APHUG-All Units
Unit 1 - Thinking Geographically
1.1 - Intro to Maps
Reference Maps: Designed for people to refer to for general info about a place. There are two types:
Political maps
Physical maps
Thematic Maps: Communication tools. They tell us how activities are distributed.
Cartogram: Distorts the size of regions based on their values
Choropleth: Colors regions based on their values; generally, darker is a higher value while lighter is less.
Dot Density: Places one dot for each value. All dots are the same size.
Isoline: Connects data points with curved lines to form regions of equal value.
Same concept as choropleth maps but more accurate since it’s not confined to political regions.
Proportional/Graduated Symbol: The size of a given symbol (commonly a dot) represents the value of a region; larger generally means larger value.
Locations
Absolute Location: Where on earth a specific thing is. Can be represented with coordinates.
Relative Location: Where something is in relation to another place.
Distance: How far two things are
Direction: Which way something is; north, south, east, and west.
Spatial Patterns
Clustering: Grouping or bunched together; agglomeration
Dispersal: Distributed over a large area
Elevation: How high/low something is located on the land
Map Projections:
Mercator Map
Shape and direction are fairly accurate
Size is distorted towards the poles
Used for navigation
Robinson Map
Compromise map; everything is distorted in small amounts.
Most accurate map
Goode
Continent sizes are accurate
Direction and distance isn’t accurate
Gall Peters
Shape of countries near the equator are distorted
Equal area projection
1.2 - Geographic Data
Geospatial Data: All information including physical features and human activities
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Layers of data used to make maps; useful for finding correlations between places and other factors.
Ex. John Snow’s cholera map
Global Positioning System (GPS): System of satellites used to pin point absolute location
Ex. Google maps
Remote sensing: The process of taking pictures of the earth’s surface remotely to provide a greater understanding of the Earth’s geography over large distances
Ex. Satellites tracking the spread of a forest fire
1.3 - The Power of Geographic Data
Census data: An official count of individuals in a population, telling the government about the demographics
Age
Gender
Race
1.4 - Spatial Concepts
Location
Absolute Location: Precise spot where something is located; can be represented with coordinates.
Relative Location: Where something is located in relation to another place.
Space: Physical space between two locations
Place: Human and physical characteristics of a location
Sense of Place: Emotions and memories attached to a place
Distance Decay: The affect of distance on interactions between two places; interactions decrease as distances increase.
Time-Space Compression: The increasing sense of connectivity as a result of globalization. Sense that distances are decreasing, despite them being the same.
Pattern: The arrangement of something in an area
1.5 - Human-Environment Interaction
Sustainability: The goal of the human race achieving equilibrium with the environment; meeting our needs while also protecting the ability of future generations to meet theirs
Natural Resources: A physical material constituting part of the Earth that people need and value
Environmental Determinism: Physical environments determined social development
Possibilism: The physical environment may limit some human actions, but people control their development
1.6 - Scales of Analysis
Scale: The relationship between the distance on the ground and the corresponding distance on a map
Large Scale: Shows more detail
Small Scale: Shows less detail
Scale of Analysis: How zoomed in or out you are while looking at geographic data; how is it “chunked”?
Local
National
Regional
Global
1.7 - Regional Analysis
Region: A place larger than a point and smaller than a planet; grouped together because of a measurable or perceived common feature
Formal Region: A region based on quantitative data; also called “Uniform”
Political boundaries
The French region of Canada
Texas
Functional Region: A region based around a node or focal point; also called “nodal”
Bus map
Radio station broadcast area
Perceptual Region: A region that shares a common qualitative characteristic; only a region because people believe it is. Boundaries vary from person to person because it’s based on opinion.
The “midwest”
Unit 2 - Population and Migration
2.1 - Population Distribution
Ecumene: Where people are settled on the earth’s surface
Physical Factors: People avoid too dry, too wet, too high, and too cold
Cultural Factors: Populations will be concentrated in areas with access to education, health care, and entertainment.
Historical Factors: Where people lived in the past tends to determine where our populations are today
Population Densities
Arithmetic Density: Total number of objects in an area divided by the amount of land
Doesn’t tell us much on its own
Physiological Density: People divided by arable land
Tells us if a country is considered overpopulated or not
Agricultural Density: Total number of farmers divided by arable land
Tells us how developed a country is
MDCs tend to have less people in agriculture, since they’re more mechanized
2.2 - Consequences of Population Distribution
Areas with larger populations have more power
Political: Greater control over laws and larger influence
Economic: Concentration of jobs, areas make more revenue
Social: Greater access to health care, better educational opportunities, greater cultural diversity
As populations grow, we begin to alter our landscapes
Carrying Capacity: The maximum size of the species that an environment can sustain
Overpopulation: There are not enough resources for the population
2.3 - Population Composition
Age/Sex Ratio: Comparison of the numbers of males and females of different ages. Population structure is unique to each area due to their own unique history and current condition.
Population Pyramid: A graph of the population of an area by age and sex
When a population is growing rapidly, it’s a pyramid.
