NEUROLEC_BRAINSTEM
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What makes up the brain stem (stalk-like shape)?
Medulla Oblongata
Pons
Midbrain
Occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull
Broad Functions of Brainstem
It serves as a conduit for the ______ tracts and _____ tracts connecting the spinal cord to the different parts of the higher centers in the forebrain
It contains important reflex centers associated with the control of _____ and the _____ system and with the control of ______
It contains the important nuclei of CNs ____ through ___.
It serves as a conduit for the ascending tracts and descending tracts connecting the spinal cord to the different parts of the higher centers in the forebrain
It contains important reflex centers associated with the control of respiration and the cardiovascular system and with the control of consciousness
It contains the important nuclei of CNs III through XII.
Medulla Oblongata GROSS
connects the ______ superiorly with the _____ inferiorly
Medulla and spinal cord junction is at the origin of the anterior and posterior roots of the _______ spinal nerve at level of foramen magnum
The central canal of the spinal cord continues upward Into the _____ half of the medulla; In the upper half of the medulla, It expands as the cavity of the _______ ventricle
connects the pons superiorly with the spinal cord inferiorly
Medulla and spinal cord junction is at the origin of the anterior and posterior roots of the C1 spinal nerve at level of foramen magnum
The central canal of the spinal cord continues upward Into the lower half of the medulla; In the upper half of the medulla, It expands as the cavity of the fourth ventricle
Medulla Oblongata ANTERIOR SURFACE
The ____________ , is continuous inferiorly with the anteromedian fissure of the spinal cord.
Swellings on each side of the median fissure are called the _______.
Composed of bundles of nerve fibers, called ______ fibers, which arise from the precentral gyrus of the cerebral cortex.
Crosses over to the opposite side inferiorly forming the ___________
_____ are oval elevations produced by the underlying Inferior olivary nuclei
In the groove between the pyramid and the olive emerge the rootlets of the ______ nerve.
Posterior to the olives are the _____ cerebellar peduncles, which connect the medulla to the cerebellum
In the groove between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle emerge the roots of the ______ and ____ nerves and the ______ portion of the accessory nerve.
The anterior median fissure, is continuous inferiorly with the anteromedian fissure of the spinal cord.
Swellings on each side of the median fissure are called the pyramids.
Composed of bundles of nerve fibers, called corticospinal fibers, which arise from the precentral gyrus of the cerebral cortex.
Crosses over to the opposite side inferiorly forming the decussation of pyramids
Olives are oval elevations produced by the underlying Inferior olivary nuclei
In the groove between the pyramid and the olive emerge the rootlets of the hypoglossal nerve.
Posterior to the olives are the inferior cerebellar peduncles, which connect the medulla to the cerebellum
In the groove between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle emerge the roots of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves and the cranial roots of the accessory nerve.
Medulla Oblongata POSTERIOR SURFACE
The posterior surface of the superior half of the medulla oblongata forms the lower part of the floor of the ______ ventricle.
The posterior surface of the inferior half of the medulla is continuous with the posterior aspect of the spinal cord and possesses a __________ .
On each side of the median sulcus. an elongated swelling, __________, is produced by the underlying gracile nucleus.
Lateral to the gracile tubercle is a similar swelling, the _______ tubercle, produced by the underlying cuneate nucleus.
The posterior surface of the superior half of the medulla oblongata forms the lower part of the floor of the fourth ventricle.
The posterior surface of the inferior half of the medulla is continuous with the posterior aspect of the spinal cord and possesses a posterior median sulcus.
On each side of the median sulcus. an elongated swelling, the gracile tubercle, is produced by the underlying gracile nucleus.
Lateral to the gracile tubercle is a similar swelling, the cuneate tubercle, produced by the underlying cuneate nucleus.
Internal Structure of MO → 4 levels
Level of decussation of _______
Level of decussation of _____
Level of the ______
Level just inferior to the _____.
Level of decussation of pyramids,
Level of decussation of lemnisci
Level of the olives
Level just inferior to the pons.
MO: Level of Pyramid Decussation
A transverse section through the inferior half of the medulla oblongata passes through the decussation of the pyramids, the ________________.
In the superior part of the medulla, the _______ fibers occupy and form the pyramid, but inferiorly, about ¾ of the fibers cross the median plane and continue down in the lateral white column as the _________ tract.
As these fibers cross the midline, they sever the continuity between the anterior column of the gray matter of the spinal cord and the gray matter that surrounds the central canal.
A transverse section through the inferior half of the medulla oblongata passes through the decussation of the pyramids, the great motor decussation.
In the superior part of the medulla, the corticospinal fibers occupy and form the pyramid, but inferiorly, about ¾ of the fibers cross the median plane and continue down in the lateral white column as the lateral corticospinal tract.
As these fibers cross the midline, they sever the continuity between the anterior column of the gray matter of the spinal cord and the gray matter that surrounds the central canal.
MO: Level of Pyramid Decussation
The__________ and the________ continue to ascend superiorly posterior to the central gray matter. The _______and the _______ appear as posterior extensions of the central gray matter.
The substantia gelatinosa in the posterior gray column of the spinal cord becomes continuous with the Inferior end of the nucleus of the spinal tract of the ________ nerve.
The lateral and anterior white columns of the spinal cord are easily identified In these sections, and their fiber arrangement is unchanged.
The fasciculus gracilis and the fasciculus cuneatus continue to ascend superiorly posterior to the central gray matter. The nucleus gracilis and the nucleus cuneatus appear as posterior extensions of the central gray matter.
The substantia gelatinosa in the posterior gray column of the spinal cord becomes continuous with the Inferior end of the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve.
The lateral and anterior white columns of the spinal cord are easily identified In these sections, and their fiber arrangement is unchanged.
MO: Level of lemnisci Decussation
A transverse section through the Inferior half of the medulla oblongata, a short distance above the level of the decussation of the pyramids, passes through the decussation of lemnisci, the ____________
The decussation of the lemnisci takes place anterior to the central gray matter and posterior to the pyramids. The lemnisci have been formed through the _______ fibers, which have emerged from the anterior aspects of the nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus.
