Grade 10 science exam
1/251
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
252 Terms
chemical properties
describes how a substance will react with something else to form a new substance
physical property
describes a substance on its own
qualitative property
describes without numbers ex.colour
quantitative property
describes using numbers ex. boiling point
hardness
the ability of a substance to resist being scratched
ductility
the ability of a substance to be stretched into a wire
clarity
to be able to see through a substance
solubility
the ability of a substance to dissolve in water
boiling point
the temperature liquid becomes gas
lusture
the shine or dullness of a substance
physical changes
a change in which a new substance IS NOT formed and is reversible. ex. state, size, colour, shape and/or density
chemical change
a new substance IS formed and is not easily reversible.
ex. new colour/odour, heat or light produced, bubbles of gases, a solid precipitate is formed
particle theory of matter
1. all matter is made of tiny particles
2. all particles in one substance are identical
3. the spaces between the particles are very large compared to the particles themselves
4. particles are in constant motions
5. particles have forces of attraction between eachother
Bohr rutherford diagram
a model used for representing the arrangements of the first 20 e-'s (only for first 20 elements)
ions
atoms with a positive or a negative charge and a full valance shell, they gain or loose electrons to achieve full outer shell
valance e-'s
electrons on the outer most shell can be lost or gained when not full valance shell
cations
positively charged ions (metals)
anions
negatively charged ions (non-metals)
ionic charge
the difference between the number of protons (positive) and the number of electrons (negative) if more e-'s negative symbol if more p+'s positive symbol
ionic compounds
compounds composed of cations and anions
lewis dot diagram
a method for representing an atom's valence electrons using dots around the element symbol.
multivalent
elements with 2 or more possible charges
*represent used charge with roman numerals
monovalent
elements with one possible charge
writing ionic compounds
write each element with their charge and CROSS & DROP.
*if polyatomic used and more than one after cross and drop put brackets
naming ionic compounds
write first element, add ide to the end of second element
* if multivalent add roman numerals (IV)
* dont add ide if polyatomic
polyatomic ions
an ion composed of two or more atoms
Ammonium= NH4+1
Phosphate= PO4-3
Sulfate= SO4-2
Carbonate=CO3-2
Hydrogen Carbonate= HC03-1
Hydroxide= OH-1
Nitrate= NO3-1
Chlorate= CLO3-1
molecular compound
two non-metals that share e-'s to form full outer shell
drawing molecular compounds
use lines to show shared electrons
writing molecular compounds
use prefixs to show how many there are of each atom
mono=1 di=2 tri=3 tetra=4 penta=5 hexa=6 hepta=7 octa=8 nona=9 deca=10
* dont criss cross
* if first element is mono dont write mono
* do not reduce
chemical formula of molecular compounds
based on drawing:
write how many of each element there is the one with less always first
or based on name:
use prefixes to determine how many of each element there is
hydrogen as the first element in molecular compounds
no prefixes are used when hydrogren comes first
use criss cross method
diatomic molecules
molecules made up of two atoms of the same element
H2= hydrogen N2=nitrogen F2=fluorine O2=oxygen I2=Iodine Cl2=chlorine Br2=bromine
properties of molecular compounds
-formed by covalent bonds
-2 non metals
- shared electrons
- doesnt conduct electricity
-low melting and boiling point
-not soluable in water
-diatomic compounds
properties of ionic compounds
-formed by ionic bond
-metal and non-metal
-electrons are transferd
-conducts electricity
-high melting and boiling points
- soluable in water
- forms cations and anions
chemical reactions
the making and breaking of chemical bonds represented as chemical equations
coefficients in chemical reactions
numbers placent in front of molecules that tells us how many are involved in the reaction to because balanced
reactants (chemical reactions)
what you start with
products (chemical reaction)
what is produced as a result of a chemical reaction
law of conservation of mass
"atoms are neither created nor destroyed, during any chemical reaction."