When a population is stabilizing, it’s a rectangle
When a population is declining, it’s an inverted pyramid
Dependents: People too young or old to work that depend on the working population
2.4 - Population Dynamics
Crude Birth Rate (CBR): The number of live births per one thousand people in the population
Crude Death Rate (CDR): The number of deaths per one thousand people in the population
Doubling Time: The time period it takes for a population to double
Fertility: The number of live births occurring in a population
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR): The number of children who don’t survive their first year of life per 1000 births in a population
Mortality: The number of deaths occurring in a population
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI or NIR): (Birth Rate - Death Rate)/10; A positive RNI means that the population is growing, while a negative RNI means that the population is shrinking.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR): The average number of children a woman is predicted to have in her productive years
Social Factors: Role of genders in society, family planning, age of marriage, traditional family sizes, etc
Cultural Factors: Religion, ethnicity, etc
Governments: Reproductive laws, natalist/antinatalist policies, etc
Economic Factors: Women in the workforce, affordability, etc
2.5 - The Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
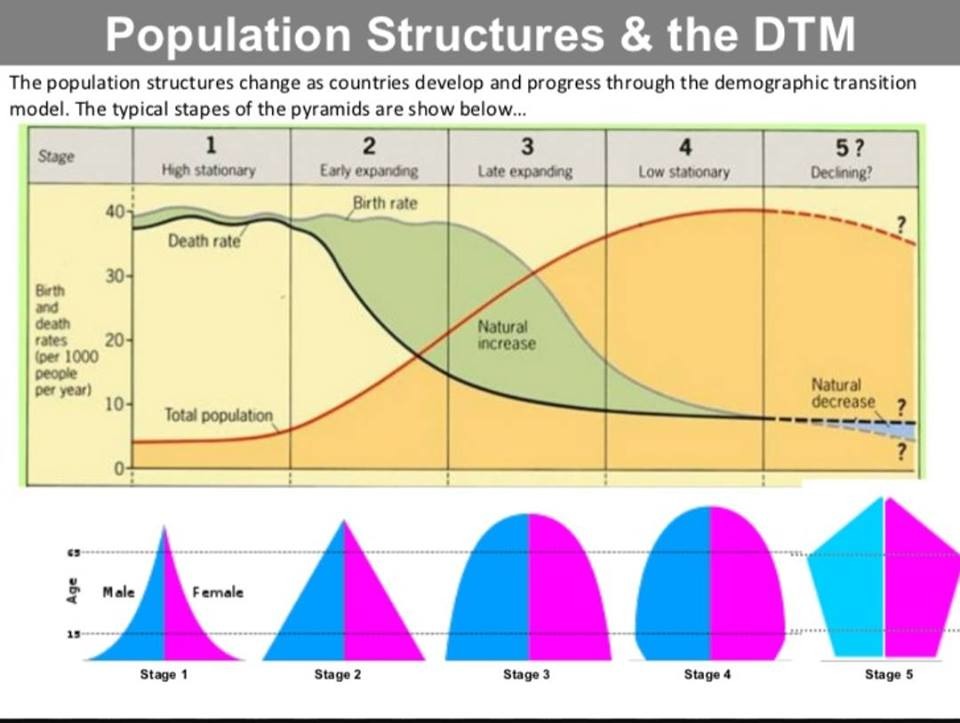
The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) has 5 stages that indicate different levels of development
Stage One: High CBR and high CDR; no population growth
No countries today are in stage one
Stage Two: Declining death rate, high CBR; population growth
Niger, Mali, etc
Stage Three: Declining CBR and CDR; still population growth
Egypt, Mexico, etc
Stage Four: Low CBR and CDR; population beginning to peak
USA, Canada, etc
Stage Five: Low CDR, lower CBR; population decline
Germany, Japan, etc
Epidemiological Transition Model (ETM): Corresponds with the DTM; what’s causing the deaths in a population as it evolves?
Stage One: Infectious disease and parasites cause the majority of human deaths
Stage Two: Improved sanitation and healthcare lowers death caused by infections and parasites
Stage Three: Deaths begin being caused by aging-related issues
Stage Four: Most deaths care caused by aging; peak population
Stage Five: Globalization and superbugs cause the reemergence of infections
Migration Transition Model
Stage One: No migration
Stage Two: Emigration, rural-to-urban
Stage Three: Suburbanization, Immigration
Stage Four: Suburbanization, Immigration
Stage Five: Suburbanization, Immigration
2.6 - Malthusian Theory
Malthusian Theory: Populations grow exponentially but food production increases arithmetically (linear)
Neo-Malthusian Theory: The earth can only support a finine number of people, and overpopulation can only be stopped by war and famine.
Cornucopian: People will always find a way to produce enough food
2.7 - Population Policies
Pronatalist Policies: A country provides incentives for people to have more children
Antinatalist Policies: A country provides incentives for people to have fewer children
Immigration Policies: States can set up policies that make it easier or harder to migrate into their territory
2.8 - Women and Demographic Change
Contraception: Methods of preventing pregnancy
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration:
The majority of migrants only go a short distance
Migration proceeds step by step (step migration)
Migrants going long distances usually go to large economic centers
Each migrating stream produces a compensating counter-stream
Natives of towns are less migratory than those of rural areas; people in urban areas are less likely to migrate
Females are more migratory within their area of birth, and males migrate more internationally
Most migrants are single young adults
Urban areas grow more as a result of migration than births
As infrastructure improves, migration increases
Most migration is rural-to-urban
Most migrants are seeking jobs
2.9 - Aging Populations
Dependency Ratio: The ratio of the number of people not in the workforce (dependents) and those in the workforce (producers)
Understanding the pressure on the producers
Life Expectancy: The average number of years someone is expected to live at birth
2.10 - Causes of Migration
Push Factors: Negatives; push people away from a place
Political instability, no jobs, slavery
Pull Factors: Positives; pull people towards an area
Jobs, freedom, stable government
Intervening Opportunity: The presence of a nearer opportunity that diminishes the attractiveness of sites father away
Intervening Obstacle: A force or factor that limits human migration
2.11 - Forced and Voluntary Migration
Chain Migration: a series of migrations within a group that begins with one person who through contact with the group, pulls people to migrate to the same area.
