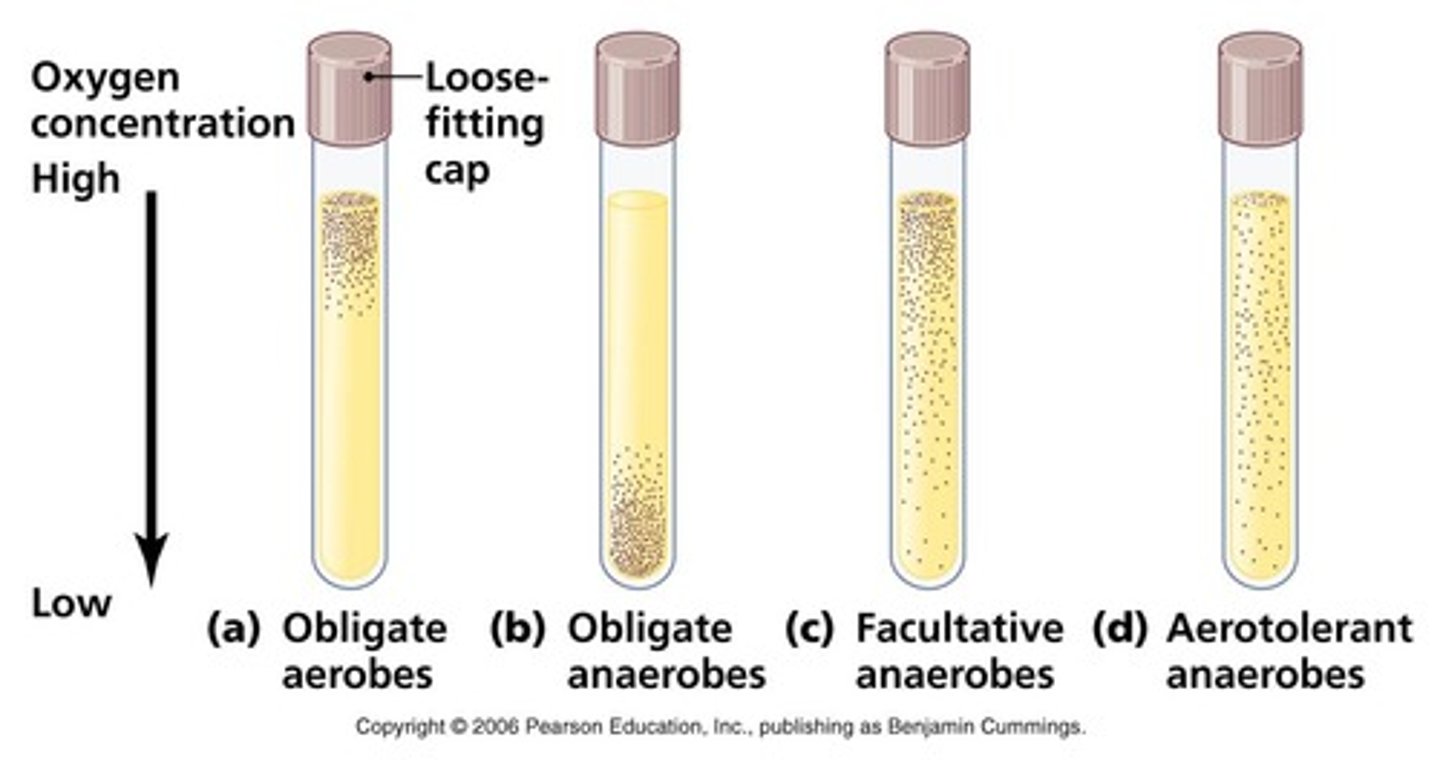
Metabolic types
Different bacteria use different approaches:
1)Obligate aerobe
2)Facultative anaerobe
3)Obligate anaerobe
OBLIGATE AEROBE
the cell an only produce energy when it has oxygen
FACULTATIVE ANAEROBE
The cell prefers oxygen, but it can produce energy using anaerobic respiration
OBLIGATE ANAEROBE
The cell can only produce energy when there is no oxygen
How do we determine bacterial metabolism?
