NCEA level 1 Genetics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Zygote
A fertilised egg.
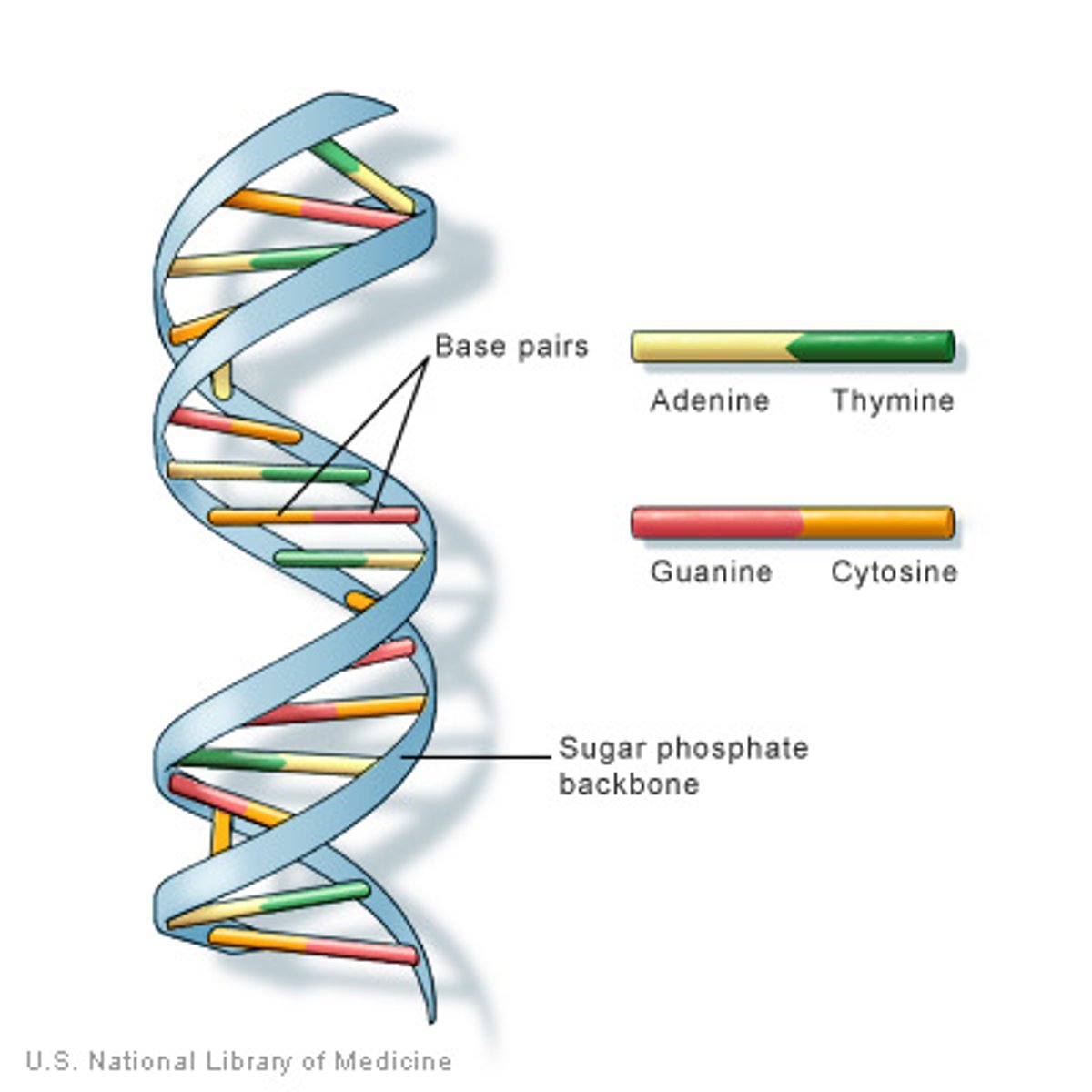
DNA
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid.
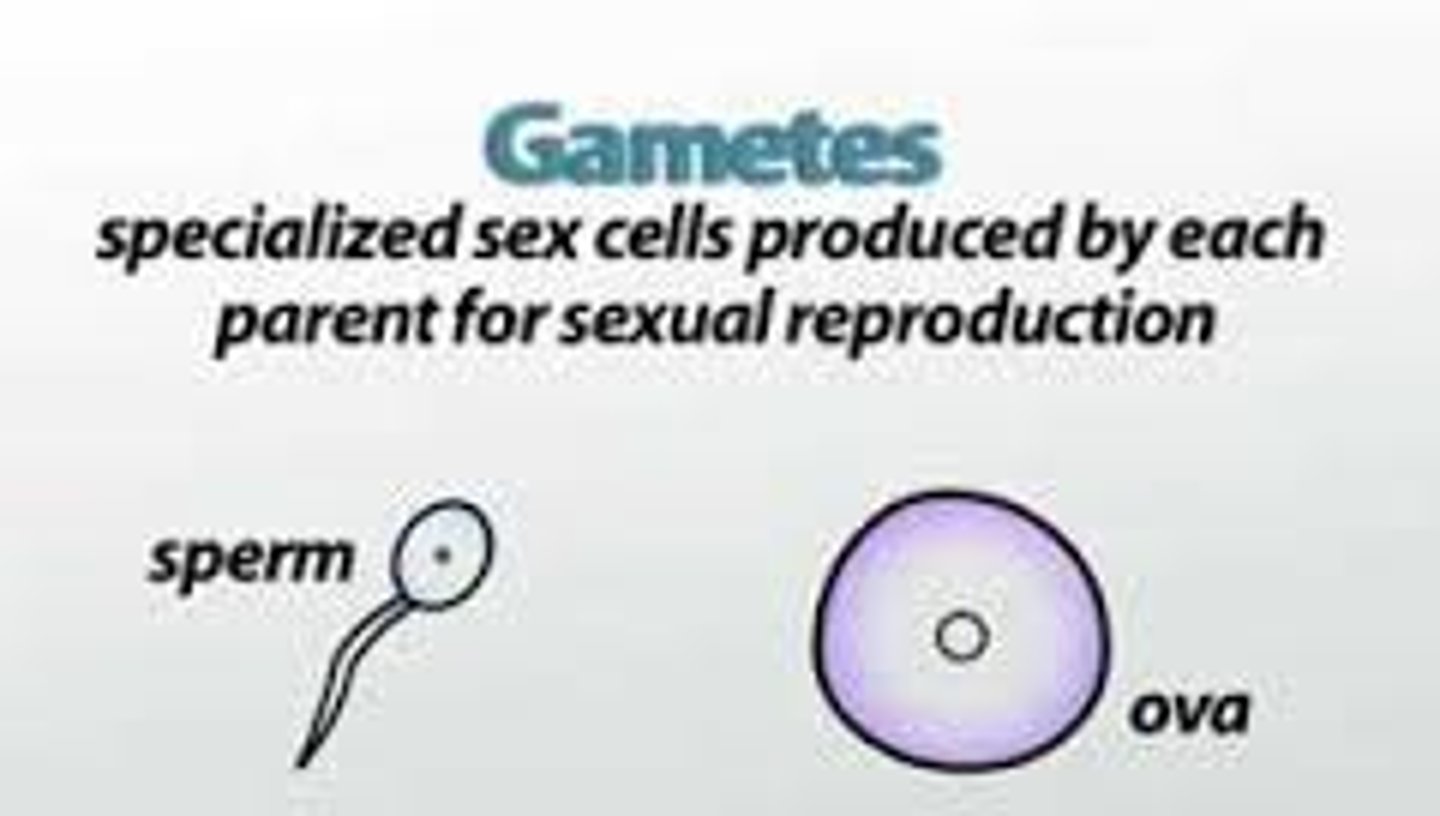
Gamete
Sex cell.
Genotype
The combination of two alleles that code for a particular gene.