*both sides of the equation MUST be equal
endothermic
when energy is absorbed (reactant)
exothermic
when energy is relesed (products)
synthesis reactions
when 2 or more chemical compound are combined to form one complicated chemical compound
a+b=ab
decomposition reaction
when one complicated chemical compound is broken down into 2 or more simpler chemical compound
ab= a+b
single displacement reactions
when a metal replaces a less reactive cation or a non-metal replaces a less reactive anion *a higher or more reactive element can go into the compound if less reactive (NO REACTION)
m+ab= mb+a
n+ab= na+ b
double displacement reactions
when the anions and cations form two different compounds and switch places
ab+cd=ad+bc
properties of acids
taste: sour
texture: rough
PH is less than 7
ALWAYS HAVE HYDROGEN
ex. fruits, vinegar, coke
binary acids
contain only 2 elements hydrogren and one other element
naming bianary acids
use hydro as the prefix and and ic acid at the end
oxy acids
these acids contain hydrogen, oxygen and one other element.
naming oxyacids
identitify the polyatomic ion, if ending is -ate then drop the ending and add -ic acid to its name. do not add hydro
properties of bases
taste: bitter
texture: slippery
PH greater than 7
ALWAYS CONTAIN HYDROXIDE (OH-1)
ex. oven cleaner, baking soda, glass cleaner
naming bases
metal + hydroxide
neutral acidity
pH of 7
red litmus paper
acid: stays red base: turns blue
blue litmus paper
acid turns red base base stays blue
phenolphthalein
colourless paper
in acid: stays colourless in base:turns pink
neutralization reactions
a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base combine to produce water and a salt (double displacement)
acid +base= salt +water
the cell theory
- all living things are made up of one or more cells
- cells are the basic unit of life
- all cells come from pre existing cells
metabolism
The process of turning food (like glucose) into energy using oxygen.
unicellular
single celled organism
multicellular
organisms with more than one cell
prokaryotes
do not have a nucleus
