Oxidative Phosphorylation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
where to electrons that are loaded into NADH and FADH2 go
the Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
what is the electron transport chain
A serial network of protiens and molecules in the inner mitochondria membrane that pass electrons to each other
ETC steps
Step 1: Electrons shuttled from earlier are delived to the ETC
Step 2: Electrons are passed from complexes 1 and 2
Step 3: Electrons are passed through each protein complex before getting captured by Oxgen (which quikcly forms water)
Step 4: As electrons are passed between the protein complexes they provide energy to pump H+ into the inter membrane space
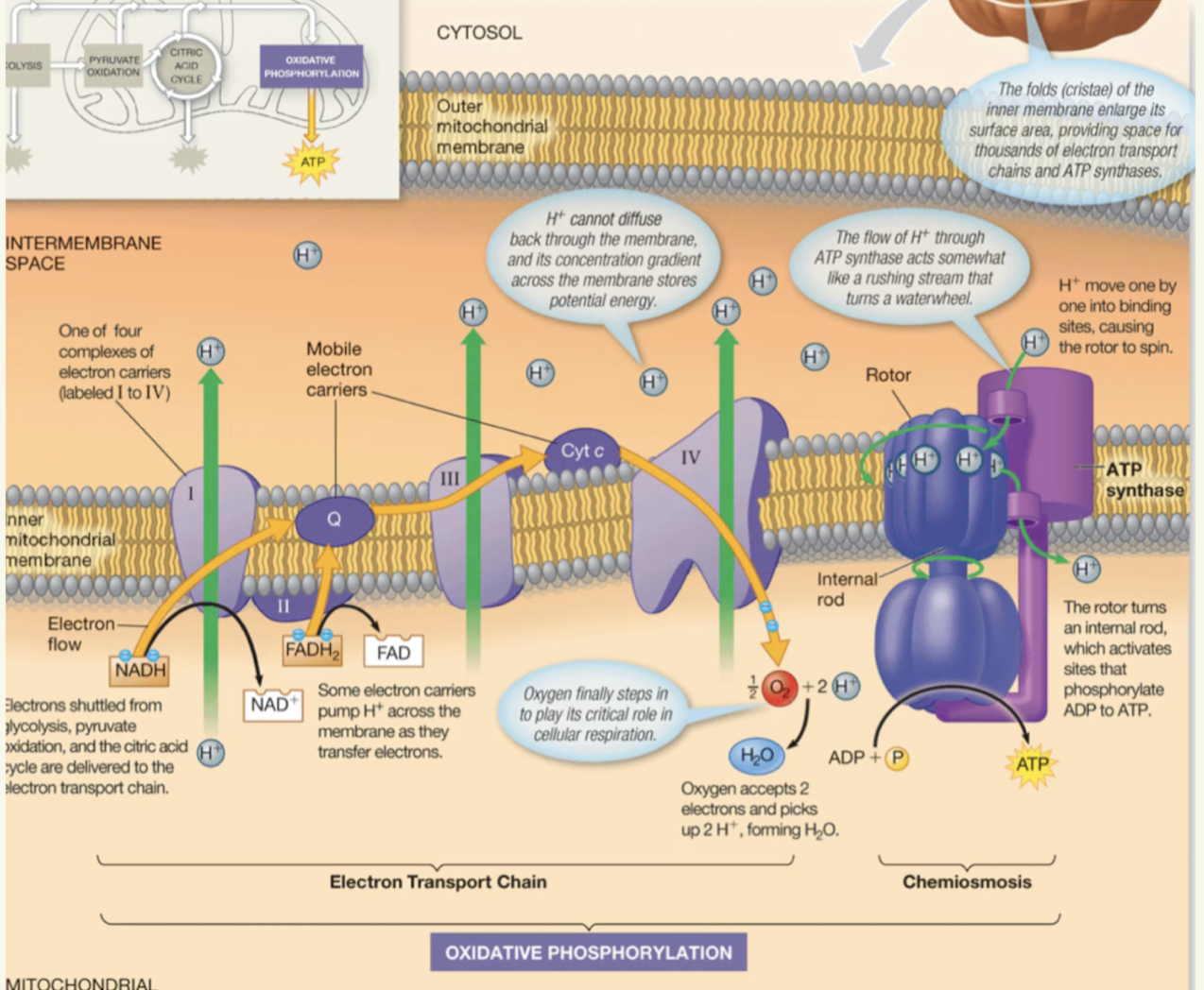
What is final electron accepter that pulls electrons through the ETC
Oxygen
what does step 4 of the ETC lead to
A high concentration of H+ in the inter membrane space
What is the final step of cellular respiration
Oxidtavtive Phosphorlation
2 steps in oxidative phosphroylation
ETC and Chemiosmosis
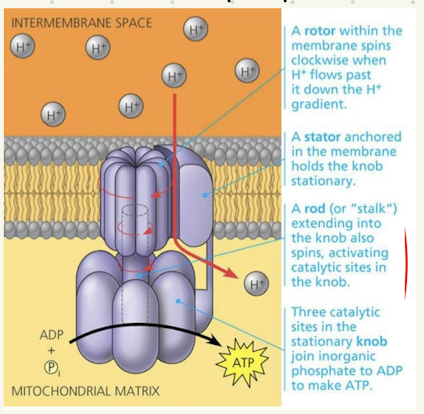
Chemiosmosis steps
H+ can passivly move through the enzyme ATP synthase due to high concentration of H+ in the intermembrane space
Flow of H+ causes rotation of the “rotor” subunit of ATP synthase
Turning of the rotor leads to conformation changes in the knob subunit, providing energy needed to add a phosphate group to ADP to make ATP
What is the general idea of oxidative phosphorylation
Whole process of ultimatley passing elecrons to oxyegn to phosphorylate ADP to ATP
How is ATP generated in Anaerobic envoirments
Substrate level phosphosrylation
All ATP for organisms in anaerobic enviroments are generated during glycolysis
VERY inefficient
What is fermentaition
Breaking down of glucose without oxyegen
two prodcuts of fermentaiton and where they are produced
Lactic acid - Some bactieria and muscle cells
Enthyl Alchhol - Other bacteria and yeasts