Biomolecules: Carbohydrates
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What functional group is present in all carbohydrates?
hydroxl OH
What is the difference between monosaccharides - oligosaccharides - polysaccharides?
mono is one sugar unit
oligo is 2-100 sugar residues
poly is 100- thousands sugar residues
What do sugars contain to prove optical isomerism exists?
chiral carbons
how do you designate the two enantiomers?
using an L or D prefix
What happens when alcohols react with aldehydes and ketones?
forms hemi acetyles or hemi ketals
what is an anoremic carbon?
when sugars are in the ring form and carbon 1 is chiral
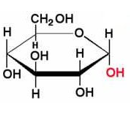
what is an anomer
OH group at C-1 is on the opposite side of the ring from the CH2OH group
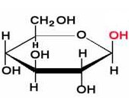
what is a b anomer
OH group at C-1 is on the same side of the ring as the CH2OH group
what anomer is preffered and why?
b is preffered as it minimises hinderance between OH group
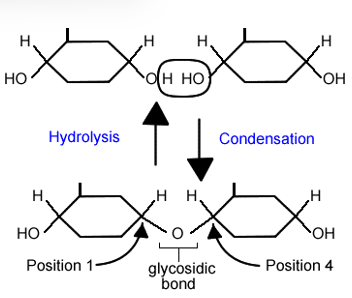
what is glycosidic linkage?
when the cyclic form of one monosaccharide can react with an alcohol group to form a disaccharide
How do you break a glyosidic bond?
hydrolyse it with acid + heat or specific enzyme
what is maltose
a disaccharide formed by the linkage of two monosaccharides with the eliminationof water
how is maltose a reducing agent
as it can exist in open chain form so possess an aldehyde group - can exist in both a nd b anomeric forms in solution
why is sucrose non reducing
the rings of glucose and fructose are locked so the disaccaride does not osses a free aldehyde
polysaccarides function
insoluble and difficult to purify
what is glycogen
energy reserve polysaccaride abundant in the liver
how is glycogen broken down
enzymic reactions
what does celluloses linearity cause?
polymers to line up in fibres with hydrogen bonding