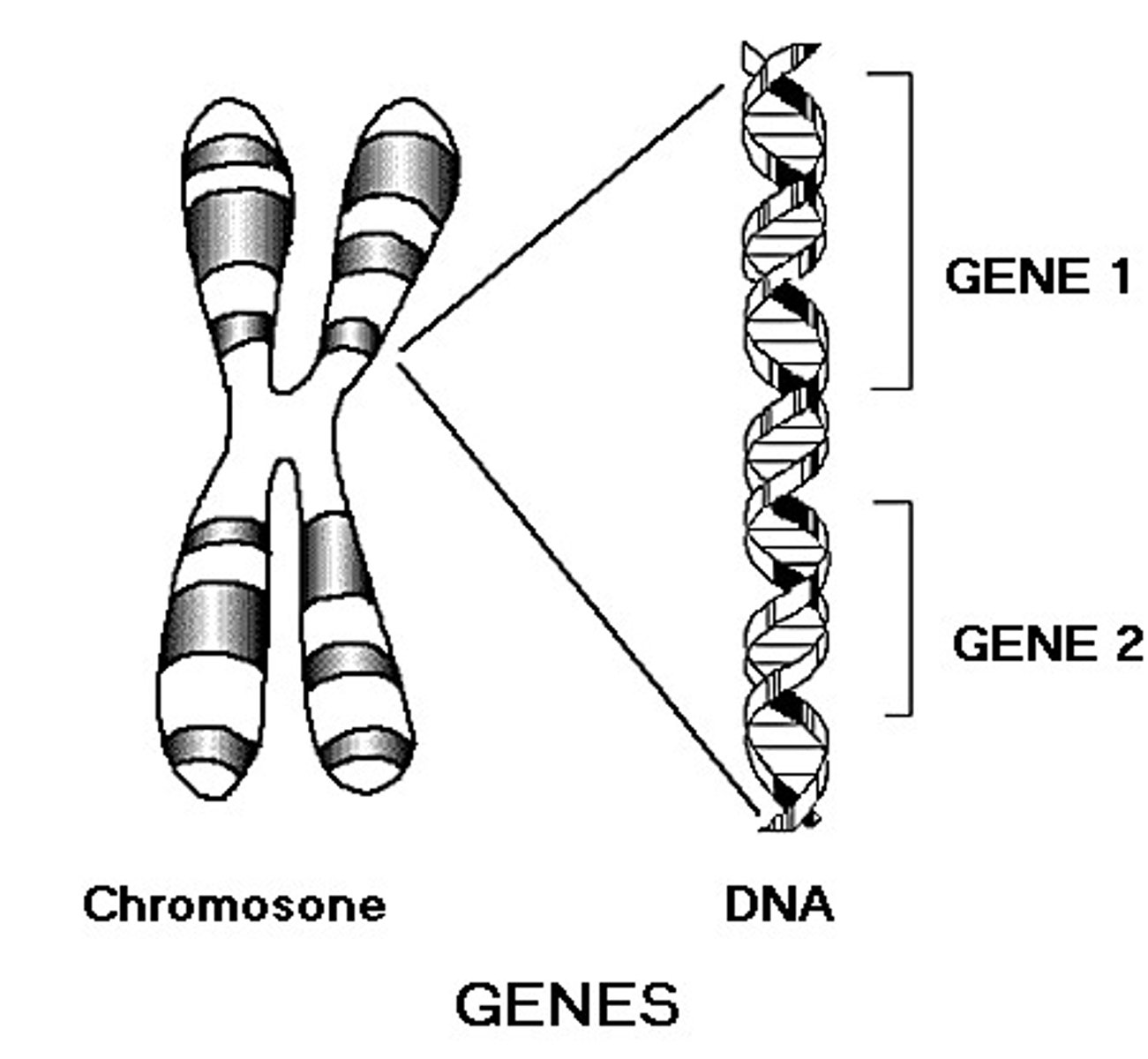
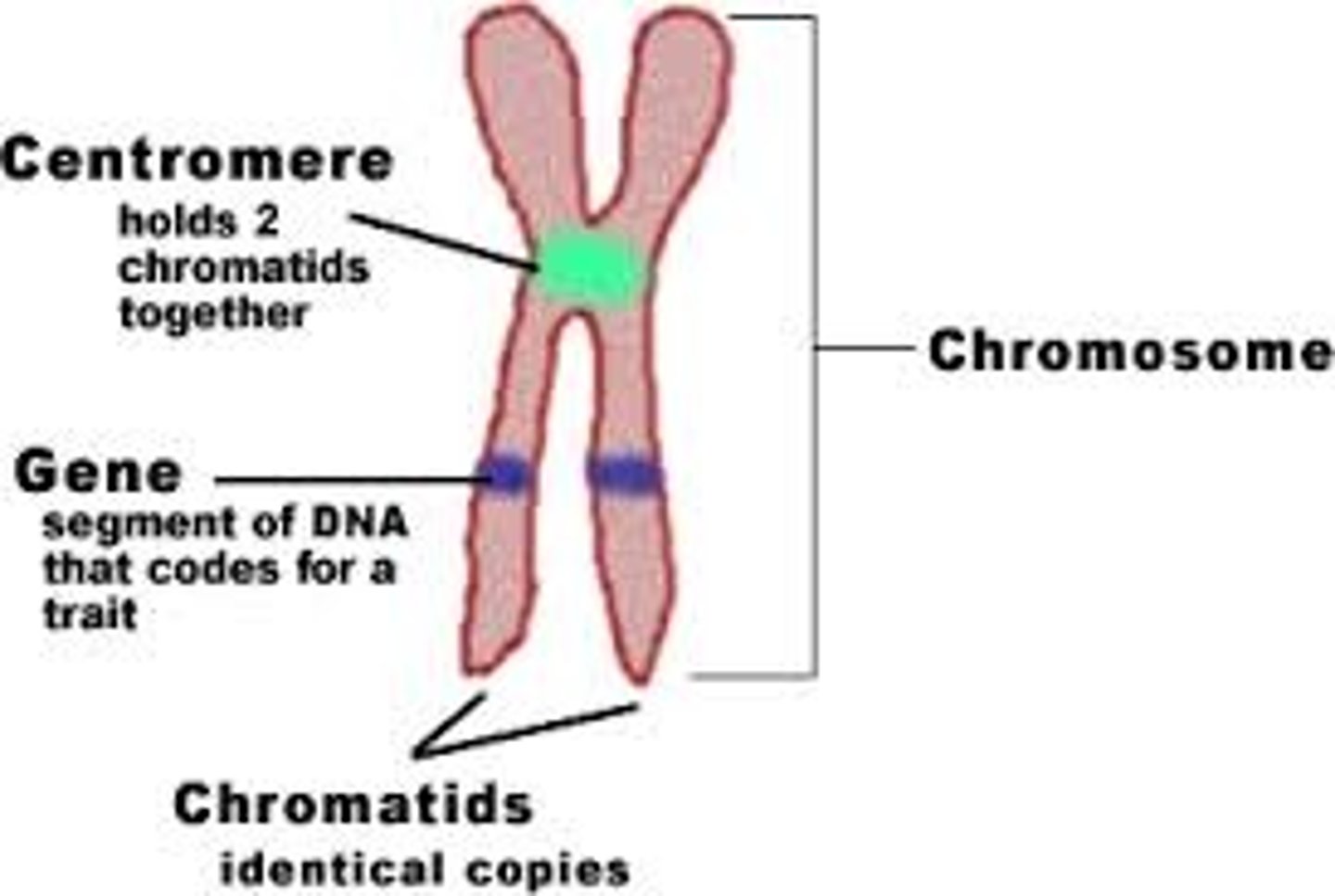
Gene
A length of DNA carrying the code for one feature.
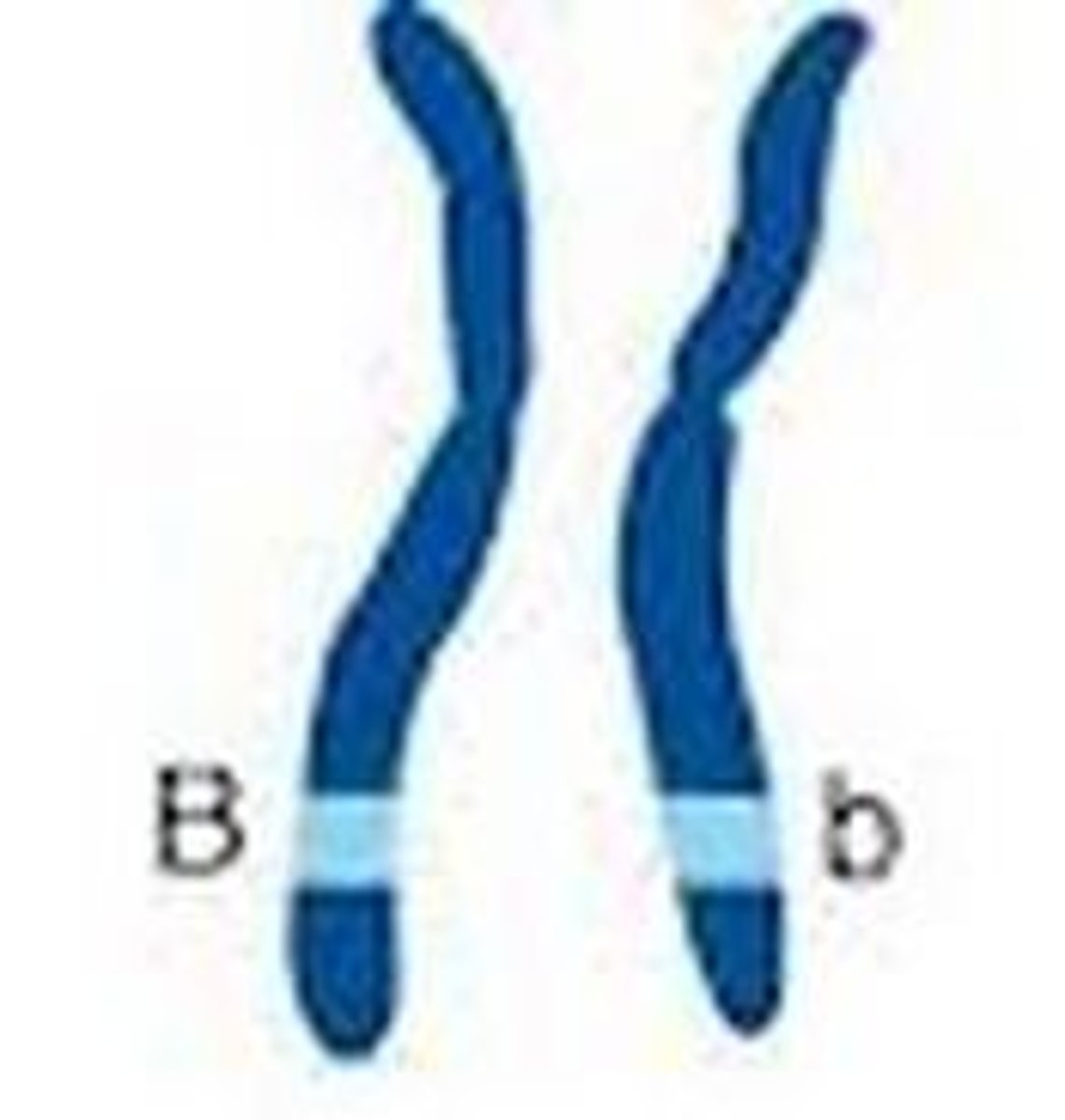
Heterozygous
Two different alleles for one particular gene.
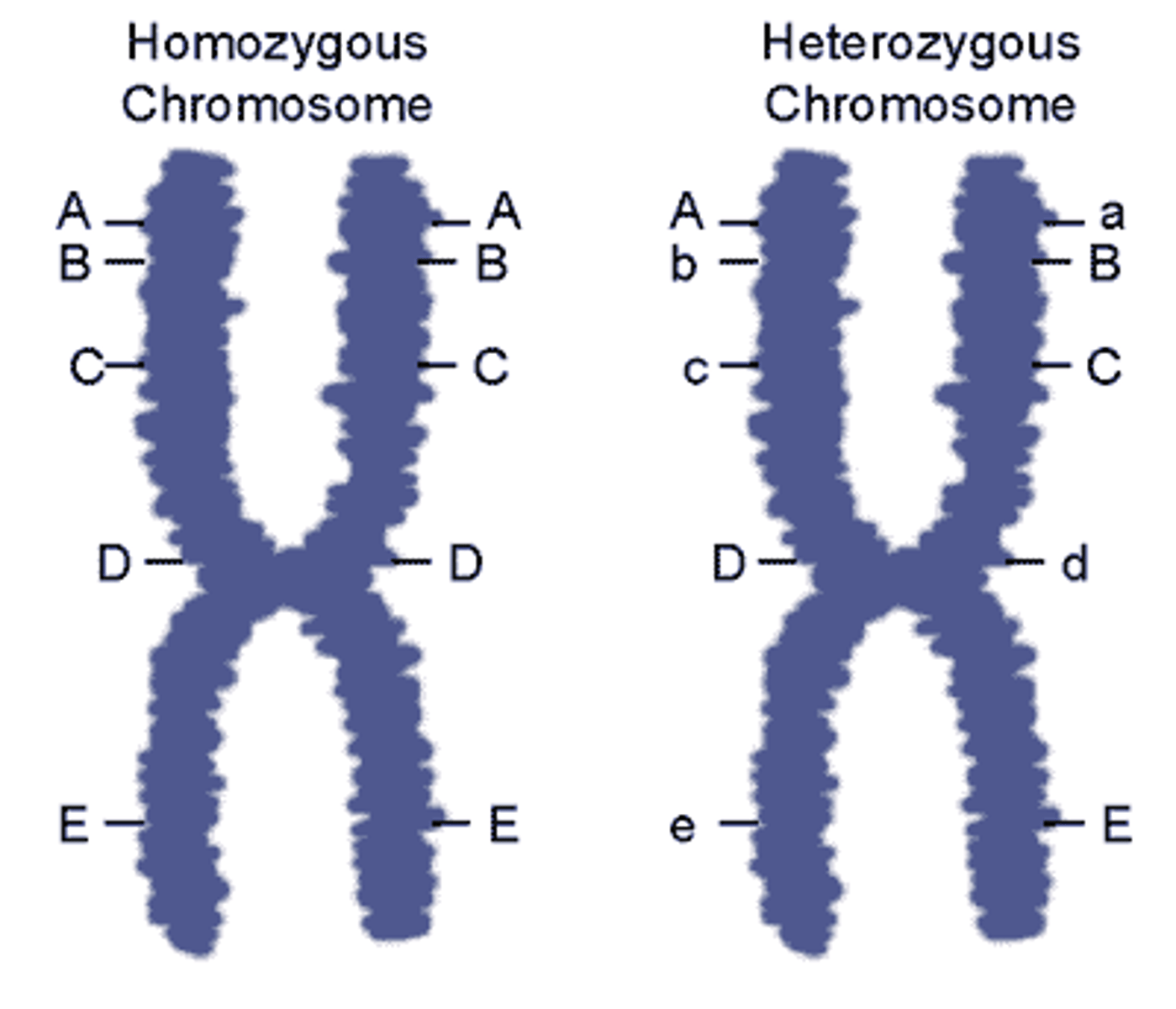
Homozygous
Two identical alleles for one particular gene.
