BCM. 26 - GLYCOLYSIS
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Kinase
An enzyme that adds a phosphate group from ATP onto another molecule. i.e. they catalyse X + ATP → phospho-X + ADP.
The phosphorylated product will usually have a name like “phospho-X/ “X-phosphate”/ “X-bisphosphate”/ X-diphosphate”,
-Hexokinase
Difference between diphosphate and bisphosphate
Diphosphate = two phosphate groups chained off the same atom
Bisphosphate = two separate phosphate groups attached at different positions
A protein kinase is
A kinase that specifically adds a phosphate group from ATP onto another protein.
This target protein is often an enzyme or a transcription factor, and the phosphorylation results in the enzyme’s or TF’s activity increasing (or decreasing).
The phosphate is almost always added to one of the three alcoholic amino acids (serine, threonine or tyrosine), and the resulting phosphorylated protein is called a phosphoprotein.
-Protein-kinase A, which phosphorylates many proteins in the cell
-Glycogen-phosphorylase kinase, which phosphorylates the enzyme glycogen-phosphorylase.
Phosphorylases
Add phosphate groups to a chemical from inorganic phosphate (not from ATP), i.e. they catalyse X + Pi → phospho-X.
- Glycogen phosphorylase, which reacts glycogen with inorganic phosphate to make glucose-phosphate, and in-so-doing reduces the length of the glycogen polymer (glycogenn + Pi → glycogenn–1 + glucose-phosphate). Glycogen phosphorylase is itself regulated by phosphorylation.
Phosphatase
The action of a kinase or a phosphorylase can be undone by a phosphatase, which is an enzyme that removes a phosphate from another molecule by hydrolysis,
i.e. they catalyse phospho-X + H2O → X + Pi.
- Fructose-bisphosphatase, which removes one of the phosphates groups from fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
- Phosphoprotein phosphatases are phosphatases that remove phosphate groups from phosphorylated proteins; thereby undoing the action of a protein kinase.
Phosphorylation
The metabolic process of introducing a phosphate group into an organic molecule.
allosteric regulation
The binding of a regulatory molecule to a protein at one site that affects the function of the protein at a different site.
Allosterically regulated enzymes are usually ...
Each catalytic subunit can exist in either a...
The R and T forms exist in ...
When substrate binds to any one relaxed subunit,...
This results in...
This is called....
...multimeric, with more than one catalytically active subunit.
Tense (T) form, which has low affinity for substrate; or a relaxed (R) form, which has high affinity.
Equilibrium when the enzyme is not bound to substrate.
This information is communicated through structural changes to some or all of the other subunits.
that other subunit converting to the relaxed form, thus making it easier for a second substrate molecule to bind.
co-operativity.
Not only do some substrates react when they bind to the enzymes, it also make the enzyme's other active sites more active. This is called .
It's positive because ...
and its homotropic ('same-changing') because...
positive homotropic modulation.
the binding of substrate makes the enzyme more active,
the substrate helps other molecules of the same type to bind.
Allosterically regulated enzymes show..
sigmoidal kinetics:
•The sigmoidal (allosteric) enzyme has a much sharper response between [S] = 1 … 2
Than MM enzymes
![<p>sigmoidal kinetics:</p><p>•The sigmoidal (allosteric) enzyme has a much sharper response between [S] = 1 … 2</p><p>Than MM enzymes </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d610efc1-637e-4303-bd8e-365806b0c486.jpg)
Le Chatelier's Principle
States that if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system shifts in the direction that relieves the stress.
Allosteric inhibitors only bind to
tense forms
Allosteric activators only bind to
relaxed form
A ligand is a ..
That includes ....
Ligands that act ...
small molecule that sticks to a larger one
substrates, but also inhibitors and activators.
as allosteric modulators can either be positive or negative in their effects.
An allosteric activator is a ...
Modulation can also be ...
positive heterotropic modulator: one molecule is facilitating the binding of a different kind of molecule.
modulator that increases the affinity of the enzyme for some molecule.
heterotropic ('other-changing').
one molecule is facilitating the binding of a different kind of molecule.
Why does positive heterotrophic modulators work?
If the concentration of the AMP-bound relaxed form [R-AMP] increases, then then the equilibrium will favour conversion of enzymes in the T form to the R form. Therefore [T] falls, and [R] increases. This is an application of Le Chatelier’s principle.