Step-Migration: migration to a far away place that takes place in stages
Guest Worker: a legal immigrant who is allowed into the country to work, usually for a relatively short time period
Transhumance: moving herds of animals to the highlands in the summer and into the lowlands in the winter
Transnational Migration: moving across a border into another country
Voluntary Migration: people choosing to migrate (not being forced)
Forced Migration: when people migrate not because the want to but because they have no other choice
Internally Displaced Persons (IDP): A person forced to flee their home who remains in their home country
Refugee: A person who flees their home country and is not able to return
Asylum Seeker: A person seeking residence in a country outside of their own because they fleeing persecution
2.12 - Effects of Migration
Political Impact
Brain drain: when the majority of educated or skilled workers leave an area to pursue better opportunities elsewhere
Cultural Impact - loss of culture or migrants bring in new languages
Economic Impact - loss or gain of income dependent on the migrant flow
Unit 3 - Cultural Patterns + Processes
3.1 - Introduction to Culture
Culture: Body of materials, customary beliefs, and social forms that together constitute the distinct tradition of a group or people.
Material Culture: The material manifestation of culture.
Artifacts
Tools, housing, systems of land use, clothing, etc.
Nonmaterial Culture:
Mentifacts
Shared ideas, values, and beliefs of a culture. Examples include religion, language, viewpoints, and ideas about right or wrong behaviour.
Sociofacts
Families, governments, education systems, sports organizations, religious groups
Cultural Relativism: The culture should be judged based on its own standards, not based on another culture.
Ethnocentrism: Judging other cultures based on the rules of your culture
Taboo: Something that is forbidden by a culture or a religion, sometimes so forbidden that it is often not even discussed
3.2 - Cultural Landscapes
Cultural Landscapes: The forms superimposed on the physical environment by people
Churches, buildings, etc
Ethnic Neighborhoods: Neighborhood that retains some cultural distinction from a larger surrounding area
Indigenous People: A cultural group that constitutes of the original people; distinct from the colonial, dominant population
3.3 - Cultural Patterns
Sense of Place: A strong feeling of identity that is deeply rooted in a location
Language: A set of mutually intelligible sounds and symbols used to communicate
Language Family
Language Branch
Language Group
Language
Dialect
Religion: The belief and worship of a superhuman controlling power, especially a god(s).
Ethnicity: The fact or state of belonging to a cultural group
Gender: How men are treated differently than women
3.4 - Types of Diffusion
Relocation Diffusion: Ideas are transmitted by their carriers during migration
Expansion Diffusion: The ideas are spread through a population without the carriers moving.
Contagious: Transmission through nearby places, like a disease
Stimulus: The idea inspires one somewhere else
Ex. Beef-free burgers in Indian McDonalds
Hierarchical: Spreading among the most influential/largest people first, before spreading to others
Reverse Hierarchical: Diffusion up a hierarchy; common people to large influencers
3.5 - Historical Causes of Diffusion
Creole: Language created by mixing two others; used as a primary language of many people and has grammar
Pidgin: Simple language used for communication between two groups with different languages; evolves into creole
Lingua Franca: Mutually understood language used in common by people with different native languages
Colonialism: An effort by one country to establish a colony and impose its political, economic, and cultural practices within the territory
Imperialism: Extending a country’s influence with the military to areas already developed
3.6 - Contemporary Causes of Diffusion
Globalization: World connectivity has played a key role in changing culture. Ideas spread much easier today, with the help of the internet especially.
Media: Exposure to western television
Technological Change: Exposure to the internet
Politics: Democracies being spread globally to encourage places to have more equality
Economics: Trade
Time-Space Convergence: The decline of travel time between two geographic locations as a result of increased transport and communication technology
Cultural Convergence: Different cultures acquire common ideas, products, and traits, becoming more similar
Cultural Divergence: Different parts of a culture are exposed to different influences and become dissimilar
3.7 - Diffusion of Religion
Indigenous Language: A language that is native to a region and spoken by anyone as their native language
Language Extinction: A language that is no longer spoken
Dialect: Different forms of the same language; varies across the globe. Different vocab, grammar, pronounciations
Nomadic Warrior Theory: Language moved through nomadic conquest (hierarchical)
Sedentary Farmer Theory: Language moved through farmers relocating (relocation)
Ethnic Religion: Focused on a single ethnic group and doesn’t appeal to others
Hinduism
Judaism
Universalizing Religion: Appeals to everyone
Christianity
Islam
Sikhism
Buddhism
Pilgrimage: A religious journey to a sacred space
3.8 - Effects of Diffusion
Acculturation: Adoption of new cultural traits, such as language, by one group under the influence of another
Assimilation: The process of a person or group losing the cultural traits that made them distinct from the people around them
Multiculturalism: Various ethnic groups coexist without sacrificing their identities
Syncretism: Blending traits from two different cultures to form a new trait
Unit 4 - Political Patterns + Processes
4.1 - Intro to Political Geography
State: Political unit with a permanent population and boundaries that are recognized by other states that allows for the administration of laws, collection of taxes, and provision of defense.