Phenotype
The characteristics of an organism produced by a particular genotype.
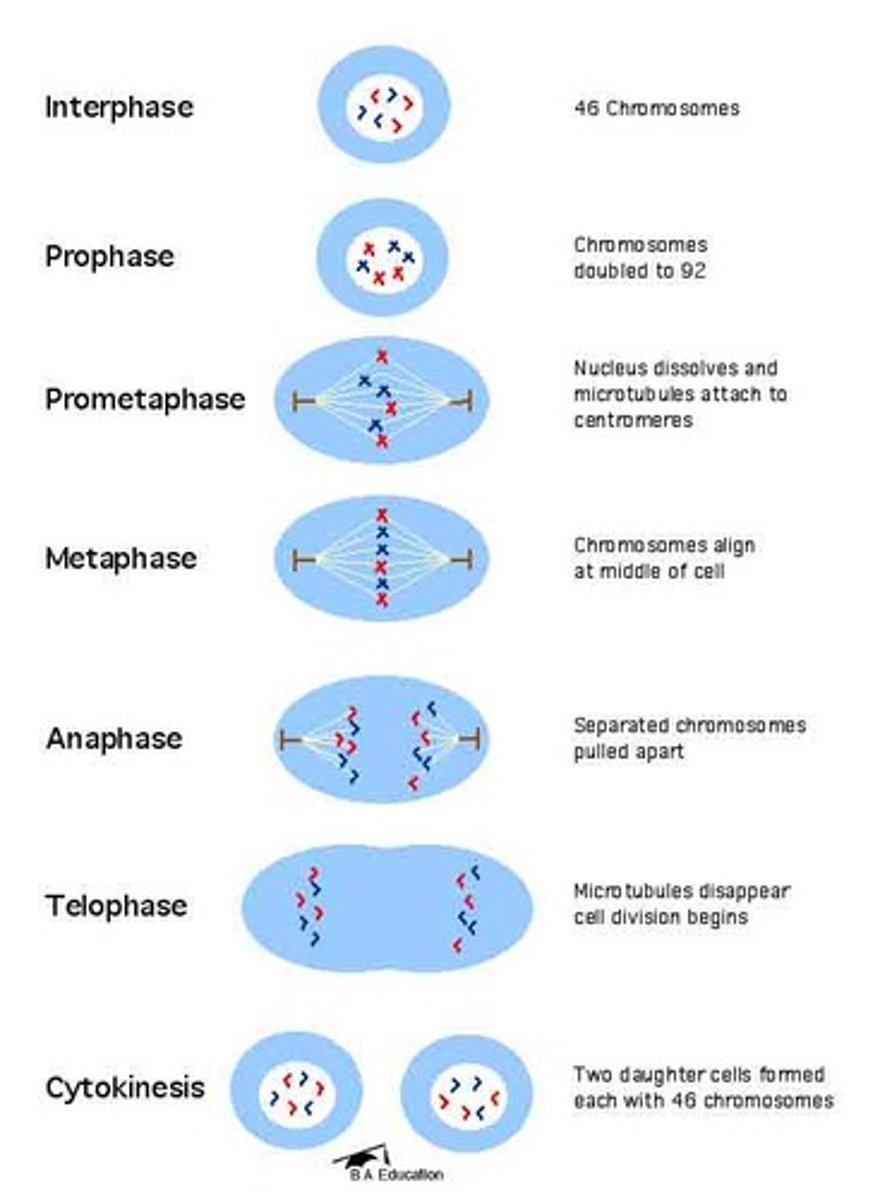
Mitosis
Cell division process which produces two identical daughter cells from one parent cell.
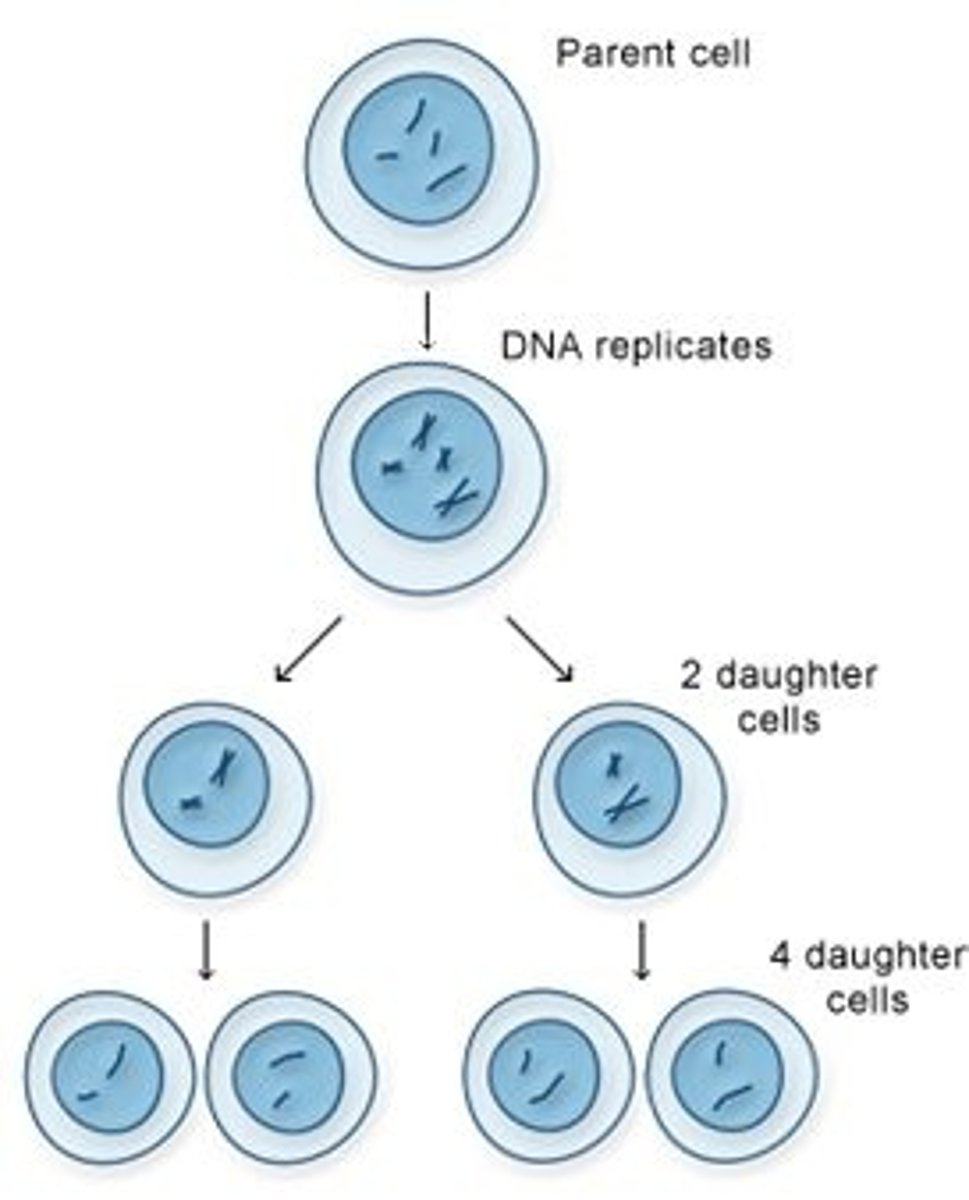
Meiosis
Cell division process which produces four gametes that are completely different from each other and the parent.
