endocrine part 1 2 3
5.0(2)Studied by 49 people
Card Sorting
1/155
Earn XP
Last updated 5:55 PM on 3/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
1
New cards
Endocrine system
The body’s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones
2
New cards
Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and thymus
Endocrine glands
3
New cards
Homeostasis
Maintenance of the internal environment ( balance )
4
New cards
Metabolic regulation
Storage and use of energy substrates
5
New cards
Homeostasis
Metabolic regulation
Responses to external stimuli
Control of growth, reposition and development
Metabolic regulation
Responses to external stimuli
Control of growth, reposition and development
Roles of endocrine system
6
New cards
Hormones
Chemical substance released by a group of cells to control the function of other types of cells
7
New cards
affect only specific target cell
\
affect many different types of cell
\
affect many different types of cell
types of hormones
8
New cards
hypothalamus
has both neural function and releases hormones
9
New cards
adipose cell, pocket of cell in wall of the small intestine, stomach, kidney, and heart
other tissue and organs that produce hormones
10
New cards
at distance
hormones can exert their effect______ from their site of production
11
New cards
neurohormones
specialized neurons that secrete chemical into the blood rather than synaptic cleft
12
New cards
endocrine signaling
a cell targets a distant cell through the blood stream
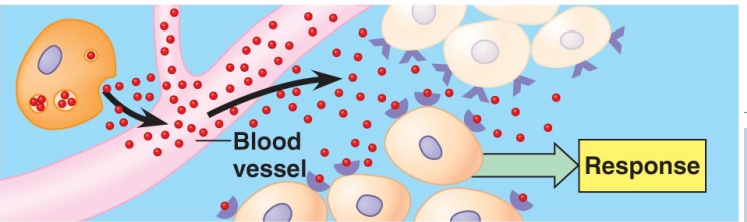
13
New cards
paracrine signaling
cell target a nearby cell
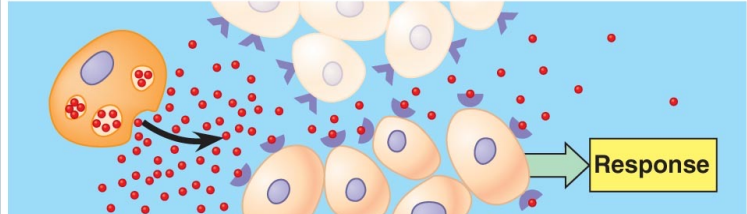
14
New cards
autocrine signaling
cell target it self
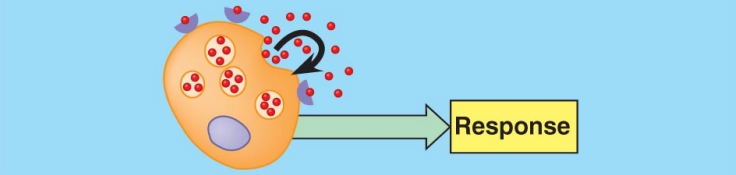
15
New cards
multiple hormone system
play a key role in regulating almost all body function
16
New cards
blood stream
released into and carried via______ to target tissue
17
New cards
target cell
refers to a cell that contain specific receptors (binding sites) for a particular hormone
18
New cards
1. proteins and polypeptides
2. steroid
3. amino acid tyrosine
what are the three general classes of hormones
19
New cards
proteins and polypeptides
secreted by the anterior and posterior pituitary gland, the pancreas \`(insulin and glucagon), the parathyroid gland ( parathyroid hormone), and many others
20
New cards
steroid
secreted by the adrenal cortex ( cortisol and aldosterone ), the ovaries (estrogen and progesterone), the testes (testosterone), and the placenta (estrogen and progesterone)
21
New cards
amino acid tyrosine
secreted by the thyroid (thyroxine and triiodothyronine ) and the adrenal medulla (epinephrine and norepinephrine ). there are no known polysaccharides or nucleic acid hormones
22
New cards
peptide (protein) hormones
they can disolves in water (plasma)
23
New cards
steroid hormones
secretedby gonads, adernal cortex, placenta
\
derived from cholesterol
\
usually bound to **carrier** proteins
\
derived from cholesterol
\
usually bound to **carrier** proteins
24
New cards
amine hormones
derived from aminoc acid tyrosine
\
they include the thyroid hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine (produced by the adrenal medulla) and dopamine (produced byh the hypothalamus)
\
they include the thyroid hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine (produced by the adrenal medulla) and dopamine (produced byh the hypothalamus)
25
New cards
nonsteroid hormones
first messenger
\
mechanism of action:
hormones recepetors interaction (first messenger)
enzyme activation
released of the second messenger
effect on cellular function
\
mechanism of action:
hormones recepetors interaction (first messenger)
enzyme activation
released of the second messenger
effect on cellular function
26
New cards
steroid
pass through the cytoplasm and enter nucleus where they bind with a receptor ( lock and key model )
27
New cards
receptors
region of tissue, or a molecule in a cell membrane, which responds specifically to a particular __neurotransmitter__, __hormone__, __antigen__, or other substance.
