SEM 2 MIDTERM
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
primary functions of the respiratory system
1) exchange gasses
2) produce vocal sounds
3) sense of smell
4) regulate blood PH
Respiration
process of gas exchange
external respiration
air enters the lungs and gas is exchanged between air and blood
internal respiration
blood travels to body parts and exchanges gas with those tissues
cellular respiration
cells use oxygen to create energy in the form of ATP
what part of the cell is responsible for cell respiration?
mitochondria
upper respiratory tract
nose, sinuses, pharynx
lower respiratory tract
larynx, trachea, bronchial tubes, lungs
nasal cavity
1
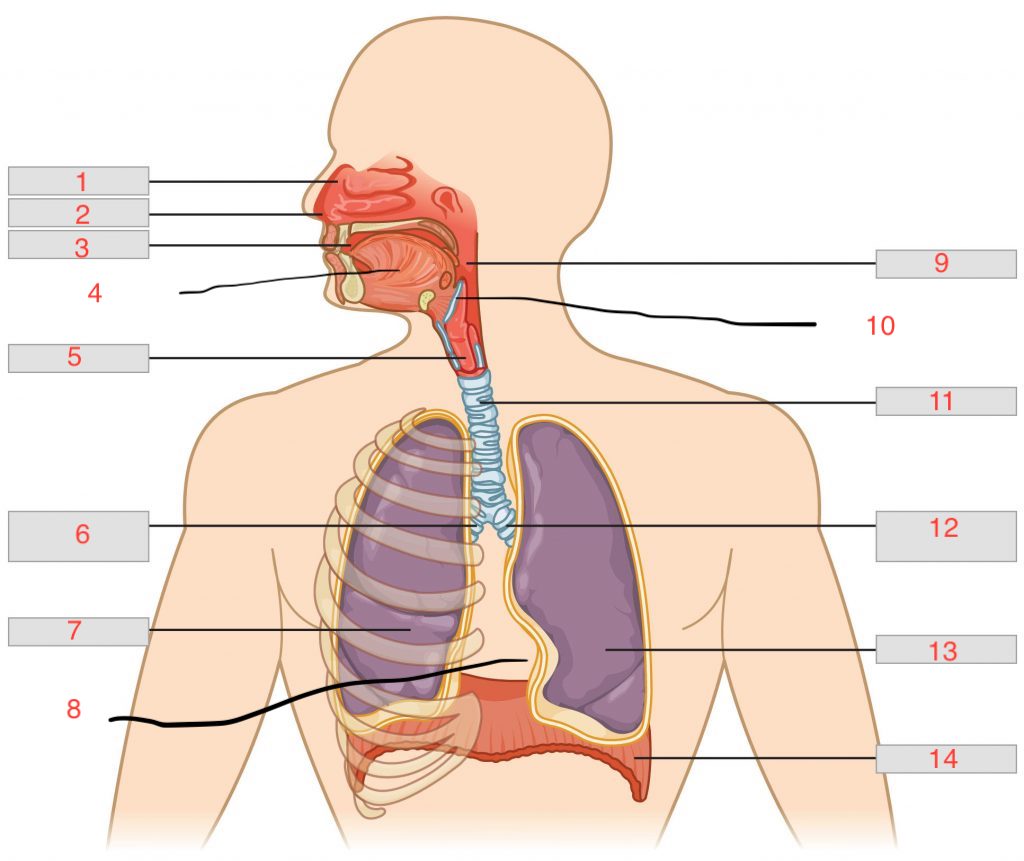
nostril
2
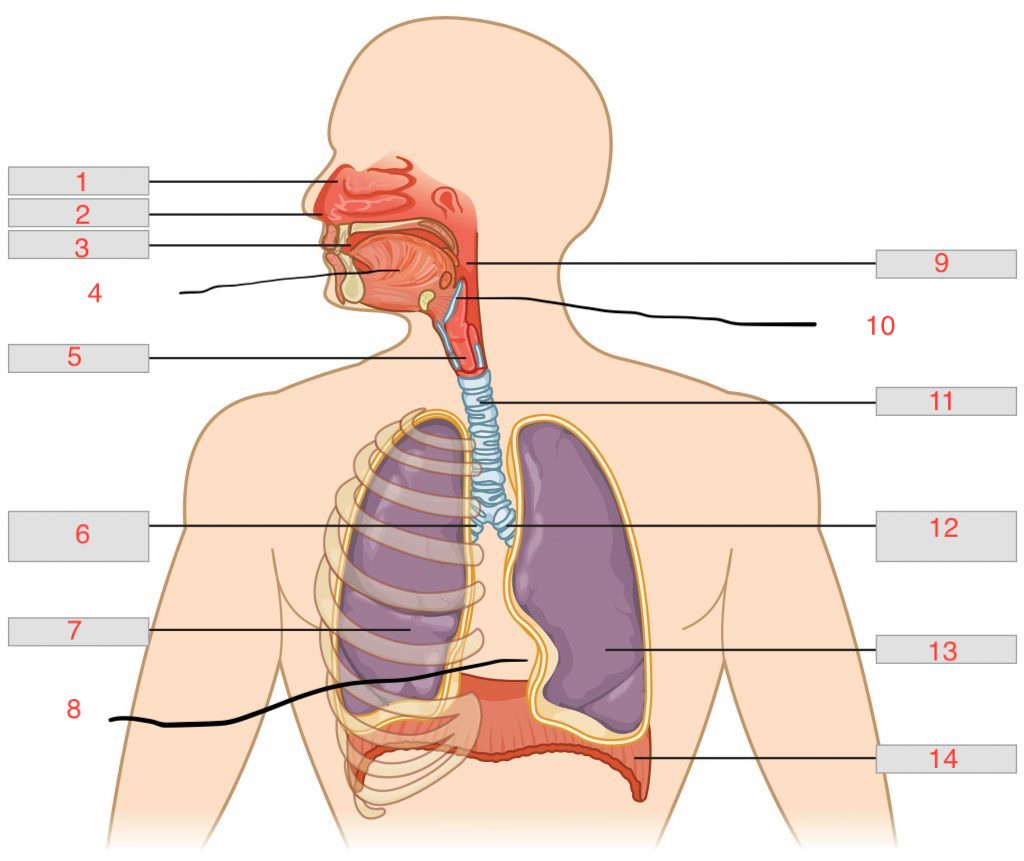
oral cavity
3
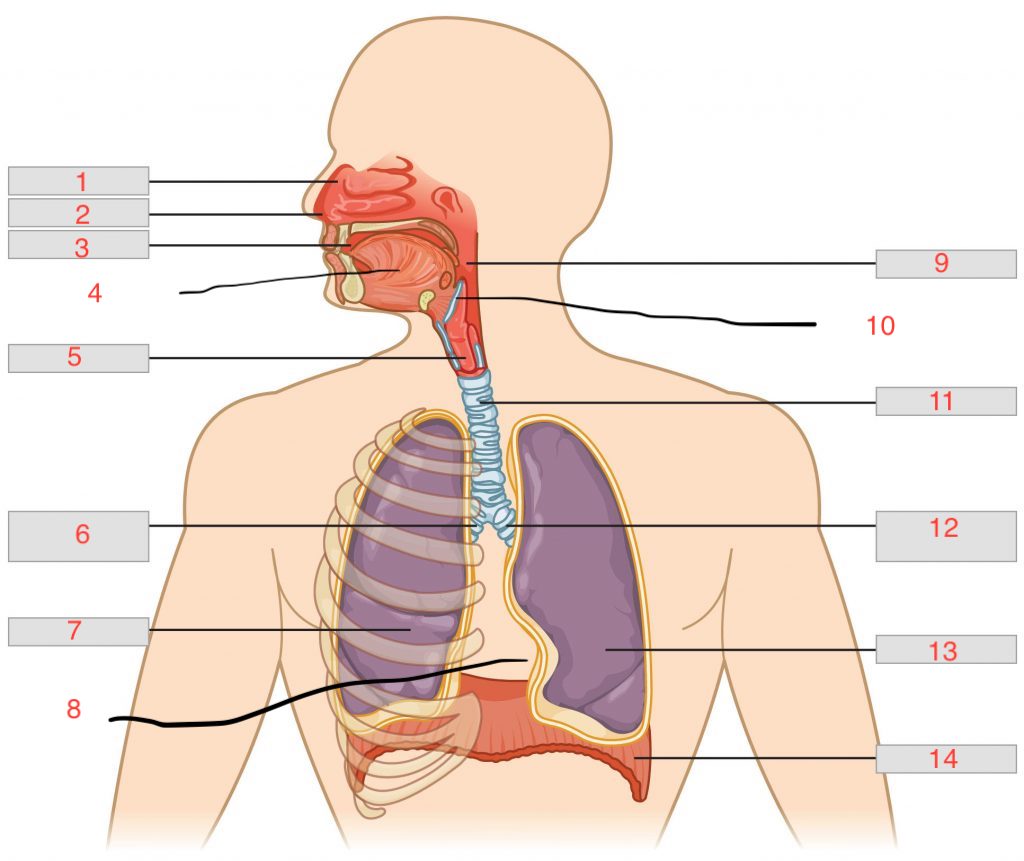
tongue
4
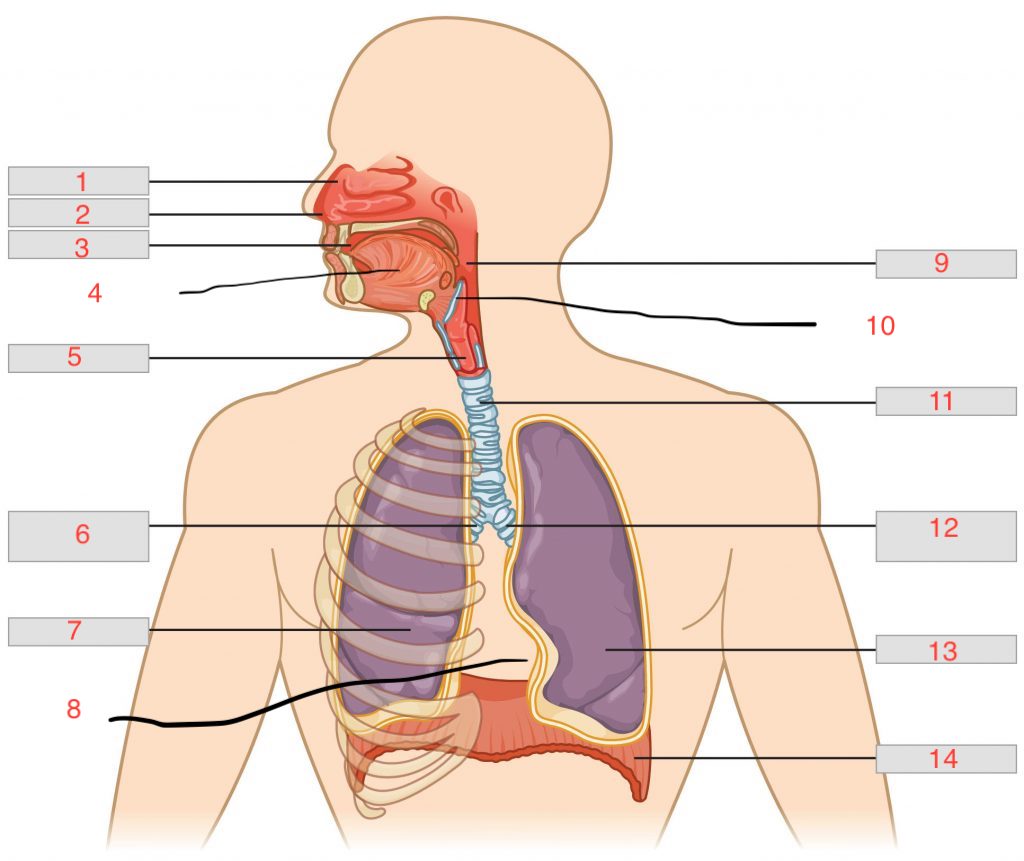
larynx
5
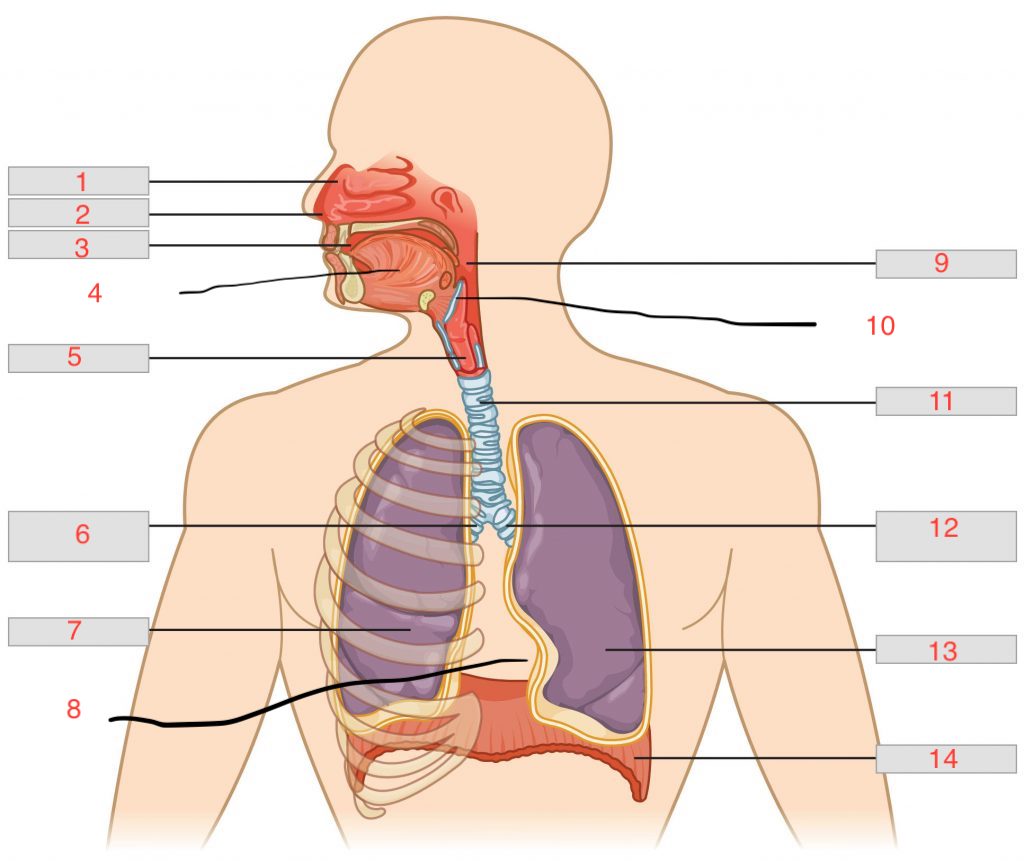
