Peds E2: Random questions
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
which ear infection typically follows a viral URI?
acute otitis media
what is the single best predictor of bronchiolitis severity?
O2 sat while feeding
what is the first line therapy for acute otitis externa?
topical otic abx
>6 months → ciprodex
>2 y/o → cortisporin
what is a classic clinical feature of AOE?
pulling on pinna/pressing on tragus causes pain
what organisms most commonly cause AOE?
pseudomonas
strep
staph
what are the 4 Ds of ear examination?
Discharge
Displacement
Discoloration
Deformity
what is the Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response (BAER) used to test?
tests neurologic function → ability to hear is inferred
"how well can baby hear?"
what is the otoacoustic emission (OAE) used to test?
tests cochlea function
"can baby hear?"
what degree of hearing loss does the Newborn hearing screening detect?
moderate/severe
not mild!
what is the MC acquired infection that causes SNHL?
meningitis
what is the MC congenital infection causing SNHL?
CMV
what medications are known to cause sensorineural hearing loss?
aminoglycosides
vancomycin
what are causes of congenital SN hearing loss?
infection → TORCH
hereditary
inner ear dysplasia
perilymph fistula
what is the typical degree of conductive hearing loss (CHL)?
20-60 dB and often treatable
conductive hearing loss has abnormal _____ conduction
air
BC>AC
hearing loss beginning after ____ years old has less language impact?
5
prior to 5 → all development can be delayed
which auditory test can distinguish CHL from SNHL?
visual reinforcement audiometry
which dx has risk factors of: exposure to cig smoke, craniofacial anomalies, drinking from bottle while lying flat?
AOM
what measures can a parent take to prevent AOM?
breastfeed x6 months
avoid bottle propping
reduce pacifier use after 6 months
which dx presents with erythematous tympanic membrane?
AOM
and bulging TM, air fluid level, diminished TM mobility, decreased hearing
what is the treatment for AOM?
amoxicillin or augmentin
when should you refer a pt with AOM to ENT?
>3 AOM episodes in less than 6 months
>4 episodes in a 12 month period with resolutions between
when should you consider tympanostomy tubes for recurrent/chronic OM?
>4 OM in 1 year
what are complications of AOM?
TM perforation
CHL
mastoiditis
cholesteatoma
what is the cause of serous otitis media?
URI causing serous effusion in middle ear
should you use abx to treat serous otitis media?
no
what is the clinical presentation of serous otitis media?
opacification of the TM or air-fluid level
appears as clear gray/yellow color behind TM and poor mobility of TM
what population is chronic recurrent OM common in?
young children and children with facial hypoplasia or deformities → cleft palate, down syndrome
in which dx does the TM appear white, thickened and scarred?
chronic recurrent otitis media → tx with tympanostomy tube
what condition consists of trapped epithelial tissue that grows beneath the surface of the membrane?
cholesteatoma → one of the most serious lesions of TM
patient who was recently treated for OM presents with complaints of pain, swelling, tenderness behind the ear. On PE, mastoid is red and tender with no pain on pinna displacement. what organism most likely caused this?
mastoiditis → pseudomonas is more commonly assoc. with recurrent OM/recently treated
other organisms for regular mastoiditis: S. pneumo, S. pyogenes, S. aureus
what is the most reliable exam for dx of mastoiditis?
CT
what is the tx for mastoiditis?
without recurrent AOM → unasyn
with recurrent AOM → zosyn
PCN allergy → vanco PLUS metronidazole
what are common causes for nasal congestion?
