Unit 3: National Income & Price Determination
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Marginal Propensity to Consumer (MPC)
The increase in consumer spending wen disposable income rises by $1.
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPC)
The increase in household savings when disposable income rises by 1$
Autonomous Change in Aggregate Spending
An initial rise or fall in aggregate spending that is the cause, not the result, of a series income and spending changes.
Spending Multiplier
The ratio of the total charge in real GDP caused by an autonomous change in aggregate spending to the size of that autonomous change. It indicates the total rise in real GDP that results from each $1 of an initial rise in spending.
Consumption Function
Shows how a household’s consumer spending varies with the household’s current disposable income.
Autonomous Consumer Spending
The amount of money a household would spend if it had no disposable income.
Aggregate Consumption Function
The relationship for the economy as a whole between aggregate current disposable income and aggregate consumer spending.
Planned Investment Spending
The investment spending that businesses intend to undertake during a given period.
Inventory Investment
The value of the change in total inventories held in the economy during a given period.
Unplanned Inventory Investment
Positive: occurs when actual sales are lower tan businesses expected, leading to unplanned increases in inventories.
Negative: result when sales in excess of expectations
Actual Investment Spending
The sum of planned investment spending and unplanned inventory investment.
Aggregate Demand Curve
Shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output demanded by households, businesses, the government, and the rest of the world.
Wealth Effect of a Change in the Aggregate Price Level
The change in consumer spending caused by the altered purchasing power of consumers’ assets.
Interest Rate Effect of a Change in the Aggregate Price Level
The change in investment and consumer spending caused by altered interest rates that result from changes in the demand for money.
Fiscal Policy
The use of government purchases of goods and services, government transfer, or tax policy to stabilize the economy.
Monetary Policy
The central bank’s use of changes in the quantity of money or the interest rate to stabilize the economy.
Aggregate Supply Curve
Shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output supplied in the economy.
Nominal Wage
The dollar amount of the wage paid.
Sticky Wages
Nominal wages that are slow to fall even in the face of high unemployment and slow to rise even the face of labor shortages.
Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve
Shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and quantity of aggregate output supplied that exists in the short run, the time period when many production costs can be taken as fixed.
Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve
Shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output supplied that would exist if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible.
Potential Output
The level of real GDP the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible.
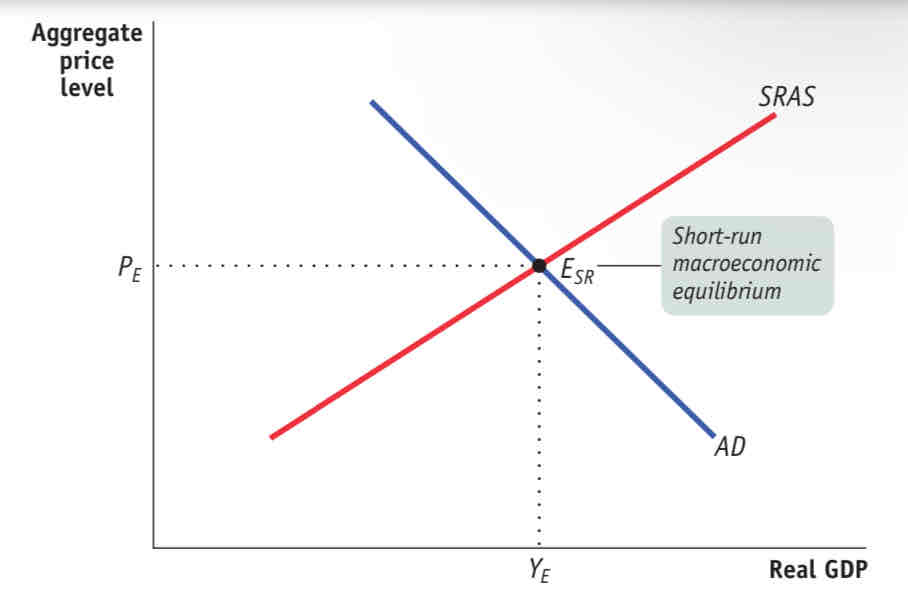
AD-AS Model
The aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve are used together to analyze economic fluctuations.
Short-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium
When the quantity of aggregate output supplied is equal to the quantity demanded.
Short-Run Equilibrium Aggregate Price Level
The aggregate price level in the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium.
Short-Run Equilibrium Aggregate Price Level
The aggregate price level in the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium.
Short-Run Equilibrium Aggregate Output
The quantity of aggregate output produced in the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium.
Demand Shock
An event that shifts the aggregate demand curve.
Supply Shock
An event that shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve.
Stagflation
The combination of inflation and stagnating (or falling) aggregate output.
Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium
When the point of short-run macroeconomic equilibrium is on the long-run aggregate supply curve.
Recessionary Gap
When aggregate output is below potential output.
Inflationary Gap
When aggregate output is above potential output.
Output Gap
The percentage difference between actual aggregate output and potential output.
Self-Correcting
When shocks to aggregate demand affect aggregate output in the short run, but not the long run.
Stabilization Policy
The use of government policy to reduce the severity of recessions and rein in excessively strong expansions.
Social Insurance
Programs are government programs intended to protect families against economic hardship.
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Reduces aggregate demand
Tax Multiplier
The factor by which a change in tax collections changes real GDP.
Balanced Budget Multiplier
The factor by which a change in both spending and taxes changes real GDP.
Lump-sum Taxes
Taxes that don’t depend on the taxpayer’s income.
Automatic Stabilizers
Are government spending and taxation rules that causes fiscal policy to be automatically expansionary when the economy contracts and automatically contractionary when the economy expands.
Discretionary Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy that is the result of deliberate actions by policy makes rather than rules.
Interest Rate
The price, calculated as a percentage of the amount borrowed, charged by lenders to borrowers for the use of their savings for one year.
Savings-Investment Spending Identity
Savings and investment spending are always equal for the economy as a whole.