Pathology set
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
OSPE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
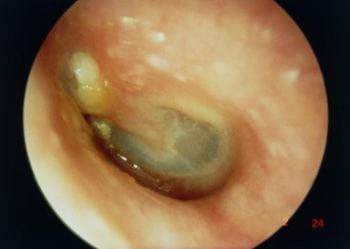
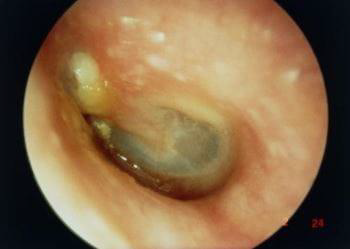
Identify?
Chronic suppurative otitis media
A long standing middle ear infection characterized by persistent hole in ear drum and discharge for at least 6 weeks.
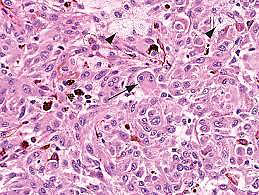
Identify?
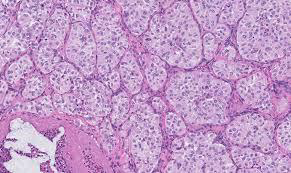
Jugular para-ganglioma of middle ear
M/P:
1.Classic nests called “zellballen”; the central cells are rounded with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm.
2.Sustentacular cells are flat cells & present at the periphery of the nests.
3.Prominent fibrovascular stroma separates the nests.
Identify?
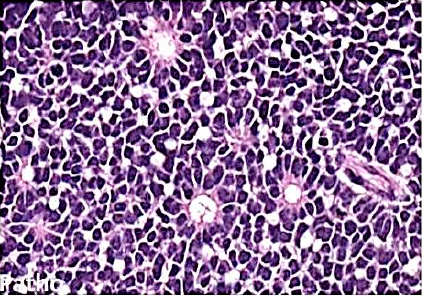
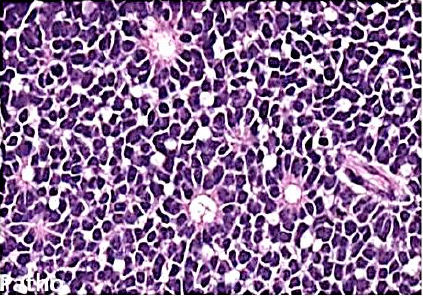
Retinoblastoma
M/P: The tumor is formed of undifferentiated retinal cells; that show characteristic rosettes which is of 2 types:
1.Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes (around a lumen). in this picture.
2.Homer-Wright rosettes (around neuri-fibrillary structure).
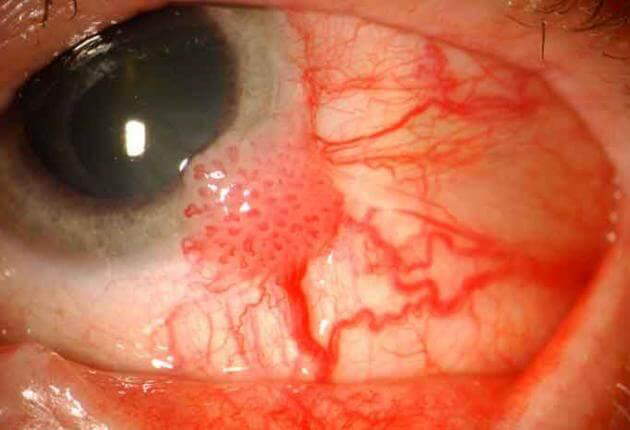
Identify?