28
New cards
protiens
hormonal receptors are large _______
29
New cards
on the surface of cell membrane ( peptides and catecholamines)
\
in the cell cytoplasm ( steroid )
\
in the cell nucleus (thyroid hormones )
\
in the cell cytoplasm ( steroid )
\
in the cell nucleus (thyroid hormones )
receptors location
30
New cards
the rate of secretion
\
the rate of its removal (metabolic clearance )
\
the rate of its removal (metabolic clearance )
two factors control the concentration of a hormones in the blood
31
New cards
metabolic destruction by tissue
\
excretion by the liver into bile
\
excretion by the kidney into urine
\
excretion by the liver into bile
\
excretion by the kidney into urine
hormones are cleared by
32
New cards
slow
clearance of protein-bound hormones is ________ than clearance of peptide hormones
33
New cards
negative feedback
\
positive feedback
\
positive feedback
blood level of hormones are controlled by feedback mechanisms
34
New cards
prostaglandins
powerful substances found in a wide variety of body tissue
35
New cards
pituitary gland
it is located in the diencephalon
36
New cards
diencephalon
where is pituitary gland locatedn
37
New cards
adenohypophysis
anterior lobe
38
New cards
neurohypophysis
posterior lobe
39
New cards
glandular tissue
what is adenohypophysis made up off
40
New cards
adenohypophysis
synthesize and secrete a number of hormones
41
New cards
neurohypophysis
receive, store and release hormones from the hypothalamus
42
New cards
infundibulum
is the stalk that connects the pituitary to the brain
43
New cards
posterior pituitary
is an extension of the neural tissue
44
New cards
anterior pituitary
is a true endocrine gland of epithelial origin
45
New cards
growth hormone (GH)
\
prolactin (PRL)
\
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
\
adrenocorticotropic hormones (ACTH)
\
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
\
luteinizing hormones (LH)
\
prolactin (PRL)
\
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
\
adrenocorticotropic hormones (ACTH)
\
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
\
luteinizing hormones (LH)
the six hormones of the anterior pituitary
46
New cards
TSH
stimulates growth of the thyroid gland; also stimulates it to secrete thyroid hormone
47
New cards
ACTH
stimulates growth of the adrenal cortex and stimulates it to secrete glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol)
48
New cards
FSH
initiates growth of ovarian follicle each month in the ovary and stimulates one or more follicles to develop to the stage of maturity and ovulation
\
stimulates sperm production in the male
\
stimulates sperm production in the male
49
New cards
LH
acts with FSH to stimulates estrogen secretion and follicle growth to maturity
\
cause ovulation
\
cause ovulation
50
New cards
GH
stimulates growth by accelerating protein anabolism
\
accelerates fat catabolism and slows glucose catabolism
\
accelerates fat catabolism and slows glucose catabolism
51
New cards
PRL
stimulates breast development during pregnancy and secretion of milk the delivery of the baby.