right main bronchus
6
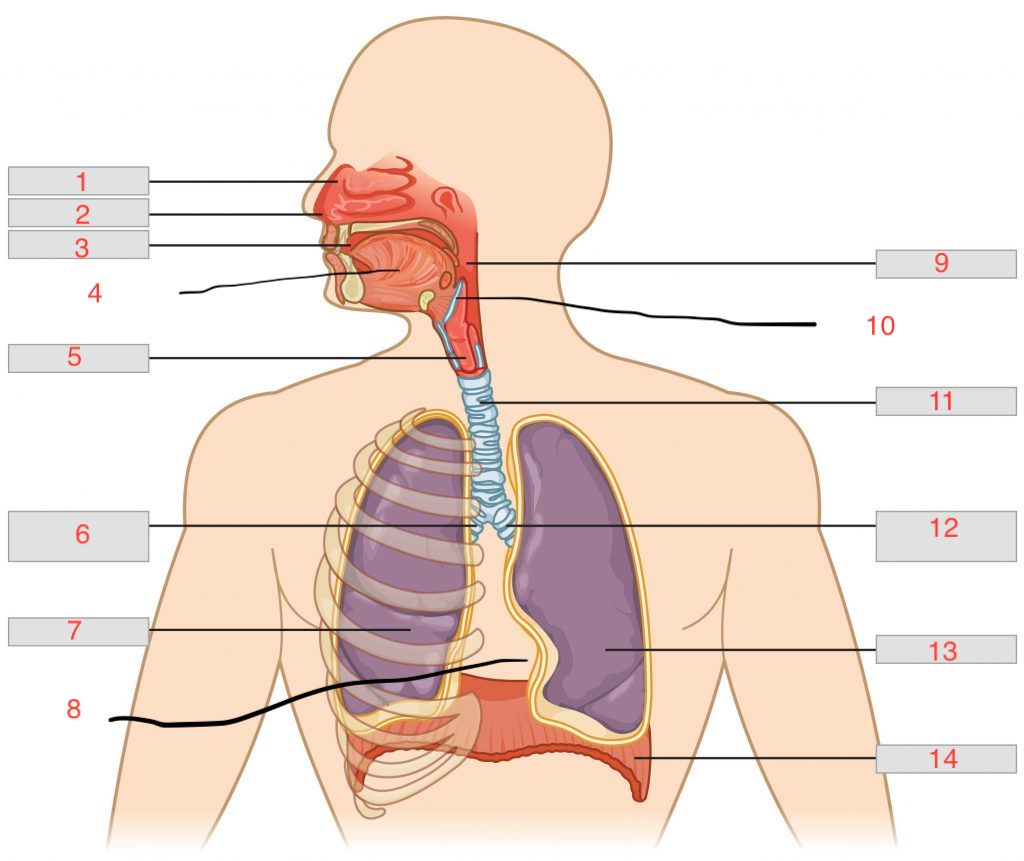
right lung
7
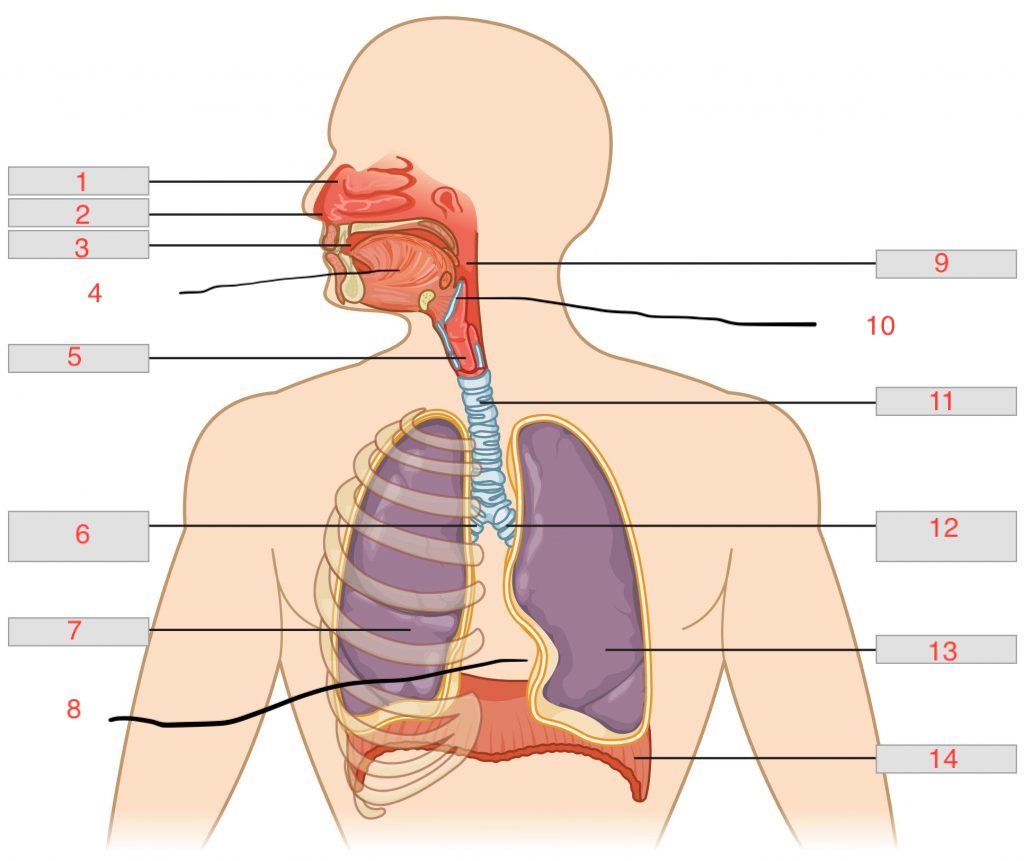
cardiac notch
8
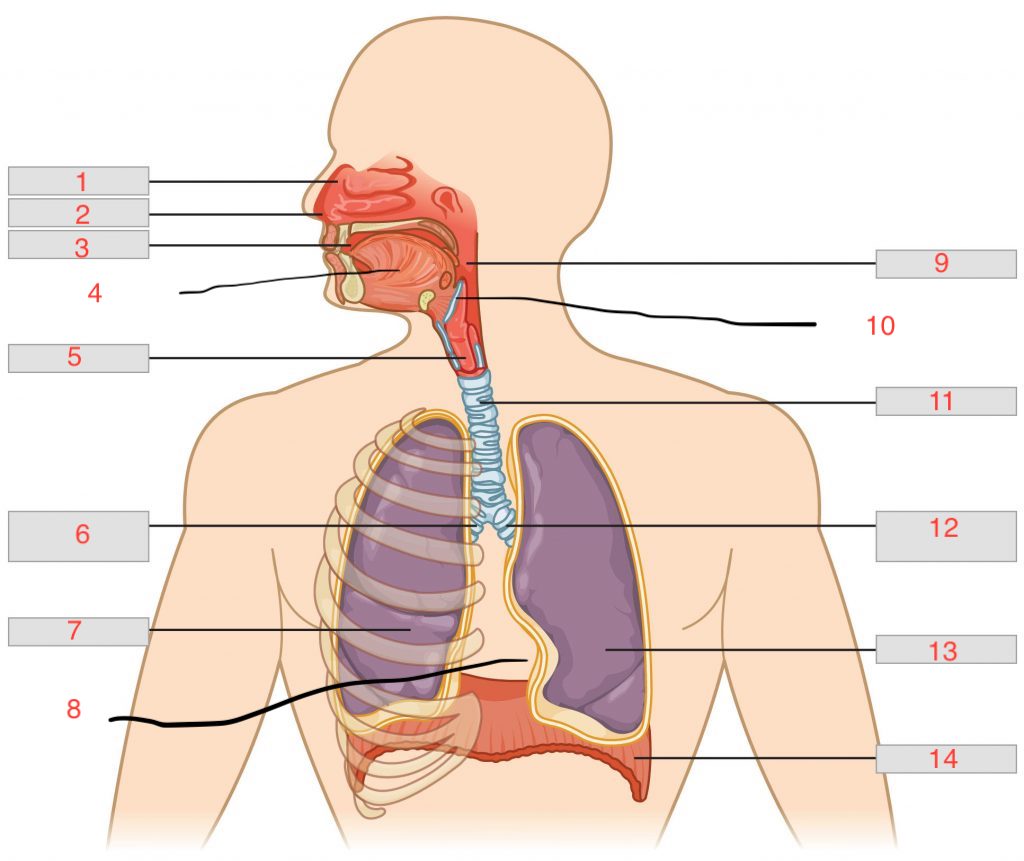
pharynx
9
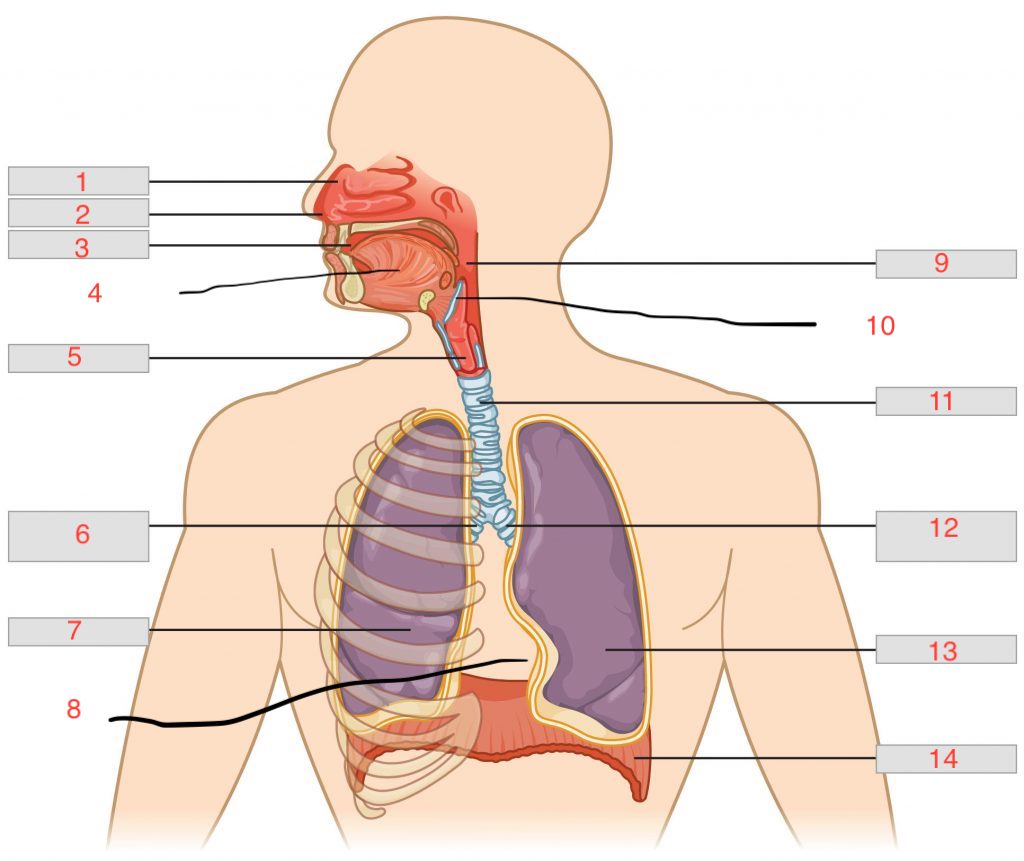
epiglottis
10
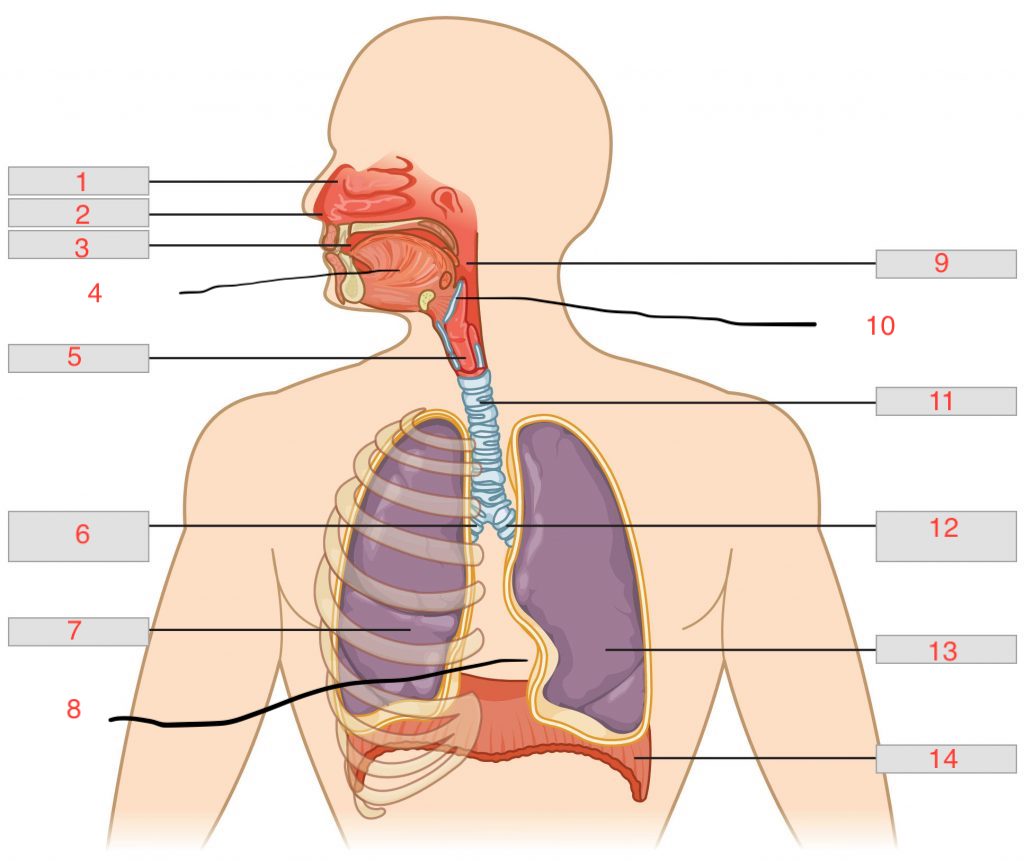
trachea
11
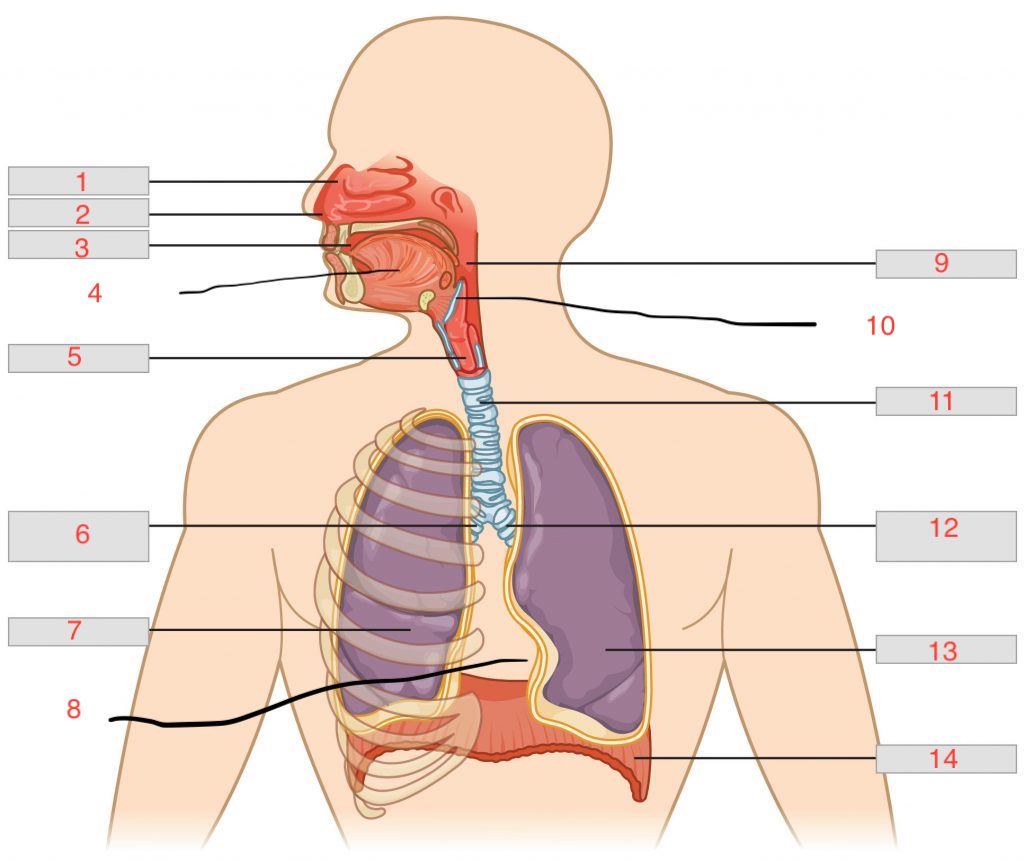