The internal arcuate fibers first travel anteriorly and laterally around the central gray matter. They then curve medially toward the midline, where they decussate with the corresponding fibers of the opposite side.
A transverse section through the Inferior half of the medulla oblongata, a short distance above the level of the decussation of the pyramids, passes through the decussation of lemnisci, the great sensory decussation
.The decussation of the lemnisci takes place anterior to the central gray matter and posterior to the pyramids. The lemnisci have been formed through the Internal arcuate fibers, which have emerged from the anterior aspects of the nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus.
The internal arcuate fibers first travel anteriorly and laterally around the central gray matter. They then curve medially toward the midline, where they decussate with the corresponding fibers of the opposite side.
MO: Level of lemnisci Decussation
The nucleus of the spinal tract of the _______ nerve lies lateral to the internal arcuate fibers. The ______ tract of the trigeminal nerve lies lateral to the nucleus.
The lateral and anterior _______ tracts and the ______ tracts occupy an area lateral to the decussation of the lemnisci.
They are very close to one another and collectively are known as the ________ .
The _______, _______, and the _____ tracts are situated In the anterolateral region of the medulla oblongata.
The nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve lies lateral to the internal arcuate fibers. The spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve lies lateral to the nucleus.
The lateral and anterior spinothalamic tracts and the spinotectal tracts occupy an area lateral to the decussation of the lemnisci. They are very close to one another and collectively are known as the spinal lemniscus. The spinocerebellar, vestibulospinal, and the rubrospinal tracts are situated In the anterolateral region of the medulla oblongata.
MO: Level of the Olives
A transverse section through the olives passes across the Inferior part of the fourth ventricle . The amount of gray matter has Increased at this level owing to the presence of the olivary nuclear complex; the nuclei of the vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, and hypoglossal nerves; and the arcuate nuclei.
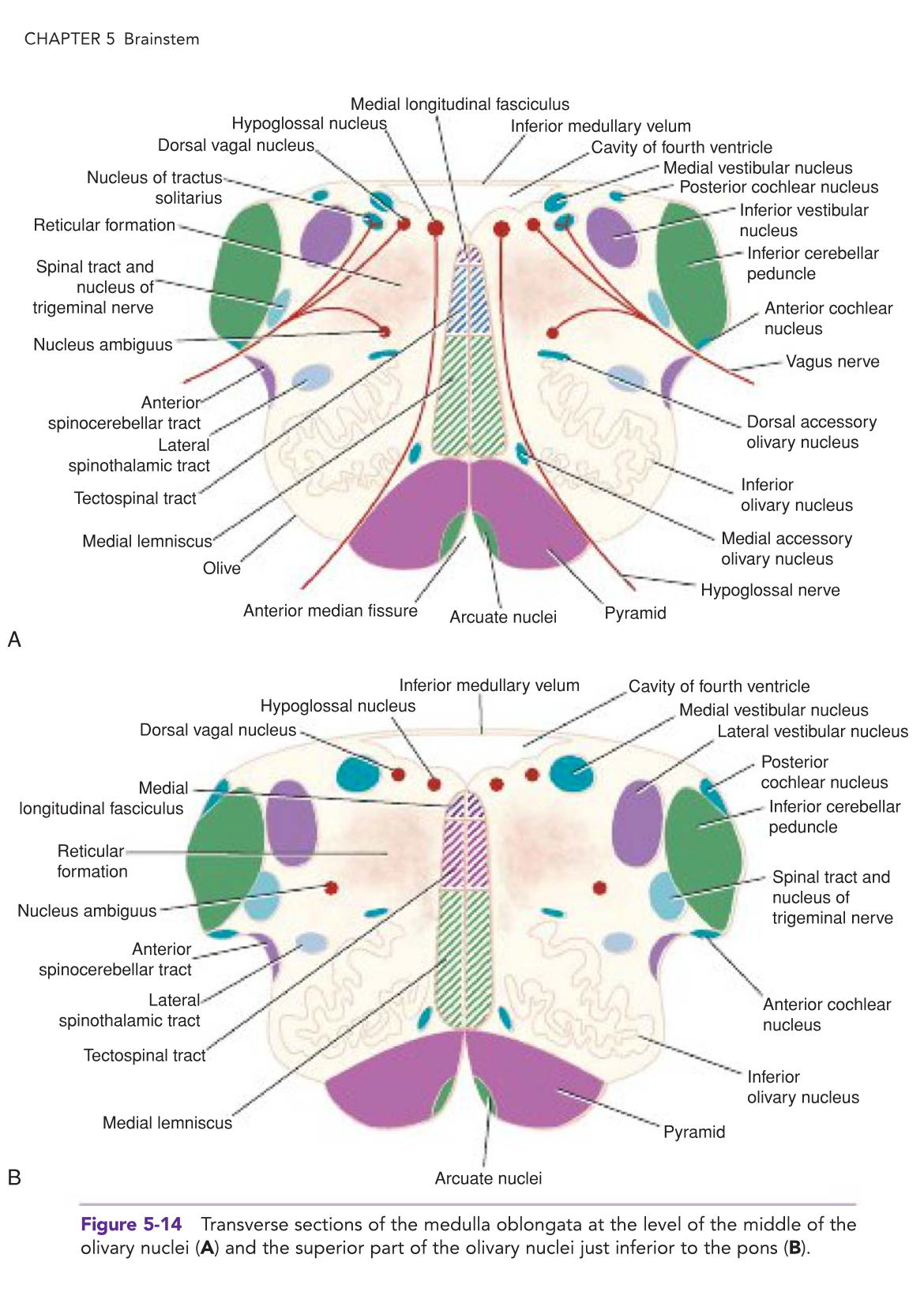
MO: Level of the Olives → Olivary Nuclear Complex
Largest nucleus of this complex is the ____________.