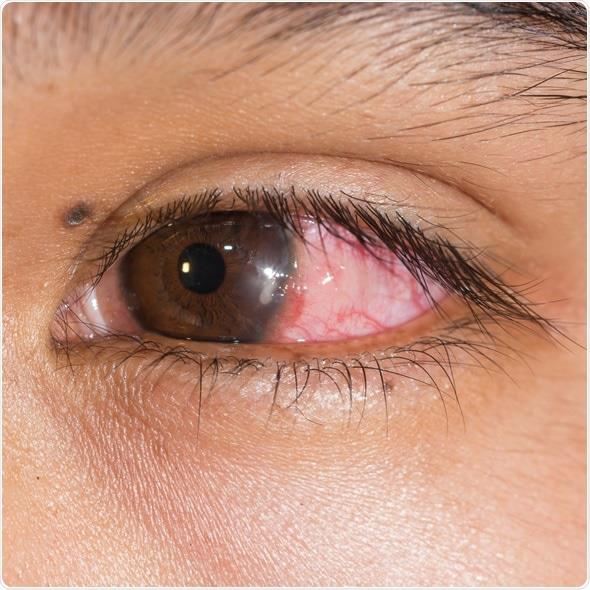
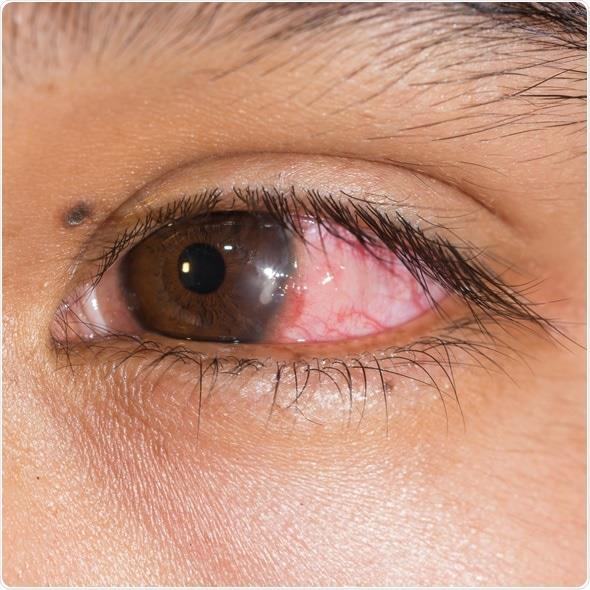
Keratitis
•Eye redness
•Excess tears or other discharge
•Difficulty opening eyelid because of pain or irritation
Identify?
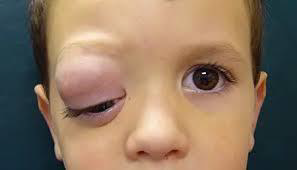
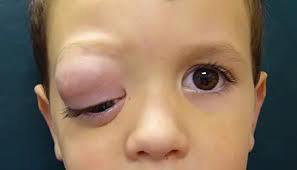
Orbital rhabdomyosarcoma
N/E:
Rapidly progressive proptosis or rapidly enlarging orbital mass.
M/P:
The tumor cells have deeply esinophilic cytoplasm (sometimes with cytoplasmic striations), with hyperchromatic atypical nuclei and atypical mitosis.
Identify?
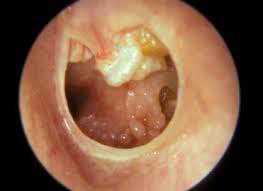
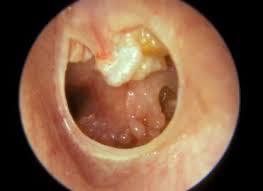
