History of Microbiology and Germ Theory
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Romans (Varro)
Ancient civilization contributing to early microbiological thought.
Microscopy
Study of small objects using magnification tools.
Hooke (1665)
First to observe and describe cells.
Leeuwenhoek (~1700)
Discovered microorganisms, termed them 'animalcules'.

Cell Theory
All living things are composed of cells.
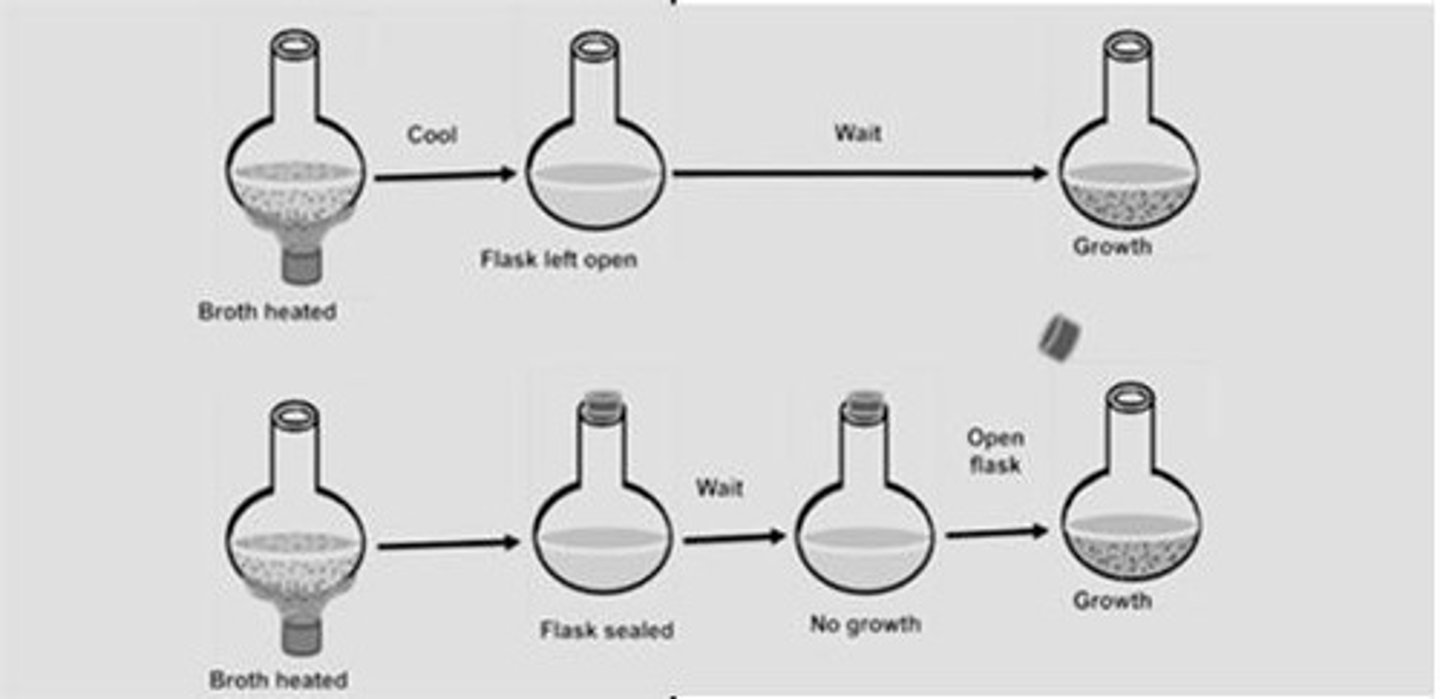
Spontaneous Generation
Theory that life arises from non-living matter.
Redi (1668)
Demonstrated maggots do not arise from meat.
Pasteur (1861)
Developed swan-necked flask experiment disproving spontaneous generation.
Miasma Theory of Disease
Belief that diseases are caused by 'bad air'.
Florence Nightingale
Pioneer in sanitation and nursing practices.
Germ Theory of Disease
Microorganisms can cause diseases in hosts.