A gray matter , shaped like a crumpled bag with its mouth directed medially
Responsible for Olive
Smaller dorsal and medial accessory olivary nuclei also are present. The cells of the inferior olivary nucleus send fibers medially across the midline to enter the cerebellum through the Inferior cerebellar peduncle.
Afferent fibers reach the inferior olivary nuclei from the spinal cord (the spino-olivary tracts) and from the cerebellum and cerebral cortex. The function of the olivary nuclei is associated with __________ movement.
Largest nucleus of this complex is the lnferior olivary nucleus.
A gray matter , shaped like a crumpled bag with its mouth directed medially
Responsible for Olive
Smaller dorsal and medial accessory olivary nuclei also are present. The cells of the inferior olivary nucleus send fibers medially across the midline to enter the cerebellum through the Inferior cerebellar peduncle.
Afferent fibers reach the inferior olivary nuclei from the spinal cord (the spino-olivary tracts) and from the cerebellum and cerebral cortex. The function of the olivary nuclei is associated with voluntary muscle movement.
MO: Level of the Olives → Vestibulocochlear Nuclei
Made up of 4 nuclei:
(1) ____ vestibular nucleus,
(2) ____ vestibular nucleus,
(3) ____ vestibular nucleus
(4) ____ vestibular nucleus.
(1) medial vestibular nucleus,
(2) Inferior vestibular nucleus,
(3) lateral vestibular nucleus
(4) superior vestibular nucleus.
MO: Level of the Olives → Vestibulocochlear Nuclei
The 2 cochlear nuclei are the _________ nucleus, situated on the anterolateral aspect of the Inferior cerebellar peduncle
__________ nucleus, situated on the posterior aspect of the peduncle lateral to the floor of the fourth ventricle
The 2 cochlear nuclei are the anterior cochlear nucleus, situated on the anterolateral aspect of the Inferior cerebellar peduncle
Posterior cochlear nucleus, situated on the posterior aspect of the peduncle lateral to the floor of the fourth ventricle
MO: Level of the Olives → __________
Consists of large motor neurons and is situated deep within the reticular formation
The emerging nerve fibers join the _______, ____, and _____ part of the accessory nerve and are distributed to voluntary skeletal muscle.
Nucleus Ambiguus
glossopharyngeal, vagus, and cranial part of the accessory nerve → voluntary skeletal muscles
MO: Level of the Olives → Central Gray Matter
The central gray matter lies beneath the floor of the. _______ ventricle at this level .
Passing from MEDIAL to LATERAL the following important structures may be recognized:
(1) ________ nucleus
(2) dorsal nucleus of the ______
3) nucleus of the________
(4) ______ and _______ vestibular nuclei
The central gray matter lies beneath the floor of the fourth ventricle at this level .
Passing from MEDIAL to LATERAL the following important structures may be recognized:
(1) hypoglossal nucleus
(2) dorsal nucleus of the vagus
3) nucleus of the tractus solitarius
(4) medial and inferior vestibular nuclei
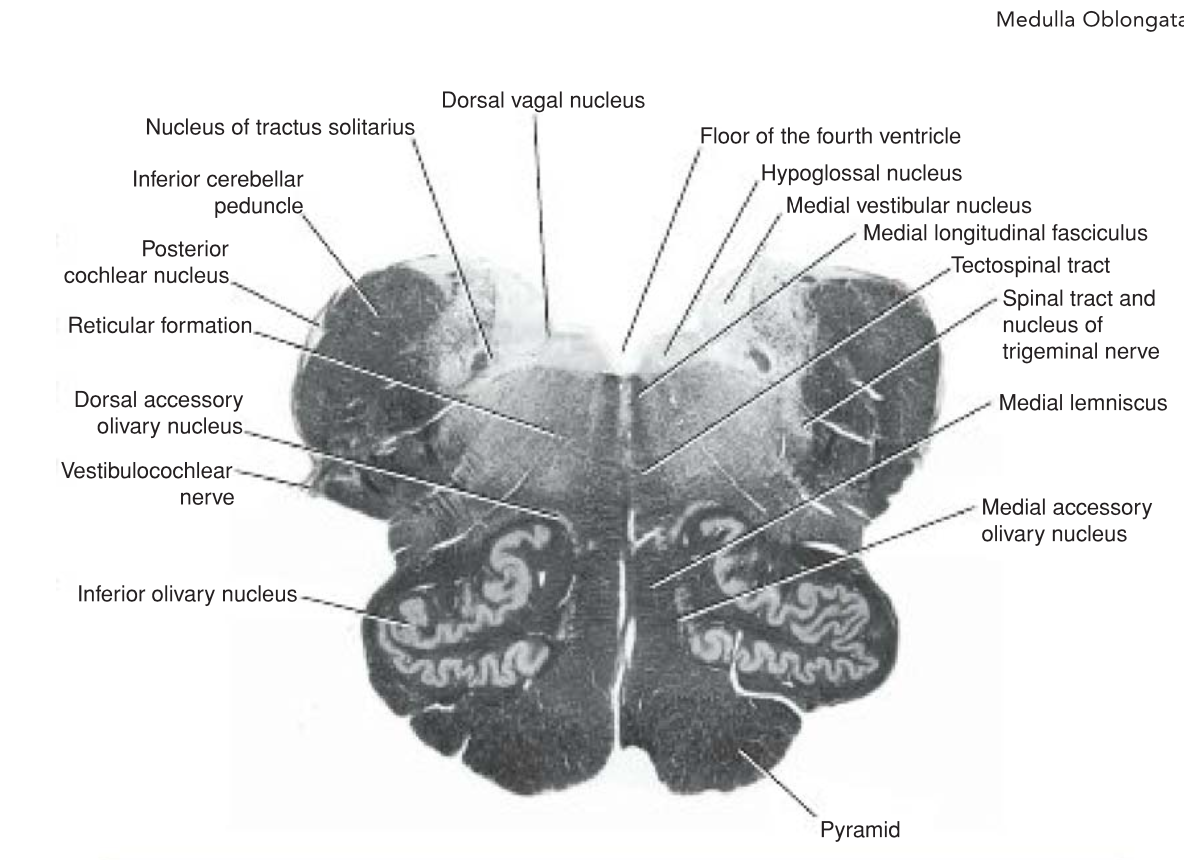
MO: Level of the Olives → Central Gray Matter
The _________ are thought to be inferiorly displaced pontine nuclei and are situated on the anterior surface of the pyramids.