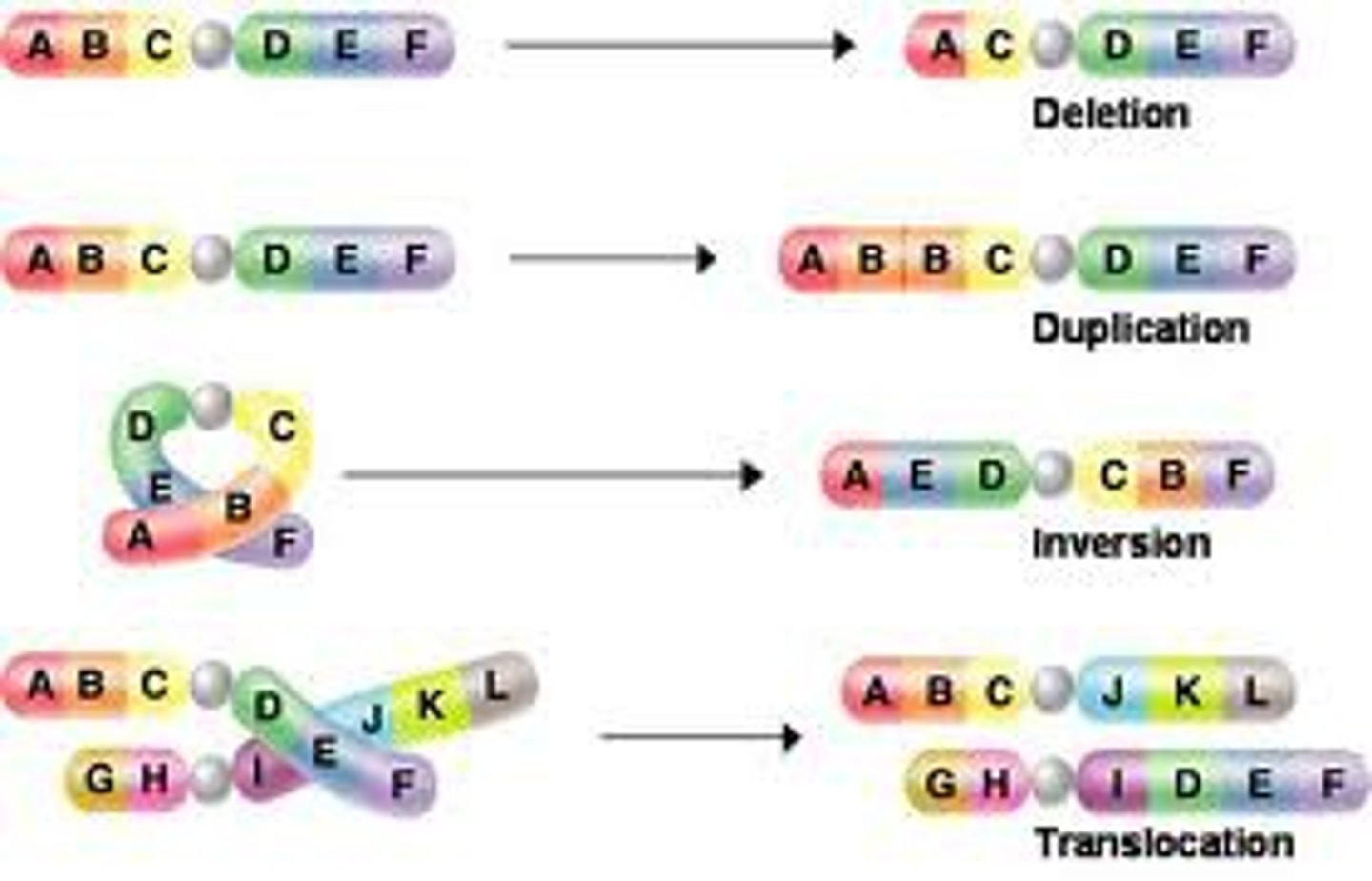
Mutation
A permanent change in the DNA base sequence
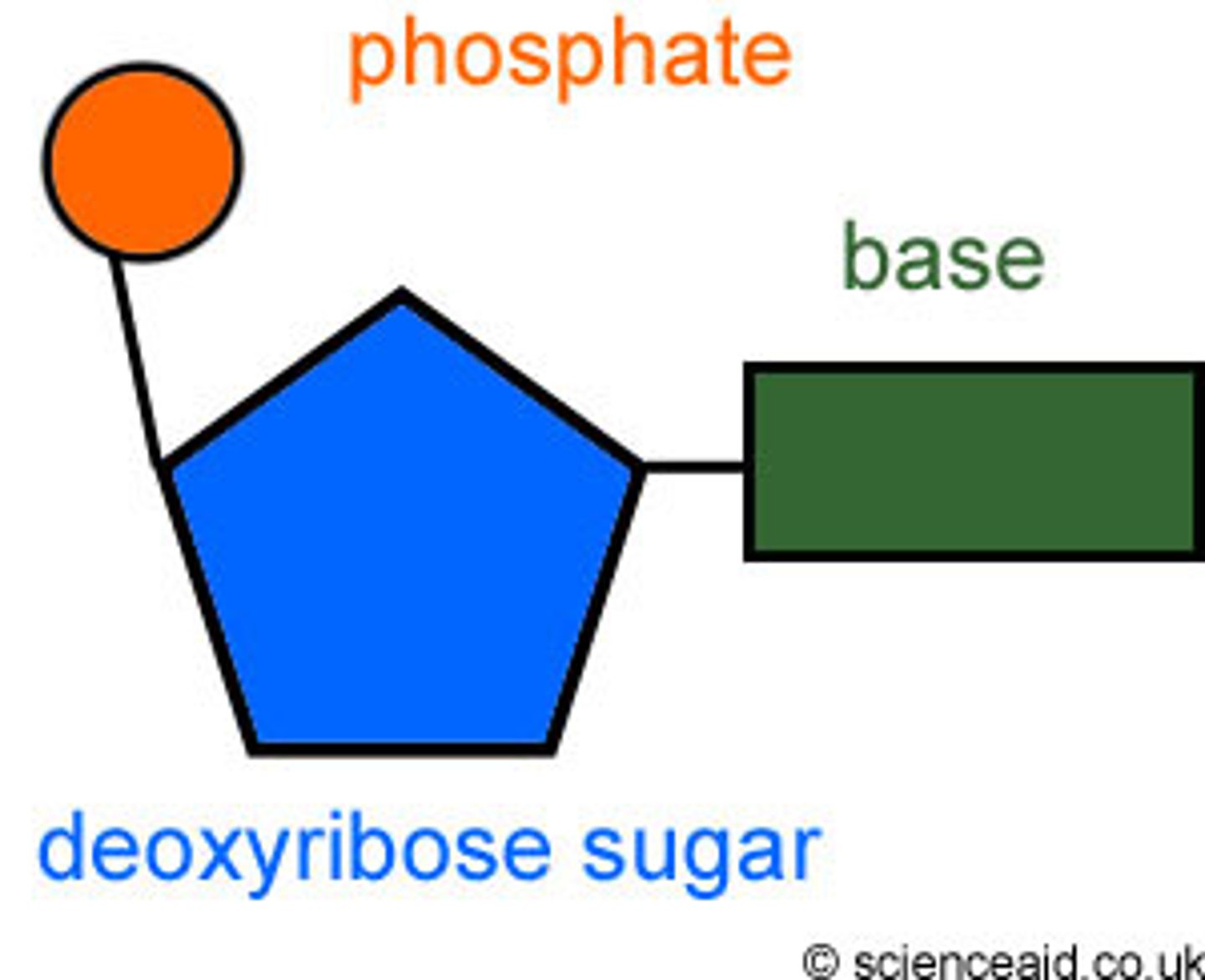
Nucleotide
A molecule that contains a sugar-phosphate-base, found in DNA.
The four bases of DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine.
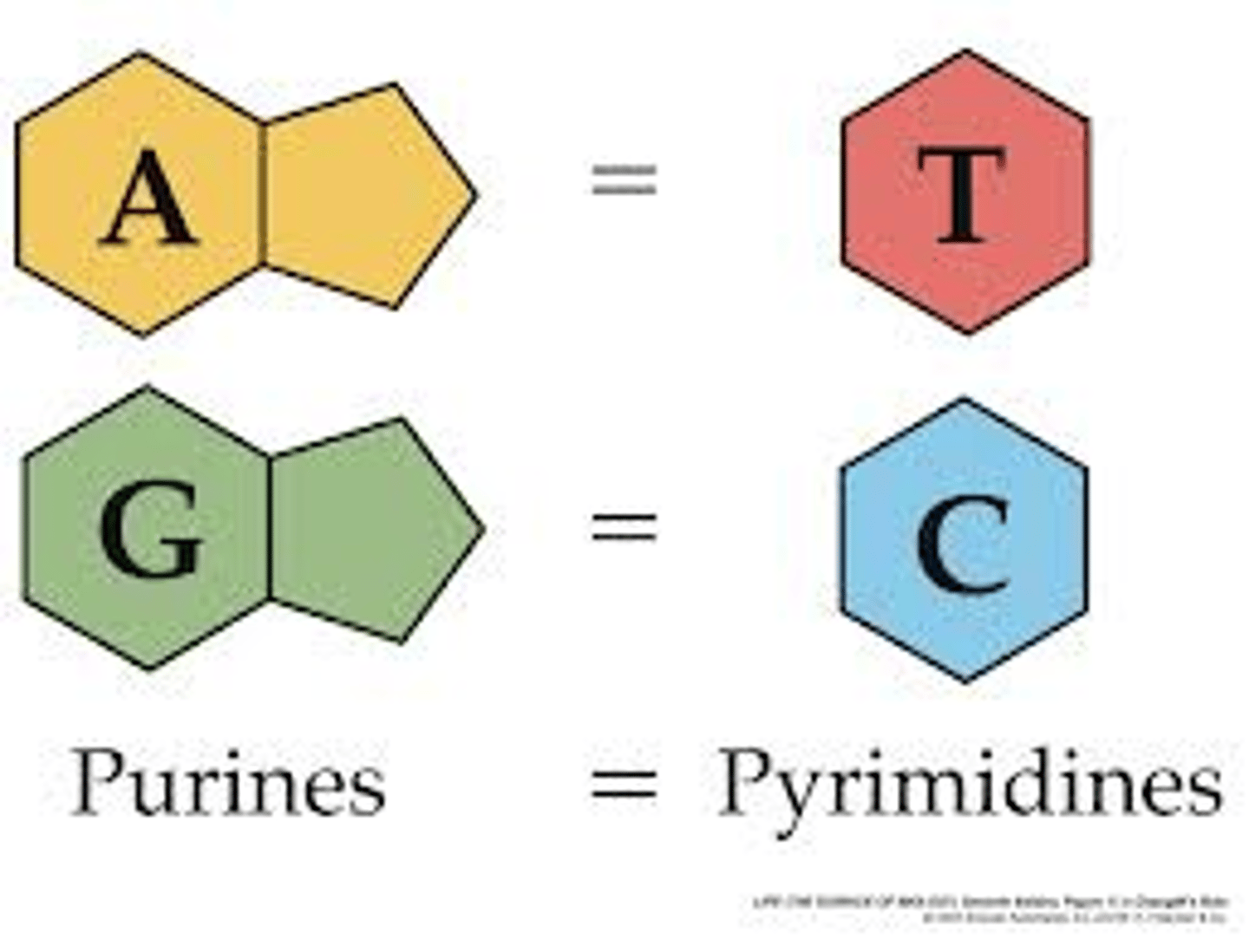
Adenine bonds with
Thymine.
Cytosine bonds with
Guanine.
Species
A group of organisms that can interbreed together.

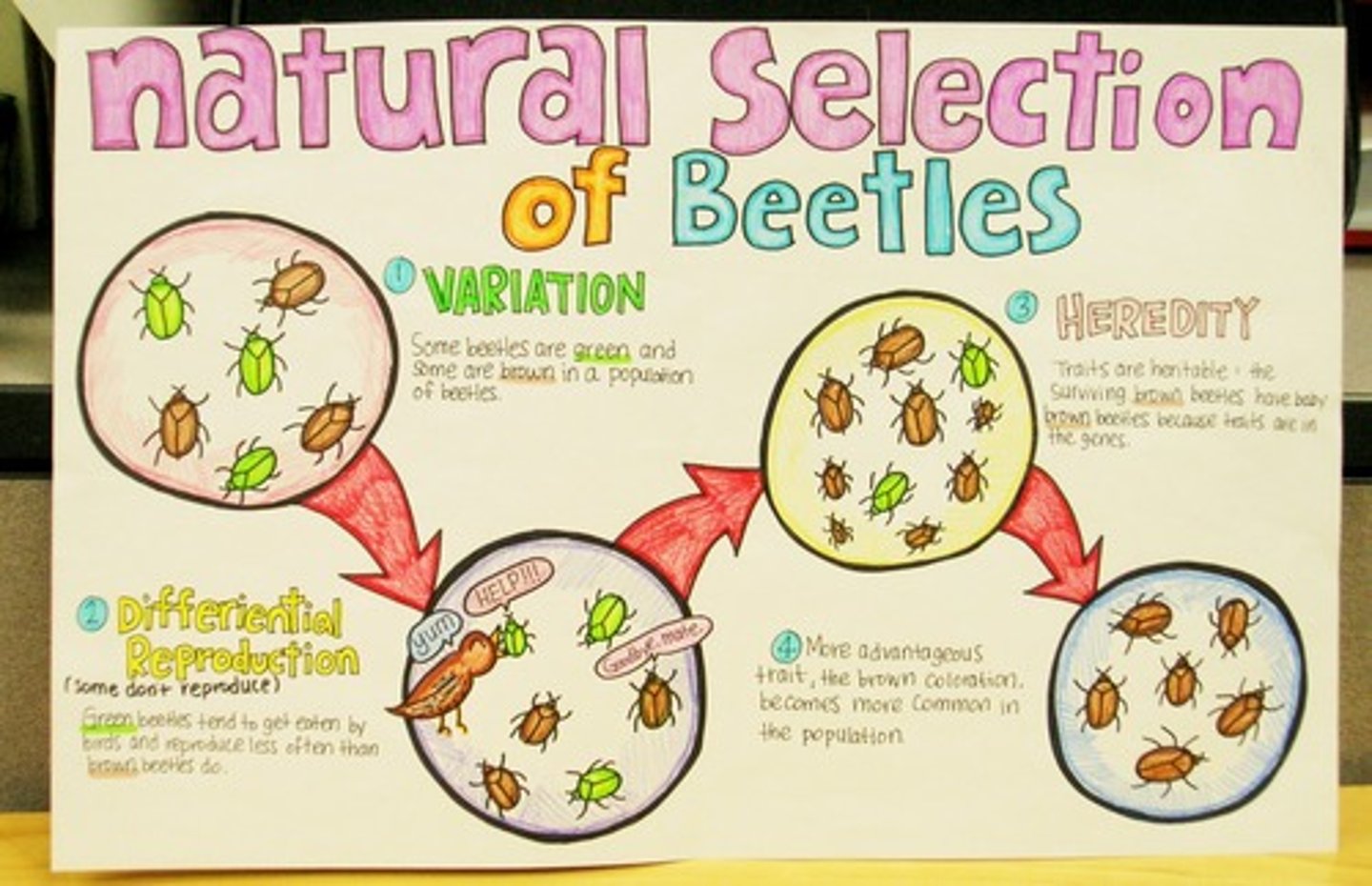
Variation
Genetic differences between individuals in a population

Inheritance
Passing on of traits from generation to generation through the genetic code.