ex. bacteria
eukaryotes
contain a nucleus and other complex structures , single or multicellular
ex. animal plants, amoeba
asexual reproduction
one, parent genetically identical
sexual reproduction
two parents, fusions of sex cells genetically different
why do cells divide?
to repair any damage
how do cells divide sucessfully
- the cells genetic information is copied
- the copies of genetic info must seperate from eachother
- the entire cell must divide
chromatid
one side of a chromosome filled with dna in the nucleus
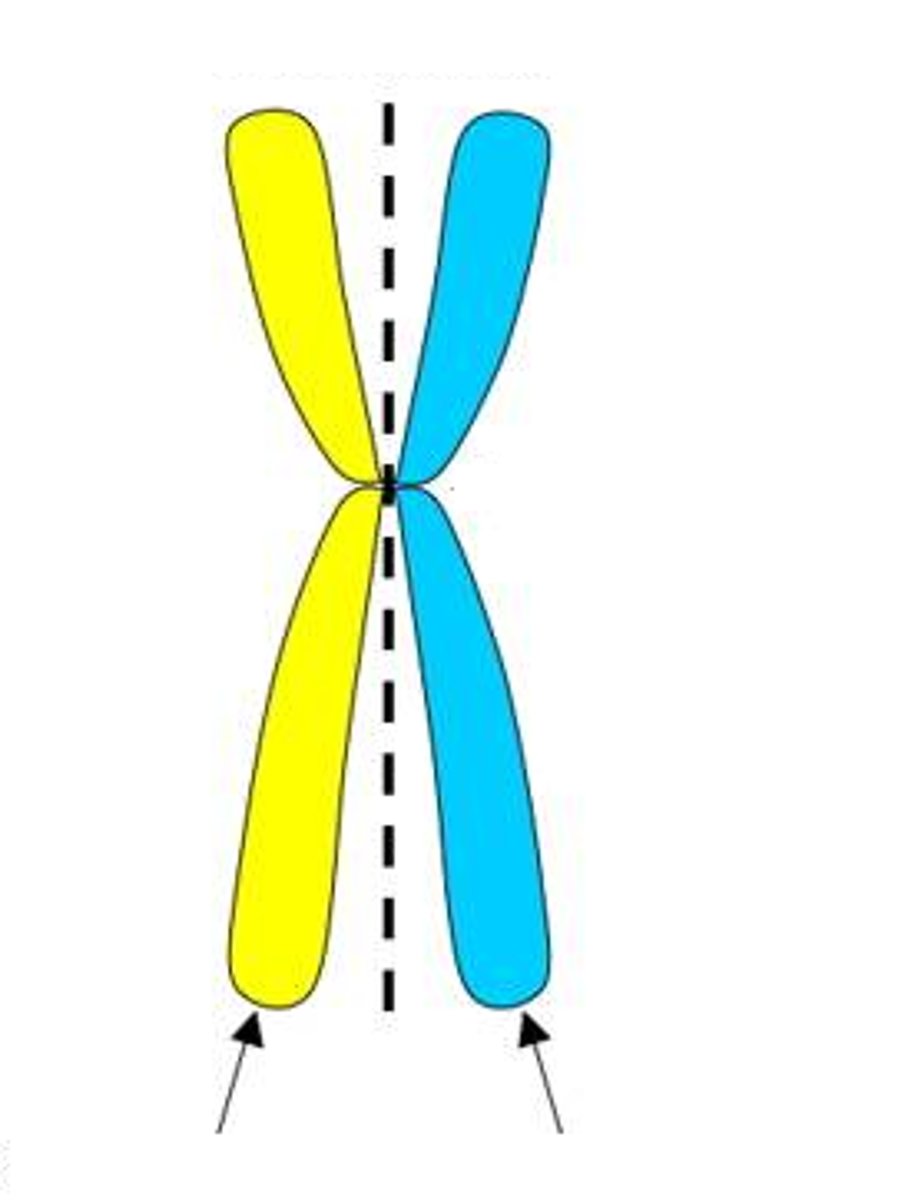
chromosomes
condensed double strands of DNA
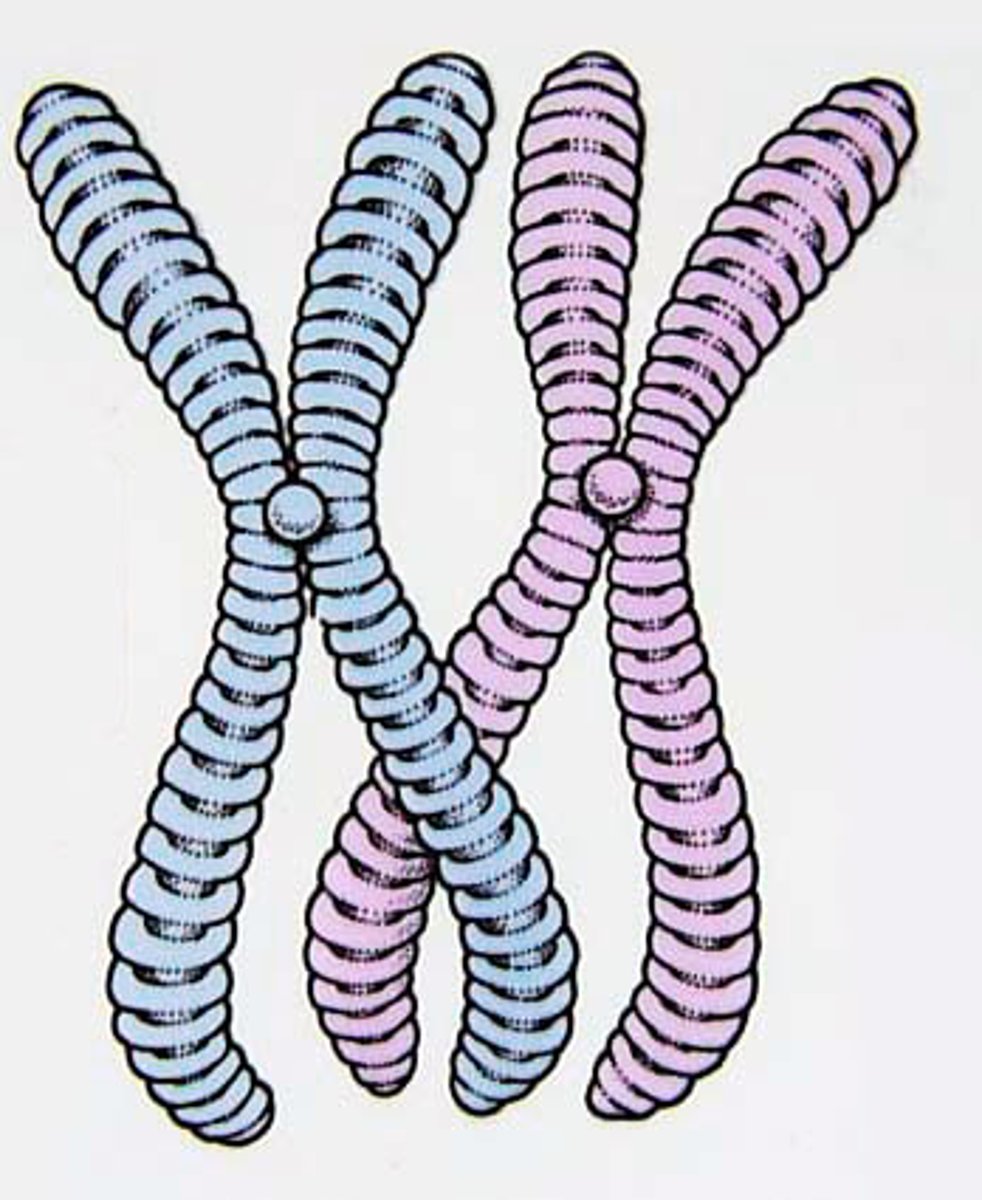
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during mitosis
daughter cells
new cells produced by cell division
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
G1 phase
Growing large enough to divide
synthesis
DNA replication is duplicated
G2 phase
make sure cell is ready to divide
mitosis
division of the nucleus consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle fibers forms

metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell spindle fibers attach to each chromatid
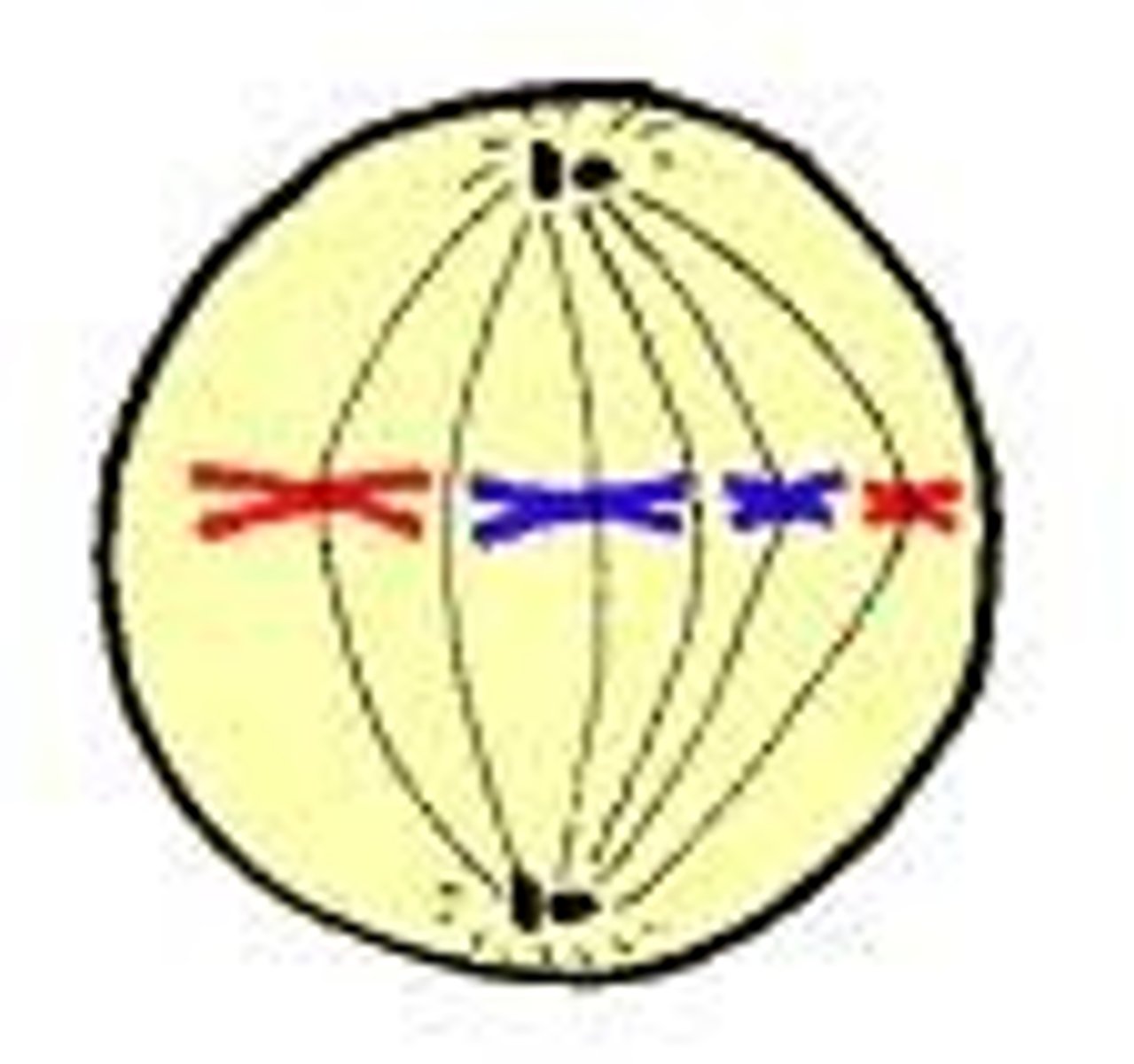
anaphase
sister chromosomes are pulled to opposite sides by spindle fibers
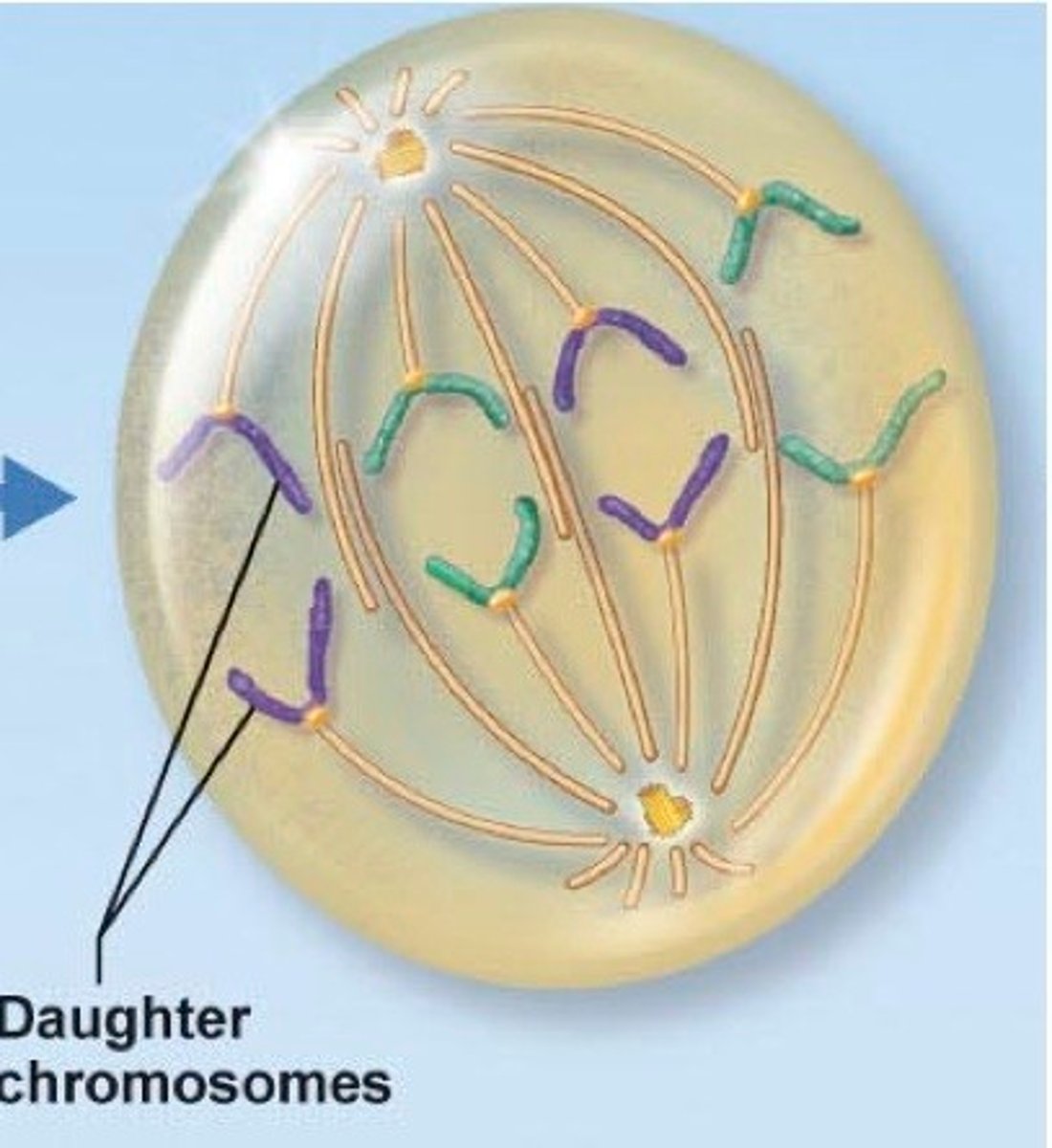
telophase
The "Reset" stage: Two new nuclei form and chromosomes turn back into chromatin.
cytokinesis
divison of cytoplasm
tumor
mass of rapidly dividing cells that can damage surrounding tissue
benign and malignant
benign tumour
cells that do not intere with function of normal cells or spread. ex. warts, cysts
malignant
cancerous tumours that can spread causing secondary tumours and have affects on surrounding tissue
metastasis
cells breaking away from tumour entering the blood stream and settles somewhere else in your body
causes of cancer
hereditary factors (specific gene mutations)
environmental factors such as chemicals, radiation, viruses
what can u do to reduce cancer
1. eat high fiber, reduce sugar and carbs
2. stop smoking and drinking
3. use protection from the sun
4. avoid radiation
5. exercise
6. good sleep, low stress
detecting cancers
1. screening
2. biopsy
3. ultrasound
4. treatment
screening of cancer
-pap test (cervical cancer)
-mammography (breast cancer)
-colonoscopy (colorectal cancer)
-digital rectal exam (prostate cancer)
biopsy
a sample of the body tissue is removed for examination
ultrasound (cancer)
- endoscopy
-x-ray
-ultrasound
-ct/cat scan
cancer treatment
1. surgery to remove tumour
2. chemotherapy drugs that target rapidly diving cells
3. radiation to kill cells
red blood cells
microscopic, no nucleus . carries oxygen from lungs to the body tissues and carbon dioxide as a waste
skin cells
flat. create a barrier between the body and outside
muscle cells
elasticity for movement
photosynthetic cells
light sensitive to capture solar energy and convert it into useable energy
stem cells
cells that are undifferentiated can turn into any kind of cell
types:
embryonic stem cells
adult stem cells
embryonic stem cells
Source: Taken from a human embryo.