Cholesteatoma of middle ear
M/P:
Cyst filled with abundant keratin + cholesterol clefts + large number of histiocytes.
Identify?
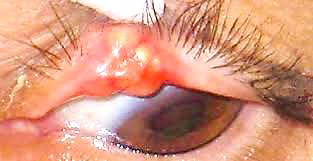
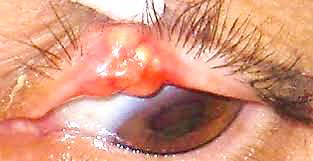
Sebaceous carcinoma
N/E:
Localized or diffuse swelling of the tarsus.
M/P:
Tumor cells with sebaceous differentiation (cells with clear, foamy cytoplasm that resembles sebocytes).
Identify?
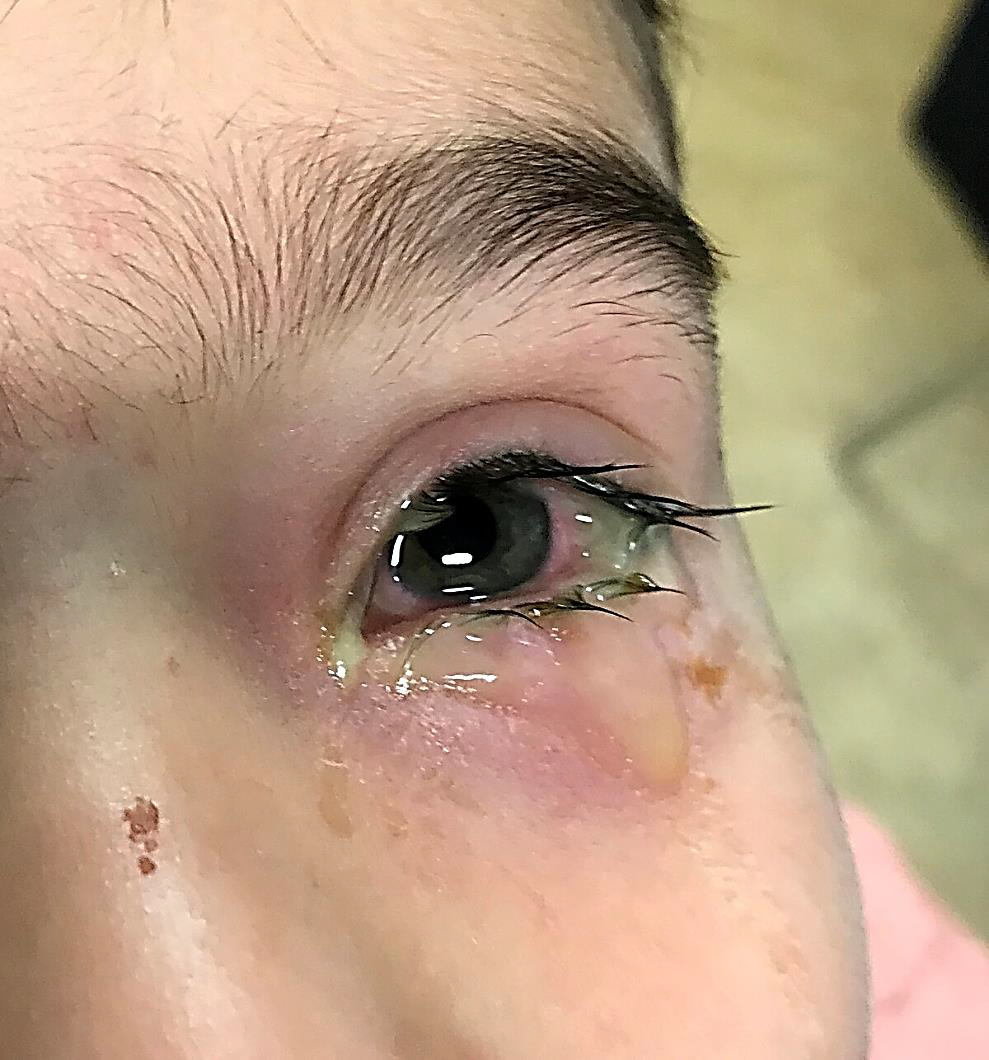
Conjunctivitis
•Eye redness
•A discharge that forms a crust during the night that may prevent eyes from opening in the morning.
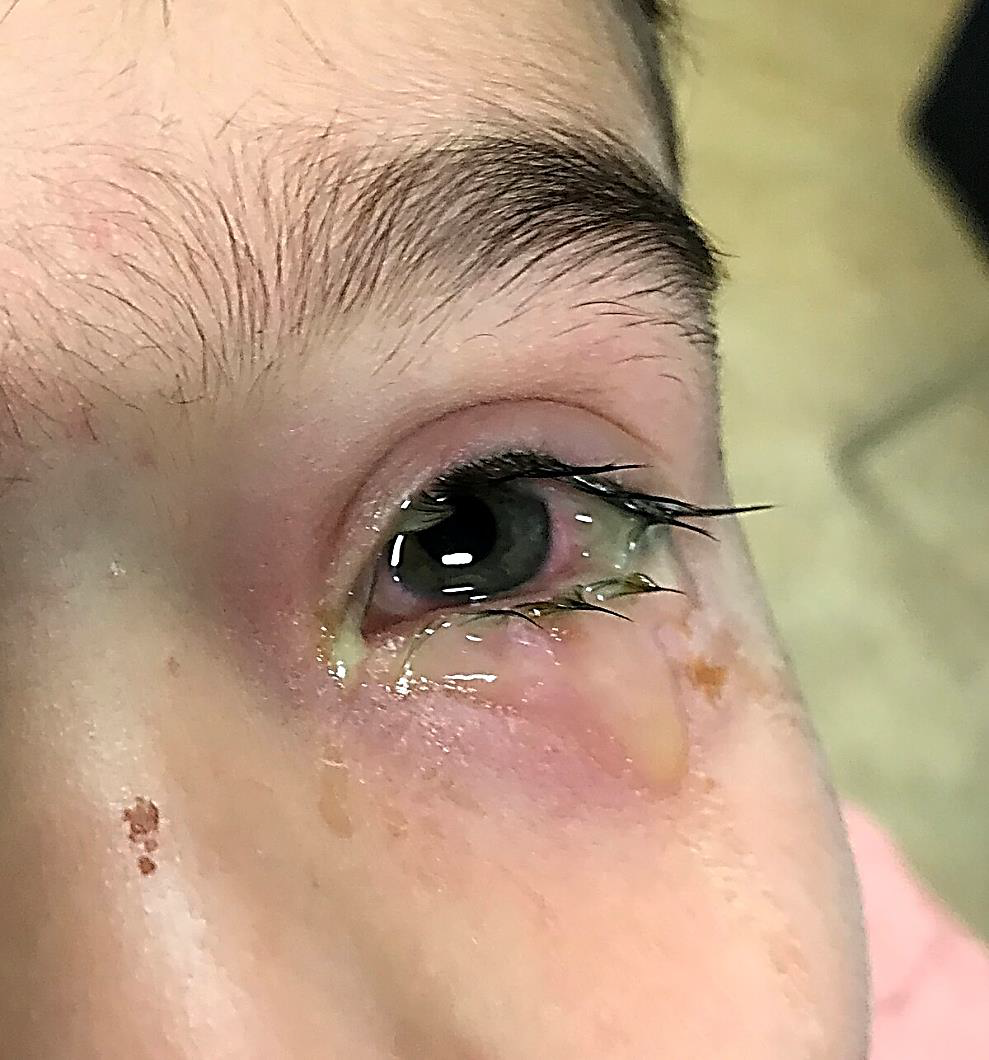
Identify?