Chromosome
Thread-like structure bearing genes that are found in the nucleus of a cell.
Test cross
The crossing of an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype
Random fertilisation
It is random to which sperm fertilises the egg first.
Independent assortment
When homologous chromosomes, one from each parent, pair up along the equator (during metaphase 1) of meiosis, the particular arrangement is determined by chance.
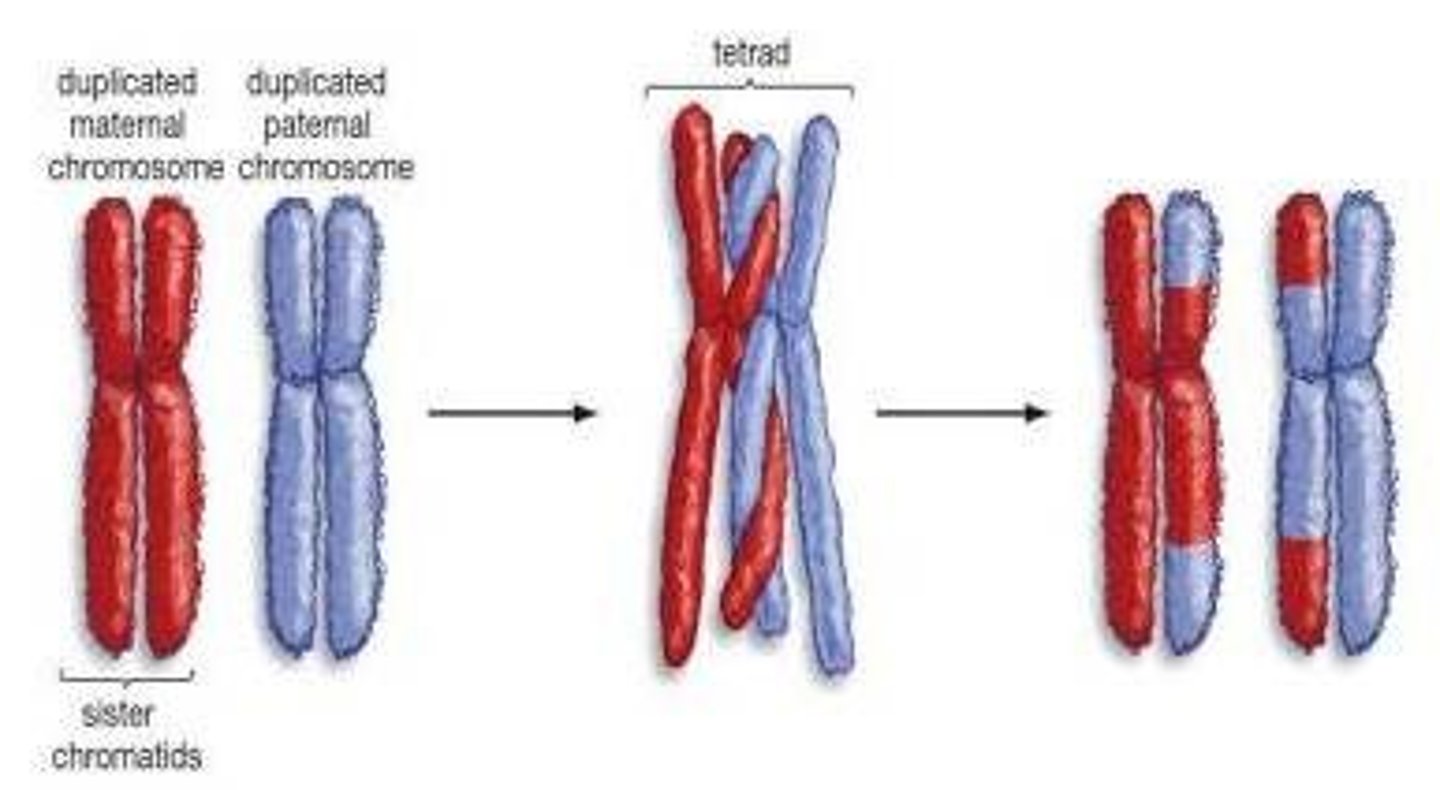
Crossing over and recombination
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during Phophase I of meiosis.
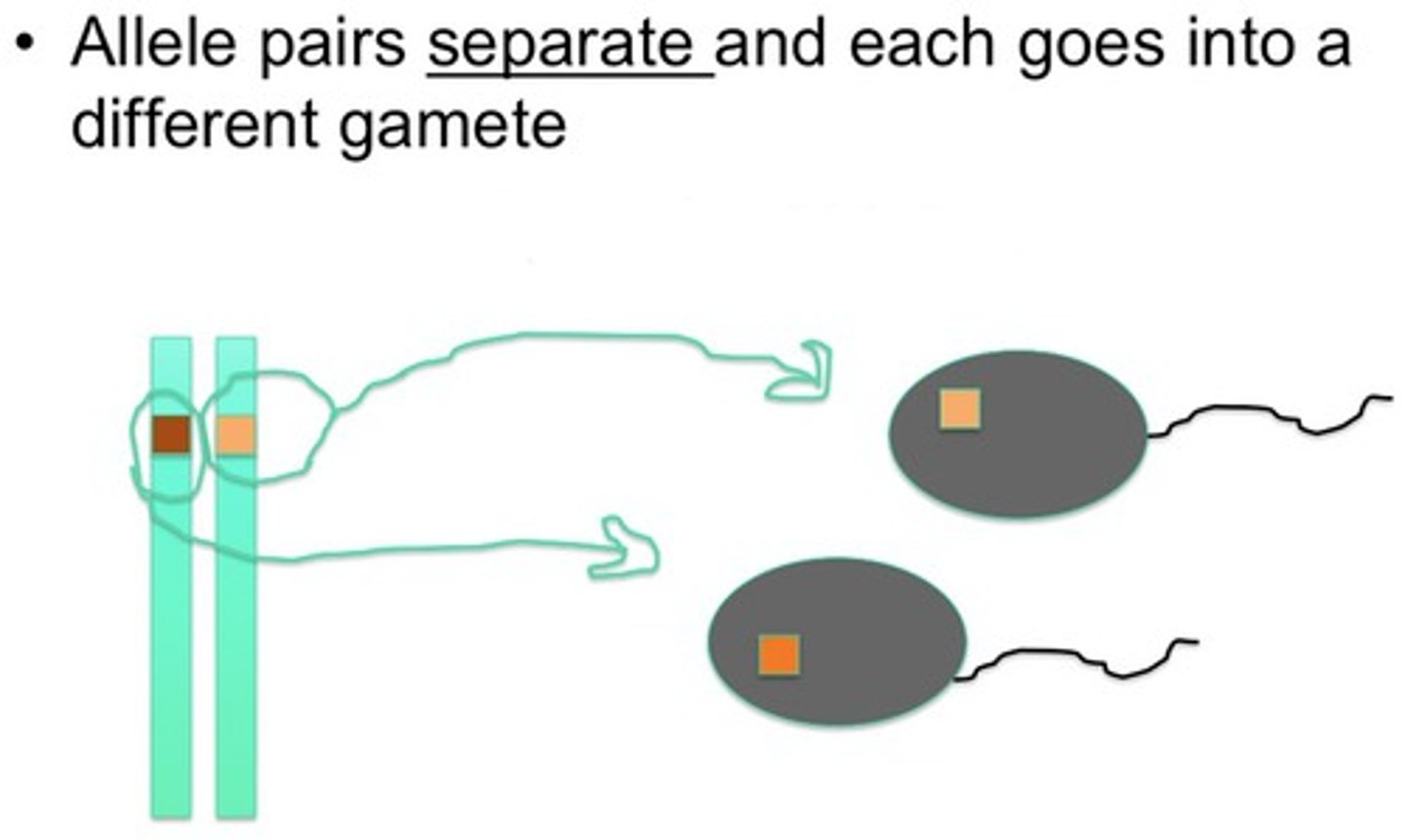
Segregation
Separation of alleles during gamete formation in meiosis, each of the haploid gametes will end up with only one allele for that trait from the parent. e.g. You could inherit B or b from your Bb parent.
