OCR A 6.1.2 Carbonyl Compounds
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
aldehyde
carbonyl group on end
-al
ketone
carbonyl grp not on end
-one
oxidation of aldehydes
-oxidised to carboxylic acids using oxidising agent
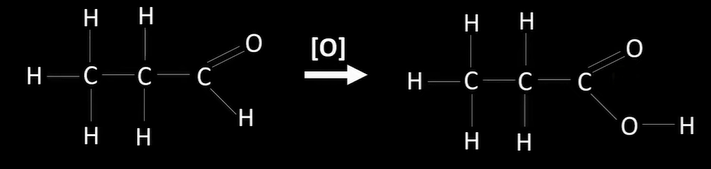
oxidation of ketones
not oxidised
tollens reagent
-used to distinguish between aldehyde and ketone
-contains [Ag(NH3)2]+
make tollens reagent
-put silver nitrate sol in test tube
-add few drops of NaOH: pale brown ppt forms
-add few drops of dilute of ammonia until ppt dissolves
test using tollens reagent
-add unknown to it in test tube
-place in hot water bath
-if aldehyde present, silver mirror forms: silver reduced and coats test tube and oxidises into carboxylic acid
-if ketone present nothing forms
Brady’s reagent
-2,4-dinitrophenylhyrazine
-2,4DNP
-used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones
-dissolved in conc sulfuric acid and methanol
testing with brady’s reagent
-when added if carbonyl grp present, bright orange ppt forms
-ppt is derivative of a carbonyl compound 2,4 dinitrophenylhyrazone
-fitlter and recrystalize to find pure
If melting point is sharp then pure if not sharp then recrastalizs
-find melting point and compare to table of known melting points
reduction agent for carbonyls
NaBH4 (sodium tetrahyrdridoborate)(III))
dissolved in methanol and water
represented by [H]
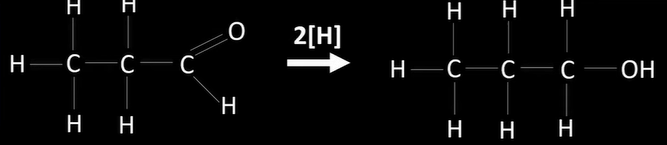
reduction of carbonyls
-reduced to alcohols
-nucleophilic addition
aldehydes reduction
-to primary alcohols
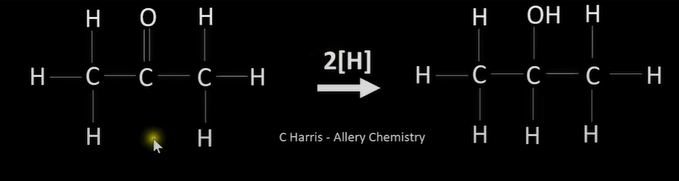
ketones reduction
-to secondary alcohols
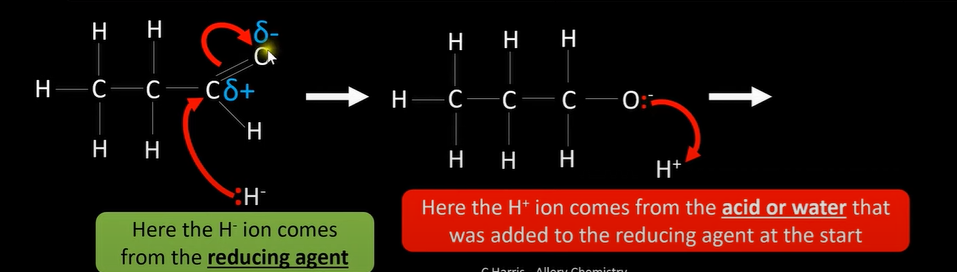
carbonyl reduction mechanism explanation
-lone pair of e- from H-(nucleophile) attracted and donated to S+ C atom in C=O bond
-dative covalent bond formed between nucleophile and C
-pi bond in C=O breaks by heterolytic fission; forming negative intermediate
-O atom of intermediate donates lone pair to H atom in H2O molecule
-alcohol forms
carbonyl reduction mechanism
KCN reactions with carbonyl
-produces hydroxynitriles
-nucleophilic addition
-nucleophile attacks C=O and adds on
-reagent is HCN
HCN
-colourless, poisonous,
-made by reacting NaCN and H2SO4
-reaction is useful as it increases chain length
HCN + carbonyl mechanism
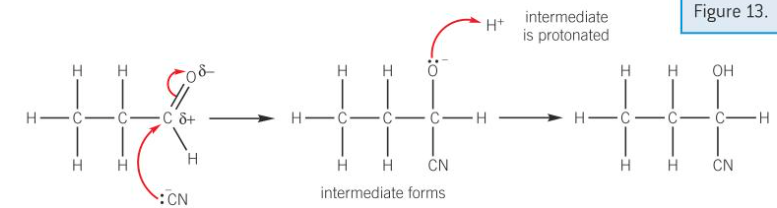
HCN + carbonyl mechanism
-lone pair from cyanide ion attracted and donated to S+ C atom in C=O bond
-dative covalent bond formed between nucleophile and C
-pi bond in C=O breaks by heterolytic fission; forming negative intermediate
-intermediate protonated by donating lone pair of electrons H ion
-hydroxynitrile forms
KCN risks
-irritant; v dangerous if ingested or inhaled
-if reacts w/ moisture can form toxic gas HCN
KCN usage precautions
wear:
-gloves
-lab coat
-safety goggles
use fume cupboard to prevent exposure to toxic fumes