Four requirements to be considered a state
Sovereignty
Territory
Population
Recognition by other states
Nation: People who think of themselves as one based on a shared sense of culture and history
French
German
Indian
Nation-States: A state with a single nation
Japan
Iceland
Stateless Nations: A nation who do not have their own independent state
Palestinians
Kurds
Multinational States: A state with two or more nations
Canada
USA
Russia
Multistate Nations: A nation living across states. Can either have a state (Russia), a state divided in two (Korea), or be stateless (Kurds)
Autonomous Region: An area which governs itself but is not an independent country
Greenland
Hong Kong
Semi-Autonomous Region: An area which can govern itself in certain areas, but does not have complete power to govern
Nunavut in Canada
Indian Reservations in USA
4.2 - Political Processes
Sovereignty: Final authority over a territory and the right to defend territorial integrity against incursion.
Self-Determination: The process by which a country determines its own statehood and forms its own allegiances and government
Independence Movements: An area that believes it should be its own country
Devolution: The transfer of decision-making power from a central government to a lower level.
4.3 - Political Power and Territoriality
Choke Point: Strategic narrow route providing passage through/to another region
Panama Canal
Strait of Gibraltar
Neocolonialism: Modern colonialism; gaining indirect control (influencing) a country through economic pressure
Shatterbelt: An unstable region that constantly breaks apart due to stress/colliding external forces
Territoriality: The willingness of people to defend their land
4.4 - Defining Political Boundaries
Boundary: A line that determines the limit of jurisdiction (the ability to make legal decisions)
Relict: Boundary that no longer exists
Berlin Wall
Superimposed: Drawn by outside powers (colonizers) ignoring cultural boundaries
Africa - Berlin Conference
Subsequent: Evolves as a cultural landscape takes place and changes
India-Pakistan
Antecedent: Boundary created before people occupied the land
US-Canada border
Geometric: Boundary that follows a straight line or arc; usually based off lines of latitude/ longitude.
US-Canada border
Consequent: Coincide with cultural groups
India-Pakistan
4.5 - The Function of Political Boundaries
How are boundaries created?
Delimit: Drawing the boundary on a map
Demarcate: Using physical objects to define the borders of a boundary
Define: Treaty agreeing to having a boundary
Administer: Enforcing the boundary
Demilitarized Zone: An area previously in conflict; now weapons and military forces have been removed
North and South Korea border
The Berlin Conference: Meeting held in Berlin in 1884 and 1885 with the purpose of the European nations dividing Africa among them for colonization purposes. The superimposed boundaries of Africa remained in place after independence, which has led to much of the current conflict and lack of ability to establish effective leadership.
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS): Established rights and responsibilities of states concerning ownership/usage of the seas and their resources.
Marinetime Boundary: The extensions of a country's territory that extends into the oceans around them
Territorial Sea: zone of water adjacent to a state’s coast (12nm) in
which a state has sovereignty
Contiguous Zone: 24nm from the coast; states can enforce laws
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ): 200nm, where the state has a right to explore, exploit, conserve, and manage resources.
South China Sea: China has built military installations on some disputed islands in the SCS.The SCS accounts for 10 percent of the world’s fisheries, making it a key source of food for hundreds of millions of people. The region is also home to major oil and natural gas reserves. There are so many countries in close proximity to one another, resulting in high competition for maritime resources and tension over sovereignty.
4.6 - Internal Boundaries
Voting District: Subdivision for electing members to a legislative body
Redistricting: Voting districts are redrawn to reflect population change
Reapportionment: Number of seats is reapportioned to reflect population change
Gerrymandering: Redrawing voting districts to give one party an unfair advantage.
Packing: Putting all of one political party into one district to give them less power
Cracking: Splitting up a party into multiple opposition dominated districts to ensure they don’t win any districts
4.7 - Forms of Governance
Democracy: A form of government in which the ultimate power rests with the people through their elected representatives
Unitary State: A country where the national government is strong and the regional governments are weak/have no power; results in quick changes and simpler laws, but less concentration on local needs
U.K
North Korea
China
Federal State: A country where power is split between the national government and local governments; results in conflicting laws but more focus on local needs
United States
Canada
Russia
4.8 - Defining Devolutionary Factors
Devolution: the transfer of decision-making power from a central government to a lower level.
Physical Geography: physical boundaries can cause devolution as it was historically hard for resources for states to maintain autonomy over difficult physical regions
Ethnic Separatism: Mainly religion, language, or ethnicity related differences.
Quebec, Canada
Ethnic Cleansing: The mass expulsion or killing of members of an unwanted ethnic or religious group in a society
Terrorism: Violence against (typically) civilians for political reasons
Economic and Social Problems: Economic or social strife can lead to the devolution and altering of states.
Irredentism: When a state wants to annex a territory whose population is ethnically similar
Russia with Ukraine
4.9 - Challenges to Sovereignty
Supranationalism: political and/or economic alliance of three or more states that is formed for mutual benefit to promote shared goals or resolve disputes. Can limit the economic or political actions of member states creating a challenge to state sovereignty.