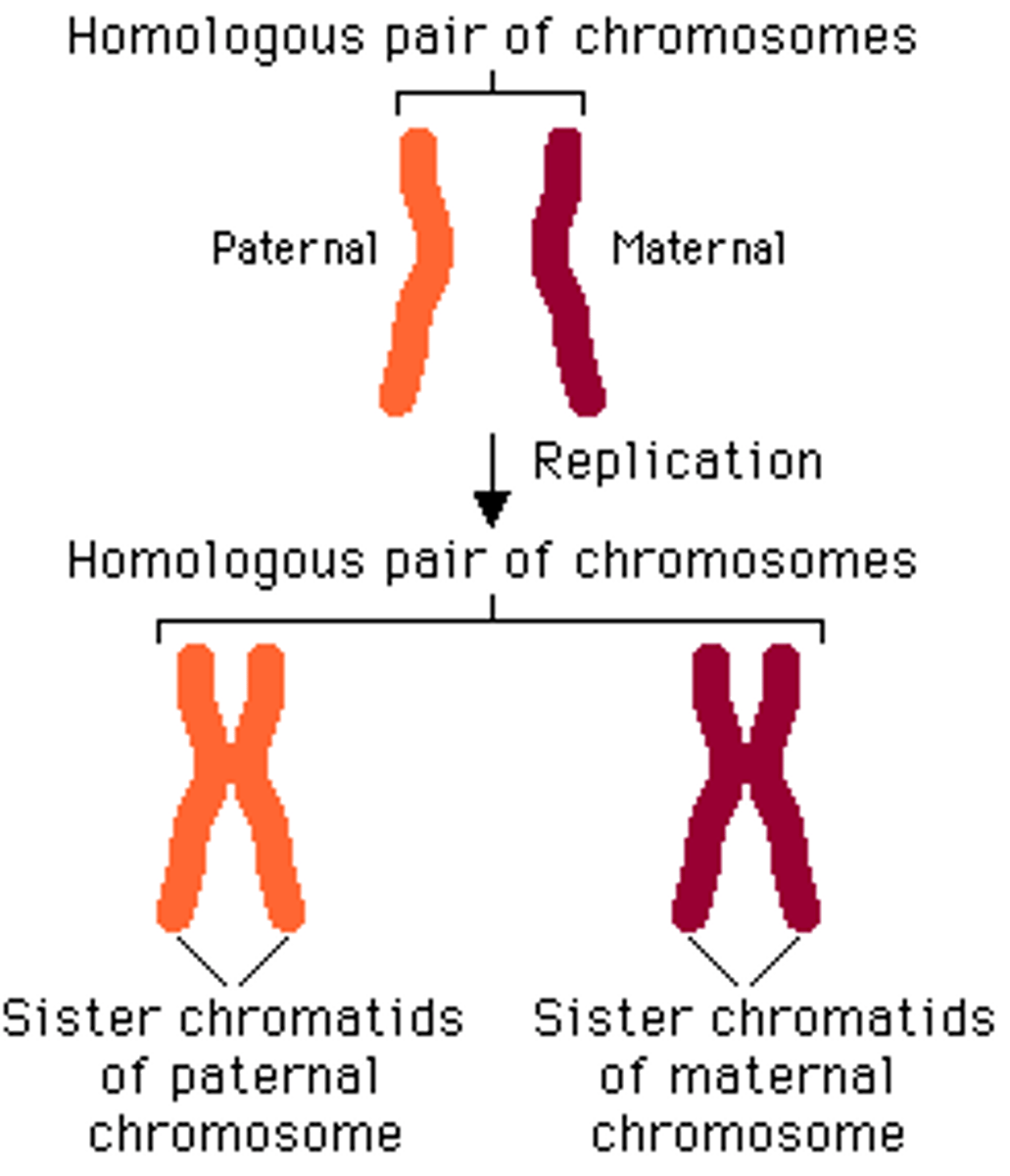
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes, that have the same structure, and that pair during meiosis.
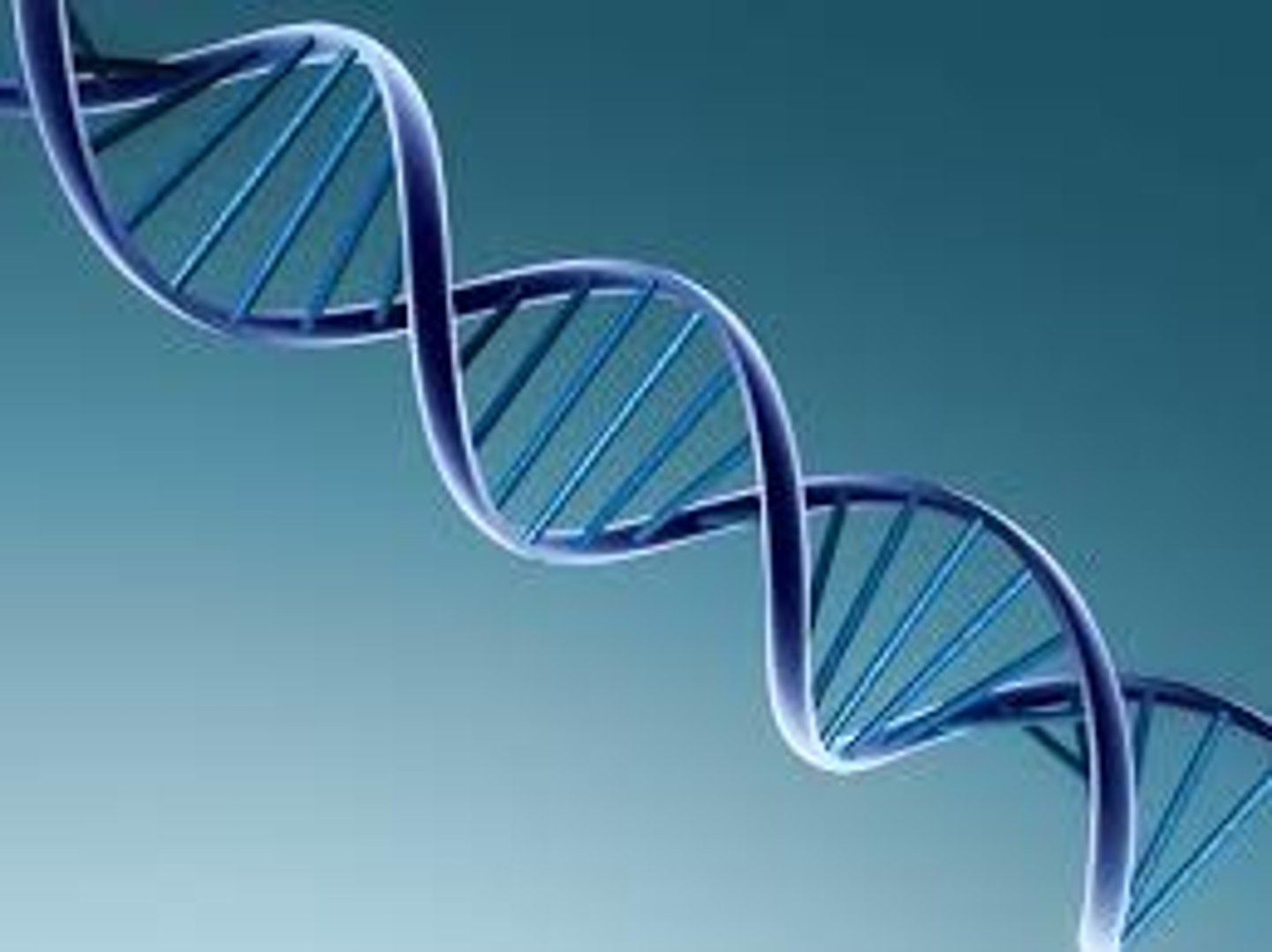
Double helix
Shape of DNA

Protein
A molecule that is made up of amino acids and that is needed to build and repair body structures and to regulate processes in the body.
Mutagen
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation.
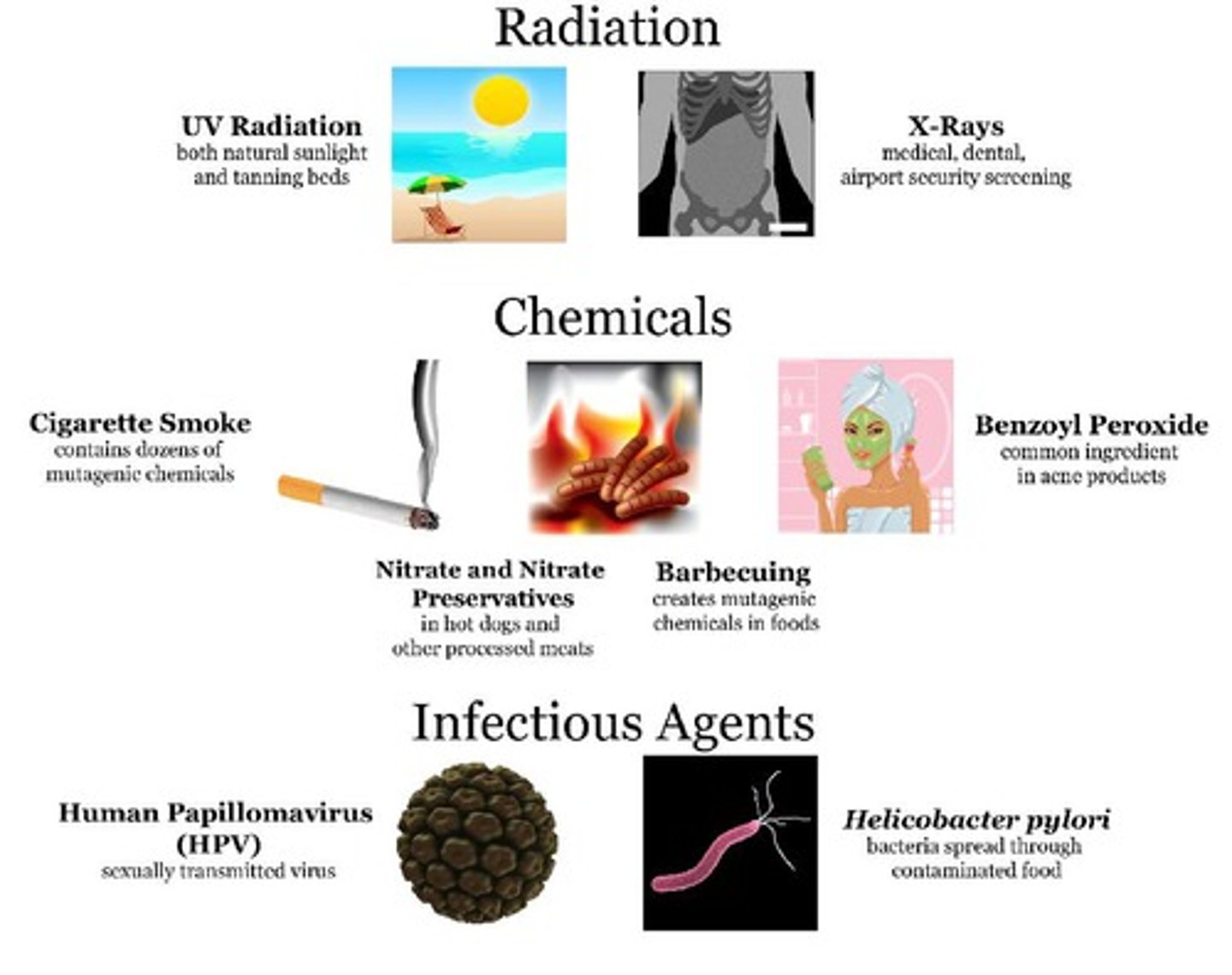
Trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes.
Dominant
Describes a trait that covers over, or dominates, another form of that trait.