left main bronchus
12
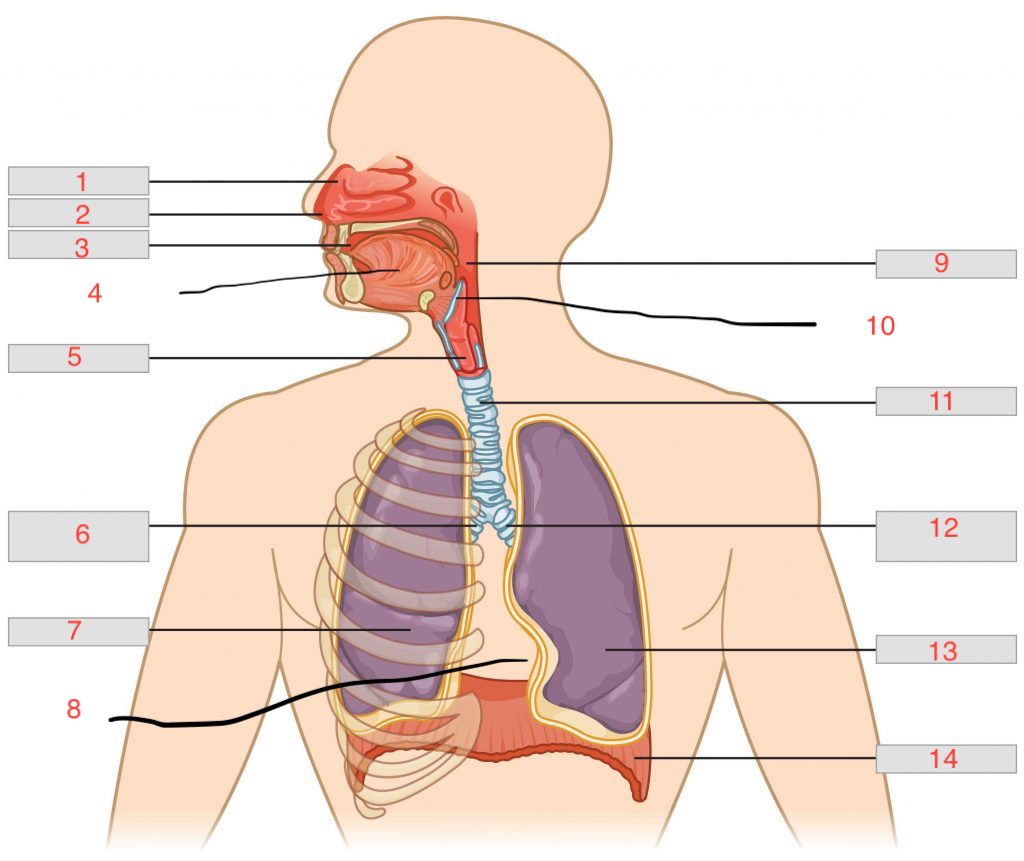
left lung
13
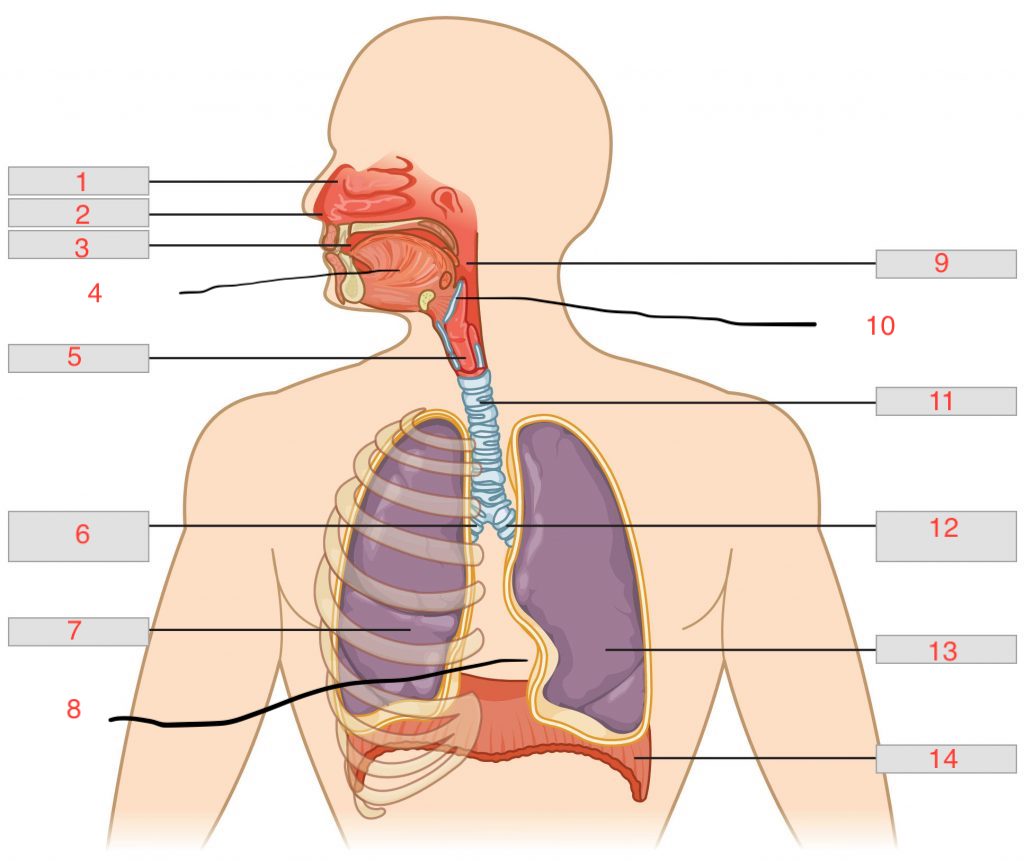
diaphragm
14
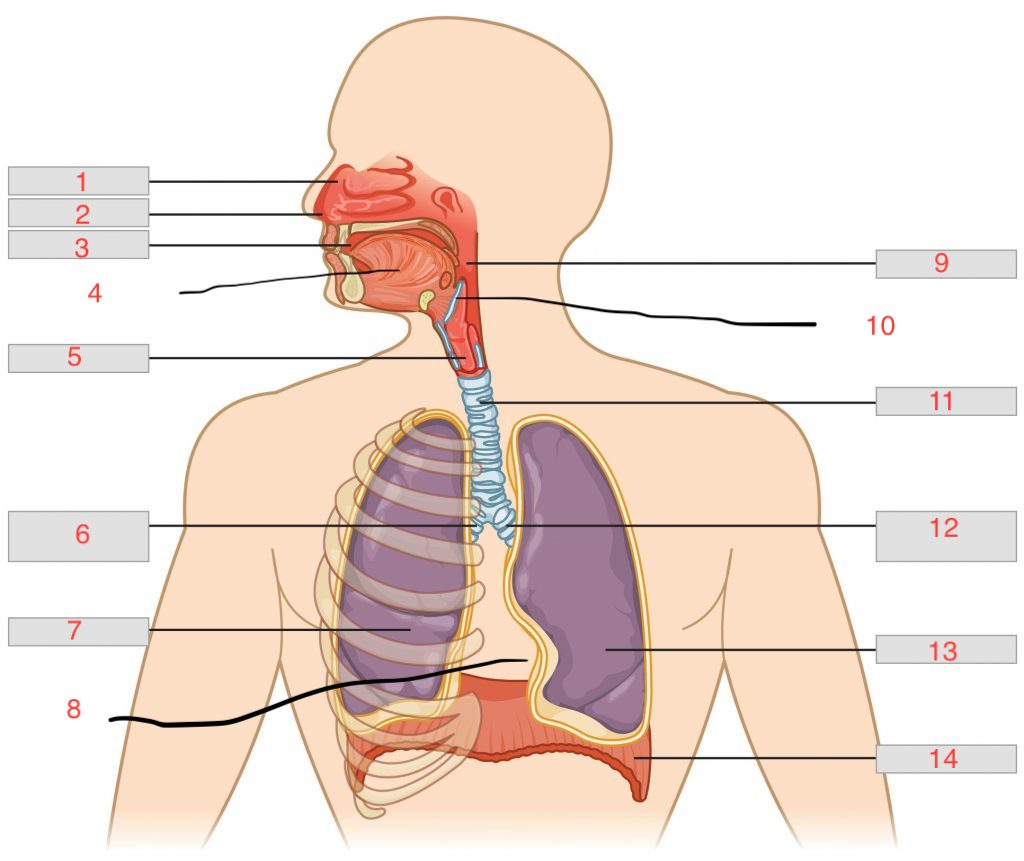
nasal concha
bones that divide nasal cavity and increase surface area
mucus membrane
warms and moistens air, traps dust.