-test tube filled with fluid thioglycollate
-thioglycollate has a gradient of oxygen
-where bacteria grow in the tube indicates their metabolic process
(bacterial growth has a cloudy appearance)
Metabolism pros
-can provide major clues to bacteria's lifecycle & environment
-useful diagnostic tool in the medical applications
Metabolism cons
-must be a bacteria that can be gown in the lab to test
-many bacteria fall in each category and subcategory
Cell walls
Cell walls can be:
-gram positive
-gram negative
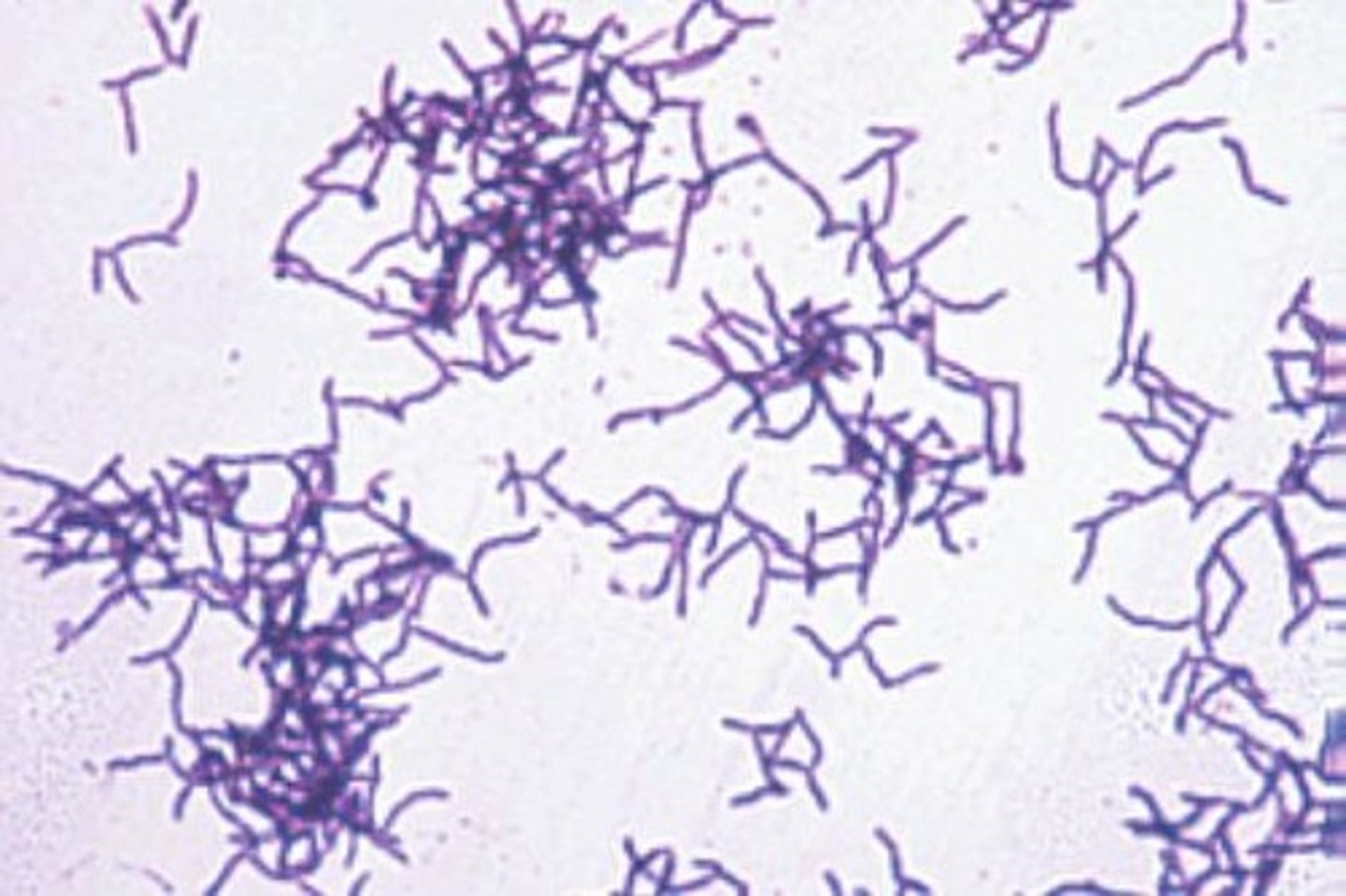
Gram positive
PURPLE
-simple cell wall gets stained darker
-simpler structure
-thick peptidoglycan layer over cell membrane
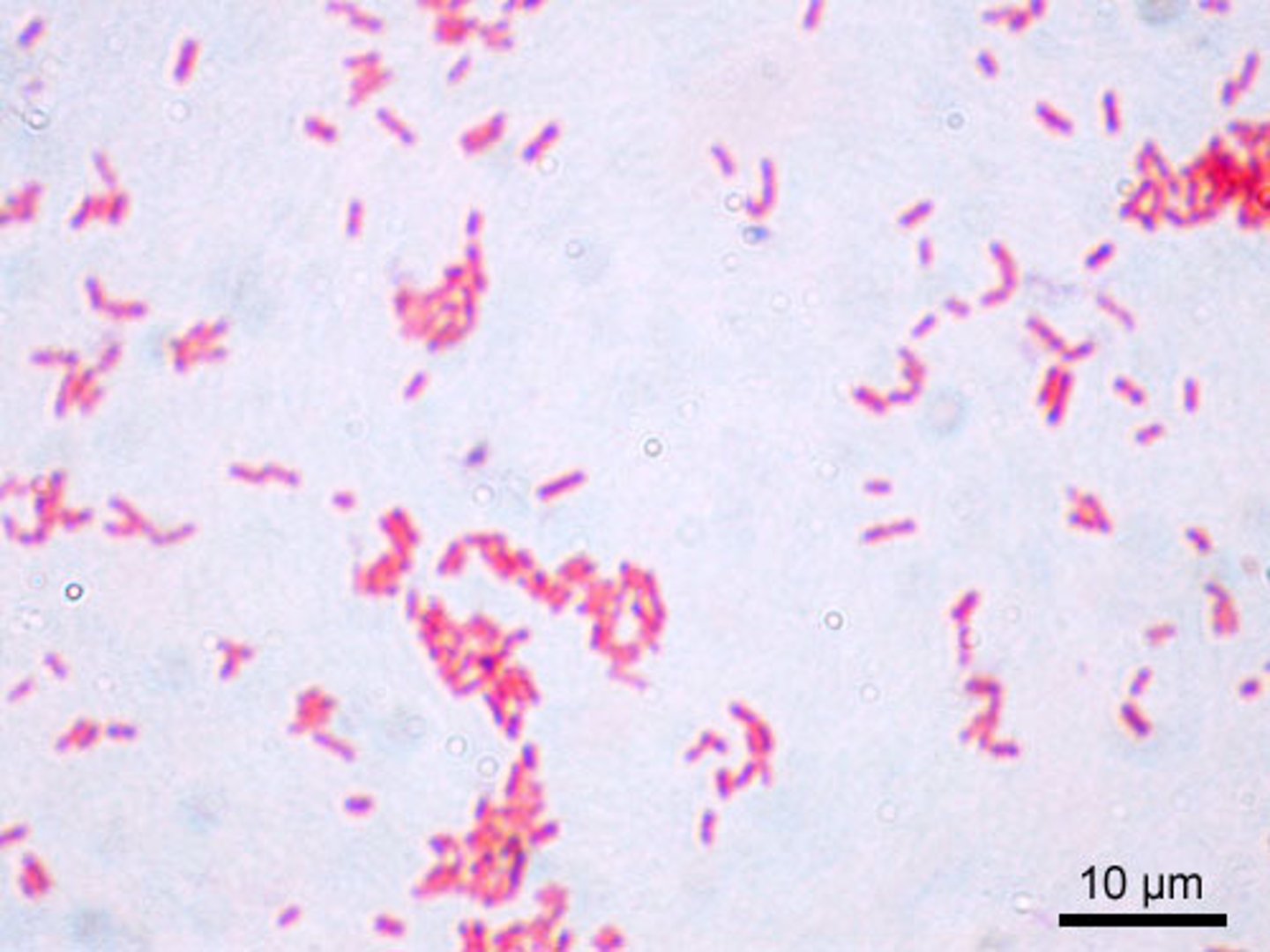
Gram negative
PINK
-complex cell wall gets stained lighter
-complex structure
-2nd outer membrane after peptidoglycan layer