NATO, EU, UN
Economies of Scale: Cost advantages gained by increasing production
Trade Agreements: Treaty between multiple states to eliminate taxes and/or tariffs to encourage trade
Military Alliance: Alliance between two or more states who agree on mutual protection in case of crisis
NATO formed to defend against communist threats after WW2
4.10 - Consequences of Centrifugal and Centripetal Forces
Centripetal Force: Force or attitude that tends to unify people and enhance support for the state
Political: Majority/minority relationships, armed conflicts
Economic: Uneven development
Cultural: Stateless nations, ethnic movements
Centrifugal Force: Force or attitude that divides the state
Political - national identity, 4th of July
Economic - equitable infrastructure development
Cultural - linguistic, religious, and ethnic similarities
Unit 5 - Agriculture and Rural Land Use
5.1 - Intro to Agriculture
Agriculture: Modifying the environment to raise plants or animals for food or other uses’
Mediterranean Climate: Hot/dry-summer climate, mild winter and a defined rainy season that produces certain fruits, vegetables, and grains such as grapes, olives, figs, dates, tomatoes, zucchini, wheat and barley. It prevails along the shores of the Mediterranean, in parts of California and Oregon, in central Chile, South Africa’s Cape, and in parts of Australia
Tropical climate: hot, humid climate that produces certain plants, such as cassava, banana, sugar cane, sweet potato, papaya, rice, maize
Extensive agriculture: agriculture that uses small amounts of labor on a large area of land
Shifting Cultivation: Farmers move from one field to another; aka slash-and-burn agriculture because farmers clear and fertilize the land by burning vegetation. When the soil loses fertility, the farmers move to a different plot of land and repeat.
Subsistence
Rice, maize
Nomadic Herding: Nomads move herds to different pastures and trade meat, milk, and hides.
Subsistence
Cattle
Ranching: Grazing of livestock.
Commercial
Cattle
Grain Farming: Farms sell their output to manufacturers of food products, such as breakfast cereals and bread.
Commercial
Wheat
Intensive agriculture: agriculture that uses a lot of labor on a small area of land
Market Gardening: Some of the fruits and vegetables are sold fresh to consumers, but most are sold to large processors for canning or freezing.
Commercial
Tomatoes, lettuce
Plantation Agriculture: A plantation specializes in one crop that is transported for sale on the global market.
Commercial
Cotton
Mixed Crop/Livestock: Farming characterized by integration of crops and livestock; most of the crops are fed to animals rather than consumed by humans.
Commercial
Cows + corn
5.2 - Settlement Patterns and Survey Methods
Clustered: A pattern of rural settlement in which the houses and farm buildings of each family are situated close to each others' fields and surround the settlement; everything is close together.
Dispersed: Settlement pattern with people living relatively far from each other on their farms.
Township and range; equal squares of land
Linear Settlement: A rural land use pattern that creates a long, narrow settlement around a river, coast, or road that looks like a line
French Long Lot; follows river
Metes and Bounds: property boundaries go to physical features
Can be linear, dispersed, and clustered
5.3 - Agricultural Origins and Diffusion
Fertile Crescent: A crescent-shaped area in the Middle East where settled farming first began to emerge leading leading to the rise of cities
Columbian Exchange: A widespread exchange of animals, plants, culture, human populations, communicable diseases, and ideas between the Americas (New World) and Europe (Old World)
Tomato, potato, maize, turkey from New → Old
Wheat, cow, pig, disease Old → New
First Agricultural Revolution (Neolithic): Transition from hunting and gathering to settled agriculture; first domestication of crops and animals
Domestication: The process of taming plants or animals for human use
Agricultural Hearths: The separate locations in which groups of people began to domesticate plants and animals.
Commonalities Among Agricultural Hearths: Fertile soil in river valleys, availability of water, moderate climates, and collective societal structures
5.4 - The Second Agricultural Revolution
Second Agricultural Revolution: Coincides with the Industrial Revolution; increasing yield and access through machines and transportation. Mechanization
Caused by the industrial revolution and the enclosure movement (private owned land)
Effects of the Second Agricultural Revolution: New technology, increased food production, better diet, longer life, and more people available for work in factories, shifting demographics (moving to cities, less farmers)
Enclosure Movement: Land becomes private
Fewer and larger farms→decrease in farm owners→improvements in farming techniques→decrease in agricultural laborers→more job diversity
Urbanization: Mass migration of people into the cities to work in newly emerging factories.
5.5 - The Green Revolution
Green Revolution: The spread of new technologies like high yield seeds and chemical fertilizers to the developing world in the 1960s and 1970s
Positive
Able to grow more crops on same amount of land
which decreases food prices
More crops grown on same size land
Improvement in variety
Negative
Destroying local land and traditional modes of
agricultural production
Decreasing biodiversity (hybrid seeds diminish local
plant diversity)
Impact of chemicals
Biotechnology: Application of scientific techniques to modify and improve plants, animals, and microorganisms to enhance their value.
5.6 - Agricultural Production Regions
Subsistence Agriculture: Only enough food is cultivated to survive
Commercial Agriculture: The production of crop for sale and profit
Monoculture: Growing one crop in a farm system each rotation
Mono-Cropping: Growing one crop in a farm system year after year.
Bid-Rent Theory: Price and intensive use of land will change as the distance from the central business district (CBD) increases
5.7 - Spatial Organization of Agriculture
Commodity Chain: Activities involved in the creation of a product: design, production of raw
materials, manufacturing and assembly, distribution
Agribusiness: System of commercial agriculture that links various industries to the farm
Economies of Scale: Cost advantages that come producing a large amount of an item
5.8 - Von Thunen Model
Explains rural land use by emphasizing the importance of transportation costs associated with distance from the market Von Thünen’s rings distribute various farming activities into concentric rings around a central market city.
