unti 1 - 🧪THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Organic Macromolecule CARBOHYDRATES
elements- carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
MONOMER - single sugar (monosaccharide)
THE FOUR CATEGORIES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES:
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acids
ALL of the organic molecules are based on which element
CARBON
organic macromolecule LIPIDS
monomers - glycerol & fatty acids
ex. saturated fats, unsaturated fats
organic macromolecules PROTEINS
monomer - amino acids ex
ex. keratin(hair,nails) muscles, silk, nuts, etc.
organic macromolecules NUCLEIC ACIDS
monomer - nucleotides
function - carries genetic information to make proteins
ex. DNA & RNA
how many different amino acids are there? (building block of protein is amino acids)
20
LIPIDS - TRIGLYCERIDES (type of lipid)
has 3 fatty acids , 1 molecule of glycerol (alcohol)
ONE type of triglyceride
saturated - solid at room temperature (red meat, etc)
SECOND type of triglyceride
unsaturated - liquid at room temperature (plant seeds, etc.)
LIPIDS - PHOSPHOLIPIDS (type of lipid)
TWO fatty acid molecules attached to glycerol molecule
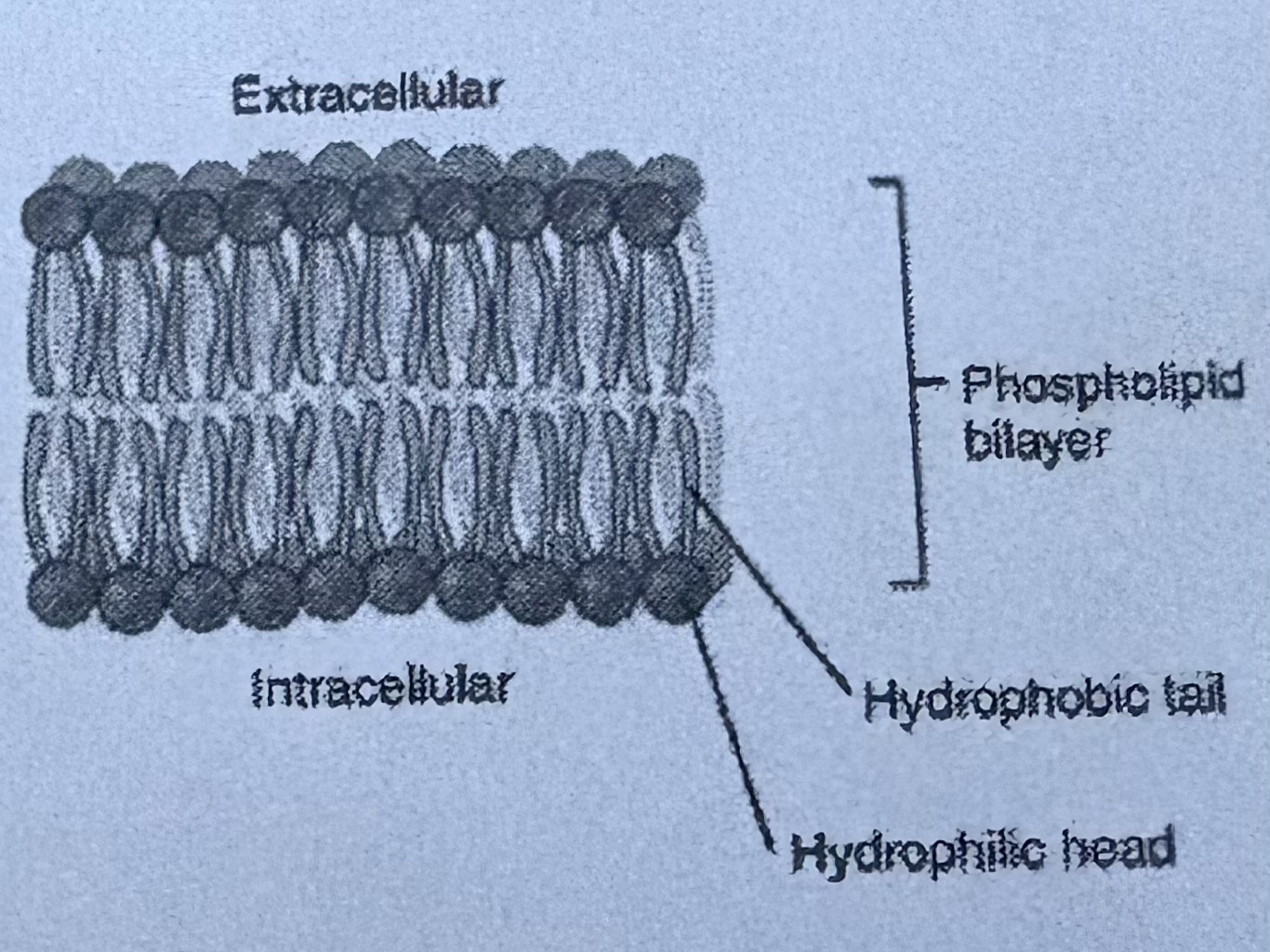