URI
Nasopharyngitis secondary to GERD
congenital
what is the cause of choanal atresisa?
blockage of nasal opening
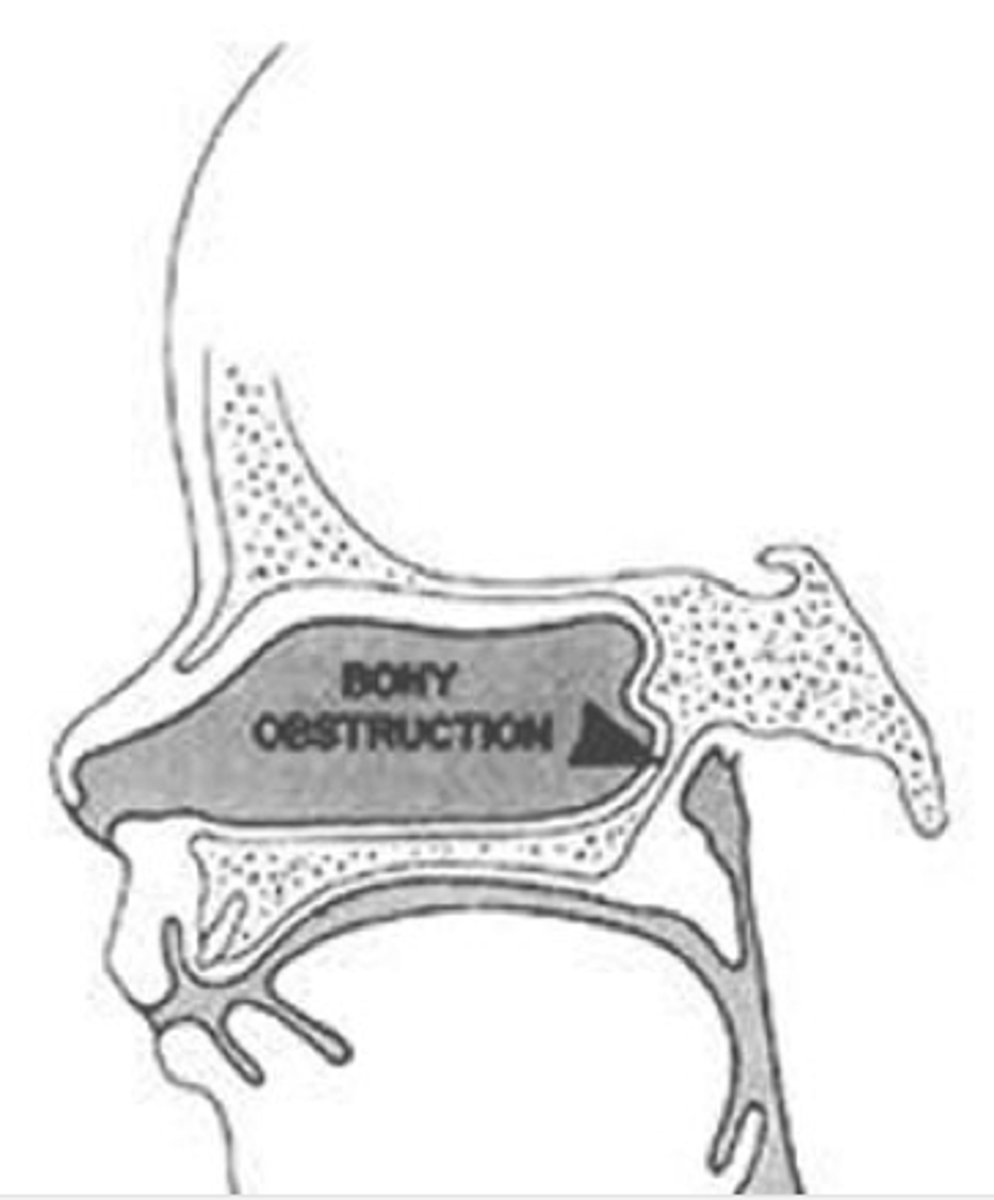
unilateral or bilateral choanal atresia: noisy breathing, cyanosis that worsens with feeds and improves w/ crying?
bilateral
unilateral or bilateral choanal atresia: presents later in life with nasal discharge or obstruction?
unilateral
what is the definitive dx study for choanal atresia?
CT
what is the treatment for choanal atresia?
bilateral is an emergency! → placement of oral airway
definitive management is surgical repair
any child presenting with nasal polyps should be evaluated for ____ and ______?
