APHUG-All Units
1/276
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
277 Terms
Reference Maps
Designed for people to refer to for general info about a place.
Political map
Physical map
Thematic Maps
Communication tools. They tell us how activities are distributed.
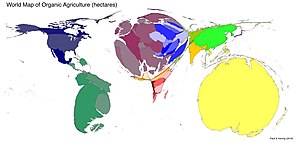
Cartogram
Distorts the size of regions based on their values
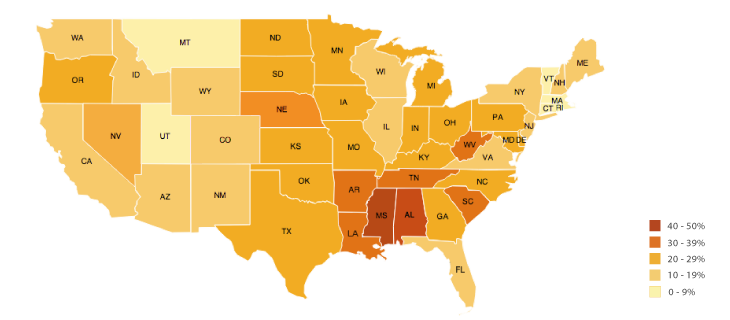
Choropleth
Colors regions based on their values; generally, darker is a higher value while lighter is less.
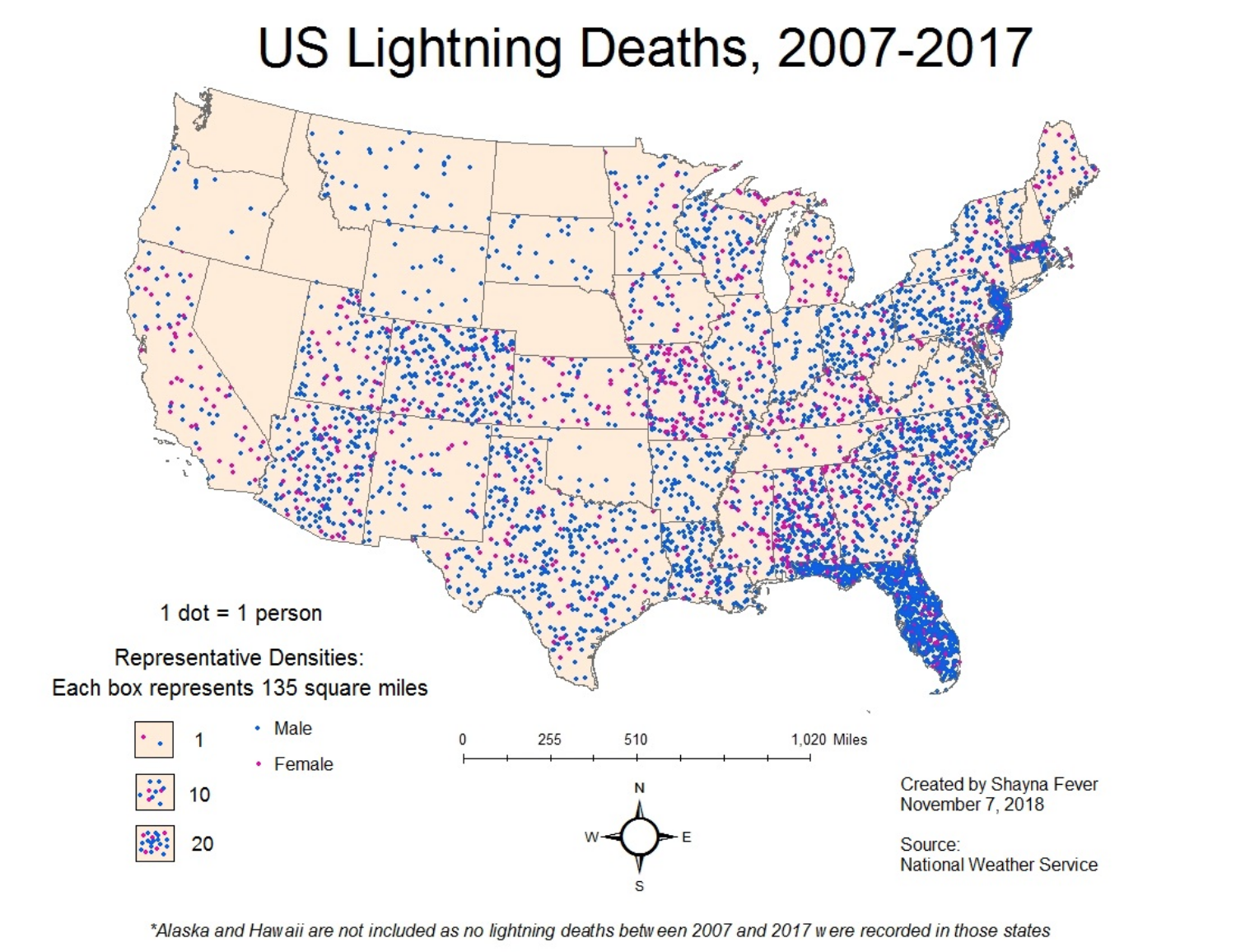
Dot Density
Places one dot for each value. All dots are the same size.