Fracastoro (1546)
Proposed 'seminaria' as seeds of disease.
John Snow (1854)
Traced cholera outbreak to contaminated water pump.

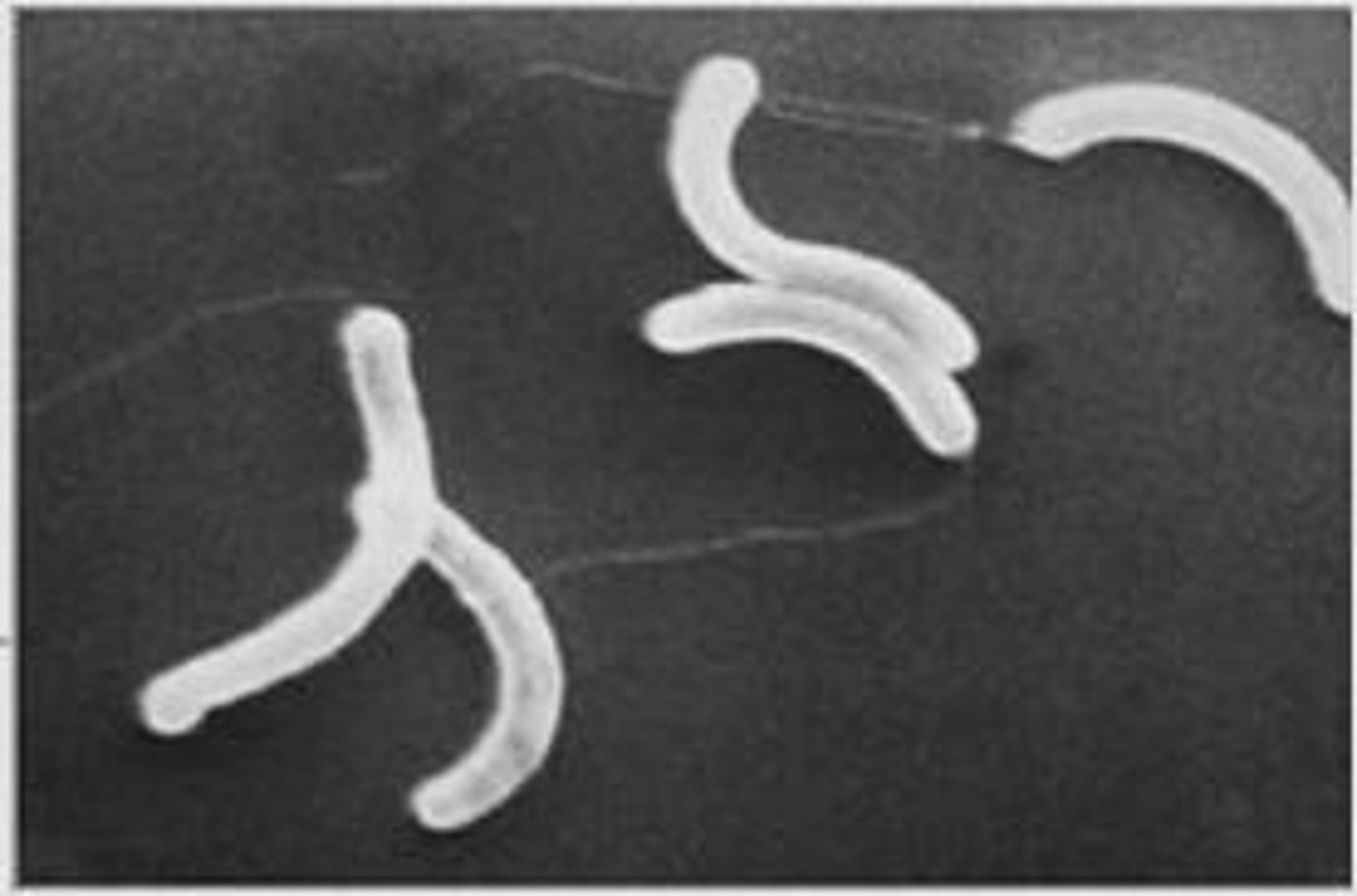
Cholera
Disease caused by Vibrio cholerae bacterium.