Gram Staining
-Hans Christian Gram invented staining
-Bacteria put through specific chemical stains will change color based on their cell wall
Cell wall pros
-gram staining can quickly differentiate between 2 major groups of bacteria
-easy and useful starting point for ID & classification
Cell wall cons
-need bacteria in the lab to test
-is only a starting point; cannot ID specific species
Bacterial adaptations
Bacterial has evolved several adaptations that help them survive:
-biofilm
-plasmids
-endospores
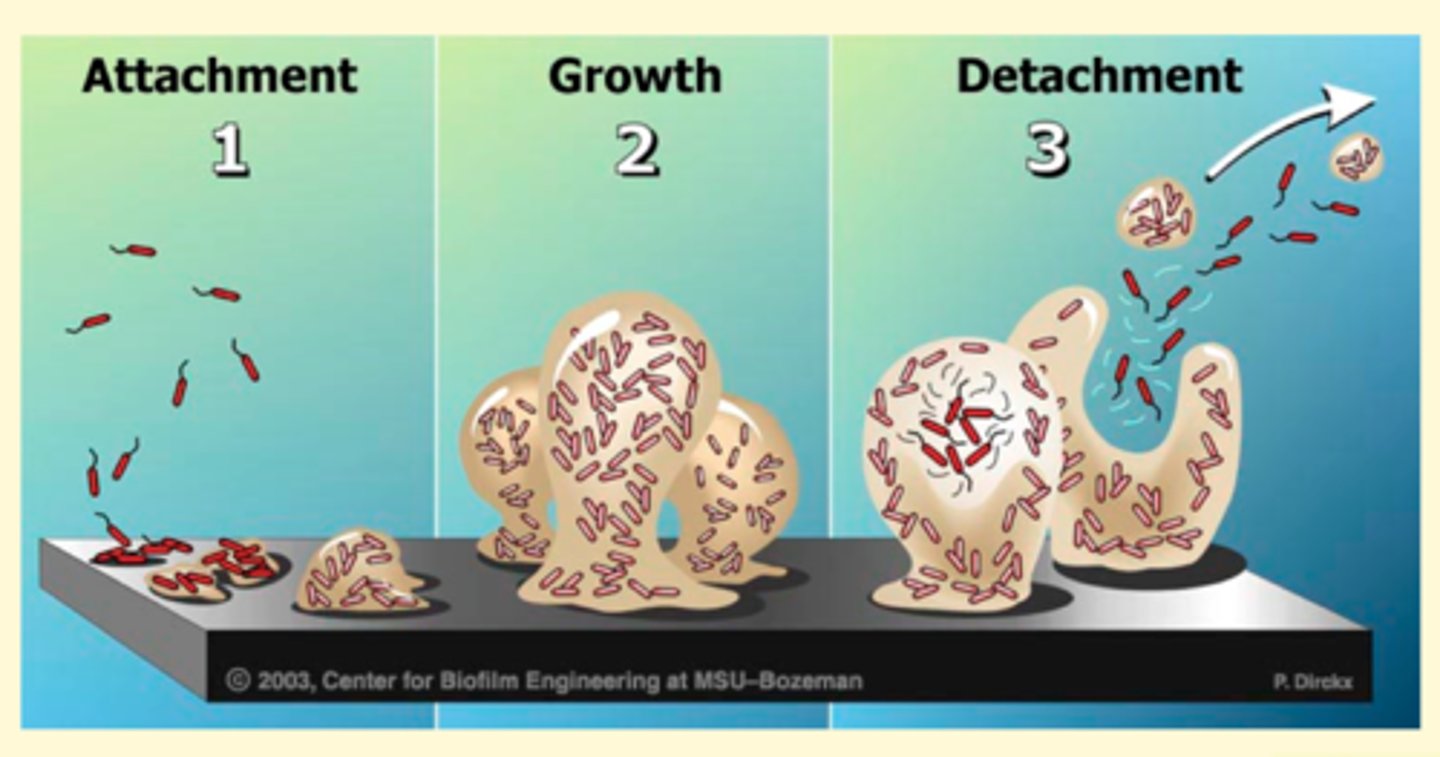
Biofilm
-group of microbes that adhere to each other and a surface
-produced by cell secretions, made mostly of sugars
-bacteria in biofilm can communicate with each other, act as a population
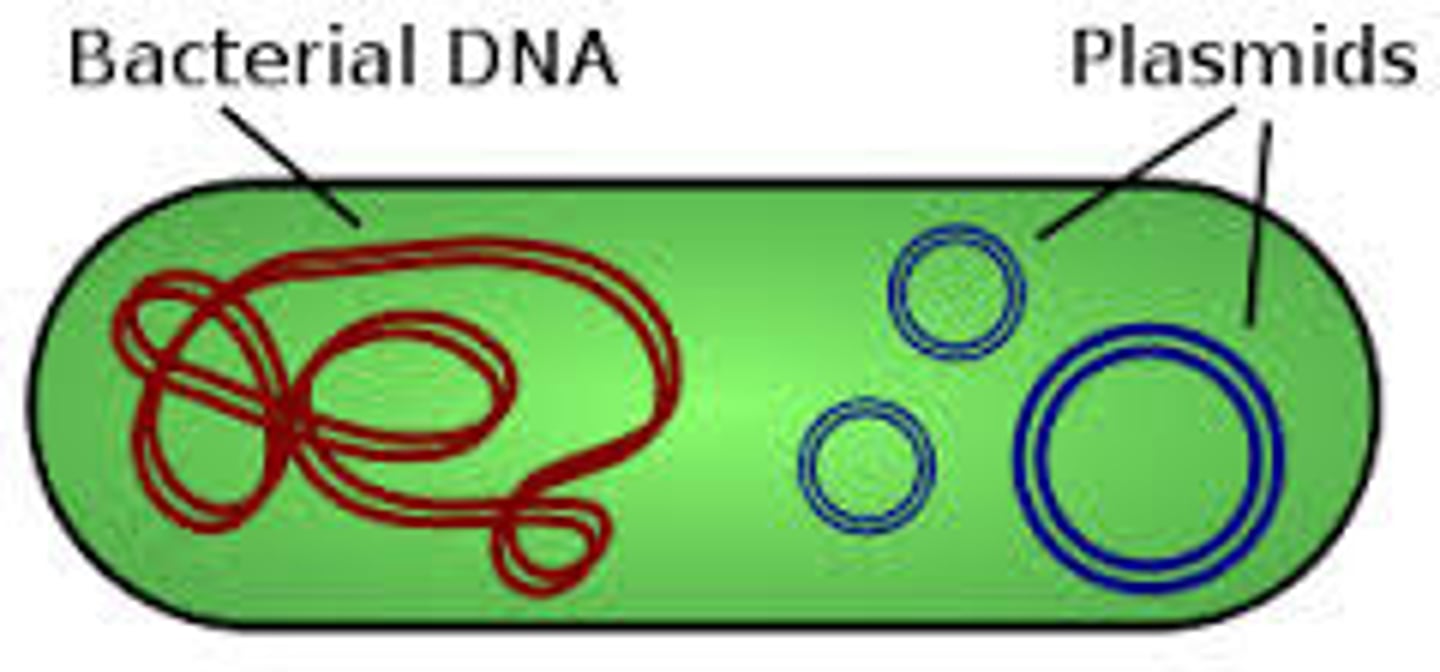
Plasmids
-additional circles of DNA in a bacterium (not part of the nucleoid DNA)