Cholesteatoma of middle ear
M/P:
Cyst filled with abundant keratin + cholesterol clefts + large number of histiocytes.
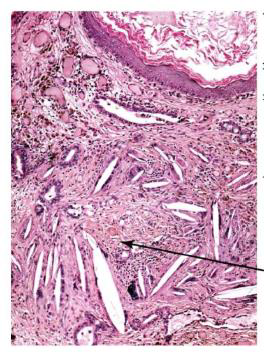
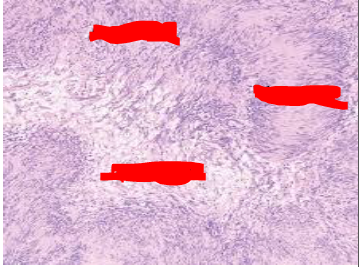
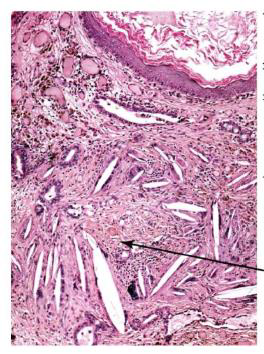
Identify?
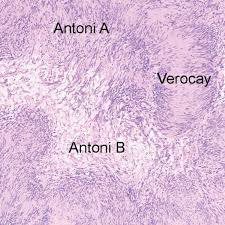
Acoustic neuroma of inner ear
M/P: Typically show a biphasic appearance with: Antoni A and Antoni B