Chapter 10 - Understanding work teams
Difference between groups and teams
- @@Work group@@: group that interacts primarily to share information and make decisions to help each group member fulfill his/her responsibilities.
- @@Work team@@: group whose individual efforts result in performance that is greater than the sum of the individual inputs.
Types of teams
- @@Problem-solving teams@@: groups of 5 to 12 employees from the same department who meet for a few hours each week to discuss ways of improving quality, efficiency and the work environment.
- @@Self-managed teams@@: groups of 10 to 15 people who take on responsibilities of their former supervisors.
- @@Cross-functional teams@@: employees from about the same hierarchical level, but from different work areas, who come together to accomplish a task.
- @@Virtual teams@@: teams that use computer technology to tie together physically dispersed members in order to achieve a common goal.
- @@Multi-team systems@@: collection of two or more interdependent teams that share a superordinate goal; a team of teams.
Creating effective teams
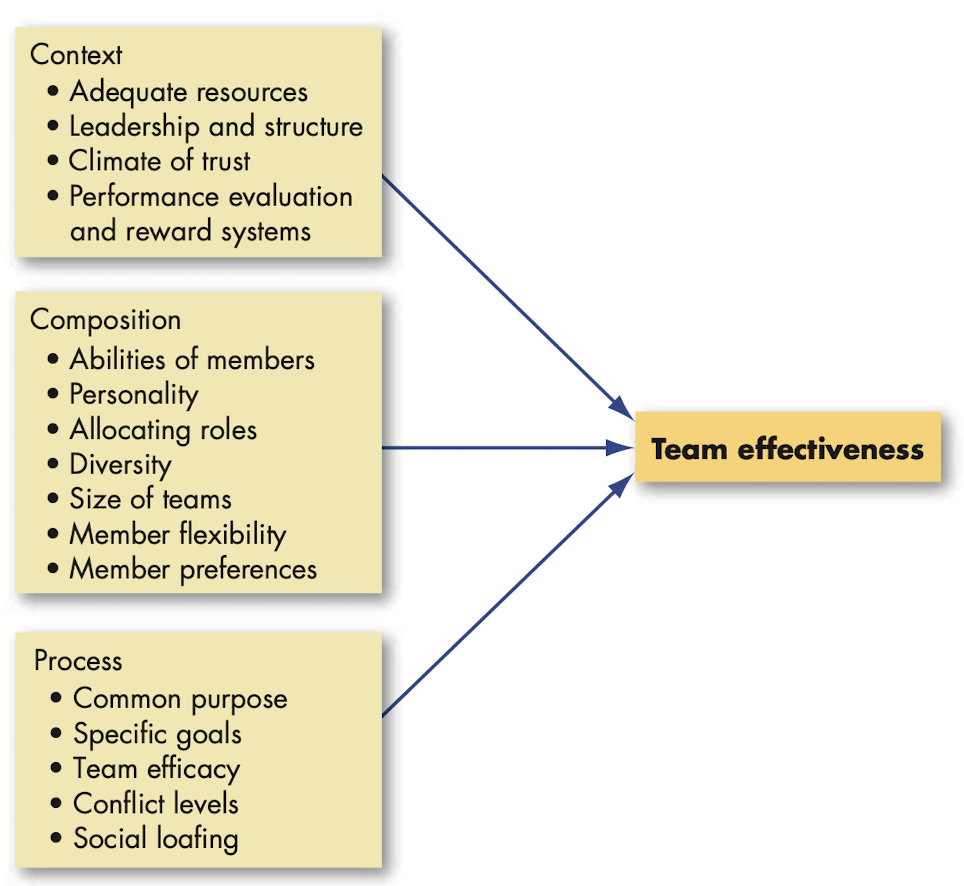
- Context: what factors determine whether teams are successful
- Team composition
- @@Organizational demography@@: degree to which team members of a work unit share a common demographic attitude (sex, age), educational background or length of service in an organization and the impact of this attribute on turnover.
- Team process
- @@Reflexivity@@: team characteristic of reflecting on and adjusting the master plan when necessary.
- @@Mental models@@: organized mental representations of the key elements within a team’s environment that team members share.
Turning individuals into team players
- Selection: hiring team players
- Training: creating team players
- Rewarding: providing incentives to be a good team player