They receive nerve fibers from the cerebral cortex and send efferent fibers to the cerebellum through the ________ fibers.
The pyramids containing the corticospinal and some corticonuclear fibers are situated in the anterior part of the medulla separated by the anterior median fissure
the _______ fibers descend to the spinal cord
the _______ fibers are distributed to the motor nuclei of the CNs situated within the medulla.
The arcuate nuclei are thought to be inferiorly displaced pontine nuclei and are situated on the anterior surface of the pyramids.
They receive nerve fibers from the cerebral cortex and send efferent fibers to the cerebellum through the anterior external arcuate fibers.
The pyramids containing the corticospinal and some corticonuclear fibers are situated in the anterior part of the medulla separated by the anterior median fissure; the corticospinal fibers descend to the spinal cord, and the corticonuclear fibers are distributed to the motor nuclei of the CNs situated within the medulla.
MO: Level of the Olives → Central Gray Matter
The ________ forms a flattened tract on each side of the midline posterior to the pyramid.
These fibers emerge from the decussation of the lemnisci and convey sensory information to the ______.
The ____________ forms a small tract of nerve fibers situated on each side of the midline posterior to the medial lemniscus and anterior to the hypoglossal nucleus. It consists of ascending and descending fibers.
The medial lemniscus forms a flattened tract on each side of the midline posterior to the pyramid.
These fibers emerge from the decussation of the lemnisci and convey sensory information to the thalamus.
The medial longitudinal fasciculus forms a small tract of nerve fibers situated on each side of the midline posterior to the medial lemniscus and anterior to the hypoglossal nucleus. It consists of ascending and descending fibers.
MO: Level of the Olives → Central Gray Matter
The ____________r peduncle is situated in the posterolateral corner of the section on the lateral side of the fourth ventricle.
The spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve and Its nucleus are situated on the _________ aspect of the Inferior cerebellar peduncle.
The Inferior cerebellar peduncle is situated in the posterolateral corner of the section on the lateral side of the fourth ventricle.
The spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve and Its nucleus are situated on the anteromedial aspect of the Inferior cerebellar peduncle.
MO: Level of the Olives → Central Gray Matter
The ______________ tract is situated near the surface In the Interval between the Inferior olivary nucleus and the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve.
The __________, consisting of the anterior spinothalamic, lateral spinothalamic, and spinotectal tracts, Is deeply placed
The _________ , consisting of a diffuse mixture of nerve fibers and small groups of nerve cells, is deeply placed posterior to the olivary nucleus.
The reticular formation represents, at this level, only a small part of this system, which is also present in the pons and midbrain.
The anterior spinocerebellar tract is situated near the surface In the Interval between the Inferior olivary nucleus and the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve.
The spinal leminiscus, consisting of the anterior spinothalamic, lateral spinothalamic, and spinotectal tracts, Is deeply placed
The reticular formation, consisting of a diffuse mixture of nerve fibers and small groups of nerve cells, is deeply placed posterior to the olivary nucleus. The reticular formation represents, at this level, only a small part of this system, which is also present in the pons and midbrain.
MO: Level of the Olives → Central Gray Matter
The ________, ______, and ______ part of the ______ nerves can be seen running forward and laterally through the reticular formation.
The nerve fibers emerge between the olives and the Inferior cerebellar peduncles.
The ________ nerves also run anteriorly and laterally through the reticular formation and emerge between the pyramids and the olives.
The glossopharyngeal, vagus, and cranial part of the accessory nerves can be seen running forward and laterally through the reticular formation.
The nerve fibers emerge between the olives and the Inferior cerebellar peduncles.
The hypoglossal nerves also run anteriorly and laterally through the reticular formation and emerge between the pyramids and the olives.
MO: Level Just Inferior to the Pons
Here the ________ nucleus has replaced the Inferior vestibular nucleus, and the cochlear nuclei now are visible on the _____ and ____ surfaces of the ______ cerebellar peduncle.
Here the lateral vestibular nucleus has replaced the Inferior vestibular nucleus, and the cochlear nuclei now are visible on the anterior and posterior surfaces of the Inferior cerebellar peduncle.