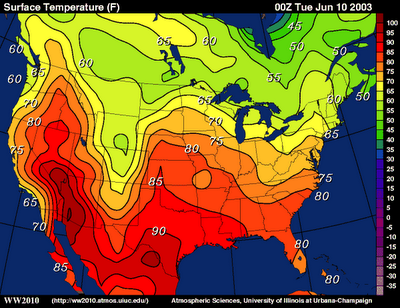
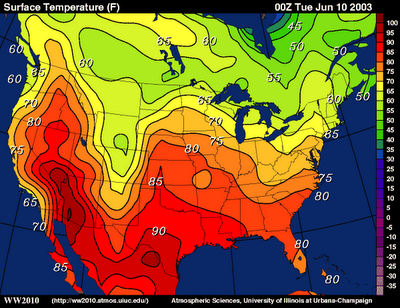
Isoline
Connects data points with curved lines to form regions of equal value.
Same concept as choropleth maps but more accurate since it’s not confined to political regions.
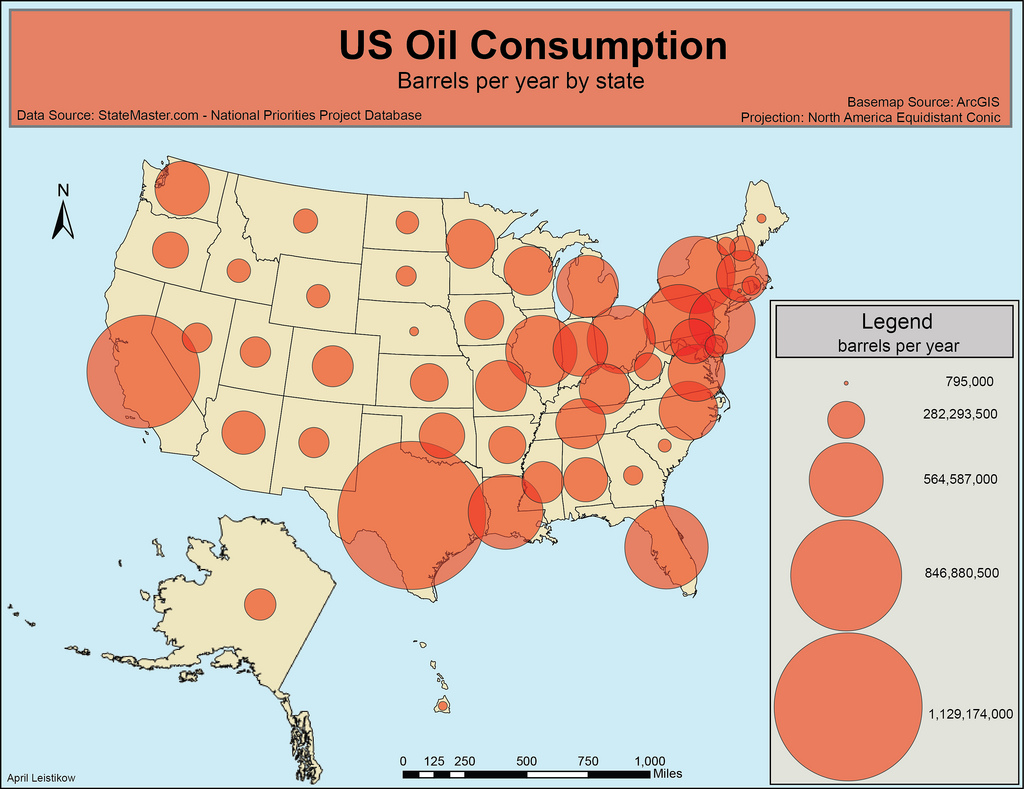
Proportional/Graduated Symbol
The size of a given symbol (commonly a dot) represents the value of a region
Larger generally means larger value.