Old model
Assumes isotropic land
Dairy and Market Gardening: Perishable intensive food is closest to the market
Forest: Expensive transport and needed for heating and cooking
Grain Farming: Cheap transport and extensive→ requires cheaper land
Ranching: Animals walk themselves and extensive land use
5.9 - The Global System of Agriculture
Global Supply Chain: Worldwide network to maximize profits in production
Export Commodity: Commodities being sold (exported) to other places
Some states have become extremely dependent on these exports for their economies
5.10 - Consequences of Agricultural Practices
Pollution: Process by which soil is contaminated by chemicals (fertilizers and pesticides)
Land Cover Change: Agricultural areas are lost to development
Conservation: Protection of wildlife and natural resources, like habitats and ecosystems
Deforestation: Human-driven loss of trees
Desertification: Area becoming arid and losing vegetation
Result of too much irrigation
Irrigation: Moving water to where you need it
Draining Wetlands: Drainage for agricultural practices
Fertile land once drained but bad for environment
Pastoral Nomadism: Overgrazing can cause desertification
Soil Salinization: Build up of salt in soil, particularly in irrigated areas, that makes soil unable to grow plants
Terrace Farming: Method of growing crops on the sides of hills or mountains by planting on man-made steps (terraces)
Changing Diets: We have to figure out a way to continue eating but sustainably
5.11 - Challenges of Contemporary Agriculture
Agricultural Biotechnology: Use of scientific tools and techniques to modify plants and animals
Pest-resistent crops
GMO: Organisms whos DNA has been genetically modified for a desired trait
Aquaculture: Raising seafood in ponds or controlled water
Value Added Crops: Foods that have been altered to increase their value
Berries→Jam
Organic Farming: Crops produced without the use synthetic or industrially produced pesticides and fertilizers or genetically engineered seeds
Fair Trade: Trade between MDC and LDC in which fair prices are paid to the producers; money is also returned to their communities
Community-Supported Agriculture (CSA): Individuals who pledge support to a farm operation so that growers and consumers provide mutual support
Urban farming: Integrating growing crops or raising animals into an urban ecosystem
Dietary Shifts: Movement from processed foods, meat, and sugars towards one more based in fruits and vegetables
Food Insecurity: Being without reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food
Food Desert: Geographic area where large grocery stores are scarce or missing and residents have limited access to fresh nutritious foods. Typically found in urban, low-income neighborhoods
Weather: agricultural production is affected by high temperatures, drought, flooding, storms, freezes
5.12 - Women in Agriculture
Women are frequently denied loans or financial support
Women may be unable to obtain or access inputs to improve productivity (e.g., land, animals, equipment, seeds, fertilizer, or infrastructure).
Women practicing subsistence agriculture may not be able to generate a surplus.
Impacts of exposure to environmental hazards (agricultural pollution, chemicals, groundwater pollution) that cause health problems for women and children
Laws and government policies preventing women from acquiring land tenure, owning, or inheriting land.
Women may lack access to political processes (voting), and institutions (representative government); or females lack political power to improve law and policy affecting women’s issues.
Empowering and investing in rural women has been shown to significantly:
Increase productivity
Reduce hunger and malnutrition
Improve rural livelihood
Unit 6 - Cities and Urban Land Use
6.1 - The Origin and Influences of Urbanization
Site: Features at the absolute location
Natural Harbor
Natural Resources
Climate
Elevation
Situation: Where the place is in relation to other things
Next to forest
Next to large city
Access to choke point
Urbanization: The movement of people from rural areas to cities
Early humans were nomadic, meaning no permanent home
First agriculture revolution (Neolithic) created permanent settlements, typically in fertile river valleys
Farmers could grow more crops to support a larger population
More jobs
Factors that influence Urbanization:
Transportation: Innovations in transportation have shaped and reshaped the layout and size of cities and their surrounding areas over time.
Car
Rural to Urban Migration: Movement of people from rural settlements to urban centers in search of jobs.
6.2 - Cities Across the World
Megacities: 10 million inhabitants or more
Cairo
Mumbai
Beijing
Metacities: 20 million inhabitants or more
Tokyo
Delhi
Shanghai
Megalopolis: Region in which several large cities and surrounding areas grow together
Metropolitan Area: Region that includes a city and its surrounding suburbs
Suburbanization: Population shift from central urban areas into suburbs
Urban Sprawl: Tendency of cities to grow outward in an unchecked manner
Edge Cities: Nodes of economic activity that have developed in the periphery of large cities
The Domain
Exurbs: Prosperous area beyond the suburbs.
Boomburbs: Large, rapidly growing, incorporated communities of more than 100,000 residents
6.3 - Cities and Globalization
World City: Control center of the global economy, in which major decisions are made about the world’s commercial networks and financial markets.
Tokyo
Paris
New York City
6.4 - The Size and Distribution of Cities
Rank-Size Rule: The country's nth-largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest
settlement.
Federal government
Primate City: Urban area that dominates its country's economy, culture, and political
affairs and is more than twice the population of the next largest city.
Uneven development
Christaller’s Central Place Theory: Explains how services are distributed and why a
regular pattern of settlements exists
Threshold: # of people required to support businesses
Range: distance people will travel to acquire a good
Low-Order Goods: Used by consumers on a regular/daily basis and, as a result, people are not willing to travel far to use them
Gas stations
High-Order Goods: are used less frequently by consumers and, as a result, people are willing to travel further for it.
Eras tour
Gravity Model: interaction of places based on their population, sizes, and distances between them
The greater the number of people in an area, the greater the number of potential customers for a service.