LIPIDS - Phospholipids (type of lipid) are
found in the CELL MEMBRANE
SATURATED FATS HAVE…
ALL single bonds
UNSATURATED FATS HAVE
AT LEAST ONE double or triple bond
organic macromolecules LIPIDS STRUCTURE
chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached to each side
organic macromolecules PROTEINS functions
form muscles , transport oxygen, determines how our bodies look & function
Carbohydrate RATIO
1:2:1
most carbs end in…
“-ose”
most proteins end in…
“-in”
‘ase’
LACTASE - LACTOSE
MALTASE - MALTOSE
in carbohydrates, a monosaccharide + a monosaccharide =
disaccharide
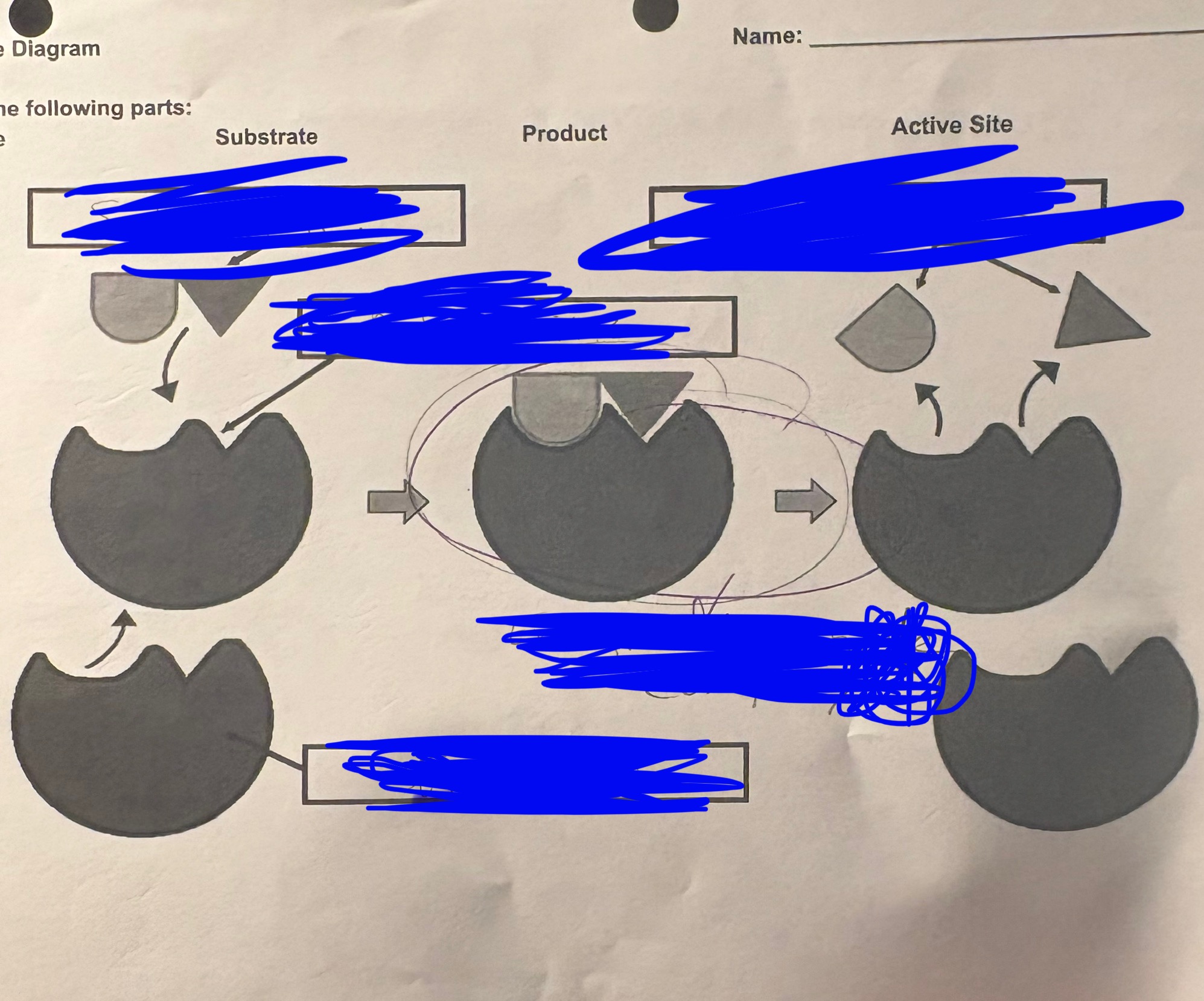
enzyme diagram - the TOP LEFT is called…
Substrate
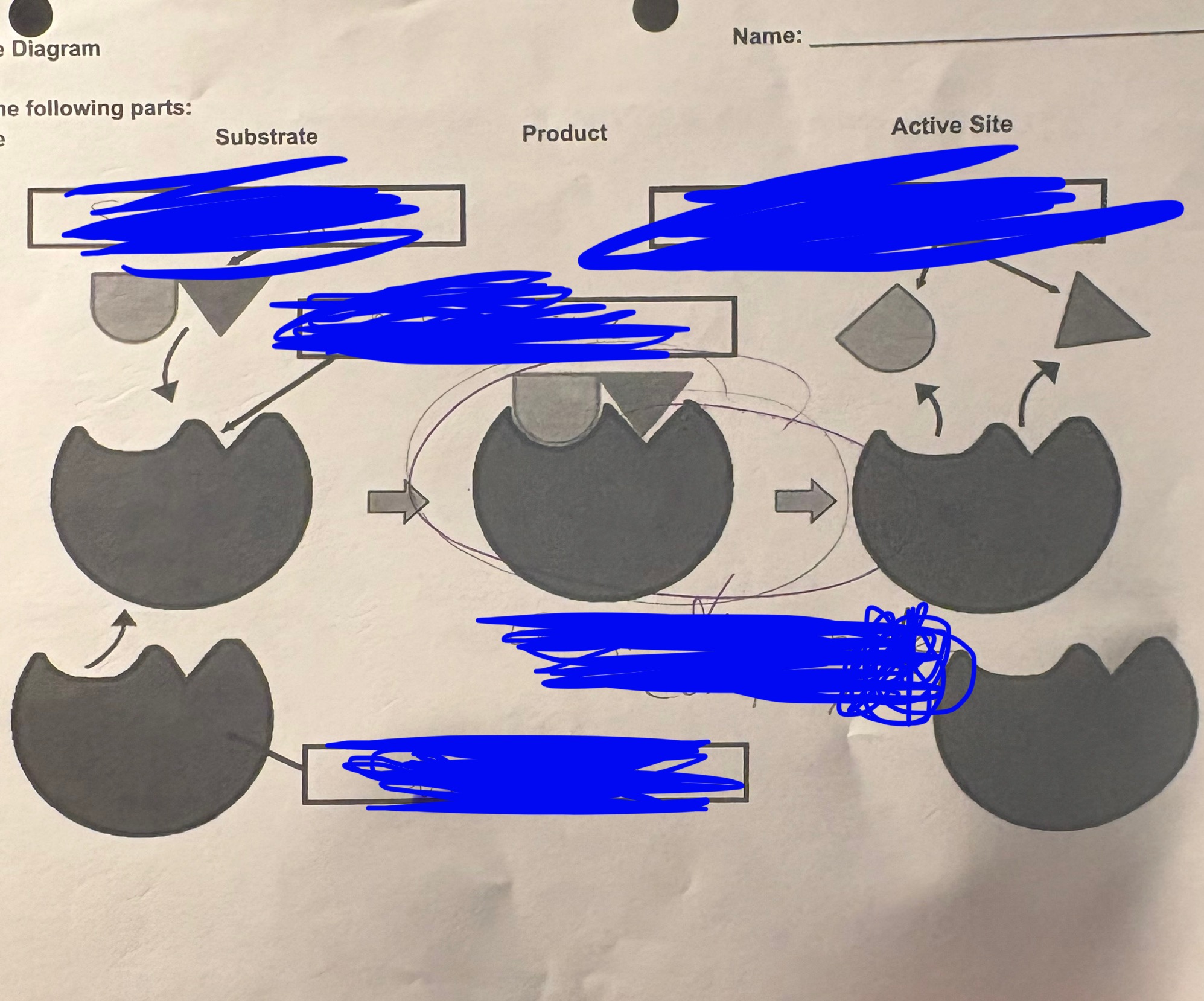
enzyme diagram - BOTTOM LEFT is…
enzyme
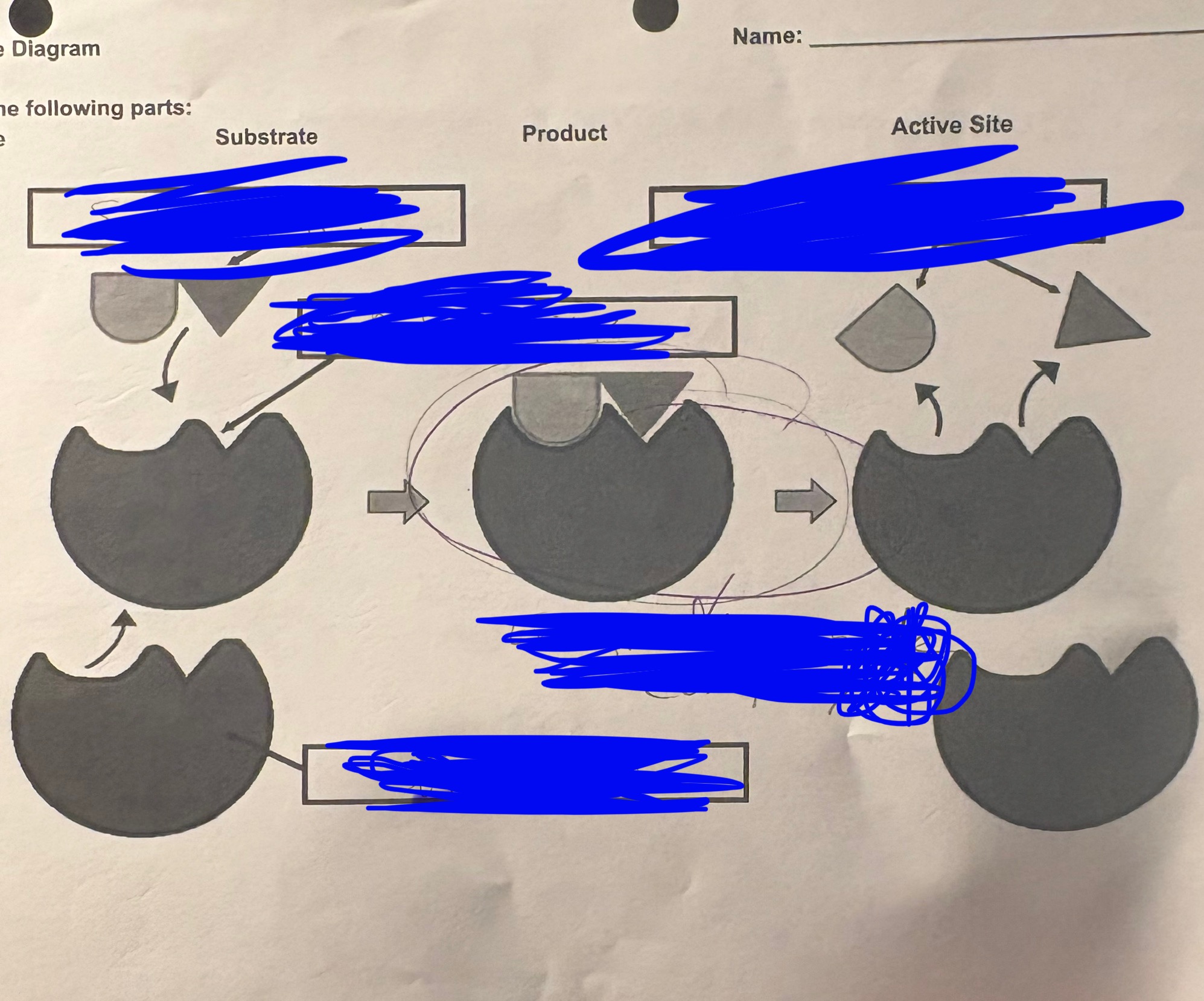
enzyme diagram - BELOW the TOP LEFT is…