paranasal sinuses
spaces within the bones, reduce weight of skull, resonance (voice)
paranasal sinus names
maxillary, frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid
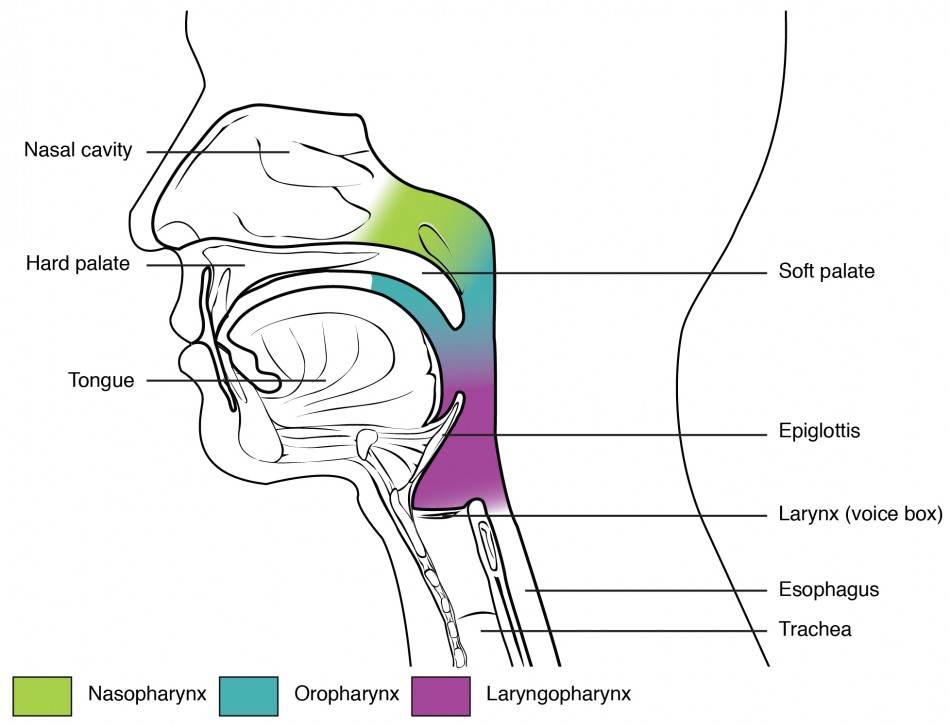
pharynx
behind the oral cavity
epiglottis
allows air to enter larynx closes when you swallow
larynx
enlargement at the top of the trachea, composed of muscles and cartilage
glottis
part of the larynx that consists of vocal chords
false vocal fold
close airway during swallowing
true vocal chords
produce sounds
laryngitis
inflammation of larynx, hoarse voice
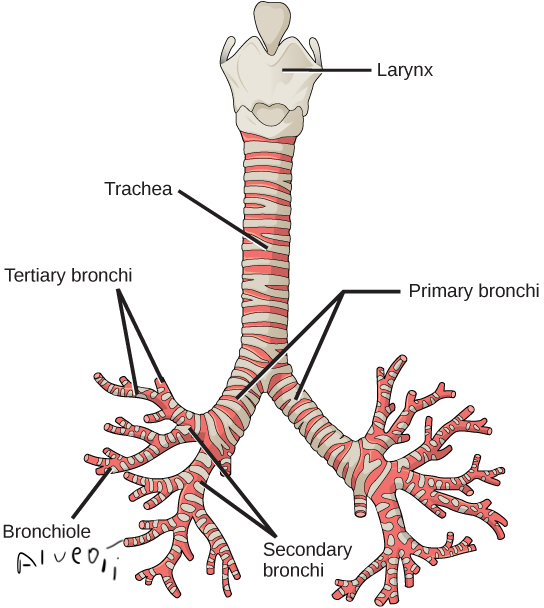
trachea
cylinder with cartilage to keep it from collapsing, leads to bronchial tree
alveoli
air sacs attached to bronchioles and the circulatory system via capillaries
respiratory epithelium
layer to help clear airway, if broken, mucus buildup
lungs
spongy tissue in pleural cavity
right lung, 3 lobes
left lung, 2 lobes
cardiac notch
space for heart
serous fluid
lubricates the lungs during breathing
steps to breath
1) diaphragm moves down forcing air into airways
2) intercostals contract, enlarging cavity
3) surface tension in alveoli and surfactant keep air sacs from collapsing
4) other muscles for deeper breath
5)relaxing the diaphragm causes elastic recoli (exhalation)
respiratory cycle
one sequence of inhalation and exhalation
spirometry
measures the volume of air moving in and out of the lungs
factors that affect breathing
rise in co2, emotional upset, fear and pain, hyperventilation
respiratory membrane
gas exchange occurs through a layer of simple squamos cells and oxygen diffuses into blood
hypoxia
lack of oxygen in tissues and organs
asphyxia
unable to breathe normally
illnesses in respiratory
COPD
bronchitis
emphysema
sleep apnea
lung cancer
altitude sickness
asthma
bacterial or viral infections
whooping cough
pneumothorax
cystic fibrosis
larynx reference picture
bronchi tree picture
tidal volume (TV)
vol. breathed in and out without thinking
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
more air that can be inhaled with max effort
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
more air that can be exhaled after normal exhalation
Vital Capacity (VC)
total vol. of air exhaled after a max inhale
TV+IRV+ERV
Residual Volume (RV)
volume of air remaining in lungs after max exhalation
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
VC+RV
hyperventilation
increased breathing lowers co2 concentration
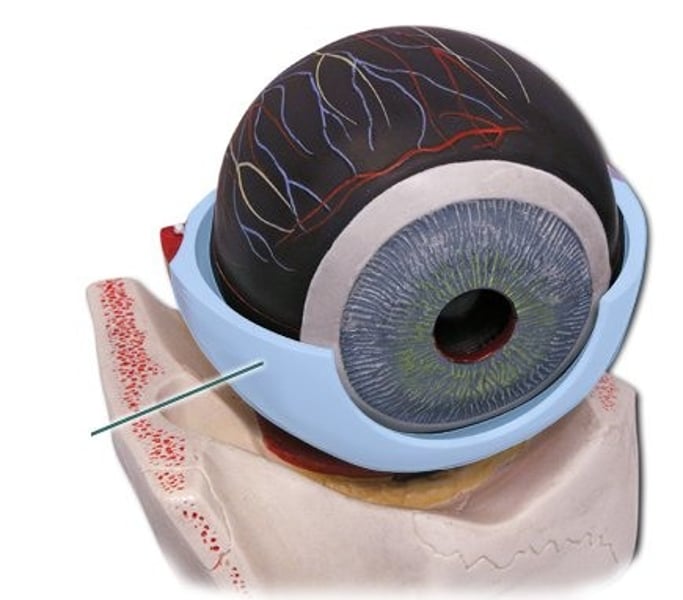
Sclera
outer protective layer of the eye (white of the eye)
cornea
transparent anterior part of the sclera; allows light rays to enter the eye
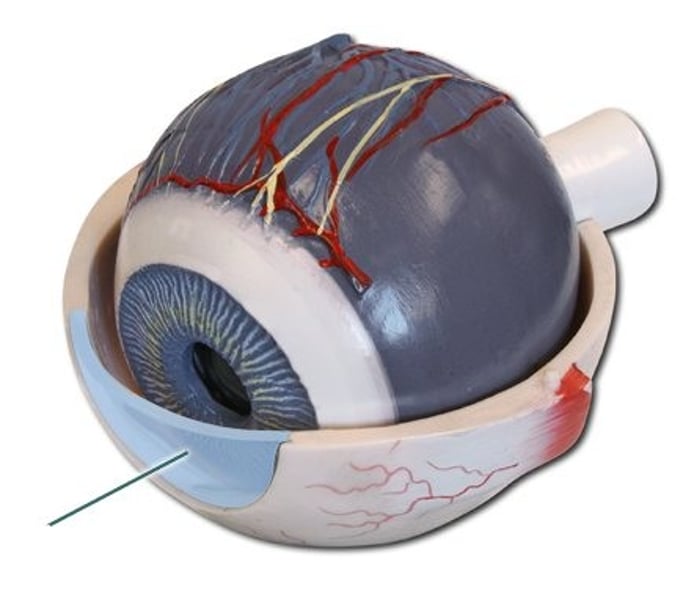
choroid
middle layer of the eye interlaced with blood vessels that supply nutrients to the eye; includes the iris.
