Chem Vocab
1/307
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
308 Terms
Systematic error
error due to the equipment accuracy or set up, ‘consistent’, cannot be averaged out
Random error
caused by human ability, different each time, can be averaged out, given by half the smallest division.
Accuracy
How close results are to the true value
Precision
a measure of how consistent you can be with your measurements
Tables should:
Plan the correct number of columns and rows to avoid adjustments later.
Use a ruler to create neat, straight lines.
Label columns and rows clearly with quantities and units (e.g., Temperature / °C) using slash notation to keep table values unitless.
Maintain consistency in significant figures.
For calculated differences, include initial, final, and difference values.
Add columns for simple conversions, like inverting or scaling.
no. of moles
m/M
Enthalpy change
-Energy/no. of moles
Unified atomic mass
the mass of one-twelth of the mass of a carbon 12 atom
Mole
the amount of a sumstance that contains the same number of stated elemtary units as there are atoms in 12g of Carbon-12
Relative molecular mass
the weighted average mass of a molecule in a given sample of that molecule compared to the vlue of the unified atomic mass
Relative formula mass
the weighted average mass of one formula unit compared to the value of the unified atomic mass
Relative atomic mass
the weighted average mass of atoms in a given sample of an element, compared to the value of the unified atomic mass
Relative isotopic mass
the mass of a particular atom of an isotope compared to the value of the unified atomic mass
Isotope
atoms of the same element which have the same atomic number nut different mass number
Heisenberg Uncertainty model
Everything we do affects the electrons so we cannot know both the speed and position at the same time
Relative abundance
different isotopes weigh differently - when one isotope is is more abundant, the relative atomic mass will be closer to that isotopic weight
mass spectometre
ionizes atoms and then sends them through an electromagnetic field where they are deflected on the basis of their mass and charge
Volatility
how easily a substance vaporizes
Ionization energies
the energy needed to remove 1mol of electrons from 1mol of atoms
Factors that affect ionization energy
less electrons in outer shell = less ionization energy (Nuclear Attraction)
more shells = less ionization energy (electron shielding)
bigger atomic radius = less ionization energy
Elastic collision
all energy is transfered
Inelastic collision
energy is lost (e.g through heat) during a collision
Ideal gas Law
a gas whose volume varies exactly in proportion to the temperature an exactly in inverse proportion to the pressure
R
Gas constant (8.31JK-1mol-1)
To convert to Kelvin
+273.15o
avagadros constant
6.02 × 1023
principle quantam number
number of shells
free radical
a species with one or more unpaired electron
Paul’s eulsion principle
No orbital may contain more than 2 electrons, the elctrons may not have the same spin.
Hund’s rule of ‘maximum mutiplicity’
when in orbitals of equal energy, electrons will try to remain unpaired
Aufbau (buildup principle)
electrons enter the lowest available energy level
molar second ionization energy
the nergy needed to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous plus 1 ions.
emperical formula
the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound
molecular formula
shows the exact number of molecules present
Atomic radius
As the Atoms get bigger, the valence electrons are further away and require less energy to be taken off.
Electron shielding
As atoms gain shells the inner electrons repel the outer electrons and the ionization energy decreases
Nuclear Attraction
the greater the number of protons in the nucleus, the greater the relative attractive forces on the outer electrons and therefore the greater the ionization energy.
fragmentation
the process in which a molecular ion breaks into smaller ions, radicals and/or neutral molecules.