![<p>If the concentration of the AMP-bound relaxed form [R-AMP] increases, then then the equilibrium will favour conversion of enzymes in the T form to the R form. Therefore [T] falls, and [R] increases. This is an application of Le Chatelier’s principle.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5b0d8f87-a7f6-46cb-80a5-a676ed9bb633.jpg)
An allosteric inhibitor is
How does it work?
a modulator that decreases the affinity of the enzyme for some molecule.
In the example shown on the left of this slide, the ATP is acting as a negative heterotropic modulator: when the ATP binds to the enzyme, it locks the subunits into the tense state, preventing the binding of substrate: one molecule (ATP) is inhibiting the binding of a different kind of molecule (the substrate).
3 stages of glycolysis
Prepatory
Cleavage
Pay off x 2
Glycolysis occurs in the
It is a ... reaction
Only involves...
cytosol
oxidation
SLP
Overall equation for glycolysis
Glucose + 2ADP + 2Pi + 2NAD > 2 pyruvate + 2ATP + 2NADH
•Glucose from
•Glycogen stored
•Starch stored in
food
in liver
amyloplasts
Glycogen phosphorylase is activated by a .... in the...in response to ..
kinase cascade
liver
glucagon
glycogen phosphorylase activation
alternative?
1) Protein kinase A activated by G-DCR/ CAMP pathway
2) PKA activates phosphorylase kinase via phosphorylation
3) PK phosphorylates and activates glycogen phosphorylase
4) GP turns glycogen > glucose phosphate
Another way may be to use hexokinase to turn glucose to the glucose-P.
Draw glycolysis steps
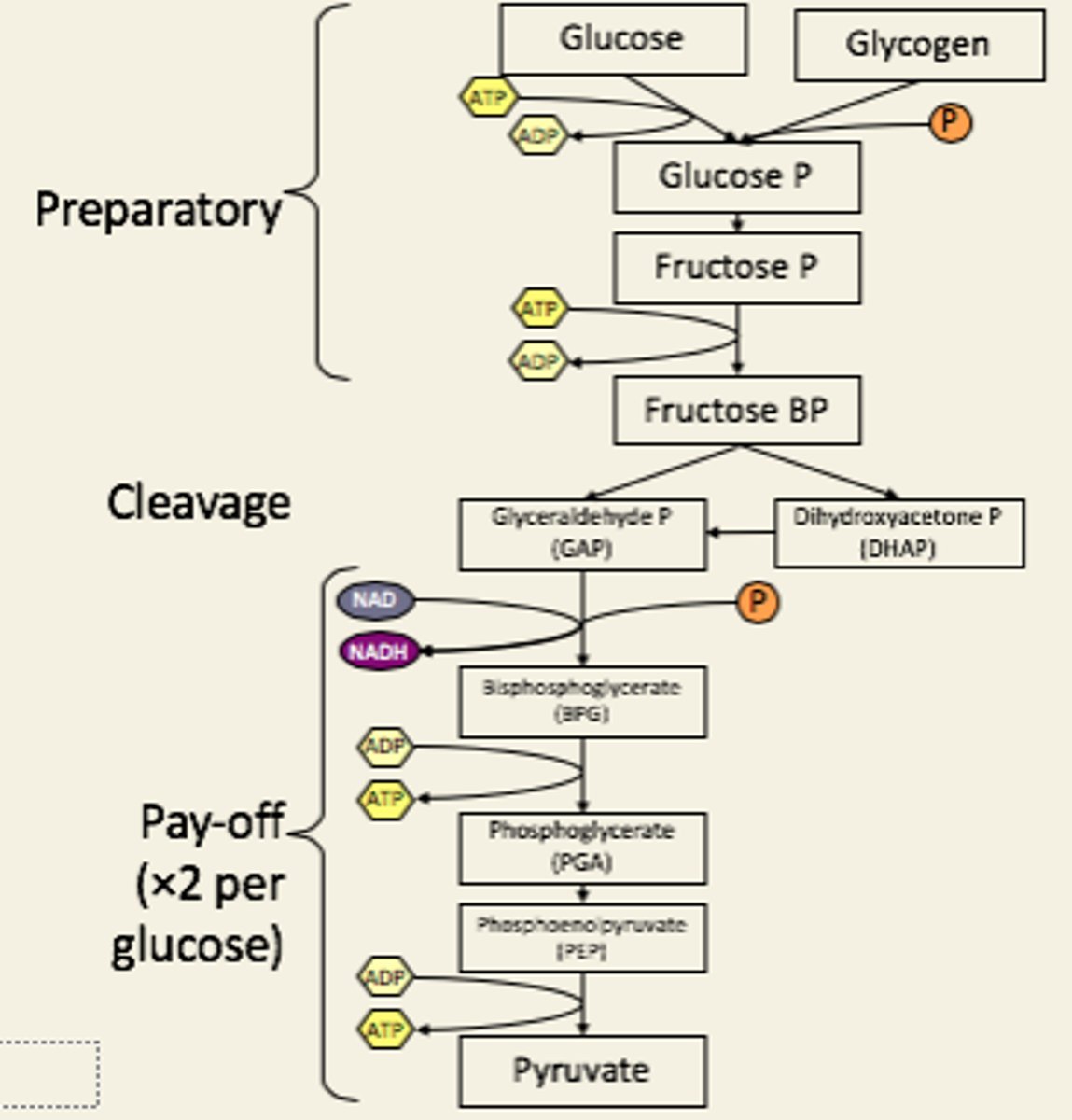
Per glucose:
-2 ATP in