-plasmids can give bacteria valuable traits (drugs or toxin production)
-Bacteria share plasmids via CONJUGATION
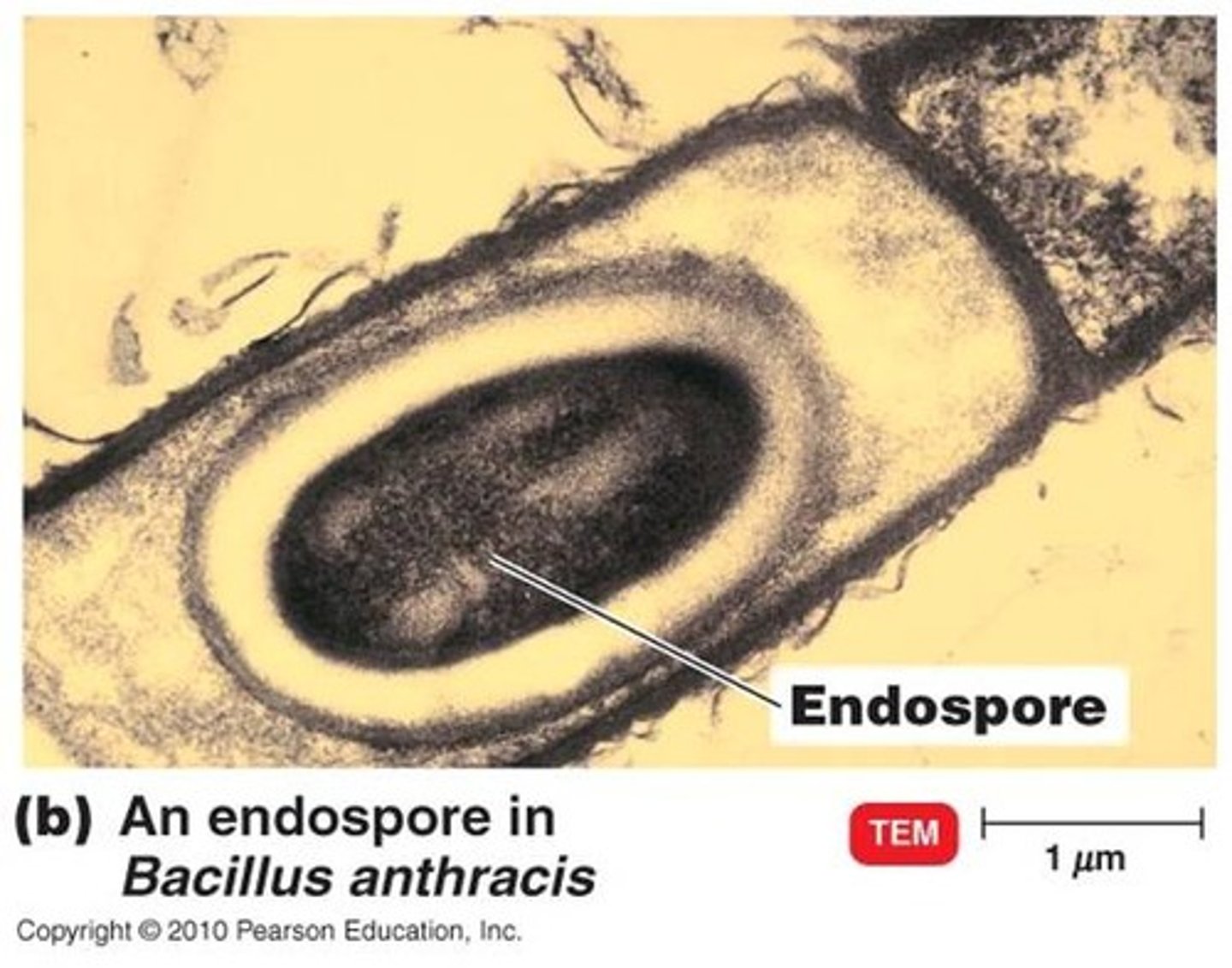
Endospores
-Only made by some genera of bacteria
-Inactive structure that stores bacterium's DNA
-VERY TOUGH; resists high temperatures, chemical damage
-When environment improves, can use its DNA to remake an active bacterial cell