free radical
a species with one or more unpaired elctrons
gas constant
8.31JK-1mol-1
To convert from degrees celsius to Kelvin
+273.15
Combustion formula
HxCy + (x+y/4)O2 → xCO2 + y/2H2O
Ideal gas Law formula
PV = nRT
electronegativity
The ability of an atom in a molecule to attrcat bonding electrons in a covalent bond to itself
Ionic bond
metal & non-metal - Electron transferred. Full charges on atoms
Nonpolar Covalent bond
Bonding lectrons shared equally between two atoms. No charges
Polar covalent bond
Bonding electrons shared unequally between two atoms. Partial charges on atoms
The pauling scale
measure electronegativity
Trend in Elctronegativity
Increases from bottom left to top right
avogadros constant value
6.02×1023
electronegativity difference of less than 0.5
bond type: pure Covalent
Electronegativity difference between 0.5 and 1.6
Bond type: polar covalent
Electronegativity difference 1.6 - 2.0 ( + a metal)
bond type: ionic
avogadros constant
the amount of particles in a mole
NO3-
Nitrate
CO32-
carbonate
SO42-
sulfate
OH-
Hydroxide
NH4+
ammonium
Zn2+
Zinc
Ag+
Silver ion
HCO3-
bicarbonate ion
PO43-
Phosphate
covalent bond
Non-metals react together, share electrons to gain full outer shells, there is electrostatic attraction between their nuclei
electron deficient
a compound in which the central atom’s octet is stable without complete octet. Boron, Beryllium, aluminium.
Expanded octet
Atoms from periods 3 or above expand their octet by moving s or p electrons into the d orbital
Dative covalent vond
one species donates a lone pair f electrons to another atom or ion.
Dimer
a molecule or molecular complex consisting of two identical molecules linked together.
ligand
an ion or molecule attached to a metal atom by dative bonding (e.g Water)
Properties of metallic bonding
Good conductors due to delocalised/free electrons
malleable and ductile due to the shiftable arrangement of particles
Lustrous
High melting point and malleability due to strong forces between lattice bonds
Giant metallic structures
Electrostatic attraction
properties of Ionic bonding
Electrostatic attraction
solid at room temperature
Giant structures
High melting points
Crystalline
Brittle - shatter easily as ions of the same charge become adjacent
Conductors in liquid or solvated state
metals & non-metals
Properties of Covalent bonds
Non-metals & non-metals
molecules are neutral
electrostatic forces
Low melting and boiling points
often amorphous (no definite form)
Remain molecules if dissolved in water
poor conductors of electricity
Lone pair
2 unpaired elctrons - can partake in dative bonding, sometimes form dimers
London dispersian forces ( Van der Waals)
A temporary attractive force that results when the electrons in two adjacent atomcs occupy postitions that make the atom form temporary dipoles
electric dipoles
arise from opposite but equal charges seperated by distance
Conditions for Hydrogen bonding
A hydrogen ato covalently bonded to an electronegative atm (N, O or F)
A lone pair of electrons on the electronegative atom
Latent heat of fusion
The amount of heat required to convert a unit mass of solid into liquid without a change in temperature
Latent heat of Vapourization
The amount of heat required to convert a unit mass of liquid into vapor without a change in temperature
allotropes
different arrangements of the same elements, in the same state. e.g Diamond and graphite.
Where are giant covalent bonds found
Molecules and macro molecules
Where are Ionic (electrostatic) bonds found?
Regular lattice structures of Ionic compounds. mostly soluble in polar sovlents
Where are Simple covalent bonds found?
covalently bonded atoms.
Where are Metallic bonds found?
3D lattice bonding in which the delocalised valence electrons are attracted to the surrounding cations
What is the Relative strength of Giant covalent bonds?
Strongest (Very strong)
What is the relative strength of Ionic (electrostatic) bonds?
Second strongest (but not by much)
What is the Relative strength of Simple covalent bonds?
Weakest
What is the Relative strength of metallic bonding?
Strong (second weakest)
What are Giant covalent bonds based on?
The Stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms which share valence electrons
What are Ionic (electrostatic) bond based on?
Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a regular lattice structure
What are Simple covalent bonds based on
Weak Van der Waals forces in between covalently bonded molecules
What are metallic bonds based on?