Absolute Location:
Where on earth a specific thing is. Can be represented with coordinates.
Relative Location
Where something is in relation to another place.
Distance
How far two things are
Direction
Which way something is; north, south, east, and west.
Clustering
Grouping or bunched together; agglomeration
Dispersal
Distributed over a large area
Elevation
How high/low something is located on the land
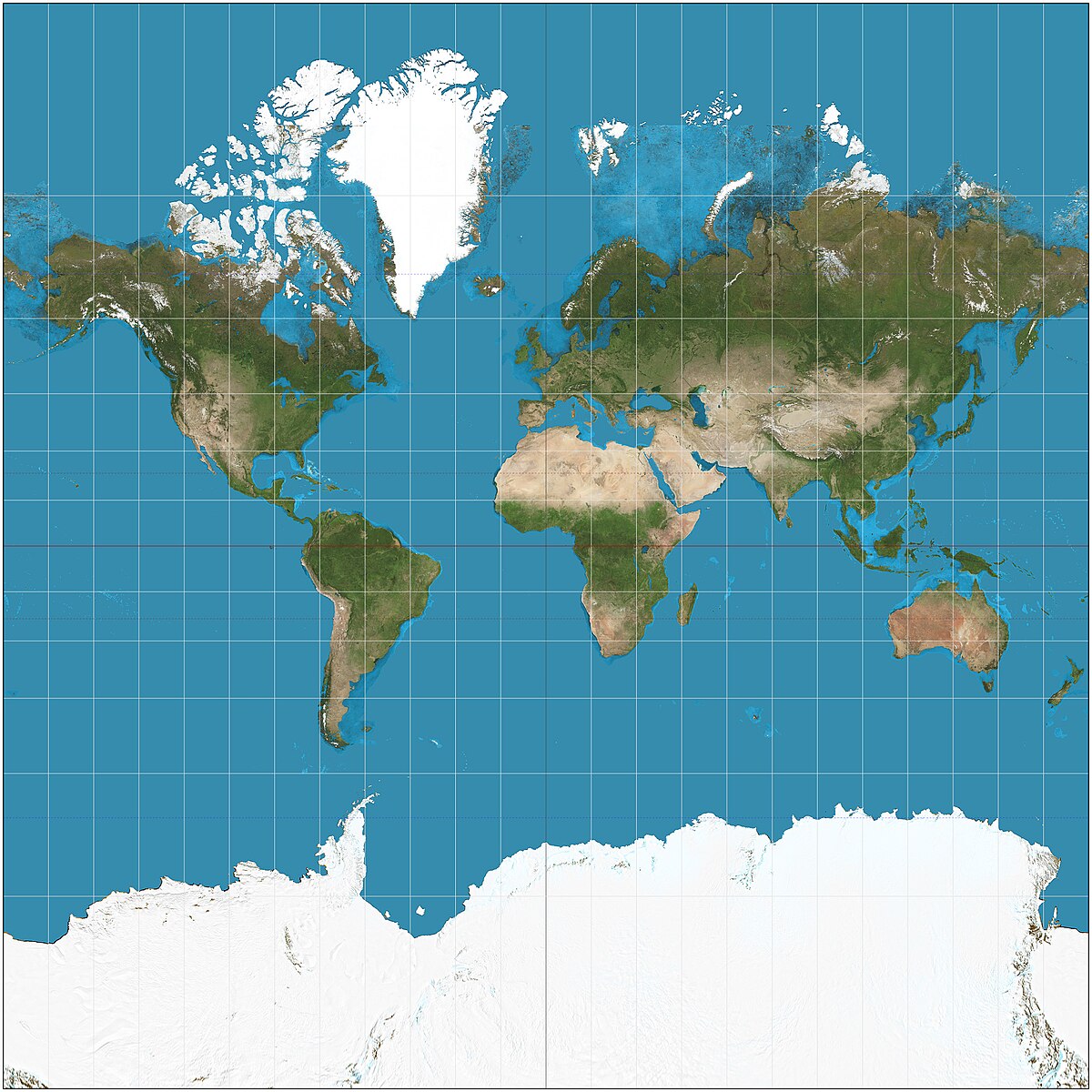
Mercator Map
Shape and direction are fairly accurate
Size is distorted towards the poles
Used for navigation
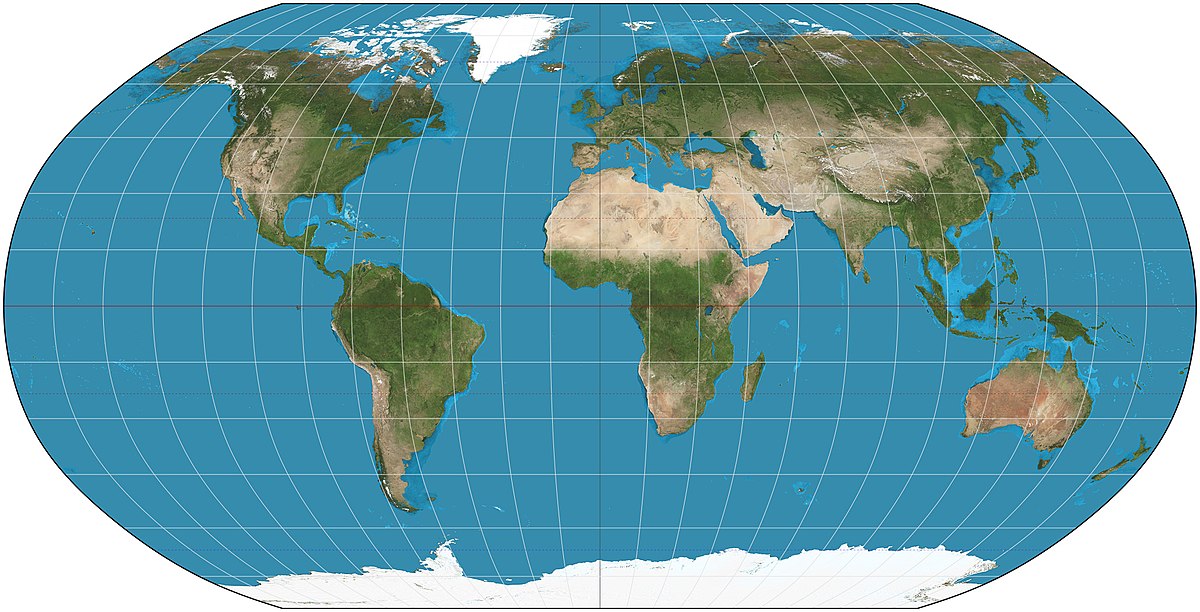
Robinson Map
Compromise map; everything is distorted in small amounts.