-4 ATP out
-2 NADH out
= net production 2 ATP
Only 1 ATP is needed if the substrate is
glycogen rather than glucose, but note that the original synthesis of glycogen from glucose requires ATP. Breaking the glycosidic bond in glycogen to make glucose-P expends the energy put in to making the glycogen, and this amount of energy is similar to that required to directly phosphorylate glucose to glucose-phosphate.
"Enzymes that are regulated" often
–Have negative ∆G
–Act in forwards/ backwards pairs e.g. PFK and PBP
Most are allosterically regulated.
The forwards/backwards reactions have to be...
because ...
different, since if ∆G is negative for the forward reaction, the backwards reaction cannot be spontaneous. Hence the 'backwards' version of the reaction must be a different reaction with a different Keq. For PFK/FBP, the sugars are the same, but the other reactants differ.
PFK and FBP reaction
catalyse different reactions in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
not a true reverse reaction as it doesnt generate ATP

Bacterial PFK is a ...
multimeric enzyme showing cooperative binding for fructose-P.
PFK is
allosterically regulated by many metabolites.
PEP uses
It is
ADP / AMP is the
negative feedback with PFK to control the process.
allosteric inhibitor
allosteric activator
PFK shows
sigmoidal kinetics w.r.t. [Frc-P], and is modulated allosterically by ATP and AMP:
![<p>sigmoidal kinetics w.r.t. [Frc-P], and is modulated allosterically by ATP and AMP:</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c9a384e4-a196-4445-84a1-072a5c1a5942.png)
Cleavage involves...