areas. Antoni A Areas: hypercellular areas with the pathognomonic Verocay Bodies Antoni B Areas: hypocellular areas of loose meshwork of Schwann cells.
Identify?
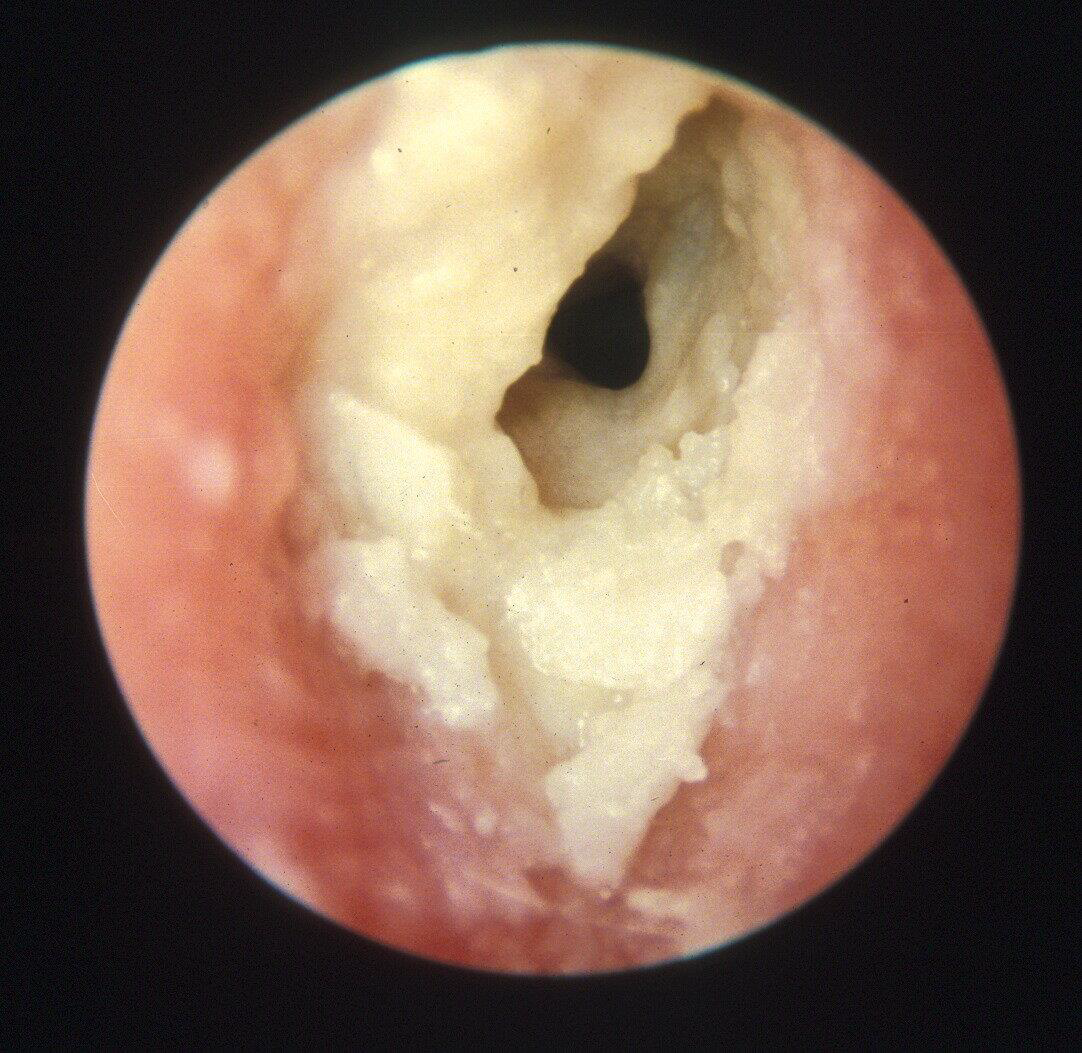
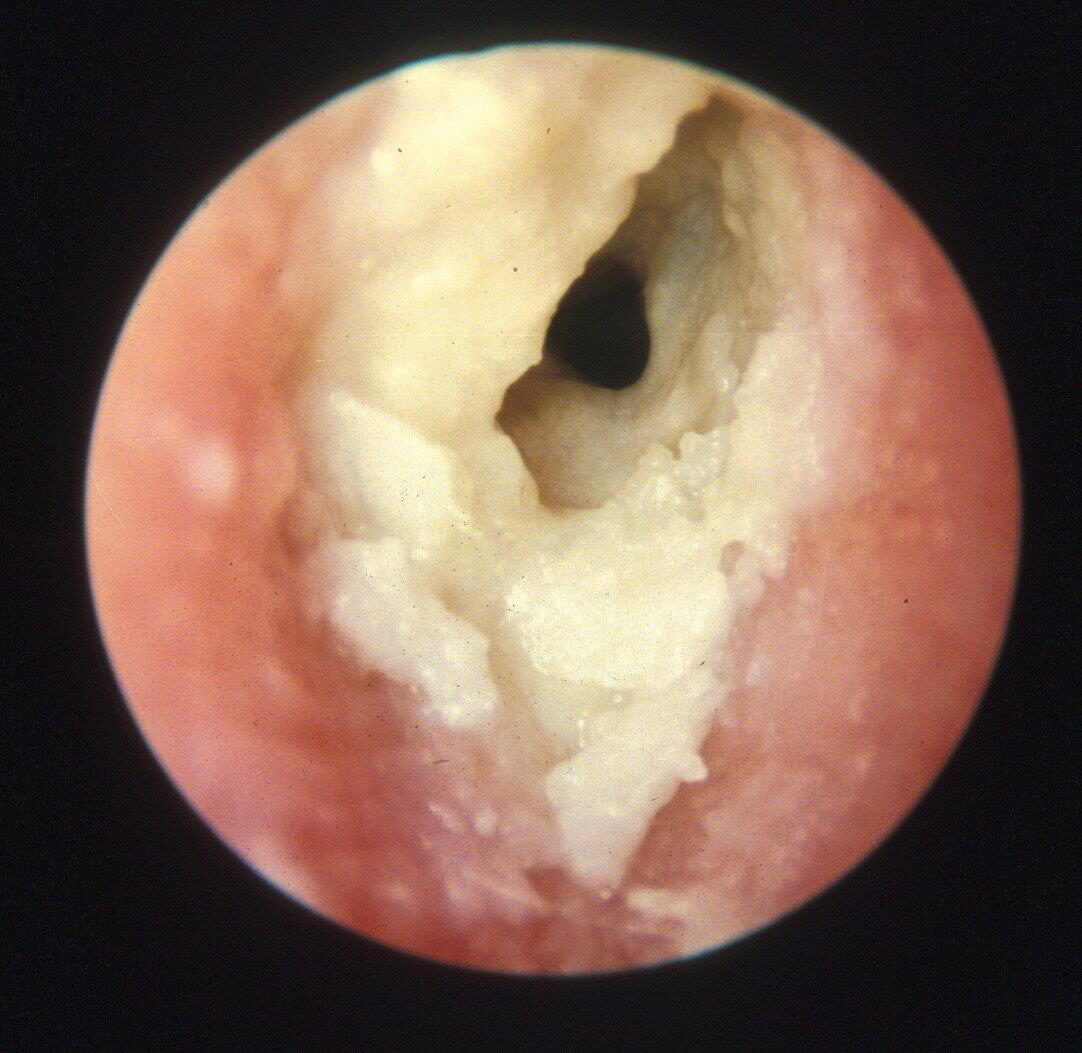
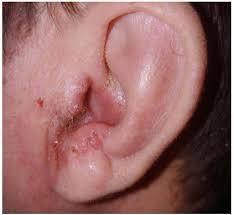
Acute diffuse otitis externa
Most commonly due to bacterial or fungal infections after minor trauma to the ear
Identify?