The farther people are from a particular service, the less likely they are to use it.
6.5 - The Internal Structure of Cities
Concentric-Zone Model: Burgess
Divides the city into five concentric zones centered around the CBD
Based on Chicago
Rich people live on periphery (commuters)
Sector Model: Hoyt
Zones expanded outward from the city center along transportation corridors creating a wedge shape.
As growth occurs, similar activities stay in the same area and extend outward.
Low income near industry
Multiple Nuclei Model: Harris & Ullman
Developed countries and large expanding cities
CBD is scattered into several nodes, with transportation hubs near industries and airports.
Low income housing is found near workers while high income housing is found in elite districts.
Galactic (Peripheral) City Model: Harris
Inner city, surrounded by large suburban residential and business areas and tied together by transportation nodes (edge cities)
Highway ring
Latin American City Model: Griffin and Ford
Spine w elite housing, disamenity zone on periphery + sectors
Mix of sector + concentric ring
African City Model: Harm DeBlij
3 CBDs: Colonial CBD, Traditional CBD, and Market CBD.
The quality of residence gets poorer the farther from the CBDs.
No rich zones
Southeast Asian Model: McGee
Old colonial port zone
Western commercial zone
Alien Commercial Zone (dominated by Chinese merchants)
No formal CBD
New suburbs + squatter settlements bc of rapid expansion
Bid Rent Theory: Geographical economic theory that refers to how the price and demand for real estate change as the distance from the central business district increases
6.6 - Density and Land Use
Low Density Housing: Residential homes, lots of open space fewest people per geographic unit
Suburbs
Medium Density Housing: Townhomes, single unit housing
High Density Housing: High rises, most people per unit. Land is more expensive in these areas and causes people to be more crammed into smaller apartments
Urban areas
Infiling: Population density in an urban center is increased by building on underused land
6.7 - Infrastructure
Economic development and interconnection within urban areas are dependent upon the location and quality of infrastructure
The fastest growing cities are found in developing countries which have just recently just industrialized
In developing countries, modern technologies in transportation and public facilities are not very available.
6.8 - Urban Sustainability
Smart-Growth: Urban planning that avoids urban sprawl and focuses on long term implications with sustainable design initiatives and guides development into more convenient patterns and into areas where infrastructure allows growth to be sustained over the long term.
New Urbanism: Walkable blocks and streets, housing and shopping in close proximity, and accessible public spaces.
Greenbelts: Areas of undeveloped land around an urban area. Limit the sprawl of urban areas.
Slow-Growth Cities: Slowing a city’s growth to limit the problems associated with growth and improve sustainability.
De Facto Segregation: Racial segregation that happens by fact rather than by legal requirement
Positive of Urban Sustainability: Reduction of sprawl, improve walkability and transportation, improved and diverse housing options, and improved livability and promotion of sustainable options.
Negatives of Urban Sustainability: Increased housing costs, possible de facto segregation, and loss of historical character.
6.9 - Urban Data
Quantitative information about a city’s population is provided by census and survey data and provides information about changes in demographics and size in urban areas.
Lawmakers can create maps to look at residential and racial segregation
Qualitative data from field studies and narratives provide information about individual attitudes toward urban change.
Maps commonly show ethnicity of neighborhoods and other characteristics like predominant gender.
6.10 - Challenges of Urban Changes
Redlining: Discriminatory real estate practice in North America in which members of minority groups are prevented from obtaining money to purchase homes or property
Blockbusting: Real estate technique to encourage people to sell their property at a very low price by giving the impression that the neighborhood was changing for the worse, especially in reference to minorities moving in, Led to the “white flight” to the suburbs
Affordable Housing: residential units that are economical for the section of society whose income is below the median household income
Environmental Injustice: disproportionate exposure to communities of color and the poor to pollution and its effects on health and the environment
Squatter Settlements: residential areas characterized by extreme poverty with shelters constructed of found materials that usually exist on land outside of cities that are neither owned or rented by its occupants with little or no access to necessary services.
Inclusionary Zoning: Planning ordinances that provide affordable housing to people with low to moderate incomes
Local Food Movements: Food that is produced within a short distance of where it is consumed
Urban Renewal: Redevelopment of areas within an urban area
Gentrification: Restoration of deteriorated urban areas by wealthier people who move into, renovate, and restore housing.
Negative: Impact to existing groups, displaces poorer residents, disregards the needs and interests of vulnerable groups
Positive: New employment opportunities, improved housing, improved infrastructure, and increase in visitors/tourism
6.11 - Challenges of Urban Sustainability
Urban sustainability: The goal of improving the social and economic conditions of an increasingly urbanized population while maintaining environmental quality.
Suburban Sprawl: Spreading of developments into suburban or rural areas.
Pollution: Increased greenhouse gasses, acid rain, and ozone depletion.
Less agriculture land + loss of habitat
Brownfield: Property, the expansion, redevelopment, or reuse of which may be complicated by the presence or potential presence of a hazardous substance, pollutant, or contaminant.