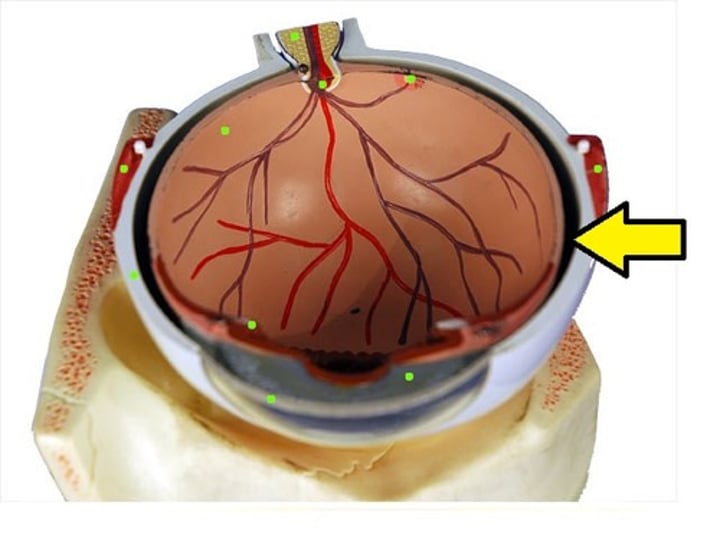
iris
pigmented muscular structure that regulates the amount of light entering the eye by controlling the size of the pupil.
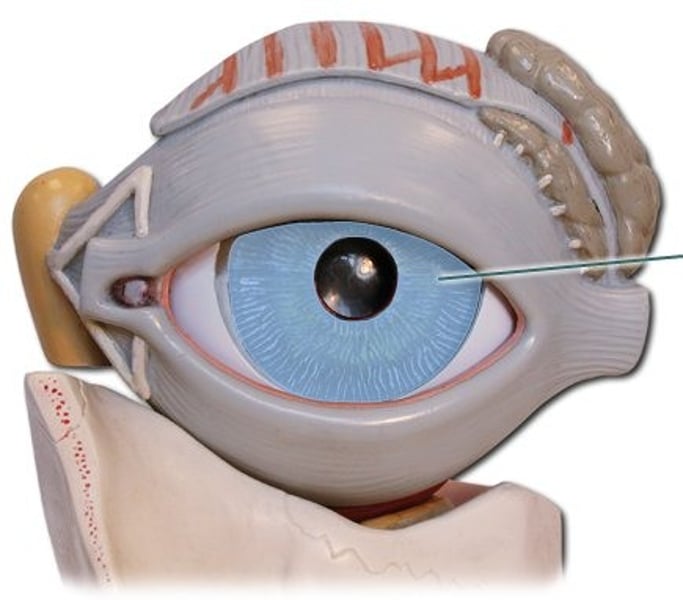
pupil
opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eye
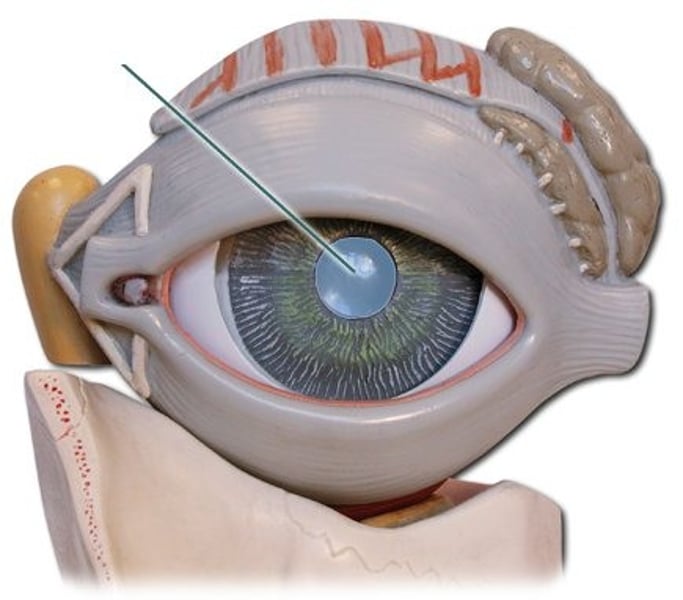
lens
directly behind the pupil; focuses and bends light
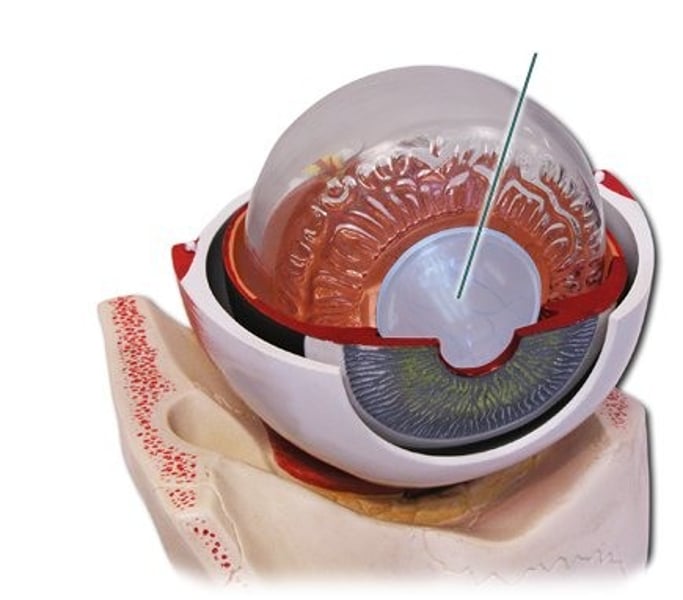
retina
innermost layer of the eye which contains photoreceptors (rods and cones)
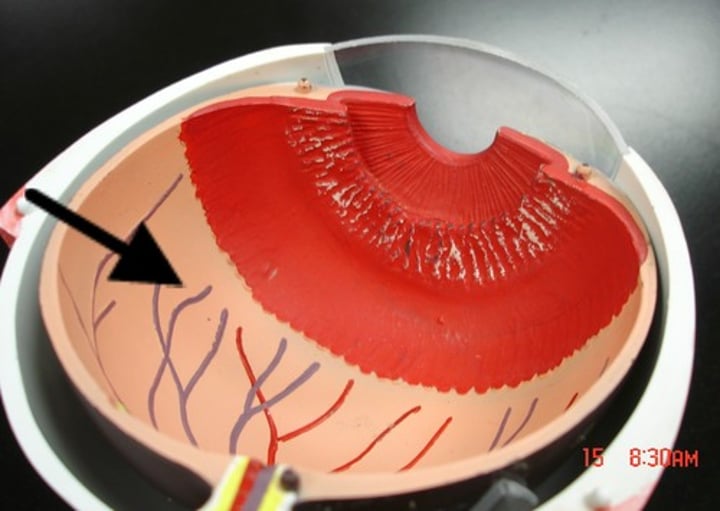
aqueous humor
watery liquid in the anterior cavity of the eyes which provides nourishment and shape to the anterior eye
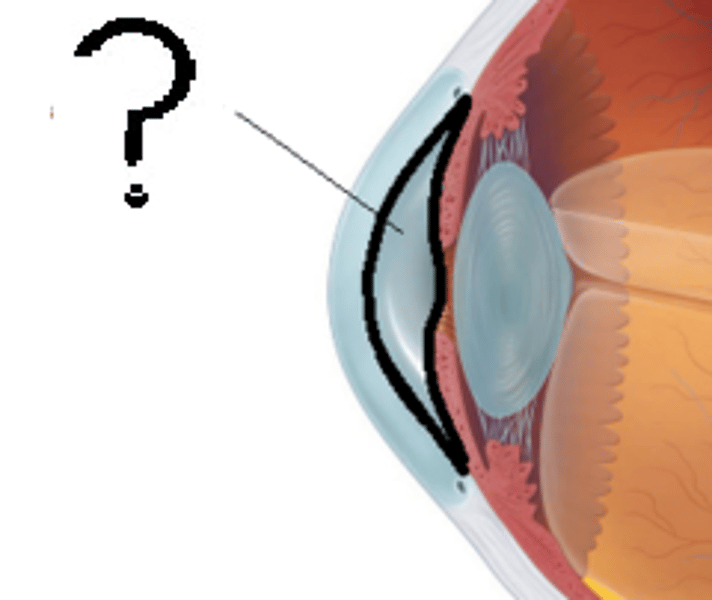
vitreous humor
Jellylike liquid found behind the lens in the posterior cavity of the eye that maintains its shape
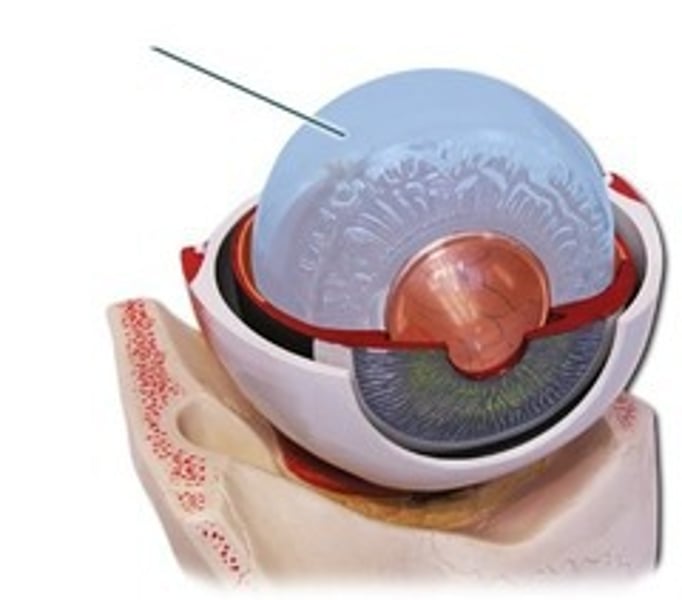
optic nerve
carries visual impulses from retina to brain
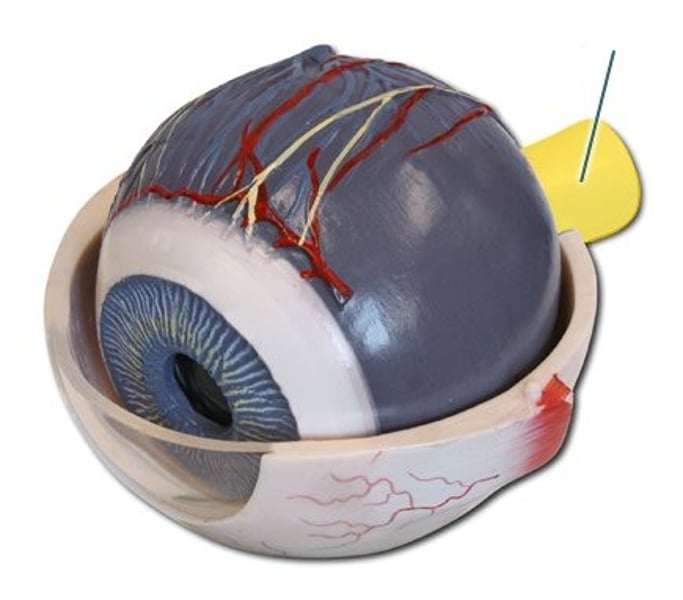
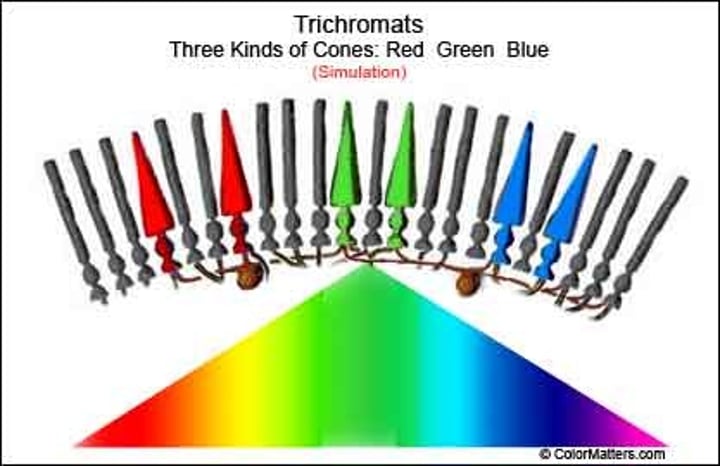
cones
Photoreceptors in the retina that distinguish different colors
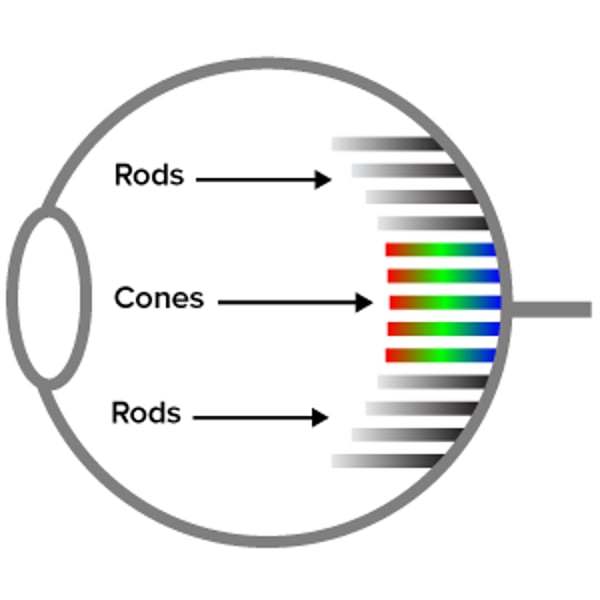
rods
Photoreceptors in the retina of the eye for black and white vision.
neuron
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
dendrites
part of neuron that receives stimuli from the environment or from other neurons
axon
part of neuron that carries information towards other cells
cell body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
myelin
a fatty covering around the axon of some neurons that speeds up transmission of the neural impulse
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath of the axons. Action potentials can 'jump' from node to node, thus increasing the speed of conduction.
multiple sclerosis
The immune system attacks myelin, forming scar tissue (sclerosis) which gives the disease its name. This damage interrupts nerve impulses traveling to and from the brain and spinal cord.
neuroglia
Supporting cells ("glue") of the nervous system that support, insulate, and protect neurons but do not transmit nerve impulses
action potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. The action potential is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon's membrane. It is an "all-or-nothing" event.
axon terminal
the end ("terminal") of the axon on the presynaptic cell