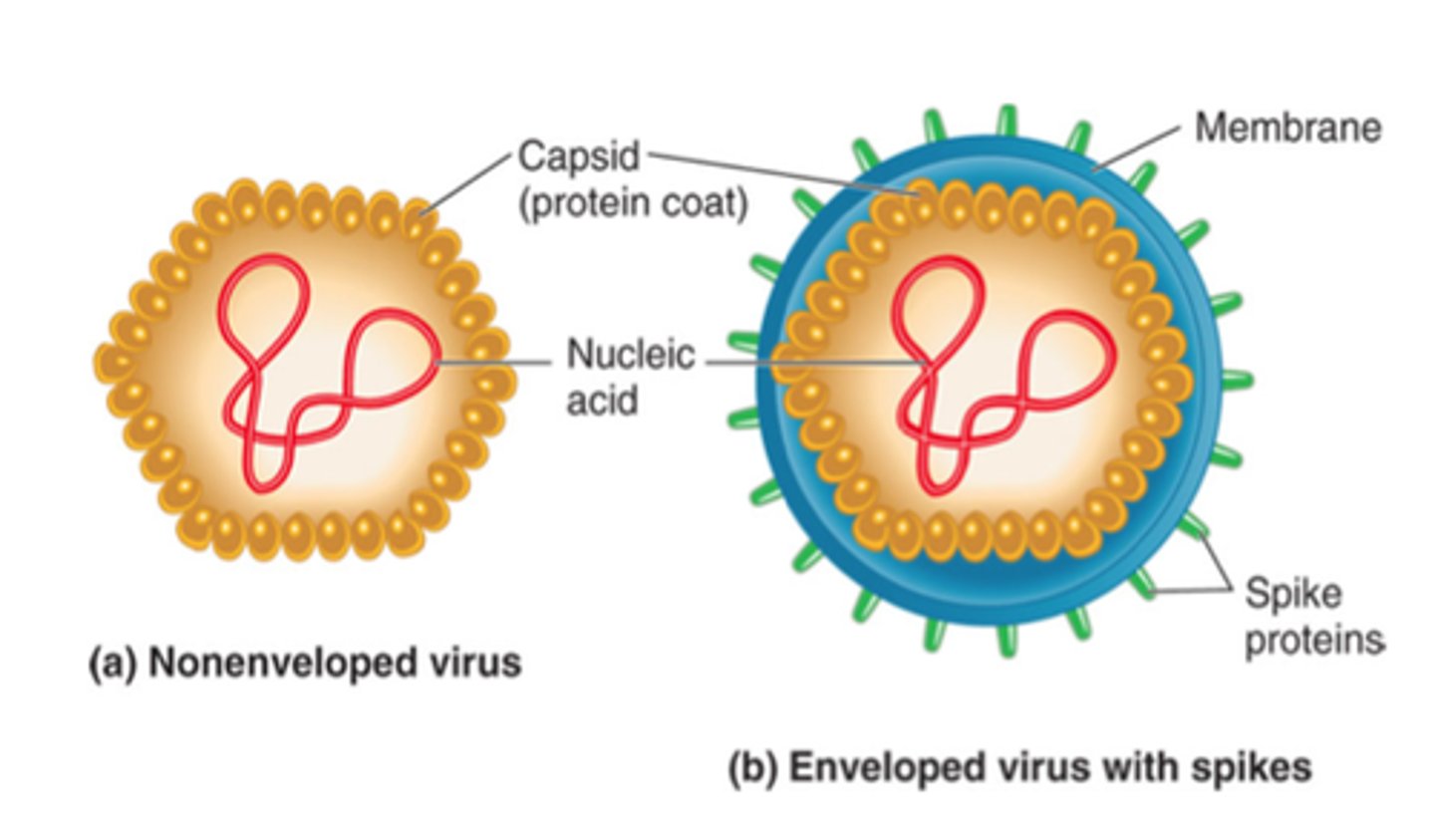
Viral structure
-Nucleic acid
-CAPSID proteins
-Envelope
-Spike proteins
NUCLEIC ACID
The nucleic acid contained in a viral capsid is either DNA or RNA
CAPSID SHAPE
-Helical
-Icosahedral
HELICAL
-Proteins tightly spiral around nucleic acid
-forms tube-like capsid
ICOSAHEDRAL
-proteins form 20-sided capsid
ENVELOPE PROTEINS
-Surround capsid
-Envelope can have SPIKED PROTEINS