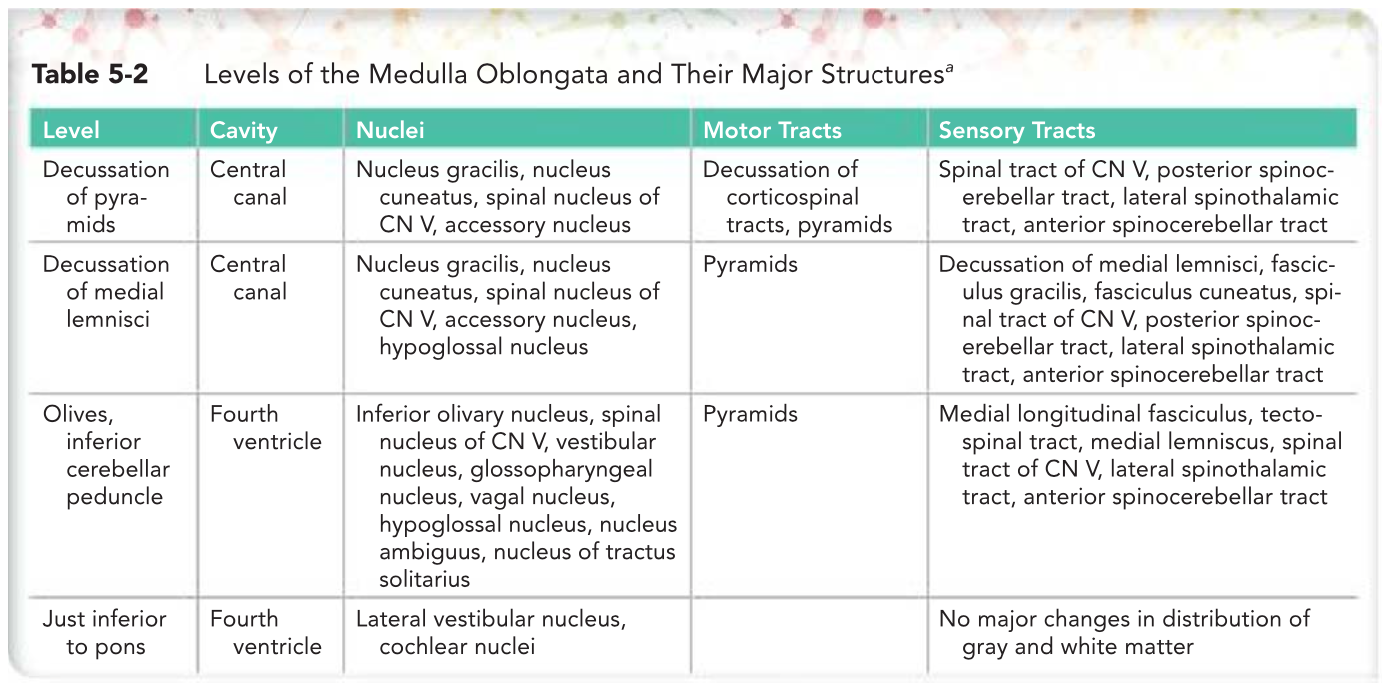
Levels of the Medulla Oblongata and Their Major Structures•
Pons
________ to the cerebellum
connects the ________ to the ______
bridge connecting the ____ and _____ cerebellar ______.
Anterior to the cerebellum
connects the medulla oblongata to the midbrain
bridge connecting the right and left cerebellar hemispheres.
Pons Anterior Surface
convex from side to side and shows many transverse fibers that converge on each side to form the middle cerebellar peduncle
A shallow groove in the midline, the _____ groove, lodges the basilar artery.
On the anterolateral surface of the pons, the ______ nerve emerges on each side.
Each nerve consists of a smaller, medial part, known as the ____ root, and a larger, lateral part, known as the ____ root.
In the groove between the pons and the medulla oblongata., from medial to lateral, the ______, _____ and ________ nerves emerge.
convex from side to side and shows many transverse fibers that converge on each side to form the middle cerebellar peduncle
A shallow groove in the midline, the basilar groove, lodges the basilar artery.
On the anterolateral surface of the pons, the trigeminal nerve emerges on each side.
Each nerve consists of a smaller, medial part, known as the motor root, and a larger, lateral part, known as the sensory root.
In the groove between the pons and the medulla oblongata., from medial to lateral, the abducens, facial and vestibulocochlear nerves emerge.
Pons Posterior Surface
It forms the upper half of the floor of the _____ ventricle and Is triangular In shape
The posterior surface Is limited laterally by the _____ cerebellar peduncles and Is divided Into symmetrical halves by a _______.
Lateral to this sulcus is an elongated elevation, the ______, which is bounded laterally by a sulcus, the _________.
The inferior end of the medial eminence Is slightly expanded to form the _________, which is produced by the root of the facial nerve winding around the nucleus of the abducens nerve
It forms the upper half of the floor of the fourth ventricle and Is triangular In shape
The posterior surface Is limited laterally by the superior cerebellar peduncles and Is divided Into symmetrical halves by a median sulcus.
Lateral to this sulcus is an elongated elevation, the medial eminence, which is bounded laterally by a sulcus, the sulcus limitans.
The inferior end of the medial eminence Is slightly expanded to form the facial colliculus, which is produced by the root of the facial nerve winding around the nucleus of the abducens nerve
Pons Posterior Surface
The floor of the superior part of the sulcus limitans is bluish-gray in color and is called the __________ ; it owes its color to a group of deeply pigmented nerve cells.
Lateral to the sulcus limitans is the _______ produced by the underlying vestibular nuclei
The floor of the superior part of the sulcus limitans is bluish-gray in color and is called the substantia ferruginea ; it owes its color to a group of deeply pigmented nerve cells.
Lateral to the sulcus limitans is the area vestibuli produced by the underlying vestibular nuclei
PONS Internal Structure
Pons is commonly divided into a posterior part, the _________. and an anterior basal part by the transversely running fibers of the ________.
Pons is commonly divided into a posterior part, the tegmentum. and an anterior basal part by the transversely running fibers of the trapezoid body.
PONS Transverse Section Through the Caudal Part
The ________ rotates as it passes from the medulla into the pons. It is situated in the most anterior part of the tegmentum, with its long axis running transversely.
The medial lemniscus is accompanied by the spinal and lateral lemnisci.
The ________ lies posterior to the lateral part of the medial lemniscus.
The fibers of the facial nerve wind around the nucleus of the _________ nerve, producing the facial colliculus.
The fibers of the facial nerve then pass anteriorly between the facial nucleus and the superior end of the nucleus of the spinal tract of the ________ nerve.
Medial lemniscus rotates as it passes from the medulla into the pons. It is situated in the most anterior part of the tegmentum, with its long axis running transversely.
The medial lemniscus is accompanied by the spinal and lateral lemnisci.
The facial nucleus lies posterior to the lateral part of the medial lemniscus. The fibers of the facial nerve wind around the nucleus of the abducens nerve, producing the facial colliculus. The fibers of the facial nerve then pass anteriorly between the facial nucleus and the superior end of the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trlgemlnal nerve.
