BOLDED TERMS ONLY - Unit 3 - National Income & Price Determination - AP Macroeconomics
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
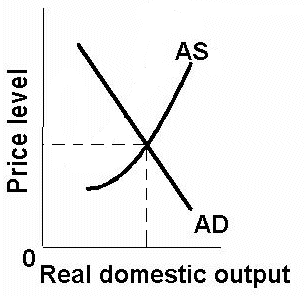
AD-AS Model
Used to analyze how changes in aggregate demand and aggregate supply affect overall price levels and real GDP.
Aggregate Demand (AD)
The total amount of goods and services demanded by households, businesses, government, and foreign buyers within an economy.
Disposable Income (YD)
The income a consumer has left over to spend or save once they have paid out their net taxes.
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
The change in consumption caused by a change in disposable income (YD).
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
The change in saving caused by a change in disposable income (YD)
Expenditure Multiplier
Effect of autonomous spending changes.
Tax Multiplier
How much people will not spend if taxes increase.
Short-Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS)
Represents the total amount of goods and services that firms are willing to produce and sell at different price levels in the short run.
Long-Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS)
The number of goods and services that an economy is capable of producing with the full employment of resources
Full-Employment level of Output
The level of real GDP where all available resources in an economy are being used efficiently, resulting in zero cyclical unemployment.
Short-run Equilibrium price level
Where demand equals supply, leading to stable production levels.
Short-run Equilibrium output level
The economic output when AD is equal to AS in the short-run.
Recessionary Gap
High unemployment & low prices
Actual Output < Potential Output
Inflationary Gap
Low unemployment & high prices
Actual Output > Potential Output
Demand-Pull Inflation
More consumption leads to an increase in price level and real GDP.
Cost-Push Inflation
Happens when production is decreased (or input costs increased, thus decreasing the amount of production).
Fiscal Policy
The government’s use of taxing and spending.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
The government aims at raising AD, therefore government spending increases AND OR taxes decrease.
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
The government aims at lowering AD, therefore government spending decreases AND OR taxes increase.
Long-Run macroeconomics equilibrium
Maximum sustainable output with stable prices & employment