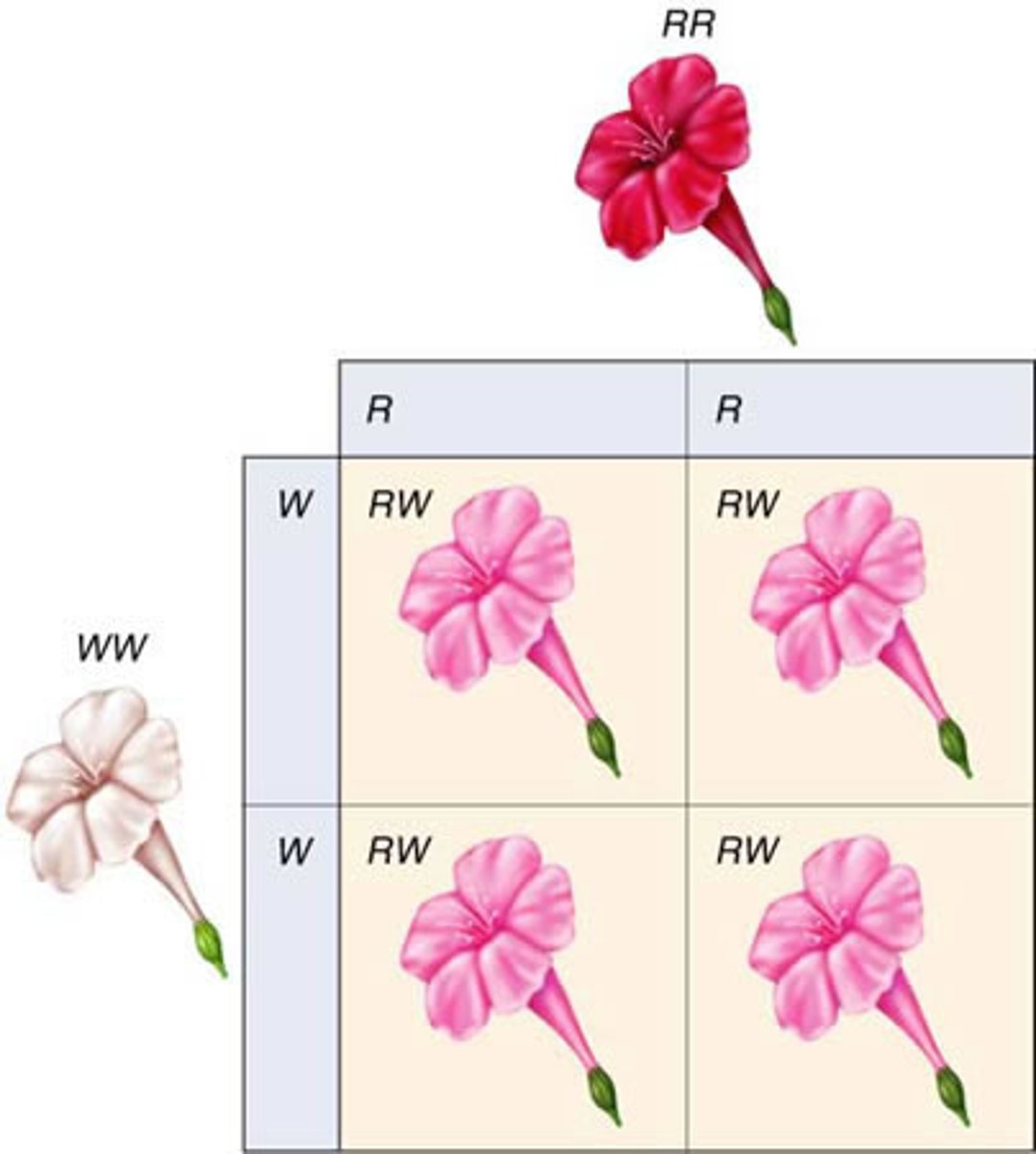
Recessive
Describes a trait that is masked when a dominant allele is present
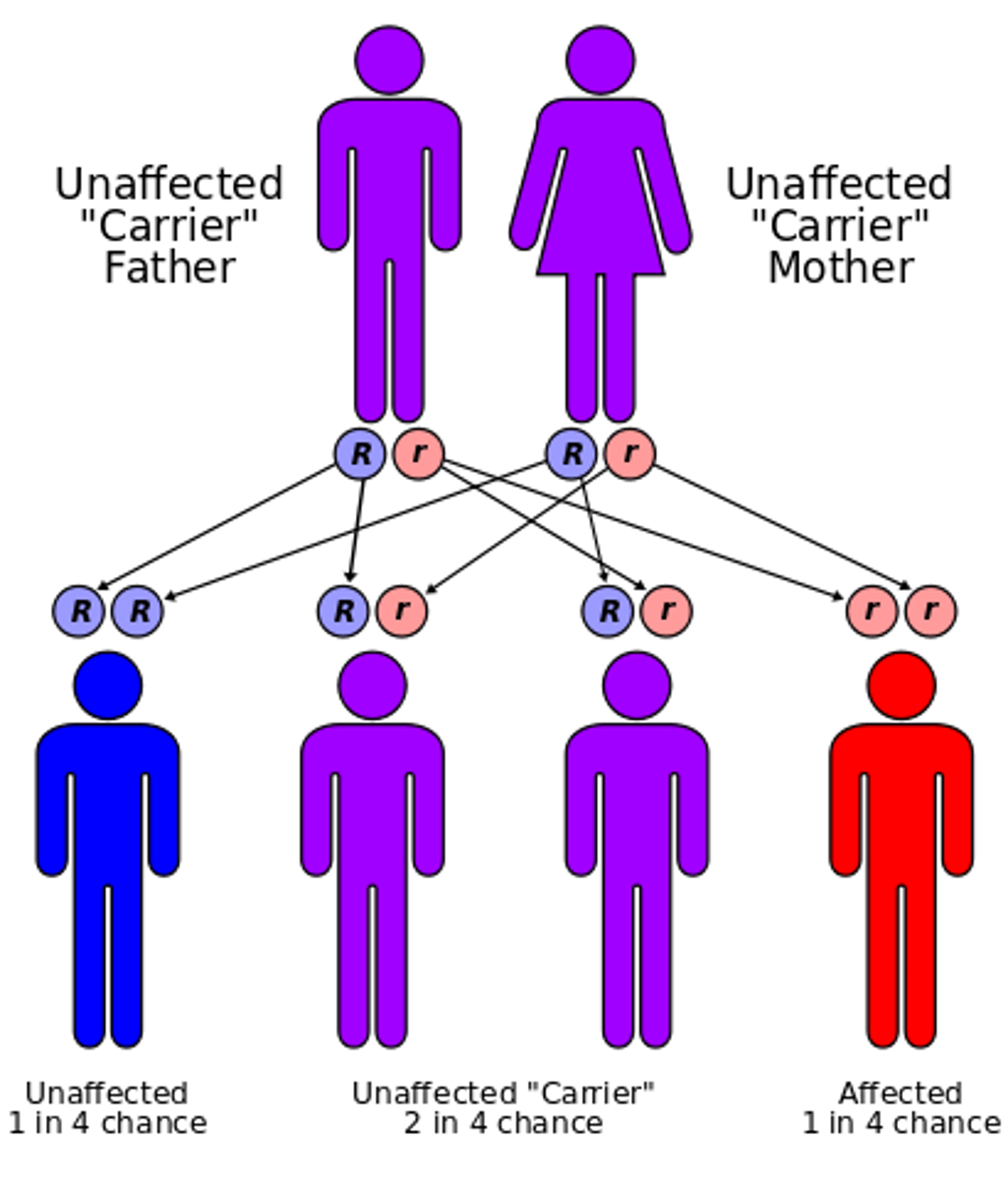
Asexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent.
Sexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves two parents that combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents.
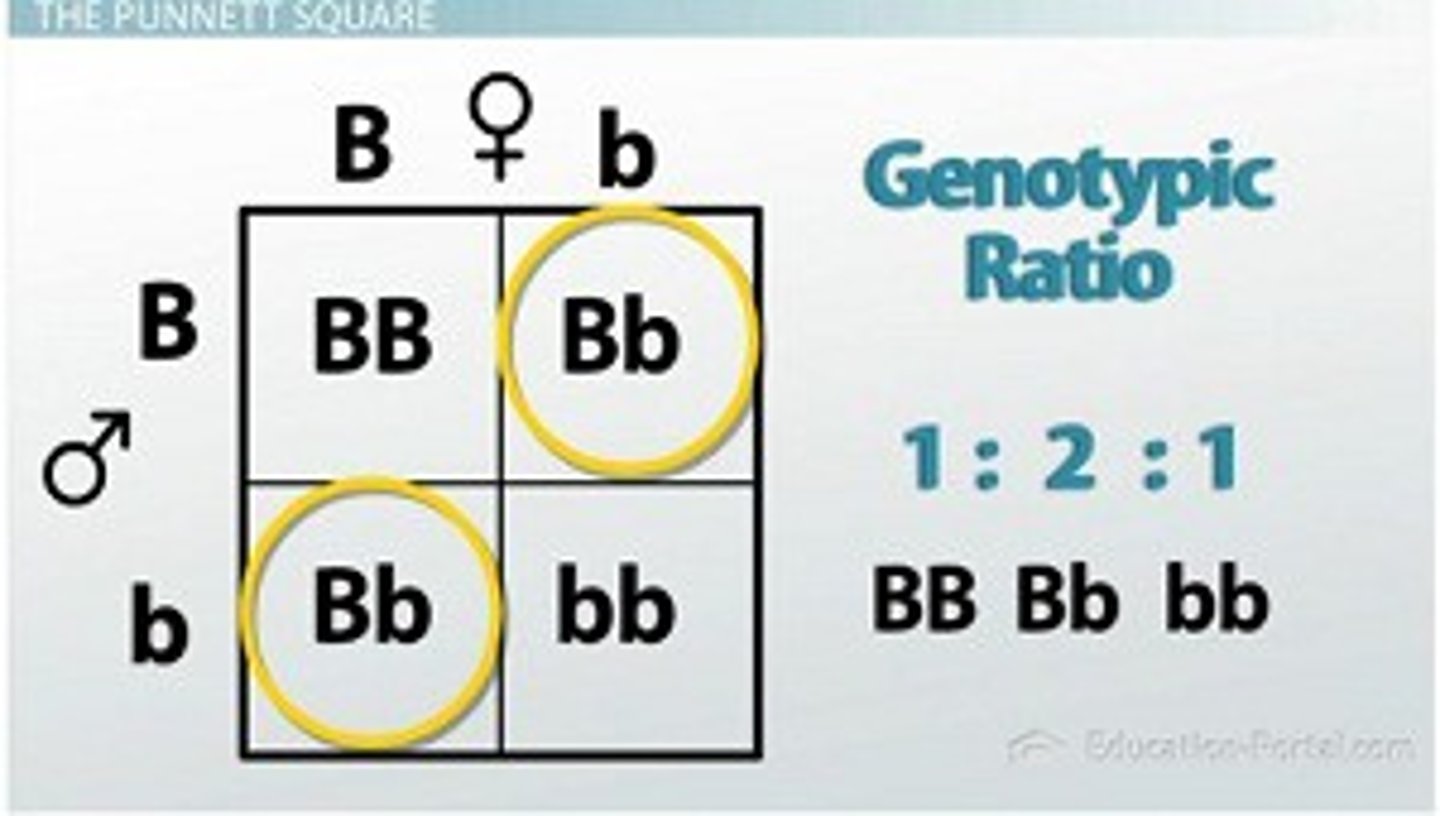
Punnett square
A chart that calculates all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
Phenotype ratio
The ratio of individuals with different phenotypes
