Unit 8 Exam - Data Management
1/98
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Enterprise Imaging
Set of strategies, initiatives and workflows implemented across a healthcare enterprise to consistently and optimally capture, index, manage, store, distribute, view, exchange and analyze all clinical imaging/multimedia content
What does enterprise imaging use instead of PACS?
Vendor Neutral Archive (VNA)
Advantages of Enterprise Imaging
All medical images into a single archive, increase efficiency, reduce storage costs
Image Distribution and Viewing
CD/DVD; cloud-based exchange giving remote access to PACS system and VPN
Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE)
Initiative by healthcare professionals/industry to improve the way computer systems in healthcare share information
Health Level Seven Standard (HL7)
Standards developed to provide a comprehensive framework and related standards for the exchange, integration, sharing and retrieval of electronic health information; allows interoperability between patient administration, laboratory information systems, billing systems, electronic medical record and health record systems
Cloud-Based Computing
Reduces operational and maintenance costs for data storage combining data from different sources
Database Health Monitoring
Ensures the integrity of data and IT operations and enterprise security as errors of fraudulent data contained in databases may be used by cybercriminals as a vector for attack
Advantages of Database Health Monitoring
Reduce organization costs, shifts from reactive to proactive monitoring, improve performance
Cybersecurity
A centralized network, while offering substantial efficiency gains and savings on storage solutions, is more vulnerable to cybersecurity threats than networks acting individually
Cybersecurity Incidents
Computer virus, ransomware, theft/publication of patient data
Prevention of Cyber Attacks
Close monitor, staff education, operational/stategic plans, firewalls, whitelisting, user authentication
Network Configuration
The process of assigning network settings, policies, flows and controls
LAN – Local Area Network
Computerized communications network generally contained within a single building or business; devices share one server
WAN – Wide Area Network
Extends to other businesses or locations that may be at great distances (ex. internet); allows different LANs to communicate
Radiology Information System (RIS)
Data system for patient-related functions in the department such as scheduling appointments, tracking patients, storage and distribution of reports
What assigns the accession number?
Radiology Information System (RIS)
Hospital/Health Information System (HIS)
Performs same functions for the entire institution (patient’s general medical file)
What assigns MRN?
Hospital/Health Information System (HIS)
Electronic Medical/Health Record (EMR/EHR)
Electronic version of patient’s medical history that is maintained by the provider and may include all the key administrative clinical data including demographics, progress notes, problems, medications, vitals, medical history, immunizations, laboratory/radiology reports
Advantages of EMR/EHR
Efficient workflow, support other care-related activities, strengthen the relationship between patients and clinicians
Network Architecture
Physical and logical design of the software, hardware, protocols and media of the transmission of data; how computers are organized/how tasks are allocated to the computer
What are the two types of network architecture?
Peer-to-peer network and client/service network
Network Protocols
Network languages computers use to communicate; set of established rules that dictate how to format, transmit and receive data
What are the three types of network protocols?
Communication, management, security
Transmission Protocols
Known as TCP, can be combined with IP; communication standard used with DICOM to enable application programs and computing devices to exchange messages over a network amongst systems
NIC (network interface card)
Hardware component used to connect a computer with another computer onto a network
HUB
Simplest method of connection, hardware device that divides the network (LAN) connection among multiple devices; sends a broadcast request to all devices connected
Switch
Hardware device that connects multiple devices on a computer network; can send data only to the device that made the initial request
Router
Hardware device which is used to connect a LAN with an internet connection
Modem
Hardware device that allows the computer to connect to the internet over the existing telephone line
Cable
Transmission media used for transmitting a signal
Raw Data
Data that has not be compressed, encrypted or processed in any manner
Image Data
Reconstructed data
Medical Image Management and Processing System (MIMPS)
Formerly PACS; comprehensive computer network that is responsible for electronic storage and distribution of medical images
What are the components of PACS (MIMPS)?
Image acquisition, display workstations, archive servers
Image Acquisition
First point of entry into PACS; image acquired in a digital format
Display Workstations
Most interactive part of PACS; any computer used to view digital images
Archive Servers
File rooms of PACS; contains all historic and current data
Navigation Functions
Customizable worklists dependent on the technologists’ selections during a procedure; ED, verbal reports, image check
Hanging Protocol
Controls the display of images on 1 or more monitors
Study Navigation
Allows images to be viewed individually or in a cine run
Image Manipulation & Enhancement
Annotations, magnify, window/level, flip/rotate, measurements
Image Management
Edit patient demographics for proper correlation; query/retrieve - locate images based on patient demographics
What is the “heart” of PACS?