CF and asthma
what is saddle nose deformity assoc. with?
septal hematoma
what is the MC cause of sinusitis?
viral URI/allergic rhinitis
what organisms cause bacterial sinusitis?
S. pneumo
H. influenzsa
M. Cat
a pt presents with complains of purulent rhinorrhea, halitosis, facial pain and HA. they recent had URI symptoms. what is the treatment?
bacterial sinusitis → augmentin
what is a complication of sinusitis that causes erythema on the forehead with swelling and tenderness as well as HA and fever?
pott puffy tumor → frontal bone osteomyelitis assoc. with subperiosteal abscess
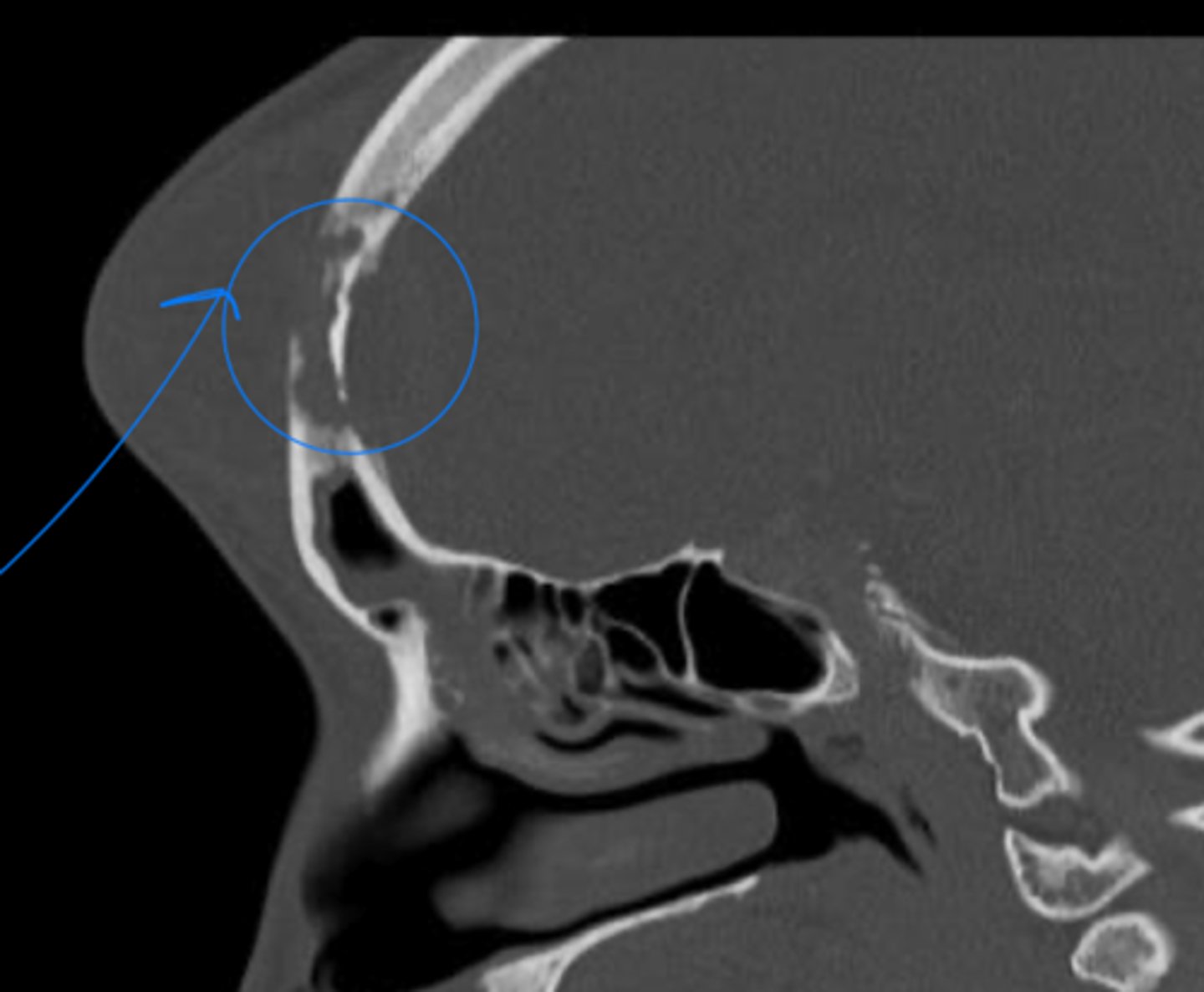
pott puffy tumor is a complication of sinus infection in which sinus?