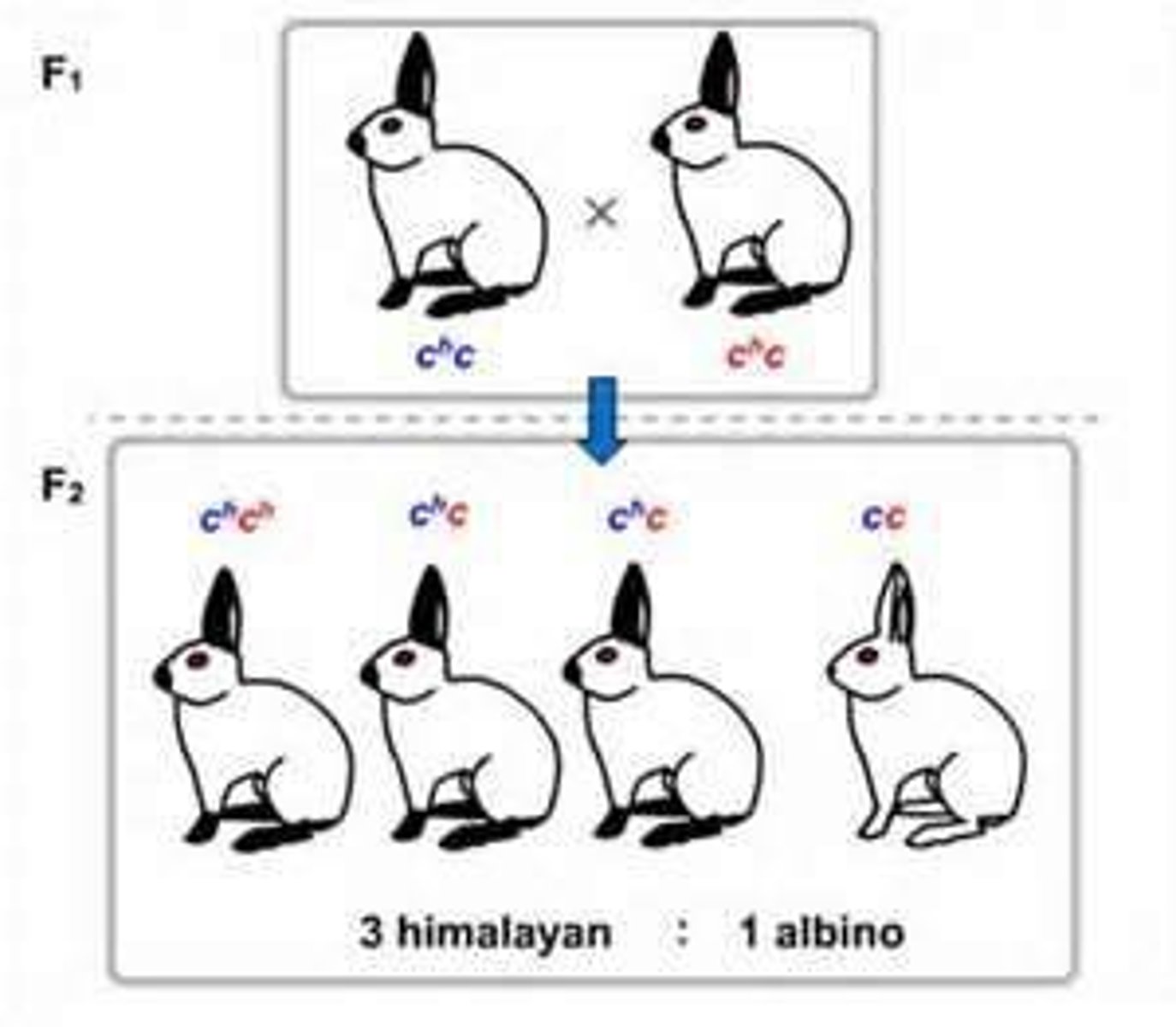
Genotype ratio
The ratio of the genotypes that appear in offspring.
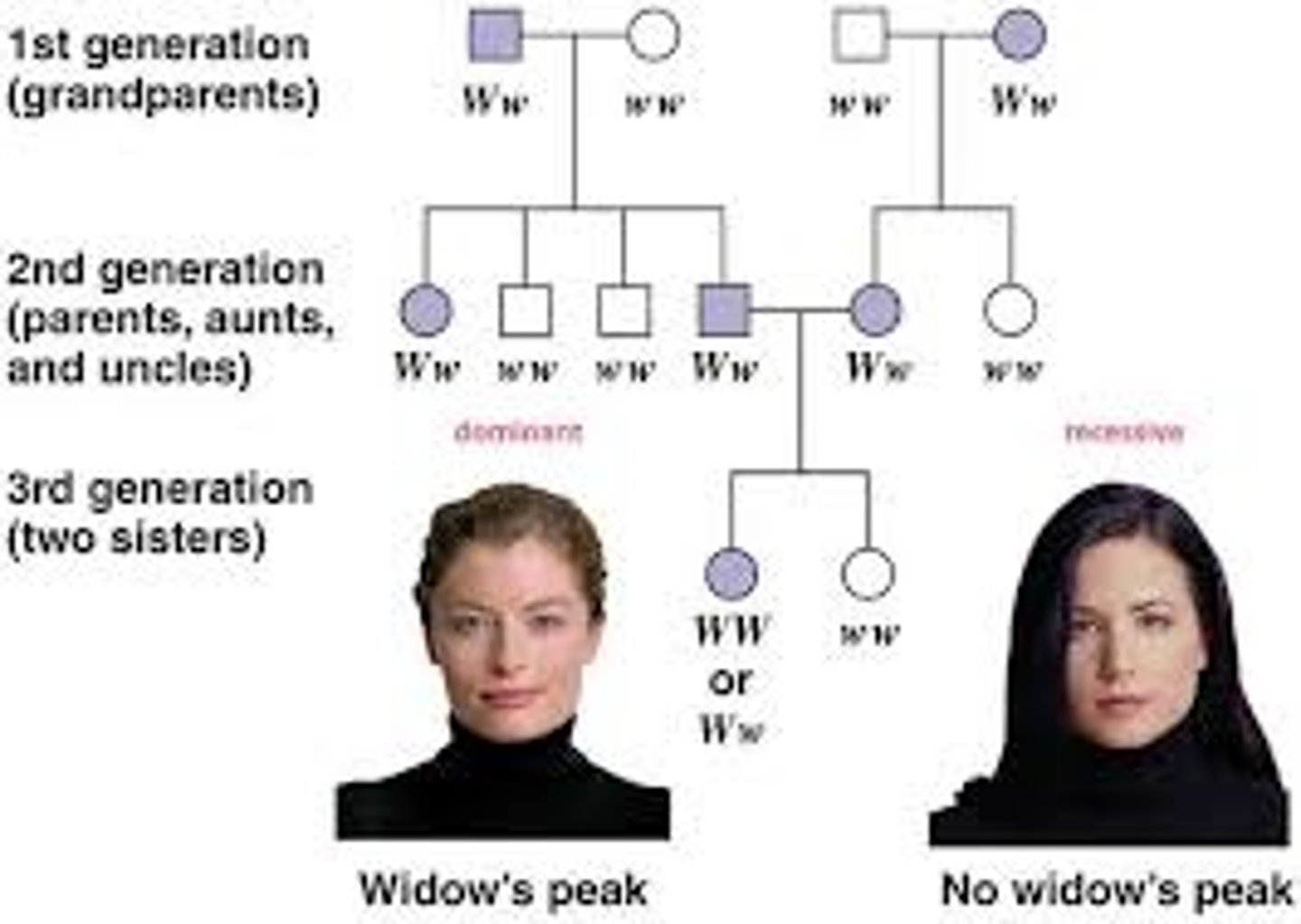
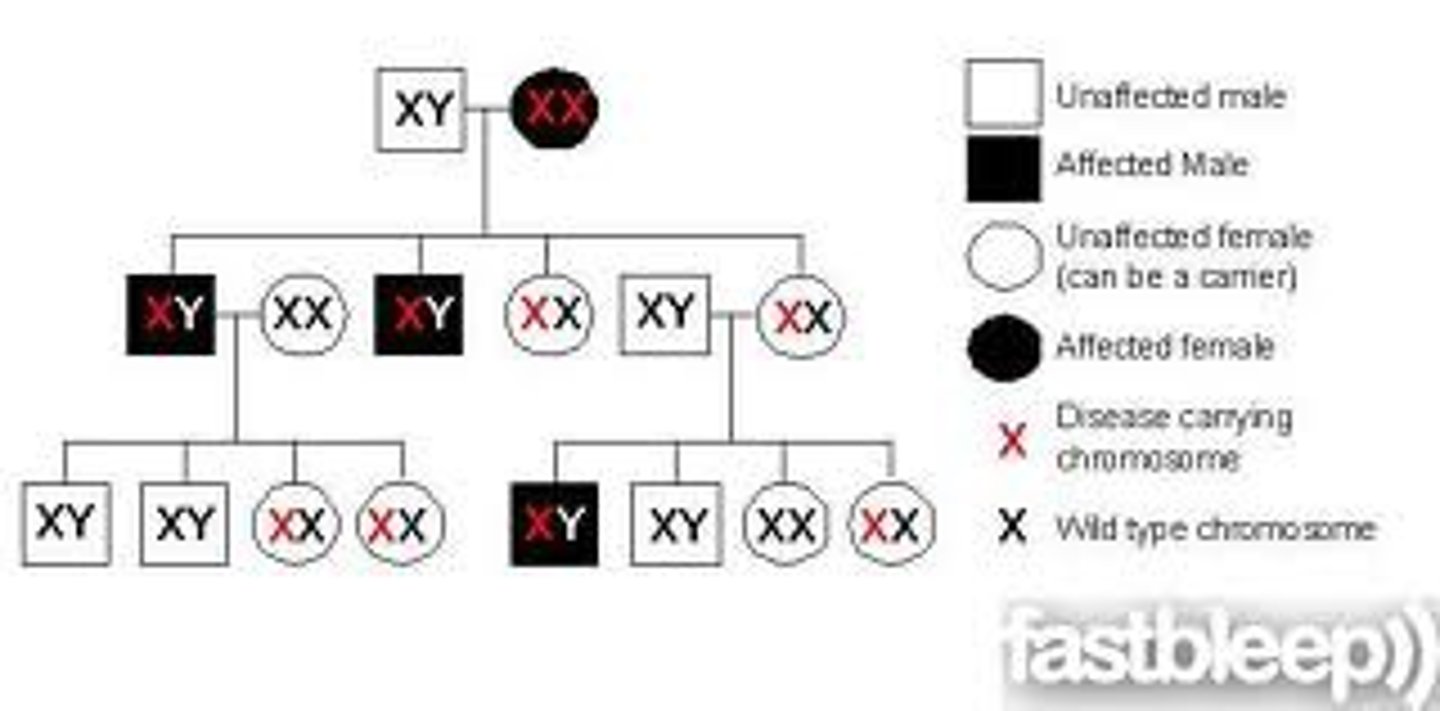
Pedigree chart
A chart which shows several generations of related families and how traits are passed down through the offspring.
Adaptations
A behavior or physical characteristic that allows an organism to live successfully in its environment.
Natural selection
A selective process determined by the environmental conditions, in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.