Ecological Footprint: Measure of the human pressures on the natural environment from the consumption of renewable resources
Responses to the Challenges of Urban Sustainability:
Redevelopment of Brownfields,
Urban Growth Boundaries
Farmland Protection Policies
Unit 7 - Industrial and Economic Development Patterns and Processes
7.1 - The Industrial Revolution
Industrial Revolution: A period of rapid growth caused by increased mechanization in manufacturing and production; began in the 1700s
Began in England
Caused an increase in food production
Urbanization
Increased the gap wage between the poor and the wealthy
Increased imperialism and colonialism as now countries need more raw materials
7.2 - Economic Sectors and Patterns
Primary Sector: Extraction of raw materials
Mining
Fishing
Lumber
Agriculture
Secondary Sector: Processing natural materials into finished goods
Manufacturing
Construction
Utilities
Tertiary Sector: Offering services to consumers
Retail
Tourism
Entertainment
Quaternary Sector: Research and administration involved often associated with technological innovation
Finance
Insurance
Marketing
Wholesale
Quinary Sector: The highest levels of decision making in a society or economy
CEO
School superintendent
Site Factors: Industrial location factors related to the cost of the factory’s production
Land: Cheap land farther from the CBD; want to be close to highways and other transport routes
Labor: Most important site factor globally; cost and availability of workers
Capital: Funds to establish new factories or expand existing ones; most important site factor in certain industries
Labor-Intensive Industry: Wages and other compensation paid to employees are the majority of expenses
Break-of-Bulk Point: Location where transfer is possible from one mode of transport to another
Plane→Truck→Ship
Weber’s Least Cost Theory: Minimize costs in three categories to determine the location of a factory
Transport
Bulk Gaining: Product gains volume or weight during production, increasing shipping costs. Factories tend to settle closer to destination to minimize transport costs
Bulk Reducing: Product looses weight during production; it’s more affordable to settle near inputs
Labor
Agglomeration
Clustering of similar activities can reduce the price of operation
7.3 - Measures of Development
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Value of total number of goods and services produced domestically in a year
Gross National Product (GNP): Value of all goods, services, and investments produced by a country in a year
Gross National Income Per Capita (GNI): Value of outputs produced in a country per year, divided by the population
Gender Inequality Index (GII): Measure of the extent of each country’s gender inequality
Human Development Index (HDI): Level of development in each country; takes into account multiple factors to be more accurate.
Literacy rate
Income
Education
Life expectancy
7.4 - Women and Economic Development
As countries develop, more women enter the workforce
They do not necessarily have equal wages
Microloans: Small loans given to people in LDCs to start a business
Helps women start their own businesses
7.5 - Theories of Development
Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth: Assumes that all countries want to modernize like the United States. Aligns with DTM
Stage One: Traditional Society
Subsistence Agriculture
No countries today are in this stage
Stage Two: Preconditions to Take Off
Improvements in infrastructure
Mali, Niger
Stage Three: Take Off
Industrialization
India
Stage Four: Drive to Maturity
Less reliance on imports
Diversification of jobs
Innovations
China
Stage Five: High Mass Consumption
Consumer-oriented economy
Tertiary sector is dominant
USA
Dependency Theory: LDCs are dependent on technology from MDCs to provide infrastructure and employment. This creates a cycle of dependency on MDCs and prevents their economies from fully developing
Wallerstein’s World Systems Theory: Attempts to explain the relationship between the core and periphery countries.
The core benefits from the periphery and semi-periphery.
The semi-periphery can benefit from the periphery while still benefiting the core.
7.6 - Trade and the World Economy
Complementarity: One place has what another wants
Flow of seasonal fruits and vegetables from California's Valley to urban markets of the American Midwest and East
Comparative Advantage: Ability of a country to produce goods and/or services at a lower
opportunity cost than others
Neoliberal Policies: Policies that favor free markets and trade
Reduce taxes and tarrifs
Free Trade Agreements: Eliminating trade barriers to encourage trade
European Union (EU): Economic union of 28 member states that are located in Europe; trade bloc
World Trade Organization (WTO): Negotiate rules of trade among the member states
MERCOSUR: Economic bloc comprising Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and Venezuela. Essentially EU for South America
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC): Control worldwide prices of gas.
Tariffs: Taxes on items leaving or entering a country, often used to raise the price of imported goods
International Monetary Fund (IMF): Provides loans to countries experiencing economic problems that threaten expansion of international trade.
7.7 - Changes as a Result of the World Economy
Outsourcing: Hiring people from outside of your company to do things for you
Newly Industrializing Countries (NICs): The NICs are Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, and Mexico
Special Economic Zones (SEZs): Specific areas within a country in which tax and investment incentives are implemented to attract foreign businesses and investment.
Free-Trade Zones: No tariffs between countries; special zones in which all trade barriers between two countries are eliminated.
Maquiladoras → Mexico
Export Processing Zones (EPZs): Provide incentives for foreign companies to conduct their business in developing regions.
Foreign investments
Improved employment opportunities.
International Division of Labor: Transfer of some types of jobs, especially those requiring low-paid less skilled workers, from MDCs → LDCs
Fordism: Form of mass production in which each worker is assigned one specific task to perform repeatedly
Assembly line
Post-Fordism: Adoption by companies of flexible work rules, such as the allocation of workers to teams that perform a variety of tasks
Economies of Scale: Increase In efficiency of production as the number of goods being produced increases
Service Sector: The portion of the economy concerned with services
Transport
Communication
Retail
7.8 - Sustainable Development
Sustainable Development: Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Ecotourism: Tourism that doesn't harm the environment + benefits local people. Usually a small-scale activity with a small number of visitors in an area at a time.
National parks
UN’s Sustainable Development Goals: A declaration with the goal of improving the living conditions of people in the least developed countries. The goals were:
Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
Achieve universal primary education
Promote gender equality and empower women
Reduce child mortality
Improve maternal health
Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases
Ensure environmental sustainability
Develop a global partnership for development