frontal
dx with head CT
pt with PMHx of sinusitis presents with fever of 103, severe HA and signs of AMS. what imaging study is most appropriate?
epidural abscess → MRI with contrast
which sinuses are MC affected by periorbital cellulitis?
ethmoid and maxillary
pt presents with unilateral bright erythema and tenderness around their left eye with associated fever. what dx study should be ordered?
periorbital cellulitis → CT without contrast
comp of sinusitis
what is the initial tx for periorbital cellulitis?
augmentin
if not improving after 24 hrs → add linezolid
what is the cause of orbital cellulitis?
spread from infected ethmoid sinus (staph and strep)
appears ill, toxic and lethargic with eyelid edema
how is orbital cellulitis diagnosed?
CT with contrast or MRI
tx → vanco and rocephin
patient presents with complaints of a sore throat, fever, and HA. on physical exam, they have erythematous tonsils with exudate and palatal petechia. what organism likely caused this infection?
GAS
GAS or EBV: anterior adenopathy and abdominal pain?
GAS!!!!!
EBV has posterior LAD
what is the treatment for GAS acute tonsillopharyngitis?
penicillin
amox
pcn allergy → azithro
what are complications of GAS tonsillopharyngitis?
scarlet fever
post strep glomerulonephritis
rhematic fever
sinus infection
ear infection
tonsillitis/peritonsillar abscess
what patient education should be given to a pt recovering from EBV tonsillopharyngitis?
no contact sports to prevent splenic rupture
what is the dx criteria for recurrent tonsillitis?
≥6 episodes in 1 year
≥5 episodes x2 consecutive years
≥3 episodes per year x3 consecutive years
where does a peritonsillar abscess form?
forms between capsule of palatine tonsil and pharyngeal muscles
what dx should you consider if your pt presents with hot potato voice, unilateral sore throat, drooling and dysphagia?
peritonsillar abscess → tx with augmentin or clinda
what should you suspect in a pt with asymmetrical enlarged tonsil without evidence of infection?
tonsillar lymphoma
3 year old pt presents with erythematous pharynx with asymmetrical swelling of the posterior pharynx, neck stiffness, and drooling. what bacteria caused this? what imaging should be ordered?
retropharyngeal abscess → S. pyogenes or S. aureus → lateral neck XR (widening of prevertebral soft tissue)
13 month old pt presents with high spiking fevers, diffuse swelling/tenderness of neck and torticollis. what is the dx?
parapharyngeal abscess → CT scan
what is the MC cause of epiglottitis in children? what is the treatment?
Hib → underimmunized/non-immunized
tx → intubate for severe
for mild → rocpehin AND vanco
what dx is suspected with sudden onset and rapid progression of fever, stridor, drooling, tripod posturing?
epiglottitis → life-threatening airway obstruction
lateral neck XR → thumb print sign
what is the cause of acute inflammation of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi? what is seen on XR?
croup → parainfluenza 1&2
lateral neck XR → steeple sign
pt presents with fever, labored breathing and barky "seal-like" cough and high inspiratory strider. what is the gold standard treatment?
croup → racemic epi
what is the MC location of FB aspiration (FBA)?
right mainstem bronchus
CXR can show asymmetric hyperinflation
what is seen on PE for FBA?
limited chest expansion
dull or hyperresonance
diminished breath sounds distal to FB
what condition is seen in a child with hx of chronic hoarseness?
laryngeal papillomas
which dx shows cobblestone appearance of posterior tracheal mucosa?