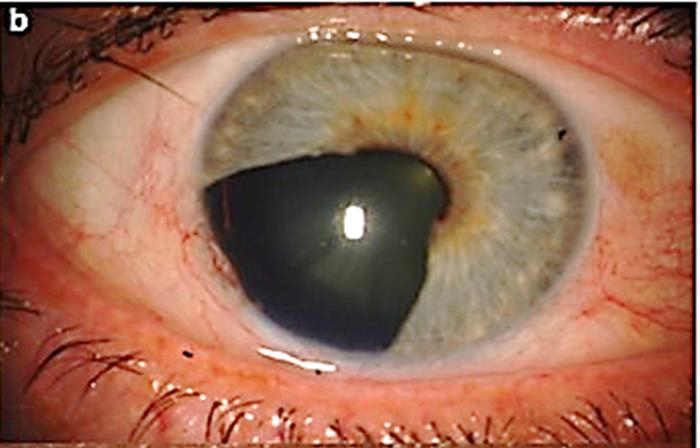
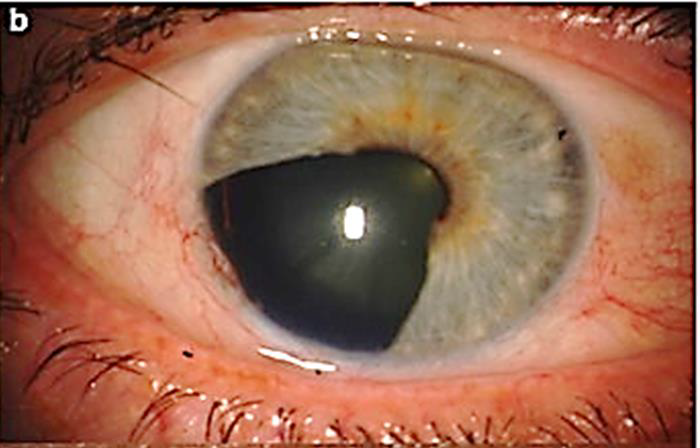
Uveal malignant melanoma
N/E: Dom-shaped pigmented mass. M/P: The epithelioid variant Larger irregular pleomorphic cells with larger nuclei and abundant acidophilic cytoplasm; that may contain melanin pigment.
Identify?
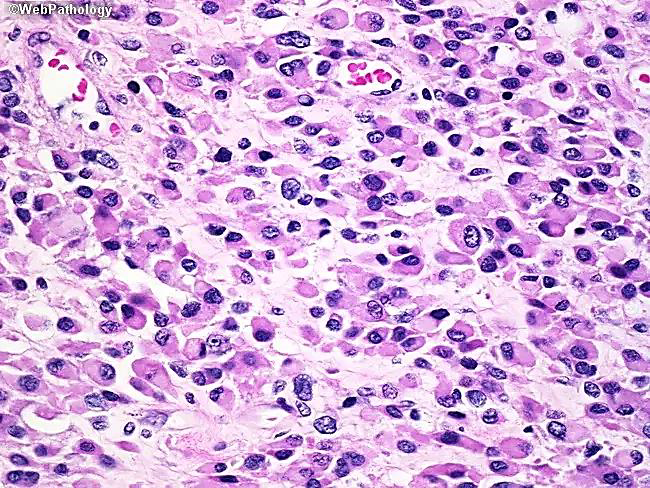
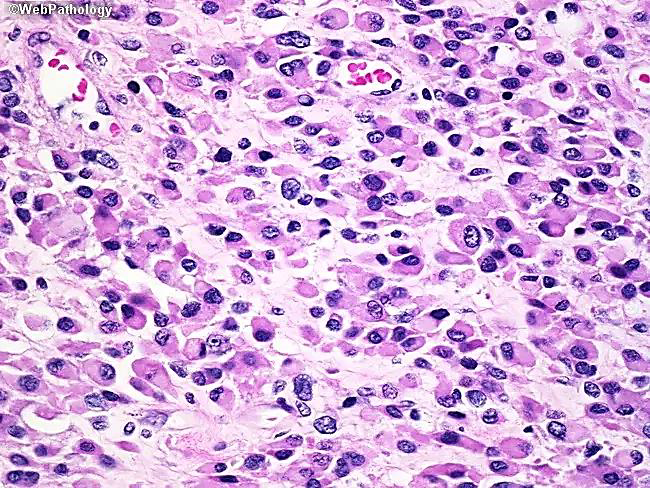
Orbital rhabdomyosarcoma
N/E:
Rapidly progressive proptosis or rapidly enlarging orbital mass.