aldolase and triose-P isomerase
1 hexose-P → 2 triose-P
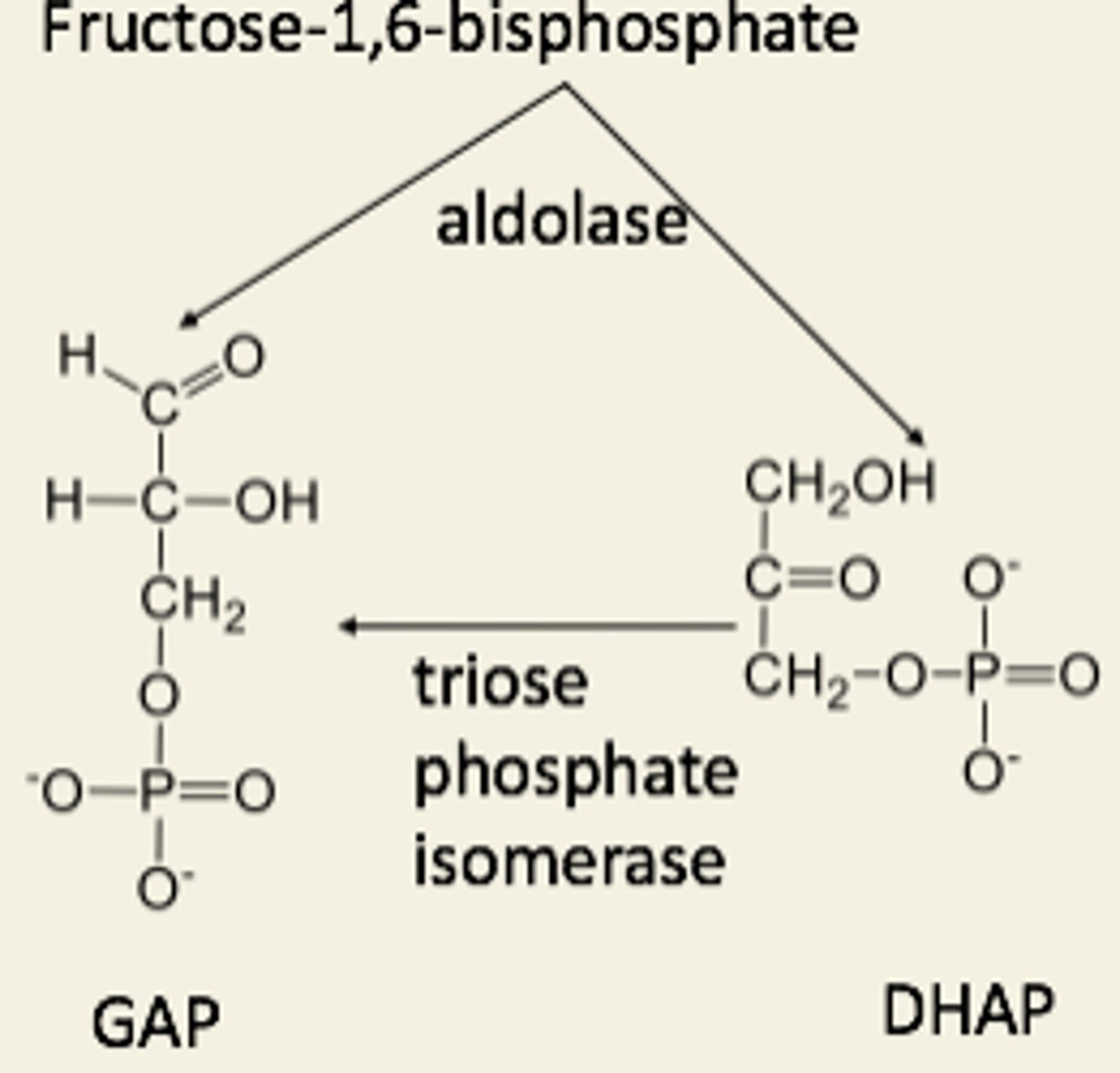
•Triose phosphate =
-Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
-Glyceraldehyde phosphate
The later steps generate
1 NADH and 2 ATP per GAP:
enol pyruvate is unstable so
this drives the PK reaction rightwards
Define SLP
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a metabolic reaction that results in the formation of ATP or GTP by the direct transfer of a phosphoryl (PO3) group to ADP or GDP from another phosphorylated compound.
Driven by instability of enol-pyruvate Vs Keto-pyruvate.
Pyruvate kinase is regulated by
positive feed-forward from Frc-BP:
•Ensures FBP and PK work in concert
The...equation can be used to model the binding of ligands showing cooperativity.
The gradient is
Hill
cooperativity coefficient.