Image manager
Image Manager
Contains master database of everything in the archive; controls the receipt, retrieval and distribution of the images & all DICOM processes running within the archive
Vendor Neutral Archives (VNA)
Allows for images and data from different systems and in different formats to be stored using a singular system on a common infrastructure
What does DICOM stand for?
Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine
DICOM
A joint commission between ACR and NEMA; standardizes programming languages between modalities, servers, workstations; different modalities can now share data with one another or a central server
Multiplanar reconstruction
Creates multiple planes of view from a single scan
Maximum intensity projections (MIP)
Enhancement of small vessels
Minimum intensity projections (MinIP)
Enhancement of air-filled structures
Volume rendering technique (VRT)
Assists in differentiating between anatomical structures by adding color shades based on pixel intensity
Shaded surface display (SSD)
Creates a 3D, moveable image based on the pixel intensity of choice
Computer aided diagnosis/detection (CAD)
Used as a “second opinion” in assisting radiologists’ image interpretations
What modality is CAD used in?
Mammography
Annotation
Describes the meaning in images
Markup
Visual presentation of the annotation
AIM Project (Annotation and Image Markup)
Pull images from a bank with the same annotations and markups
Teleradiology
Allows remote transmission and viewing of radiographic images via modems over phone or cable lines
Network attached storage (NAS)
Dedicated file storage that enables multiple users and heterogenous client devices to retrieve data from a centralized disk capacity; users on LAN access shared storage via an ethernet connection
Storage area network (SAN)
Dedicated, independent high-speed network that interconnects and delivers sharped pools of storage devices to multiple servers
Direct attached storage (DAS)
Server or storage device that is not connected to a network; computer internal HDD
What is the required storage time of a patient’s images?
5-7 years
What is the required storage time of a pediatric patient’s images or images involved in litigation?
Indefinitely
Short-term storage
RAID
Long-term storage
RAID, optical discs, tapes
RAID
Several magnetic disks or hard drives that are linked together in an array (RAID 5 is most common level used for a PACS archive)
Cloud-Based Storage
Offsite storage and servers supported by a secure network
Service object pair (SOP)
2-way communication between a pair of objects; made up of service class user (SCU) and service class provider (SCP)
Image compression
Technique applied to digital images to decrease the amount of space required to store an image and increase the speed with which image can be retrieved or transmitted
Lossless (reversible) compression
Defined as “visually acceptable” images; example: PNG, TIFF
Lossy (irreversible) compression
Example: JPG
Compression ratio
Lossless compression ratios are those at less than 8:1 and are defined as “visually acceptable” for medical imaging community
What is the standard communication between HIS and RIS?
HL7
Allows interoperability between different systems including patient administration, laboratory information systems, billing systems, electronic medical record and health record systems, and more
HL7
What allows a company to avoid the need to purchase/invest in new IT equiptment?
Cloud-based computing
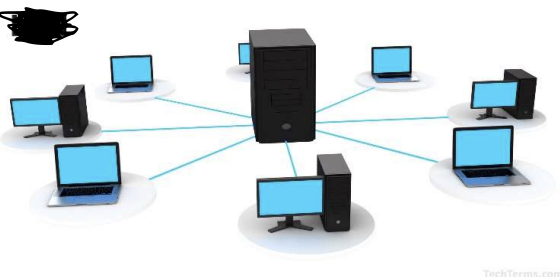
LAN
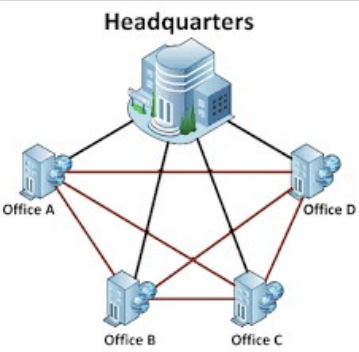
WAN
What allows different LANs to communicate?
WAN
RIS, HIS & EMR is a type of (LAN or WAN)?
LAN
What is the patient’s general medical file (RIS or HIS)?
HIS
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
IP
Internet Protocol
What is a network switch that examines all data and limits the scope of data by identifying the sender and the receiver?
Router
What is the first point of entry to PACS?