M/P:
The tumor cells have deeply esinophilic cytoplasm (sometimes with cytoplasmic striations), with hyperchromatic atypical nuclei and atypical mitosis.
Identify?
Cerumen-gland adenocarcinoma
Atypical glands lined by several layers of atypical cells, show solid areas & invasive pattern.
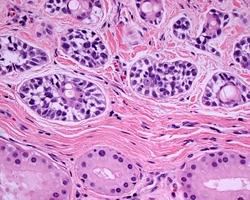
Identify?
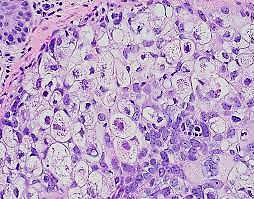
Sebaceous carcinoma
N/E:
Localized or diffuse swelling of the tarsus.
M/P:
Tumor cells with sebaceous differentiation (cells with clear, foamy cytoplasm that resembles sebocytes).
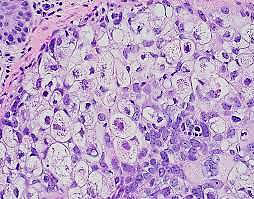
Identify?
Squamous cell carcinoma of the Conjunctiva and Cornea
N/E: Thickened well-demarcated leukoplakic lesion at the corneal limbus extending into the corneal center. M/P:
1.Replacement of the epithelium by atypical cells.
2.Mitoses are common.
3.Usually “insitu or intra-epithelial neoplasia”.
4.Occasionally invade deeper structures with central keratinization.
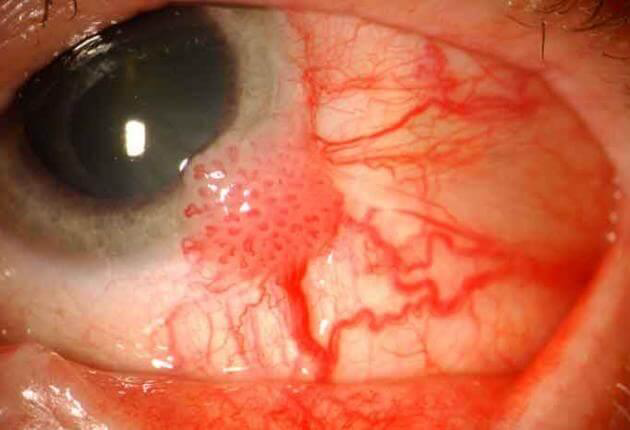
Identify?
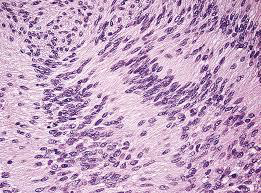
Acoustic neuroma of inner ear
M/P: Typically show a biphasic appearance with: Antoni A and Antoni B areas. Antoni A Areas: hypercellular areas with the pathognomonic Verocay Bodies Antoni B Areas: hypocellular areas of loose meshwork of Schwann cells.
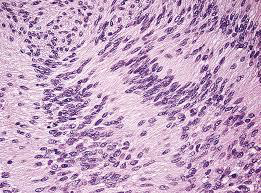
Identify?
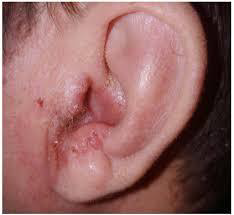
Acute diffuse otitis externa
Most commonly due to bacterial or fungal infections after minor trauma to the ear
Identify?