PONS Transverse Section Through the Caudal Part
The ______________ is situated beneath the floor of the fourth ventricle on either side of the midline. It is the main pathway that connects the vestibular and cochlear nuclei with the nuclei controlling the extra-ocular muscles {oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nuclei).
The medial longitudinal fasciculus is situated beneath the floor of the fourth ventricle on either side of the midline. It is the main pathway that connects the vestibular and cochlear nuclei with the nuclei controlling the extra-ocular muscles {oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nuclei).
PONS Transverse Section Through the Caudal Part
The _________ nucleus Is situated lateral to the abducens nucleus and is in close relationship to the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
The superior part of the lateral and the inferior part of the superior vestibular nucleus are found at this level.
The posterior and anterior cochlear nuclei are also found at this level.
The medial vestibular nucleus Is situated lateral to the abducens nucleus and is in close relationship to the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
The superior part of the lateral and the inferior part of the superior vestibular nucleus are found at this level.
The posterior and anterior cochlear nuclei are also found at this level.
PONS Transverse Section Through the Caudal Part
The spinal nucleus of the _______ and its tract lie on the anteromedial aspect of the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
The _________ Is made up of fibers derived from the cochlear nuclei and the nuclei of the trapezoid body.
They run transversely In the anterior part of the tegmentum.
The spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve and its tract lie on the anteromedial aspect of the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
The trapezoid body Is made up of fibers derived from the cochlear nuclei and the nuclei of the trapezoid body. They run transversely In the anterior part of the tegmentum.
PONS Transverse Section Through the Caudal Part
The basilar part of the pons, at this level, contains small masses of nerve cells called ____________.
The corticopontine fibers of the _______ of the midbrain terminate in the pontine nuclei.
The axons of these cells give origin to the transverse fibers of the _______, which cross the midline and intersect the corticospinal and corticonuclear tracts, breaking them up into small bundles.
The transverse fibers of the pons enter the _____ cerebellar peduncle and are distributed to the cerebellar hemisphere. This connection forms the main pathway linking the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum.
The basilar part of the pons, at this level, contains small masses of nerve cells called pontine nuclei.
The corticopontine fibers of the crus cerebri of the midbrain terminate in the pontine nuclei.
The axons of these cells give origin to the transverse fibers of the pons, which cross the midline and intersect the corticospinal and corticonuclear tracts, breaking them up into small bundles.
The transverse fibers of the pons enter the middle cerebellar peduncle and are distributed to the cerebellar hemisphere. This connection forms the main pathway linking the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum.
PONS Transverse Section Through the Cranial Part
The _____ nucleus of the _______ nerve is situated beneath the lateral part of the 4th ventricle within the reticular formation .
The emerging motor fibers travel anteriorly through the substance of the pons and exit on its anterior surface.
The _________ nucleus of the _______ nerve is situated on the lateral side of the motor nucleus
it is continuous inferiorly with the nucleus of the spinal tract.
The entering sensory fibers travel through the substance of the pons and lie lateral to the motor fiber
The motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve is situated beneath the lateral part of the 4th ventricle within the reticular formation .
The emerging motor fibers travel anteriorly through the substance of the pons and exit on its anterior surface.
The principal sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve is situated on the lateral side of the motor nucleus
it is continuous inferiorly with the nucleus of the spinal tract.
The entering sensory fibers travel through the substance of the pons and lie lateral to the motor fibers
The Superior cerebellar peduncle is situated posterolateral to the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve. It is joined by the anterior spinocerebellar tract
PONS Transverse Section Through the Cranial Part
The _______ cerebellar peduncle is situated posterolateral to the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve. It is joined by the ________ spinocerebellar tract
The trapezoid body and the medial lemniscus are situated In the same position as they were in the previous section.
The _______ and _________ lemnisci at the lateral extremity of the medial lemniscus
The Superior cerebellar peduncle is situated posterolateral to the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve. It is joined by the anterior spinocerebellar tract
The trapezoid body and the medial lemniscus are situated In the same position as they were in the previous section.
The lateral and spinal lemnisci at the lateral extremity of the medial lemniscus
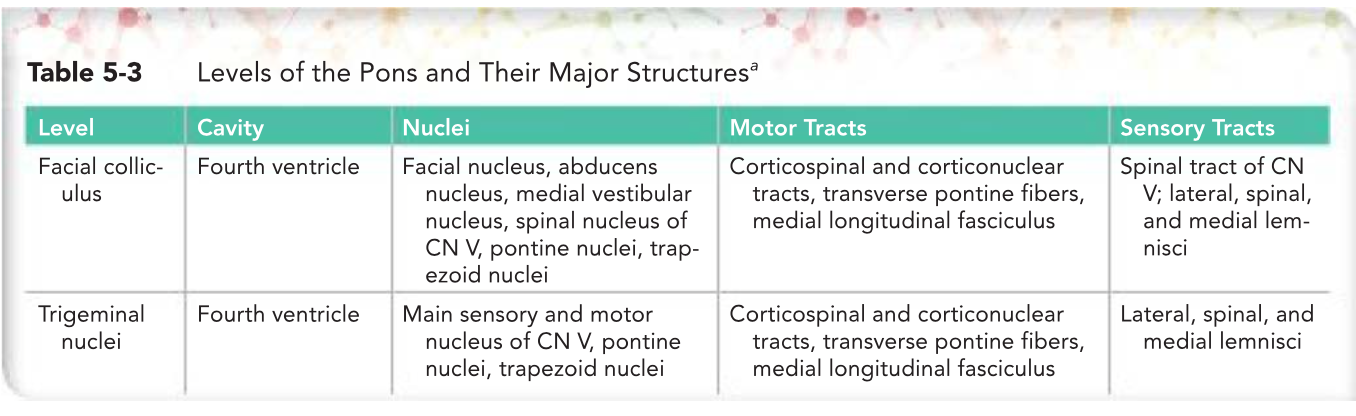
Levels of the Pons and Their Major Structures
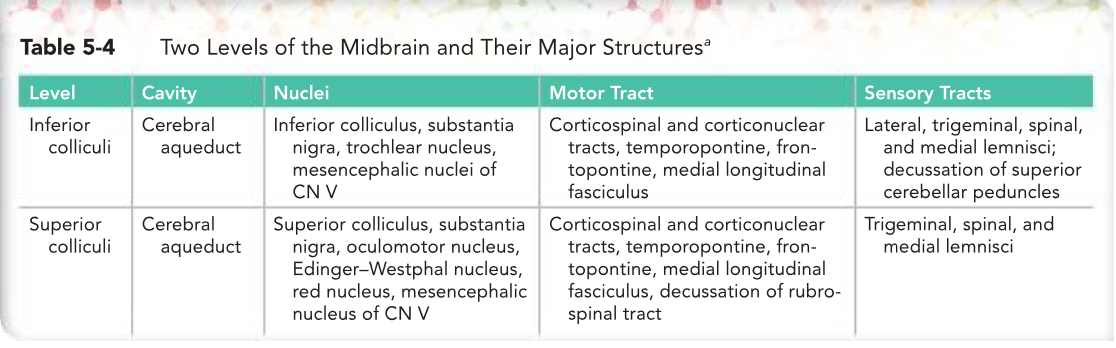
MIDBRAIN
connects the _____ and ______ with the _____
Its long axis inclines anteriorly as it ascends through the opening in the ______ _______.
