Chemistry Ch8: The Basics of Chemical Bonding
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
ionic bonding
transfer of electrons between a metal and non-metal
covalent bonding
sharing of electrons between two non-metals
metallic bonding
bonding between 2 metals (alloys)
Octet rule
when elements react they want to have 8 electrons in their outer shell achieving noble gas configuration
electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself; cornerstone of understanding behavior of atoms/electrons
EN scale
0.0-4.0 Pauling Units (Linus Pauling)
Fluorine & Francium
fluorine is the most, francium is the least. increases as you go from lower left to upper right on Periodic table
The numerical difference between any two atoms determines its
polarity
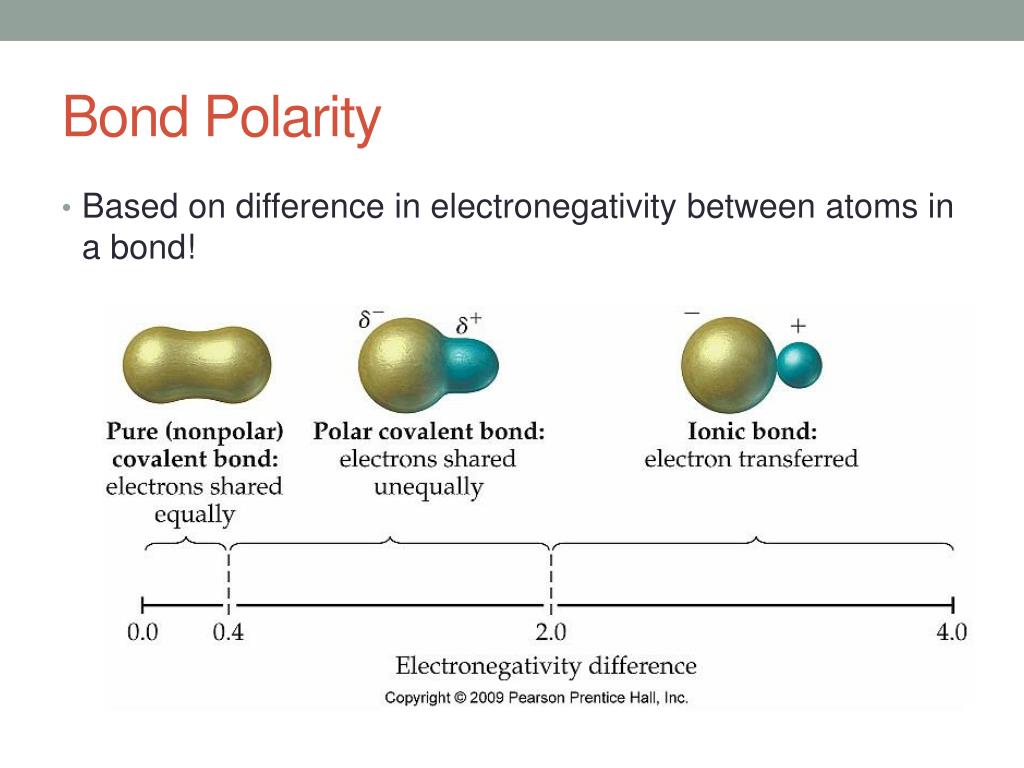
if change in electronegativity is 1.7 or greater
the bond between the two elements will be ionic. This is the case for a metal and a non-metal where the electrons are transferred. The electron is being pulled away from the least EN element to the most EN.
If less then .5
the bond is nonpolar covalent, the electrons are being equally shared
if 0.5<c. in EN<1.7
bond is polar covalent, the electrons are not being shared equally, the electrons are being pulled towards the most EN elements but not totally away from the least EN
ionic bonds are stronger than
covalent bonds
polar compounds contain
polar covalent bonds and have diploids present
either a pair of electrons is bonded or not…if not…
it is lone, unshared, or unbonded pair
bond order
the number of bonds shared between two atomsthe
the same amount of of energy it takes to make a bond is the same amount of energy
it takes to break a bond
bond length
the length of a covalent bond between two sharing nucleus. the more electron pairs being shared, the shorter and stronger the bonds
energy released or absorbed during a chemical change is due to the differences between the
reactant bond energies and the product bond energies
if there is a single bond which is ionic in the compoound
the compound is ionic
majority rules of polarity type of a compound between
polar and non-polar
both physical and chemical characteristics are to the
type of bonding present in a molecule
Formal charge (FC)
number of valence electrons (group #)-(#of bonds + # of unshared electrons
the sum of the formal charge (FC) must equal
the charge of the molecule/polyatmoic ion
FC is used to decided
which “resonant” structure is the most stablemost
most stable structure has the lowest FC on
central atom, the lowest set of numbers
rules for resonance:
a double bond must exist, ligands must be the same to move the bond
ligand
an atom which is not the central atom