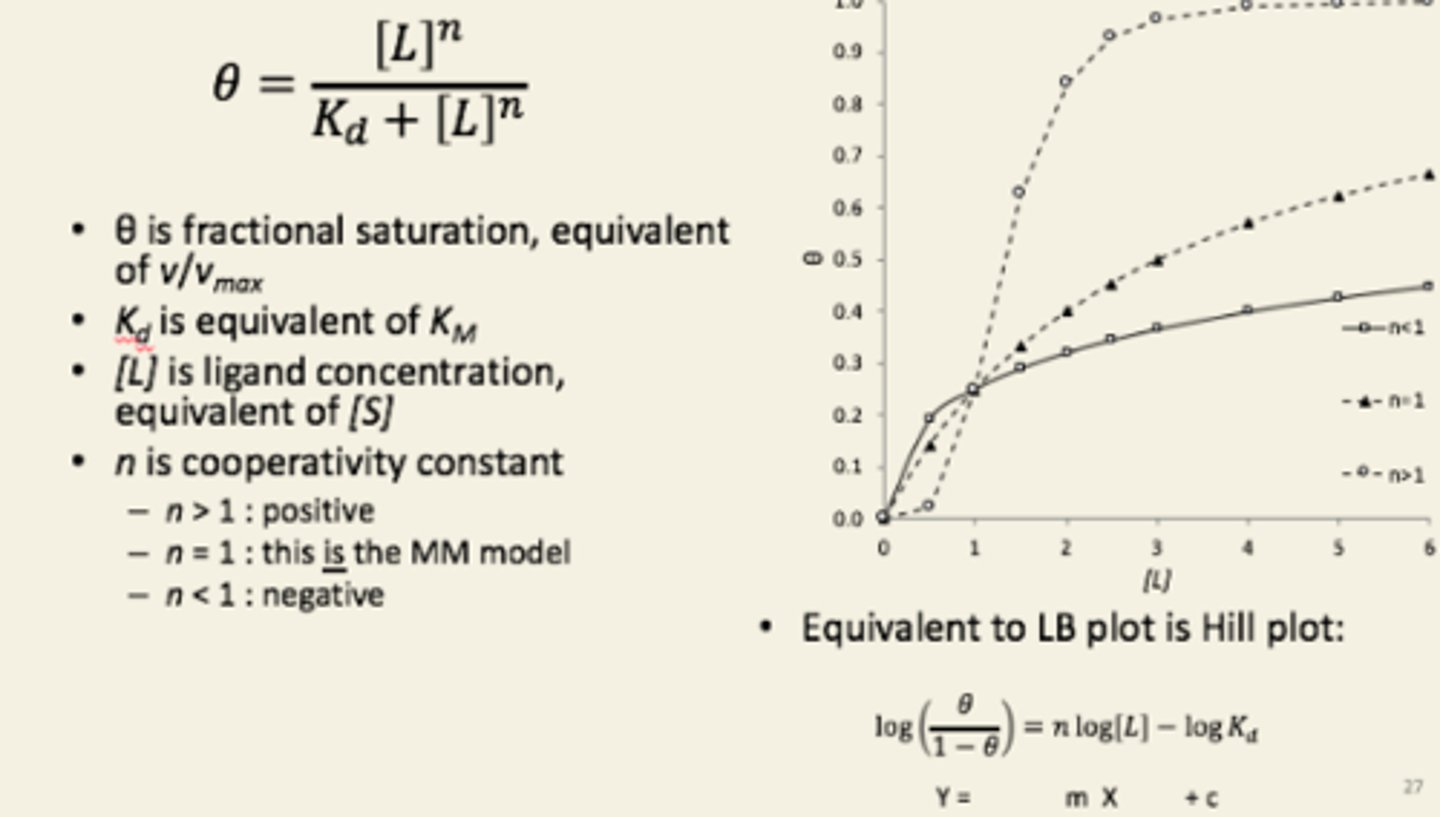
Values of n in Hills equation
Note that if n is 1, and L is the substrate then the kinetics are just Michaelis-Menten-like, with a hyperbolic shape, and a Kd that simply is the KM.
If n is larger than 1, then the ligands are cooperating: see that the kinetics are now sigmoidal, with a much sharper increase to θ approaching 1: the ‘upstroke’ is nearly vertical here – no activity…no activity…suddenly all the activity).
If n is less than 1, then the ligands are interfering: you get slightly more activity than for n=1 at very low [L], but then the increase is even slower than for a Michaelis-Menten-like kinetics
Ancestral vs Diverged mammalian PK
Ancestral:
- Sensitive to PEP inhibitor
- Active site shows cooperative binding for Frc-P in the ancestral enzyme (homotropic positive modulation by a phosphosugar)
Diverged:
- Sensitive to inhibition by citrate and AMP/ATP
- Lower subunit cannot phosphorylate
- Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate is an extremely potent activator of PFK1 made by PK2 when [fructose-P] is too high
- One of the ‘active sites’ has been repurposed as a allosteric activator binding site (heterotropic positive modulation by a phosphosugar)