The midbrain is traversed by a narrow channel, the ______ ______, which ls filled with cerebrospinal fluid
connects the pons and cerebellum with the forebrain
Its long axis inclines anteriorly as it ascends through the opening in the tentorium cerebelli.
The midbrain is traversed by a narrow channel, the cerebral aqueduct, which ls filled with cerebrospinal fluid
MIDBRAIN POSTERIOR SURFACE
On the posterior surface are four colliculi (____________).
These are rounded eminences that are divided into superior and inferior pairs by a vertical and a transverse groove .
The superior colliculi are centers for ______ reflexes , and the inferior colliculi are lower ______ centers.
In the midline below the inferior colliculi, the _____ nerves emerge.
These are small-diameter nerves that wind around the lateral aspect of the midbrain to enter the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus.
On the posterior surface are four colliculi (corpora quadrigemina).
These are rounded eminences that are divided into superior and inferior pairs by a vertical and a transverse groove .
The superior colliculi are centers for visual reflexes , and the inferior colliculi are lower auditory centers.
In the midline below the inferior colliculi, the trochlear nerves emerge.
These are small-diameter nerves that wind around the lateral aspect of the midbrain to enter the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus.
MIDBRAIN LATERAL SURFACE
On the lateral aspect of the midbrain, the superior and inferior brachia ascend in an anterolateral direction.
The Superior brachium passes from the superior colliculus to the _____ geniculate body and the optic tract.
The Inferior brachium connects the inferior colliculus to the ______ geniculate body.
On the lateral aspect of the midbrain, the superior and inferior brachia ascend in an anterolateral direction.
The Superior brachium passes from the superior colliculus to the lateral geniculate body and the optic tract.
The Inferior brachium connects the inferior colliculus to the medial geniculate bod.y.
MIDBRAIN ANTERIOR SURFACE
a deep depression in the midline, the _______ fossa, is bounded on either side by the________.
Many small blood vessels perforate the floor of the interpeduncular fossa, and this region is termed the ____________ .
The _________ nerve emerges from a groove on the medial side of the crus cerebri and passes forward In the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus.
a deep depression in the midline, the interpeduncular fossa, is bounded on either side by the crus cerebri.
Many small blood vessels perforate the floor of the interpeduncular fossa, and this region is termed the posterior perforated substance .
The oculomotor nerve emerges from a groove on the medial side of the crus cerebri and passes forward In the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus.
MIDBRAIN INTERNAL STRUCTURE
Comprised of 2 lateral halves, called the _______ peduncles; each of these ls divided into
an anterior part → ________
and a posterior part → _________, by a pigmented band of gray matter, the ________ .
The narrow cavity of the midbrain is the________ which connects the third and fourth ventricles.
Comprised of 2 lateral halves, called the cerebral peduncles; each of these ls divided into
an anterior part → crus cerebri,
and a posterior part → tegmentum, by a pigmented band of gray matter, the substantia nigra.
The narrow cavity of the midbrain is the cerebral aqueduct, which connects the third and fourth ventricles.
MIDBRAIN INTERNAL STRUCTURE
The ________ is the part of the midbrain posterior to the cerebral aqueduct; it has four small surface swellings referred to previously
these are the 2 _____ and 2 _____ colliculi.
The cerebral aqueduct is lined by ependyma and is surrounded by the central gray matter.
On transverse sections of the midbrain, the ________ fossa can be seen to separate the crura cerebri, whereas the tegmentum is continuous across the median plane
The tectum is the part of the midbrain posterior to the cerebral aqueduct; it has four small surface swellings referred to previously; these are the 2 superior and 2 inferior colliculi.
The cerebral aqueduct is lined by ependyma and is surrounded by the central gray matter.
On transverse sections of the midbrain, the interpeduncular fossa can be seen to separate the crura cerebri, whereas the tegmentum is continuous across the median plane
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Inferior Colliculi
The __________ ,consisting of a large nucleus of gray matter, lies beneath the corresponding surface elevation and forms part of the auditory pathway.
It receives many of the terminal fibers of the lateral lemniscus.
The pathway then continues through the inferior brachium to the medial geniculate body.
The ________ ls situated In the central gray matter close to the median plane just posterior to the medial longitudinal fasciculus.
The emerging fibers of the trochlear nucleus pass laterally and posteriorly around the central gray matter and leave the midbrain just below the inferior colliculi.
The fibers of the trochlear nerve now decussate completely in the superior medullary velum.
