Ch 5 - Supply
Supply: the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to supply at different prices in a given time period
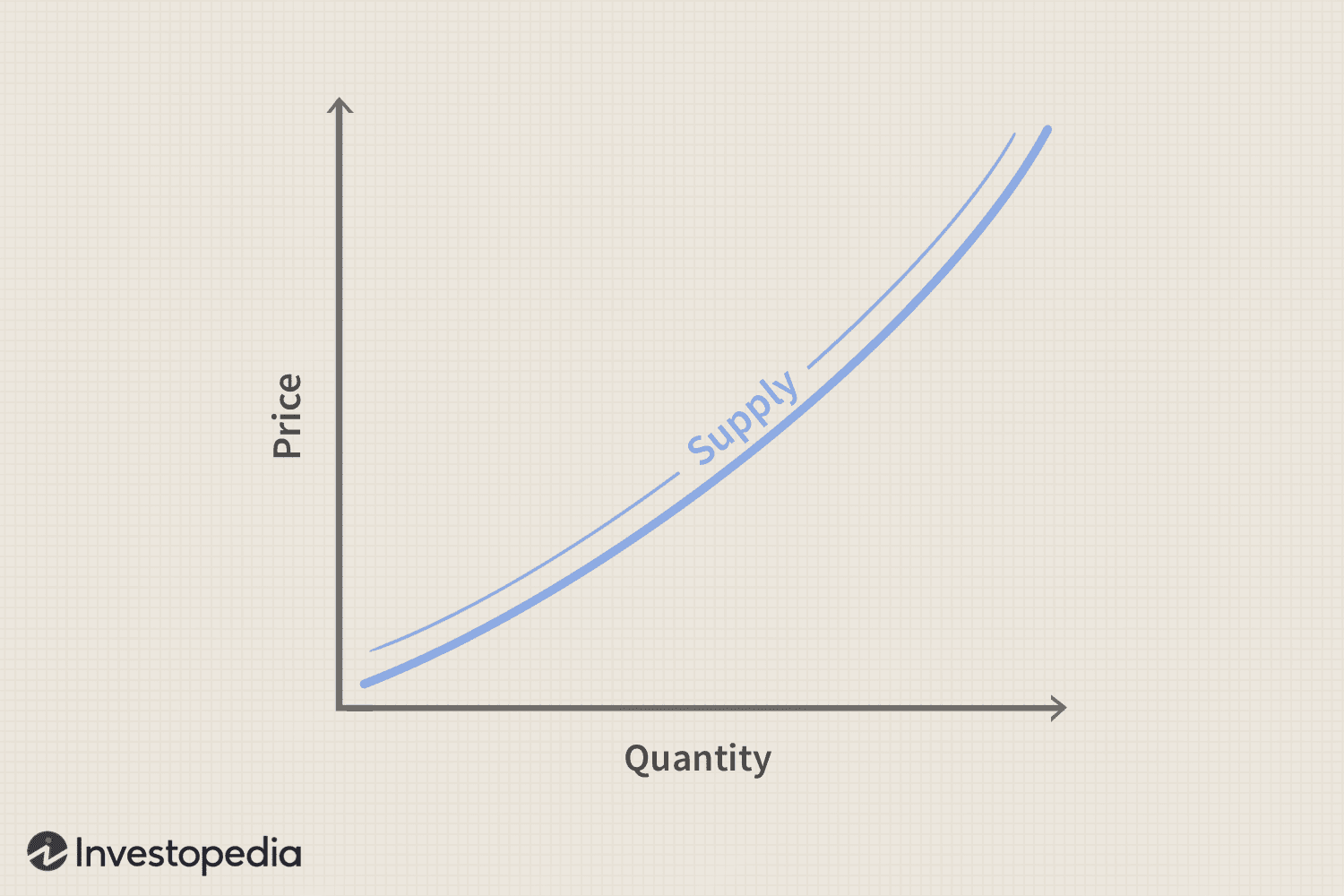
Law of supply: as the price of a product rises, the quantity supplied of the product will eventually increase
- The supply curve normally slopes upwards
- Price rises but costs don't change → profitability increases → supply more
Supply curve: represents the relationship between the price and the quantity supplied of a product
Non-price determinants of supply:
- Changes in factors of production: (supply shifts to left) → land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship
- Improvements in tech (supply shifts to the right)
- Expectations: supply increases if product is expected to gain profit
- Indirect taxes → increase costs → supply shifts left
- Competition: if another product is produced with higher profit, supply for existing product decreases
- Subsidies → reduce costs → supply shifts right
- More firms → supply shifts to the right → more being supplied at each price level
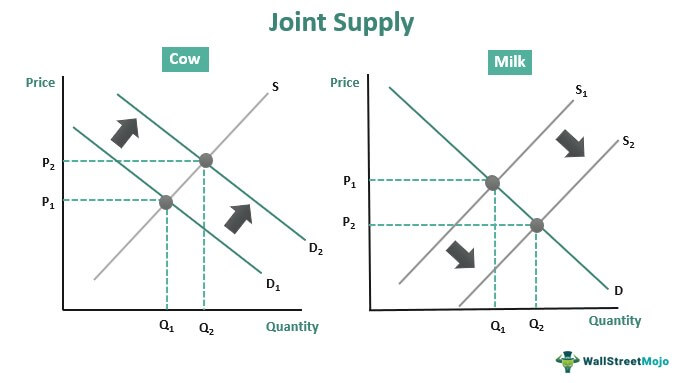
Joint supply:
The law of diminishing marginal returns: as more variable factors are added to a given quantity fixed factors, holding tech constant, marginal product eventually drops
Fixed factor: employment remains constant
Variable factor : employment increases as output increases
Short run: period with fixed + variable factors
- firms can expand output by employing variable factors only
Long run: period when all factors are variable
- firms can expand output by increasing the use of all factors
Marginal Product (MP): change in total product as a result of change in input
- Formula: MP of the nth unit = TP of n units - TP of (n-1) units
- MP = △TP /△V
Why does this happen?
- Workers fully utilise fixed factors initially so MP rises
- when more workers are added, too many workers relative to the amount of fixed factors, MP eventually drops
Total product: total output that a firm producers using variable and fixed factors in a given time period
Average product: output that is produced, an average, by each unit of the variable factors
- Formula: AP = TPV
Rules:
- As supply increases, price decreases, and demand increases
- As supply decreases, price increases, and demand decreases