Image Acquistion
What is the most interactive part of PACS?
Display workstation

Hanging protocol
What is the file room of PACS?
Archive servers
What are the two components of PACS archive servers?
Image manager and image storage
What is an enterprise storage system that requires images to be stored in nonproprietary format?
VNA
What is the main function of PACS?
Act as a database
All information in a DICOM header is stored as ___________.
Metadata
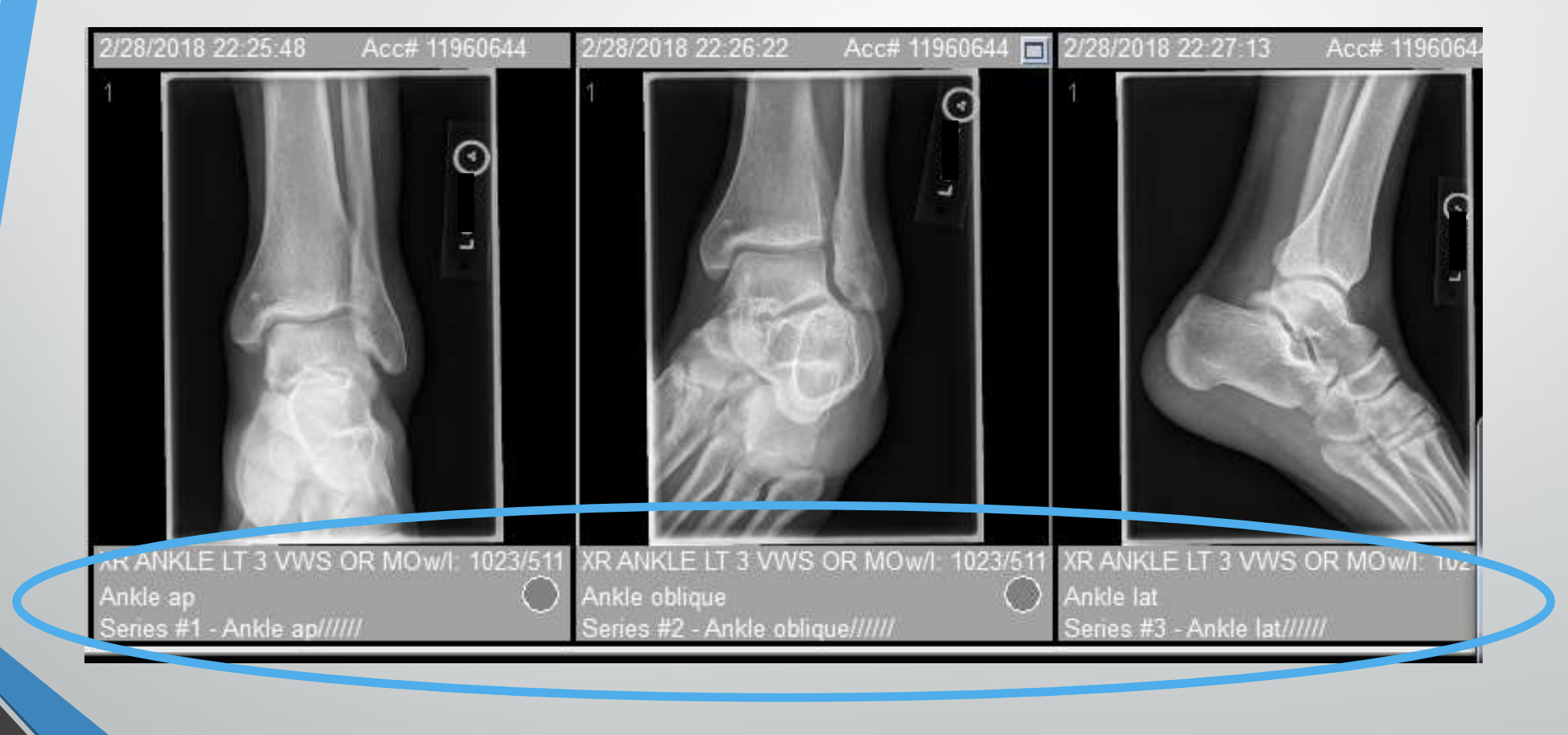
DICOM header