Inferior colliculus
Trochlear nucleus
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Inferior Colliculi
The _________ nuclei of the ________ nerve are lateral to the cerebral aqueduct.
The decussation of the _____ cerebellar peduncles occupies the central part of the tegmentum anterior to the cerebral aqueduct.
The reticular formation is smaller than that of the pons and is situated lateral to the decussation.
The mesencephalic nuclei of the trigeminal nerve are lateral to the cerebral aqueduct. The decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles occupies the central part of the tegmentum anterior to the cerebral aqueduct.
The reticular formation is smaller than that of the pons and is situated lateral to the decussation.
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Inferior Colliculi
The medial lemniscus ascends _______ to the substantia nigra
the spinal and trigeminal lemnisci are situated ______ to the medial lemniscus.
The lateral lemniscus is located ______ to the trigeminal lemniscus.
The _________ is a large motor nucleus situated between the tegmentum, and the crus cerebri and is found throughout the midbrain.
The medial lemniscus ascends posterior to the substantia nigra
the spinal and trigeminal lemnisci are situated lateral to the medial lemniscus.
The lateral lemniscus is located posterior to the trigeminal lemniscus.
The substantia nigra is a large motor nucleus situated between the tegmentum, and the crus cerebri and is found throughout the midbrain.
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Inferior Colliculi
SN is composed of medium-size multipolar neurons that
possess inclusion granules of melanin pigment within their cytoplasm.
It is concerned with______ and is connected to the cerebral cortex, spinal cord, hypothalamus, and basal nuclei.
The ________ contains important descending tracts and is separated from the tegmentum by the substantia nigra.
The ______ and _____ fibers occupy the middle two thirds of the crus.
The ______ fibers occupy the medial part of the crus,
the _____ fibers occupy the lateral part of the crus
These descending tracts connect the cerebral cortex to the anterior gray column cells of the spinal cord, the CN nuclei, the pons, and the cerebellum
SN is composed of medium-size multipolar neurons that
possess inclusion granules of melanin pigment within their cytoplasm.
It is concerned with muscle tone and is connected to the cerebral cortex. spinal cord, hypothalamus, and basal nuclei.
The crus cerebri contains important descending tracts and is separated from the tegmentum by the substantia nigra.
The corticospinal and corticonuclear fibers occupy the middle two thirds of the crus.
The frontopontine fibers occupy the medial part of the crus,
the temporopontine fibers occupy the lateral part of the crus
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Superior Colliculi
The _________ , a large nucleus of gray matter that lies beneath the corresponding surface elevation, forms part of the visual reflexes.
It Is connected to the _____ geniculate body by the superior brachium.
It receives afferent fibers from the _____ nerve, the _____ cortex, and the _____ tract.
Efferent fibers form the __________ and _______ tracts, responsible for the reflex movements of the eyes, head, and neck in response to visual stimuli
he superior colliculus , a large nucleus of gray matter that lies beneath the corresponding surface elevation, forms part of the visual reflexes.
It Is connected to the lateral geniculate body by the superior brachium.
It receives afferent fibers from the optic nerve, the visual cortex, and the Spinotectal tract.
Efferent fibers form the tectospinal and tectobulbar tracts, responsible for the reflex movements of the eyes, head, and neck in response to visual stimuli
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Superior Colliculi
The afferent pathway for the light reflex ends in the ________ nucleus.
This is a small group of neurons situated close to the lateral part of the superior colliculus.
After relaying In the pretectal nucleus, the fibers pass to the parasympathetic nucleus of the oculomotor nerve (Edinger-Westphal nucleus).
The emerging fibers then pass to the _______ nerve.
The oculomotor nucleus Is situated in the central gray matter close to the median plane, Just posterior to the medial longitudinal fasciculus
pretectal
oculomotor
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Superior Colliculi
The _____, _____ and ______ lemnisci form a curved band posterior to the substantia nigra, but the lateral lemniscus does not extend superiorly to this level.
The ______ nucleus is a rounded mass of gray matter situated between the cerebral aqueduct and the substantia nigra.
Its reddish hue is due to its vascularity and the presence of an iron-containing pigment in the cytoplasm of many of its neurons.
The medial, spinal and trigeminal lemnisci form a curved band posterior to the substantia nigra, but the lateral lemniscus does not extend superiorly to this level.
The red nucleus is a rounded mass of gray matter situated between the cerebral aqueduct and the substantia nigra. Its reddish hue is due to its vascularity and the presence of an iron-containing pigment in the cytoplasm of many of its neurons.
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Superior Colliculi
Sensory fibers of the red nucleus from
(1) the cerebral cortex through the ________ fibers,
(2) the cerebellum through the _____ cerebellar peduncle,
(3) the _____ nucleus, _____ and ________ nuclei, ____ nigra, and _______ cord.
Sensory fibers of the red nucleus from
(1) the cerebral cortex through the corticospinal fibers,
(2) the cerebellum through the superior cerebellar peduncle,
(3) the lentiform nucleus, subthalamic and hypothalamic nuclei, substantia nigra, and spinal cord.
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Superior Colliculi
Motor fibers of the red nucleus pass to
(1) the spinal cord through the ________ tract (as this tract descends, it decussates)
(2) the reticular formation through the _______ tract,
(3) the ______
(4) the ______ nigra.
Motor fibers of the red nucleus pass to
(1) the spinal cord through the rubrospinal tract (as this tract descends, it decussates)
(2) the reticular formation through the rubroreticular tract,
(3) the thalamus
(4) the substantla nlgra.
Transverse Section of the Midbrain at the Level of the Superior Colliculi
________: situated in the tegmentum lateral and posterior to the red nucleus.
________ : contains the descending tracts → corticospinal, corticonuclear , and corticopontine fibers ~ that are present at the level of the Inferior colliculus
Reticular formation
Crus cerebri
Two Levels o f the Midbrain and Their Major Structures•
"The single most important thing for optimizing brain function is sleep."
yes 100%