Attraction between free valence electrons and the nuclei of neighbouring metal atoms
How are sigma (σ) bonds formed
by direct overlap of orbitals between the boning atoms
How are Pie (π) bonds formed
by the sideways overlap of adjacent p orbitals
Hybrid orbtals
Orbitals formed by mixing of atomic orbitals
What does VSEPR stand for
Valence shell electron pair repulsion
What does the VSEPR model mean
To minimise repulsion by maximising seperation
2 bonding pairs, 0 lone pairs, 180
linear

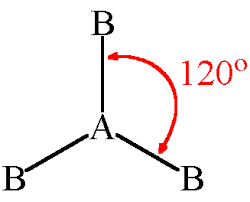
3 bonding pairs, 0 lone pairs, 120
trigonal planar
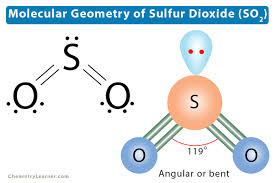
2 bonding pair, 1 lone pair
bent I, 119
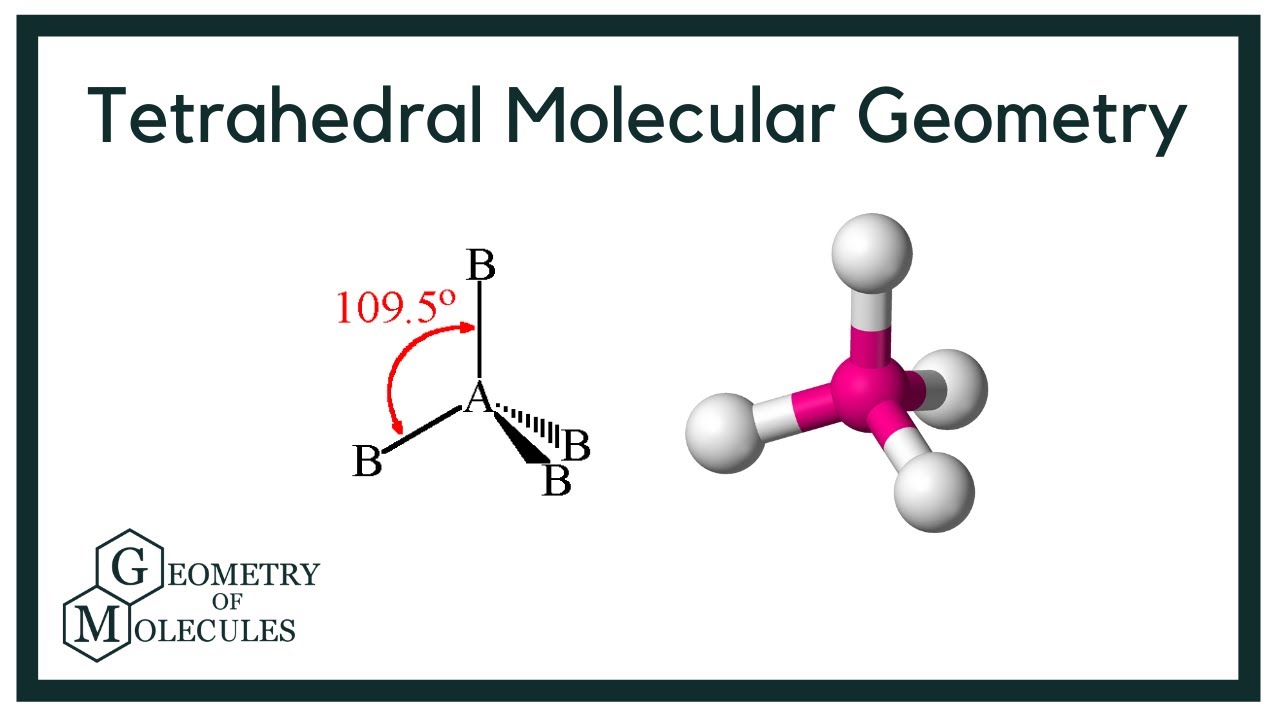
4 bonding pairs, 0 lone pairs.
tetrahedral, 109.5