Most accurate map
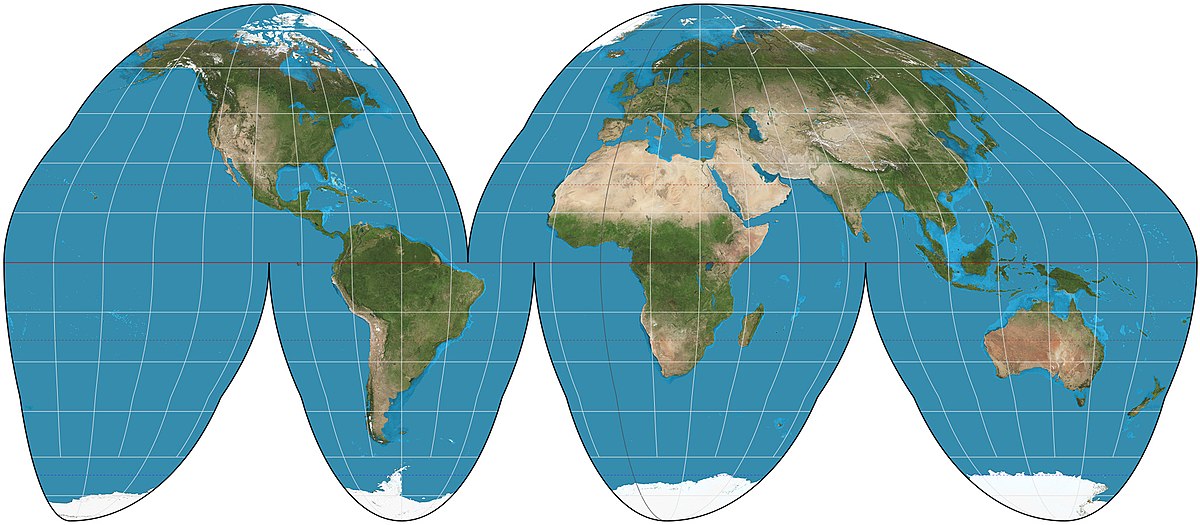
Goode
Continent sizes are accurate
Direction and distance isn’t accurate

Gall Peters
Shape of countries near the equator are distorted
Equal area projection
Geospatial Data
All information including physical features and human activities
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Layers of data used to make maps; useful for finding correlations between places and other factors.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
System of satellites used to pin point absolute location
Remote sensing
The process of taking pictures of the earth’s surface remotely to provide a greater understanding of the Earth’s geography over large distances
Census data
An official count of individuals in a population, telling the government about the demographics
Age
Gender
Race
Absolute Location
Precise spot where something is located; can be represented with coordinates.
Relative Location
Where something is located in relation to another place.
Space
Space: Physical space between two locations
Place
Human and physical characteristics of a location
Sense of Place
Emotions and memories attached to a place
Distance Decay
The affect of distance on interactions between two places; interactions decrease as distances increase.
Time-Space Compression
The increasing sense of connectivity as a result of globalization. Sense that distances are decreasing, despite them being the same.
Pattern
The arrangement of something in an area
Sustainability
The goal of the human race achieving equilibrium with the environment; meeting our needs while also protecting the ability of future generations to meet theirs
Natural Resources
A physical material constituting part of the Earth that people need and value
Environmental Determinism
Physical environments determined social development
Possibilism
The physical environment may limit some human actions, but people control their development
Scale
The relationship between the distance on the ground and the corresponding distance on a map
Large Scale: Shows more detail
Small Scale: Shows less detail
Scale of Analysis
How zoomed in or out you are while looking at geographic data; how is it “chunked”?
Local
National
Regional
Global
Region
A place larger than a point and smaller than a planet; grouped together because of a measurable or perceived common feature
Formal Region
A region based on quantitative data; also called “Uniform”
Functional Region
A region based around a node or focal point; also called “nodal”
Perceptual Region
A region that shares a common qualitative characteristic; only a region because people believe it is. Boundaries vary from person to person because it’s based on opinion.
Ecumene
Where people are settled on the earth’s surface
Physical Factors: People avoid too dry, too wet, too high, and too cold
Cultural Factors: Populations will be concentrated in areas with access to education, health care, and entertainment.
Historical Factors: Where people lived in the past tends to determine where our populations are today
Arithmetic Density
Arithmetic Density: Total number of objects in an area divided by the amount of land
Doesn’t tell us much on its own
Physiological Density
People divided by arable land
Tells us if a country is considered overpopulated or not
Agricultural Density:
Total number of farmers divided by arable land
Tells us how developed a country is
MDCs tend to have less people in agriculture, since they’re more mechanized
Consequences of Population Distribution
Areas with larger populations have more power
Political: Greater control over laws and larger influence
Economic: Concentration of jobs, areas make more revenue
Social: Greater access to health care, better educational opportunities, greater cultural diversity
As populations grow, we begin to alter our landscapes
Carrying Capacity
The maximum size of the species that an environment can sustain
Overpopulation
There are not enough resources for the population
Age/Sex Ratio
Comparison of the numbers of males and females of different ages. Population structure is unique to each area due to their own unique history and current condition.