active sight
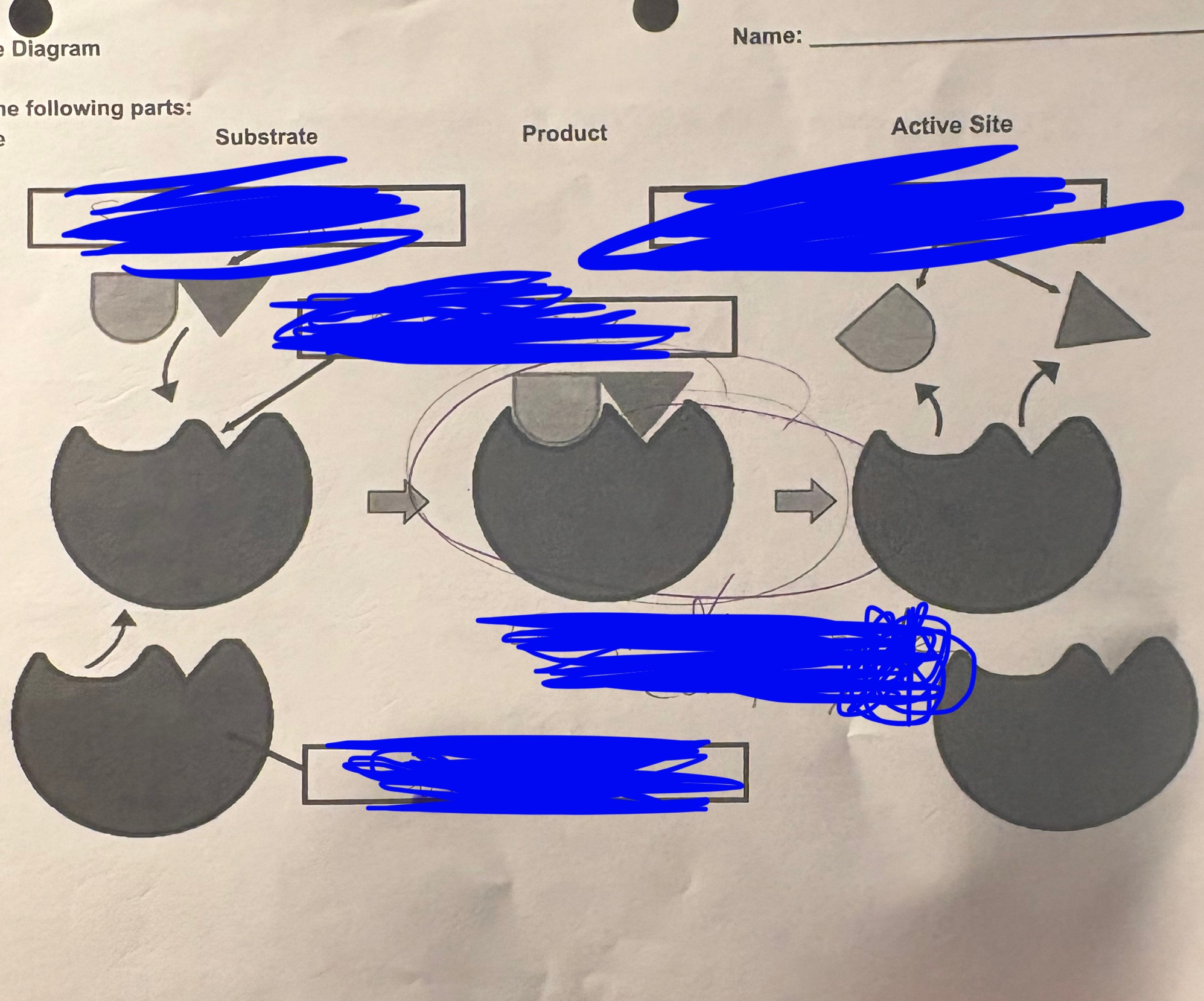
enzyme diagram - TOP RIGHT is…
products
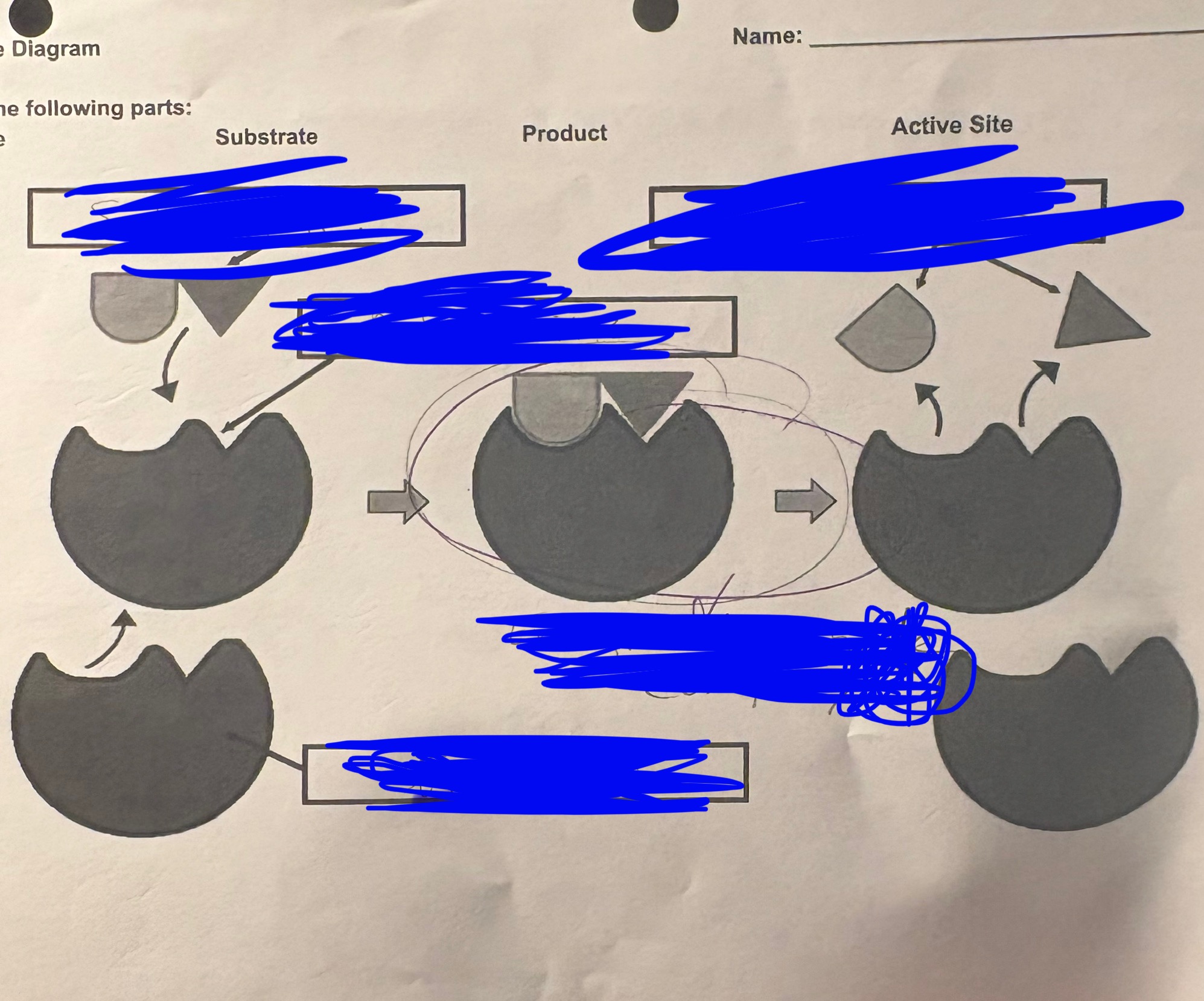
enzyme diagram - the MIDDLE is…
enzyme substrate complex
NUCLEIC ACIDS function ____ and _____ important information in the cell
store, transfer
Nucleic acids are…
VERY LARGE AND COMPLEX MOLECULES
Nucleic acids have two different types and the are…
DNA. RNA.