52
New cards
adernal cortex
target tissue of ACTH
53
New cards
thyroid gland
target tissue of TSH
54
New cards
most tissue
target tissue of GH
55
New cards
gonads
target tissue of FSH
56
New cards
gonads
target tissue of LH
57
New cards
mammary glands and other sex accessory organ
target tissue or PRL
58
New cards
releasing and inhibiting hormones
hypothalamus neurons synthesize
59
New cards
ADH: supraoptic nuclei and Oxytocin:paraventricular
hypothalamus neruon cell bodies produced
60
New cards
vasopressin
ADH also known as
61
New cards
ADH and oxytocin
posterior pituitary homones
62
New cards
secretory vesicle and neurophysin
these hormones are synthesized in the neuron cell bodies in hypothalamus and pack in______ __with__ _________
63
New cards
does not synthesize hormones and consists of axon terminal neurons
posterioir pituitary gland
64
New cards
hypothalamic neural tissue
the posterior lobe is a downgrowth of
65
New cards
hypothalamus (hypothalamic- hypophyseal tract )
has a neural connection with the
66
New cards
nervous signal from hypothalamus
secretions of the posterior pituitary are controlled by
67
New cards
ADH
synthesized in the cell bodies of hypothalamic neurons(supraoptic nucleus)
68
New cards
posterior pituitary
where is ADH stored
69
New cards
V1 and V2
what are the two types of receptors for ADH
70
New cards
vasoconstriction
v1 receptors mediate
71
New cards
kidneys
v2 receptors located in the principle cells in distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct in the _____
72
New cards
principle cell
ADH binds to V2 receptors on the _______ of the distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts
73
New cards
reducing urine output w
what is the most important function of ADH to conserve body waste by____
74
New cards
osmotic pressure
75
New cards
baroreceptor
in carotid artery and aortic arch
76
New cards
stretch receptors
in left atrium
77
New cards
ADH high
when the osmotic pressure is high
78
New cards
ADH low
when the osmotic pressure is low
79
New cards
ADH secretion low
when the blood pressure is high
80
New cards
ADH secretion high
when the blood pressure is low
81
New cards
oxytocin
is synthesized in the cell bodies of hypothalamic neurons (paraventricular nucleus)
82
New cards
posterior pituitary gland
where is oxytocin located
83
New cards
stimulates the pregnant uterus to contract
\
may initiate labor
\
cause glandular cell of the breast to release milk to ducts
\
enhande social bonding
\
may initiate labor
\
cause glandular cell of the breast to release milk to ducts
\
enhande social bonding
function of oxytocin
84
New cards
hypothalamus
where is the actual production of ADH and ocytocin occurs ?
85
New cards
nervous stimulation
the secretion and release of posterior pituitary hormones is controlled by ?
86
New cards
hypothalamus
controls many body functions related to homeostasis ( temperature, appetite, and thirst )
87
New cards
where is thyroid located
t the base of the neck, just below the Adam's apple
88
New cards
vascular
the thyroid is highly_____
89
New cards
metabolic rate
thyroids hormones profoundly **increase** the________ if the body
90
New cards
thyroid hormones
the body’s major metabolic hormones
91
New cards
thyroxine 90%
T4
92
New cards
triiodothyronine 10%
T3
93
New cards
accelerate catabolism
increase the body metabolic rate
94
New cards
calcitonin
CT
95
New cards
calcitonin
decrease the blood calcium concentration by inhibiting breakdown of bone, which would release calcium into the blood
96
New cards
follicular cells and parafollicular cell
the thyroid tisse is made up of two type of cells
97
New cards
follicular cell
most of the thyroid tissue consist of the______
98
New cards
thyroid hormones
most of the thyroid tissue consist of the follicular cell, which secret the iodine-containing________
99
New cards
c cell
parafollicular cell is also called
100
New cards
calcitonin
the parafollicular cells secrete hormone