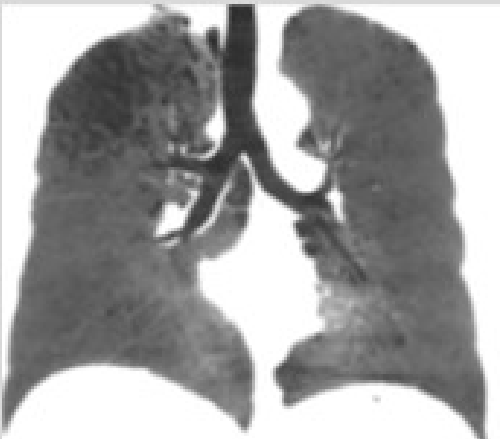
MinIP
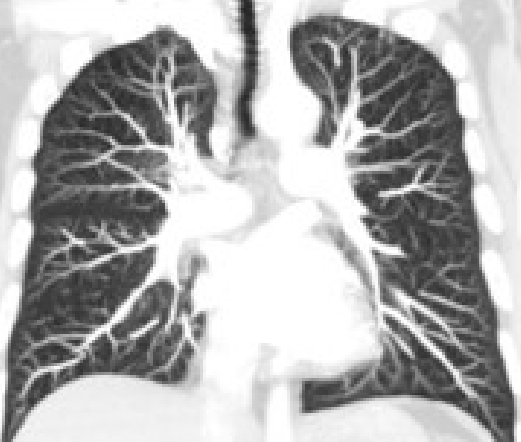
MIP
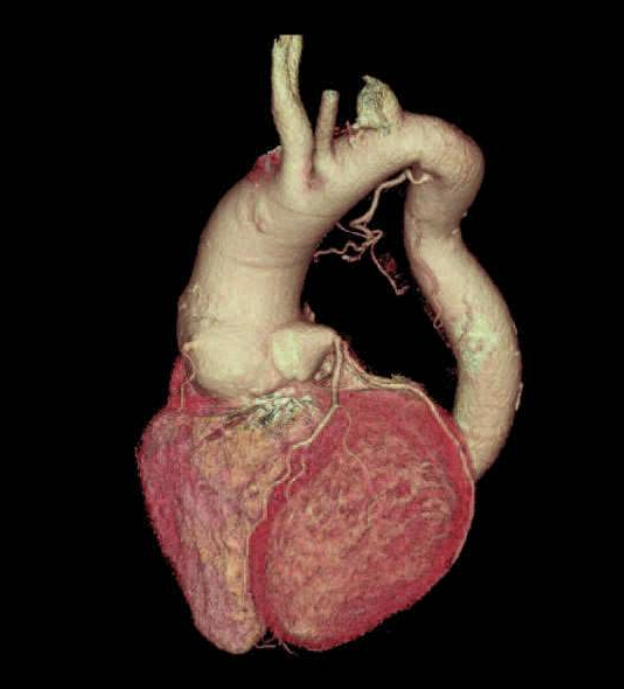
Volume Rendering Technique (VRT)
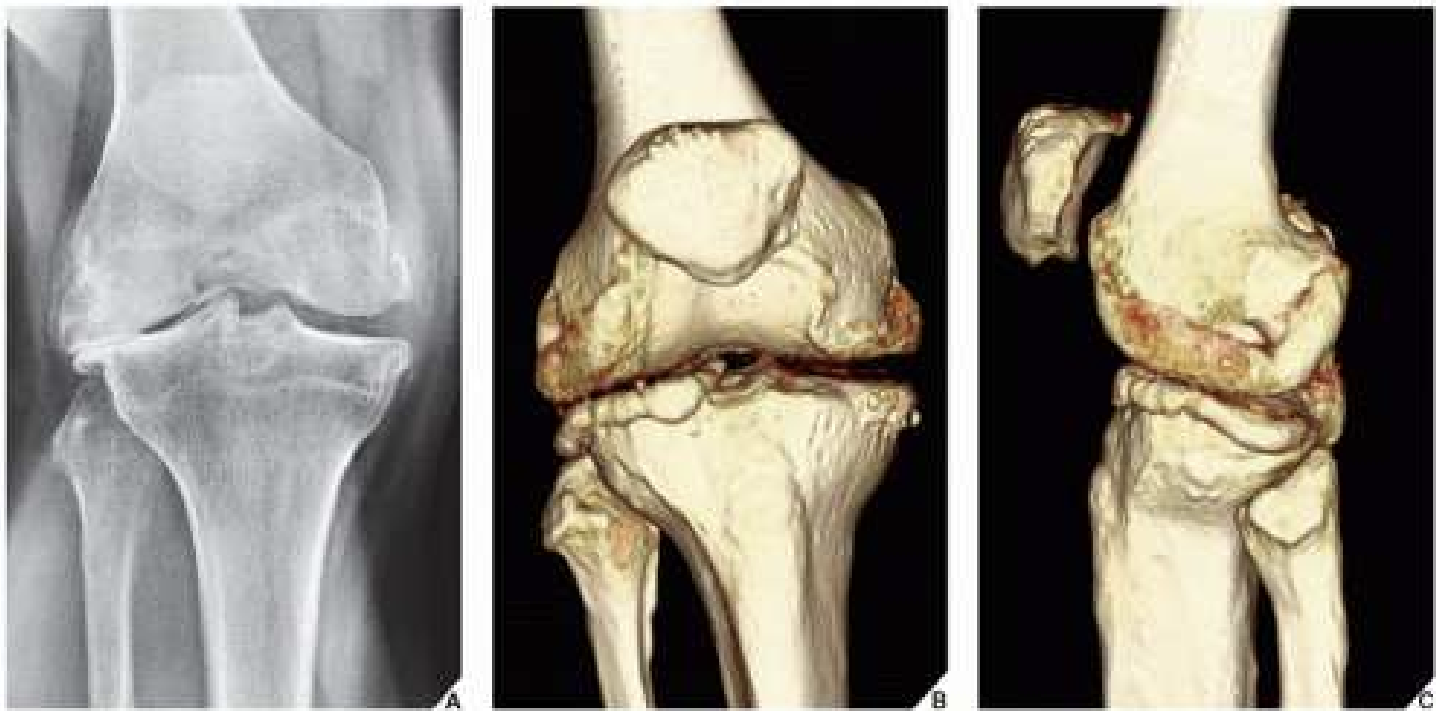
Shaded Surface Display (SSD)
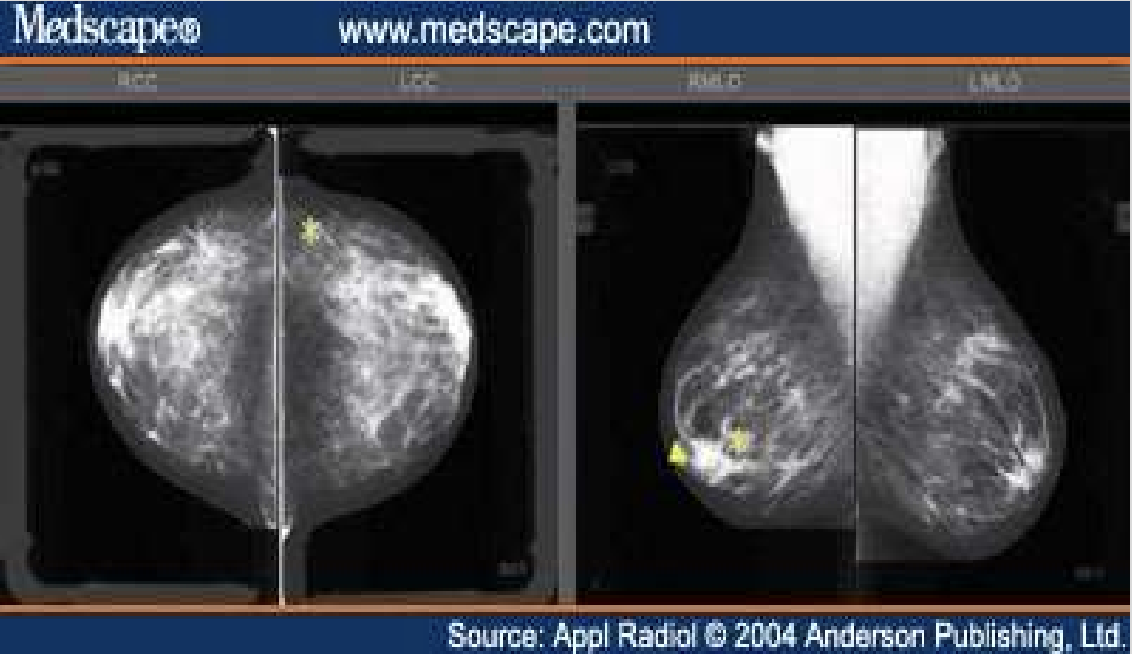
CAD