Vibrio cholerae
Gram-negative, comma-shaped bacterium causing cholera.
Contaminated Water
Primary transmission route for cholera infection.
Symptoms of Cholera
Include watery diarrhea and 'rice-water stools'.
Enterotoxin
Toxin produced by cholera bacterium affecting intestinal cells.
Koch's Postulates
Criteria to establish causative agent of disease.
Pure Culture Techniques
Methods to isolate and grow microorganisms.
Agar
Gelatinous substance derived from algae for culturing.
Exceptions to Koch's Postulates
Not all diseases follow Koch's criteria.
Treponema pallidum
Bacterium causing syphilis, cannot be cultured.
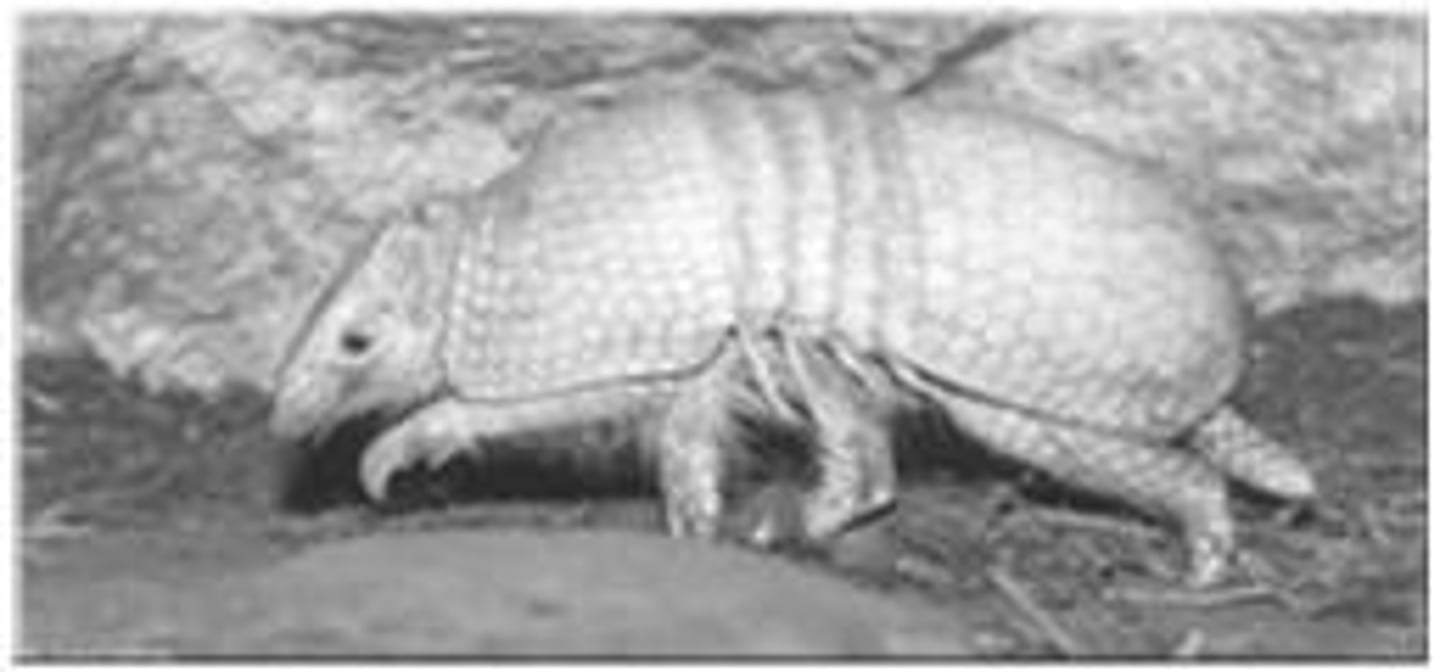
Mycobacterium leprae
Bacterium causing leprosy, grows in armadillos.

HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus affecting only humans.