Population Pyramid
A graph of the population of an area by age and sex
When a population is growing rapidly, it’s a pyramid.
When a population is stabilizing, it’s a rectangle
When a population is declining, it’s an inverted pyramid
Dependents
People too young or old to work that depend on the working population
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The number of live births per one thousand people in the population
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The number of deaths per one thousand people in the population
Doubling Time
The time period it takes for a population to double
Fertility
The number of live births occurring in a population
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The number of children who don’t survive their first year of life per 1000 births in a population
Mortality
The number of deaths occurring in a population
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI or NIR)
(Birth Rate - Death Rate)/10; A positive RNI means that the population is growing, while a negative RNI means that the population is shrinking.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman is predicted to have in her productive years
Social Factors: Role of genders in society, family planning, age of marriage, traditional family sizes, etc
Cultural Factors: Religion, ethnicity, etc
Governments: Reproductive laws, natalist/antinatalist policies, etc
Economic Factors: Women in the workforce, affordability, etc
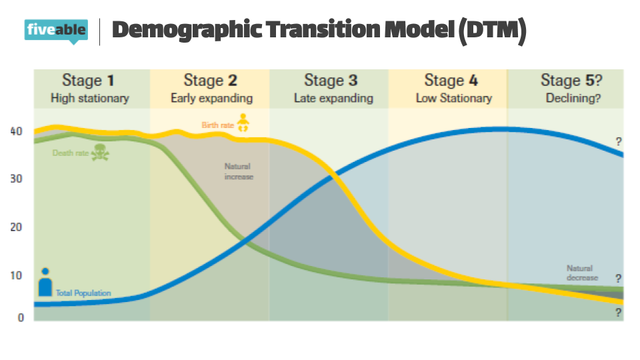
The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) has 5 stages that indicate different levels of development
Stage One: High CBR and high CDR; no population growth
No countries today are in stage one
Stage Two: Declining death rate, high CBR; population growth
Niger, Mali, etc
Stage Three: Declining CBR and CDR; still population growth
Egypt, Mexico, etc
Stage Four: Low CBR and CDR; population beginning to peak
USA, Canada, etc
Stage Five: Low CDR, lower CBR; population decline
Germany, Japan, etc
ETM
Epidemiological Transition Model (ETM): Corresponds with the DTM; what’s causing the deaths in a population as it evolves?
Stage One: Infectious disease and parasites cause the majority of human deaths
Stage Two: Improved sanitation and healthcare lowers death caused by infections and parasites
Stage Three: Deaths begin being caused by aging-related issues
Stage Four: Most deaths care caused by aging; peak population
Stage Five: Globalization and superbugs cause the reemergence of infections
Migration Transition Model
Migration Transition Model
Stage One: No migration
Stage Two: Emigration, rural-to-urban
Stage Three: Suburbanization, Immigration
Stage Four: Suburbanization, Immigration
Stage Five: Suburbanization, Immigration
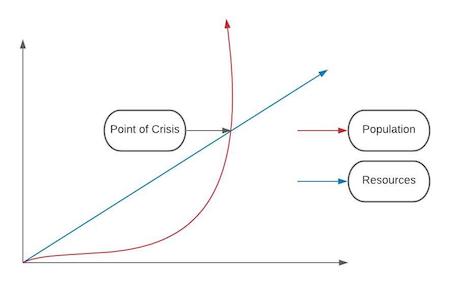
Malthusian Theory: Populations grow exponentially but food production increases arithmetically (linear)
Neo-Malthusian Theory
The earth can only support a finine number of people, and overpopulation can only be stopped by war and famine.
