Vocabulary Terms for Chapter 10
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary terms from Ch. 10 to study in preparation for the exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Cue Approach to Depth Perception
Focuses on identifying information in the retinal image that is correlated with depth in the scene.
Occlusion
When one object hides or partially hides another object from view, causing the hidden object to be perceived as being farther away.
Monocular Cues
Cues based on the visual information available within 1 eye.
Binocular Cues
Cues that depend on visual information within both eyes.
Oculormotor Cues
Depth cue that depends on our ability to sense the position of our eyes & the tension in our eye muscles.
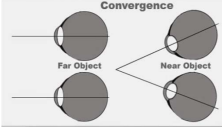
Convergence
Inward movement of the eyes that occurs when we look at nearby objects.
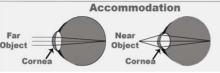
Accommodation
Change in the shape of the lens that occurs when we focus on objects at various distances.
Oculomotor
Sources of depth information in a two-dimensional picture.
Relative Height
Objects below the horizon that are higher in the field of vision are more distant.
Familiar Size
Distance information is based on our knowledge of the object size.

Perspective Convergence
The perception that parallel lines in the distance converge as distance increases.

Atmospheric Perspective
Distant objects are fuzzy & have a blue tint.

Texture Gradient
Equally spaced elements are more closely packed as distance increases.
Shadows
Decreases in light intensity caused by the blockage of light can provide information regarding the locations of these objects.
Motion-Produced Cues
When the observer is not stationary, the observer is moving.
Motion Parallax
As an observer moves, nearby objects appear to move rapidly across the visual field whereas far objects appear to move more slowly.

Deletion
Covering an object.
Accretion
Uncovering an object.
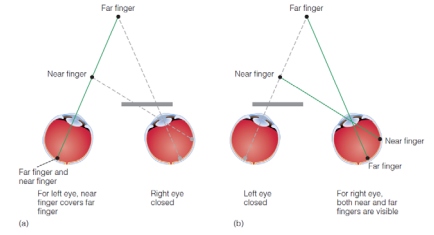
Stereoscopic Depth Perception
Depth perception created by input from both eyes.
Binocular Disparity
Occurs when the retinal images of an object fall on disparate points on the 2 retinas.
Corresponding Retinal Points
Points on the retina that would overlap if the eyes were superimposed on each other (EX: if there is overlap, there is no disparity).
Horopter
An imaginary surface that passes through the point of fixation (all this area is in focus).
Noncorresponding Points
2 points, 1 on each retina, that wouldn’t overlap if the retinas were slid onto each other.
Absolute Disparity
The visual angle between the images of an object on the 2 retinas.
Crossed Disparity
Occurs whenever an object is closer to the observer than where the observer is looking.
Uncrossed Disparity
Occurs whenever an object is behind the horopter.
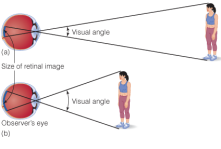
Visual Angle
The angle of an object relative to an observer’s eyes.

Size Constancy
Occurs when the size of an object is perceived to remain the same even when it’s viewed from different distances.
Size-Distance Scaling
A hypothesized mechanism that helps maintain size constancy by taking an object’s perceived distance into account.

Relative Size
When 2 objects are of equal size, the one that is farther away will take up less of the field of view. We often use the sizes of familiar objects as a yardstick to judge the size of other objects.