GER
what dx has pathognomonic sign of vertical motion of the mass with swallowing and tongue protrusion?
thryoglossal duct cyst→ midline cystic mass in neck that rapidly inc in size with infection/URI
where do branchial cleft cysts arise from?
1st and 2nd branchial arches → often contain lymphoid tissue and located on lateral neck
what is the only mass that consistently transilluminates?
lymphangioma
if a 9 month old pt presents with noisy breathing, resp distress that worsens with feeding and improves with crying, which dx should you consider?
pyriform aperture stenosis → bony overgrowth at the anterior bony opening
what should you suspect if a child has unilateral foul-smelling nasal discharge?
nasal FB
which condition are nasal polyps assoc. with?
CF
tx nasal polyps with nasal steroid
wht is the cause of lingual thyroid?
failure of thyroid to descend into the neck → thyroid tissue found at the base of the tongue
which dx is expiratory stridor seen in?
laryngeal lesions
tracheomalacia
what is the MC congenital anomaly of the larynx?
laryngomalacia → causes inspiratory strider in infants
which dx presents most commonly as recurrent croup?
subglottic stenosis → narrowing of the cricoid lumen
what congenital conditions causes complete upper airway obstruction, requiring emergent trach?
laryngeal atresia
what is a rare congenital anomaly resulting in incomplete separation of the vocal cords?
laryngeal webs
in what rare condition do patients present in respiratory distress and die soon after birth?
tracheal atresia
if a pt presents with monophonic wheeze that doesn't respond to bronchodilators, sternal retractions, and dyspnea, what is your dx?
tracheal stenosis
which dx has risk factor of Hemorrhagic hereditary telangiectasia (osler-weber rendu syndrome)?
pulmonary AV fistula → abnormal fistula between pulm arteries and veins creating pathologic intrapulmonary R→L shunt
which anomaly is characterized by a non-functioning mass of lung tissue that lacks normal communication with the tracheobronchial tree and receives its arterial blood supply from the systemic circulation?
bronchopulmonary sequestrations
what are the two types of bronchopulmonary sequestrations?
intralobar → contained within normal lung parenchyma
extralobar → separate from the normal lung and visceral pleura, usually has its own pleural covering
what are the causes of viral URI?
rhinovirus, coronavirus, adenovirus, coxsackie
sx: low grade fever, rhinorrhea, cough, congestions
if a 14 year old presents with cough that progressed from dry to productive and rhonchi are heard on auscultation, what is your dx?
acute bronchitis → may be assoc. with recent viral URI
older children
when does acute bronchitis become chronic?
persistent cough lasting >4 weeks
a 14 month old pt presents with fever, tachypnea, nasal flaring, and retraction. on PE, you auscultate wheezing and crackles. what is the etiology of their dx? what would you expect to see on CXR?
acute bronchiolitis → RSV is MC
CXR → hyperinflation of lungs, increased AP diameter, atelectasis if severe
what dx should be at the top of your ddx for bronchiolitis?
asthma
what is the treatment for bronchiolitis?
saline spray and nasal suctioning
1 trial of albuterol in office→if O2 improves prescribe for use q4-6 hrs
what is the discharge criteria for bronchiolitis?
<6 months → <60 breaths per min
6-11 months → <55 breaths per min
>12 → <45 breaths per min
what are the most common causes of PNA in children <5?
virus is MC casue → RSV
bacterial → s. pneumo, s. aureus, s. pyogenes
which virus can cause severe PNA in older children and adolescents?
SARS-CoV-2
if you have a <2 year old pt with fever, cough, resp distress, what should you suspect?
PNA
what dx tests should be obtained for (RSV) viral PNA?
CXR → perihilar and parenchymal infiltrates
sputum culture → definitive dx
what is the MC cause of typical bacterial PNA?
S. pneumo → tx with amox