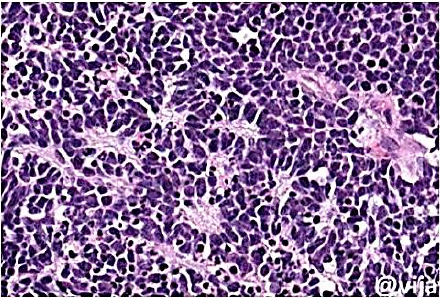
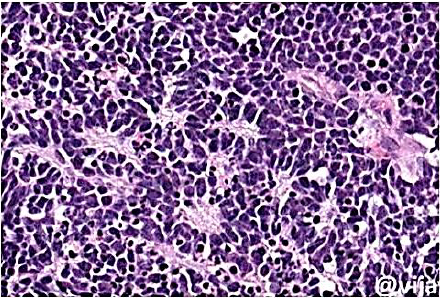
Retinoblastoma
M/P: The tumor is formed of undifferentiated retinal cells; that show characteristic rosettes which is of 2 types:
1.Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes (around a lumen).
2.Homer-Wright rosettes (around neuri-fibrillary structure). Shown n this picture
Identify?
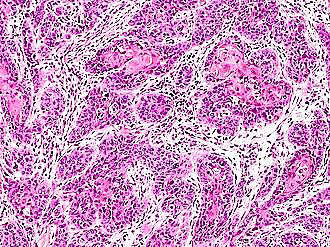
Squamous cell carcinoma of the Conjunctiva and Cornea
N/E: Thickened well-demarcated leukoplakic lesion at the corneal limbus extending into the corneal center. M/P:
1.Replacement of the epithelium by atypical cells.
2.Mitoses are common.
3.Usually “insitu or intra-epithelial neoplasia”.
4.Occasionally invade deeper structures with central keratinization.
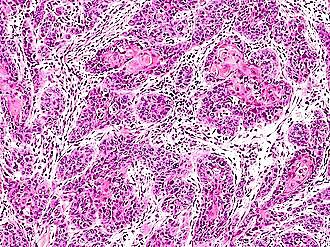
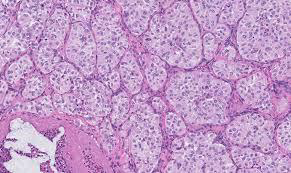
Identify?
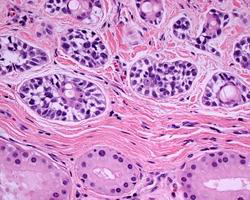
Cerumen-gland adenoma
Composed of glands lined by 2 layers of cells;
-Inner luminal layer of cuboidal cells.
-Outer layer of myoepithelial cells.
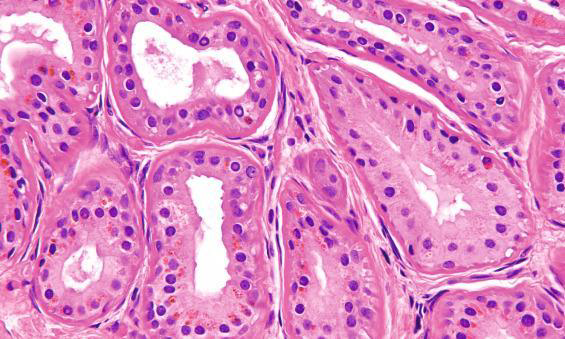
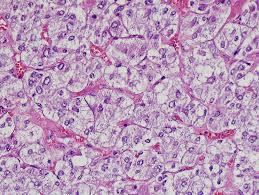
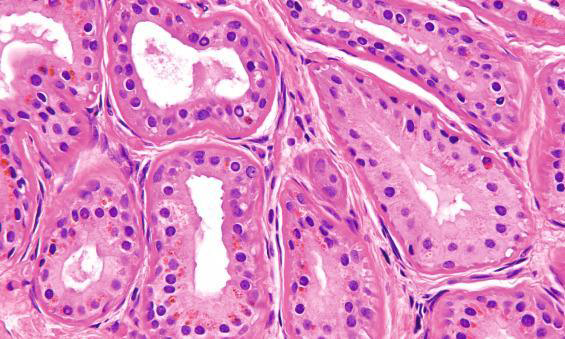
Identify?
Jugular para-ganglioma of middle ear
M/P:
1.Classic nests called “zellballen”; the central cells are rounded with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm.
2.Sustentacular cells are flat cells & present at the periphery of the nests.
3.Prominent fibrovascular stroma separates the nests.
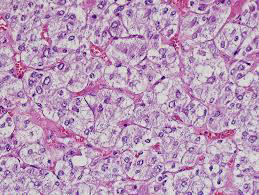
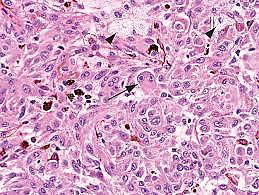
Identify?
Uveal malignant melanoma
N/E: Dom-shaped pigmented mass. M/P: The epithelioid variant Larger irregular pleomorphic cells with larger nuclei and abundant acidophilic cytoplasm; that may contain melanin pigment.