Cornucopian
People will always find a way to produce enough food
Pronatalist Policies
A country provides incentives for people to have more children
Antinatalist Policies
A country provides incentives for people to have fewer children
Immigration Policies
States can set up policies that make it easier or harder to migrate into their territory
Contraception
Methods of preventing pregnancy
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration:
The majority of migrants only go a short distance
Migration proceeds step by step (step migration)
Migrants going long distances usually go to large economic centers
Each migrating stream produces a compensating counter-stream
Natives of towns are less migratory than those of rural areas; people in urban areas are less likely to migrate
Females are more migratory within their area of birth, and males migrate more internationally
Most migrants are single young adults
Urban areas grow more as a result of migration than births
As infrastructure improves, migration increases
Most migration is rural-to-urban
Most migrants are seeking jobs
Dependency Ratio
The ratio of the number of people not in the workforce (dependents) and those in the workforce (producers)
Understanding the pressure on the producers
Life Expectancy
The average number of years someone is expected to live at birth
Push Factors
Push Factors: Negatives; push people away from a place
Political instability, no jobs, slavery
Pull Factors
Pull Factors: Positives; pull people towards an area
Jobs, freedom, stable government
Intervening Opportunity
The presence of a nearer opportunity that diminishes the attractiveness of sites father away
Intervening Obstacle
A force or factor that limits human migration
Chain Migration
Chain Migration: a series of migrations within a group that begins with one person who through contact with the group, pulls people to migrate to the same area.
Step-Migration
Step-Migration: migration to a far away place that takes place in stages
Guest Worker
Guest Worker: a legal immigrant who is allowed into the country to work, usually for a relatively short time period
Transhumance
Transhumance: moving herds of animals to the highlands in the summer and into the lowlands in the winter
Transnational Migration
Transnational Migration: moving across a border into another country
Forced Migration
Forced Migration: when people migrate not because the want to but because they have no other choice
Internally Displaced Persons (IDP): A person forced to flee their home who remains in their home country
Refugee: A person who flees their home country and is not able to return
Asylum Seeker: A person seeking residence in a country outside of their own because they fleeing persecution
Migration Impacts
Political Impact
Brain drain: when the majority of educated or skilled workers leave an area to pursue better opportunities elsewhere
Cultural Impact - loss of culture or migrants bring in new languages
Economic Impact - loss or gain of income dependent on the migrant flow
Culture
Culture: Body of materials, customary beliefs, and social forms that together constitute the distinct tradition of a group or people.
Material Culture
Material Culture: The material manifestation of culture.
Artifacts
Tools, housing, systems of land use, clothing, etc.
Nonmaterial Culture
Nonmaterial Culture:
Mentifacts
Shared ideas, values, and beliefs of a culture. Examples include religion, language, viewpoints, and ideas about right or wrong behaviour.
Sociofacts
Families, governments, education systems, sports organizations, religious groups
Cultural Relativism
Cultural Relativism: The culture should be judged based on its own standards, not based on another culture.
Ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism: Judging other cultures based on the rules of your culture
Taboo
Taboo: Something that is forbidden by a culture or a religion, sometimes so forbidden that it is often not even discussed
Cultural Landscapes
Cultural Landscapes: The forms superimposed on the physical environment by people
Churches, buildings, etc
Ethnic Neighborhoods
Ethnic Neighborhoods: Neighborhood that retains some cultural distinction from a larger surrounding area
Indigenous People
Indigenous People: A cultural group that constitutes of the original people; distinct from the colonial, dominant population
Languages
Language: A set of mutually intelligible sounds and symbols used to communicate
Language Family
Indo-European
Language Branch
Germanic
Language Group
West Germanic
Language
English
Dialect
American English
Religion
Religion: The belief and worship of a superhuman controlling power, especially a god(s).
Ethnicity
Ethnicity: The fact or state of belonging to a cultural group
Gender
Gender: How men are treated differently than women
Relocation Diffusion
Relocation Diffusion: Ideas are transmitted by their carriers during migration
Expansion Diffusion
Expansion Diffusion: The ideas are spread through a population without the carriers moving.
Contagious: Transmission through nearby places, like a disease
Stimulus: The idea inspires one somewhere else
Ex. Beef-free burgers in Indian McDonalds
Hierarchical: Spreading among the most influential/largest people first, before spreading to others
Reverse Hierarchical: Diffusion up a hierarchy; common people to large influencers
Creole
Creole: Language created by mixing two others; used as a primary language of many people and has grammar
Pidgin
Pidgin: Simple language used for communication between two groups with different languages; evolves into creole