Power: They are undifferentiated, meaning they can turn into ANY type of cell in the body (muscle, nerve, bone, etc.).
adult stem cells
can form specific types of cells
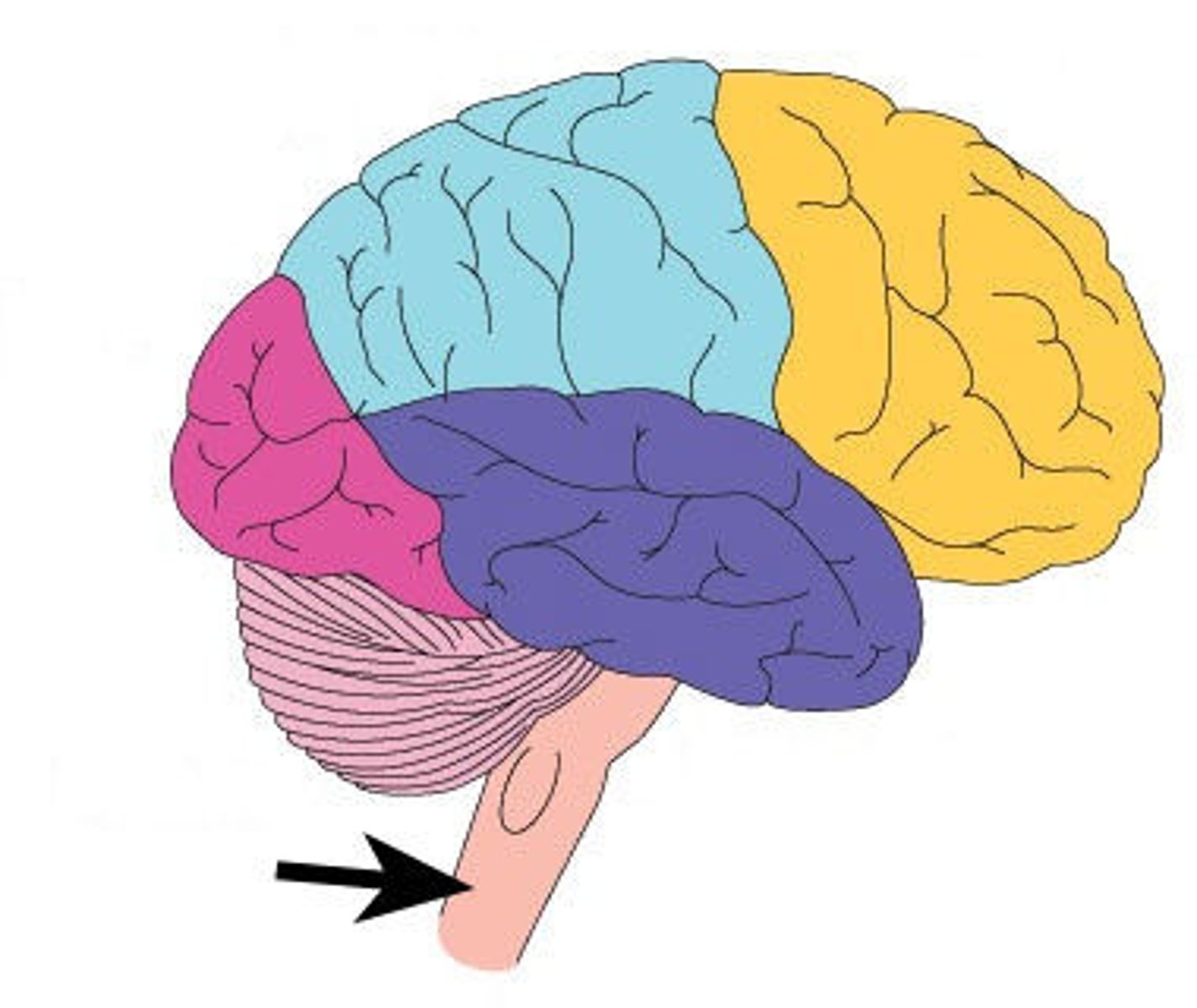
brain
controls every process that regulates the body