synaptic vesicles
contain neurotransmitters
presynaptic cell
neuron that transmits a signal toward the synapse
postsynaptic cell
The neuron, muscle, or gland cell that receives the signal from a neuron
synaptic cleft
space separating presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter widespread in CNS and PNS
polarized membrane
An axon membrane at rest where the inside of the cell is negative (-70 mv) compared with the outside of the cell
depolarized membrane
An axon membrane that becomes less negative (closer to 0 mv) than the resting potential of -70 mv
repolarized membrane
An axon membrane that is restored to its resting potential of -70 mv after depolarization
hyperpolarization
A change in the axon membrane potential from -70 mV (resting) to -90 mV, becoming more negative
sodium channels
voltage-gated channels in the axon's plasma membrane that allow sodium to move into the cell
potassium channels
voltage-gated channels in the axon's plasma membrane that allow potassium to move out of the cell
sodium-potassium pump
A protein pump in the plasma membrane of an axon that restores the membrane to its original polarized condition by using ATP to pump sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell
calcium channels
voltage-gated channels in the presynaptic terminal that allow calcium to enter and trigger the release of acetylcholine
resting potential
The difference in electric charge between the inside and outside of a neuron's cell membrane (more K ions inside, more Na ions outside); -70 mv
threshold
The level of stimulation required to activate a neuron
all-or-none principle
If the threshold is reached the action potential in the axon occurs either 100% or not at all.
central nervous system
A division of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
A division of the nervous system consisting of all sensory and motor neurons that are not part of the brain or spinal cord
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's voluntary skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary activity of smooth and cardiac muscle, and internal organs and glands.
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations; the "GAS"
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy; the "BRAKE"