DNA is….
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid
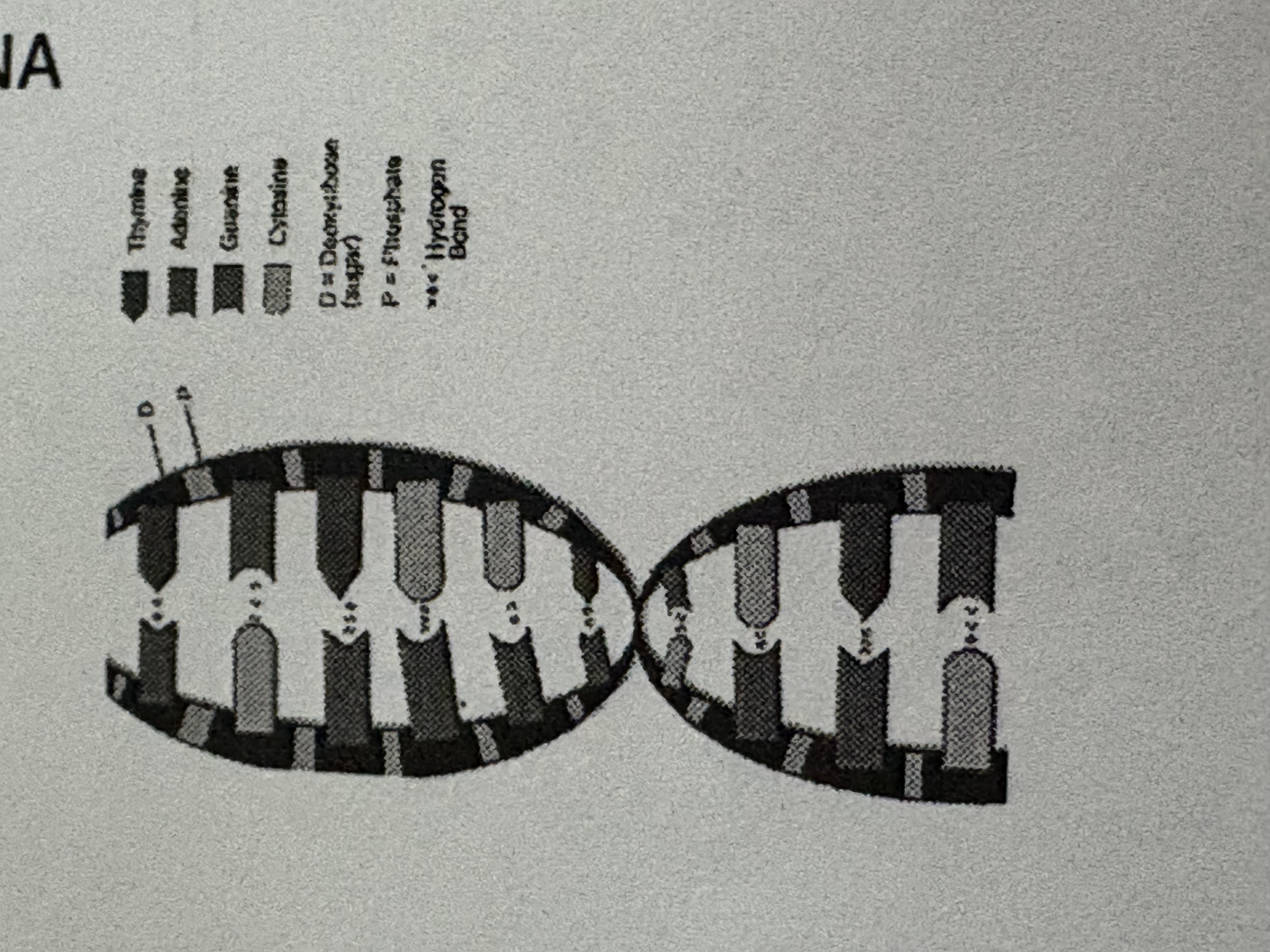
DNA can…
contain info that determines characteristics of an organism … DIRECTS CELL ACTIVITIES
RNA is….
RiboNucleic Acid
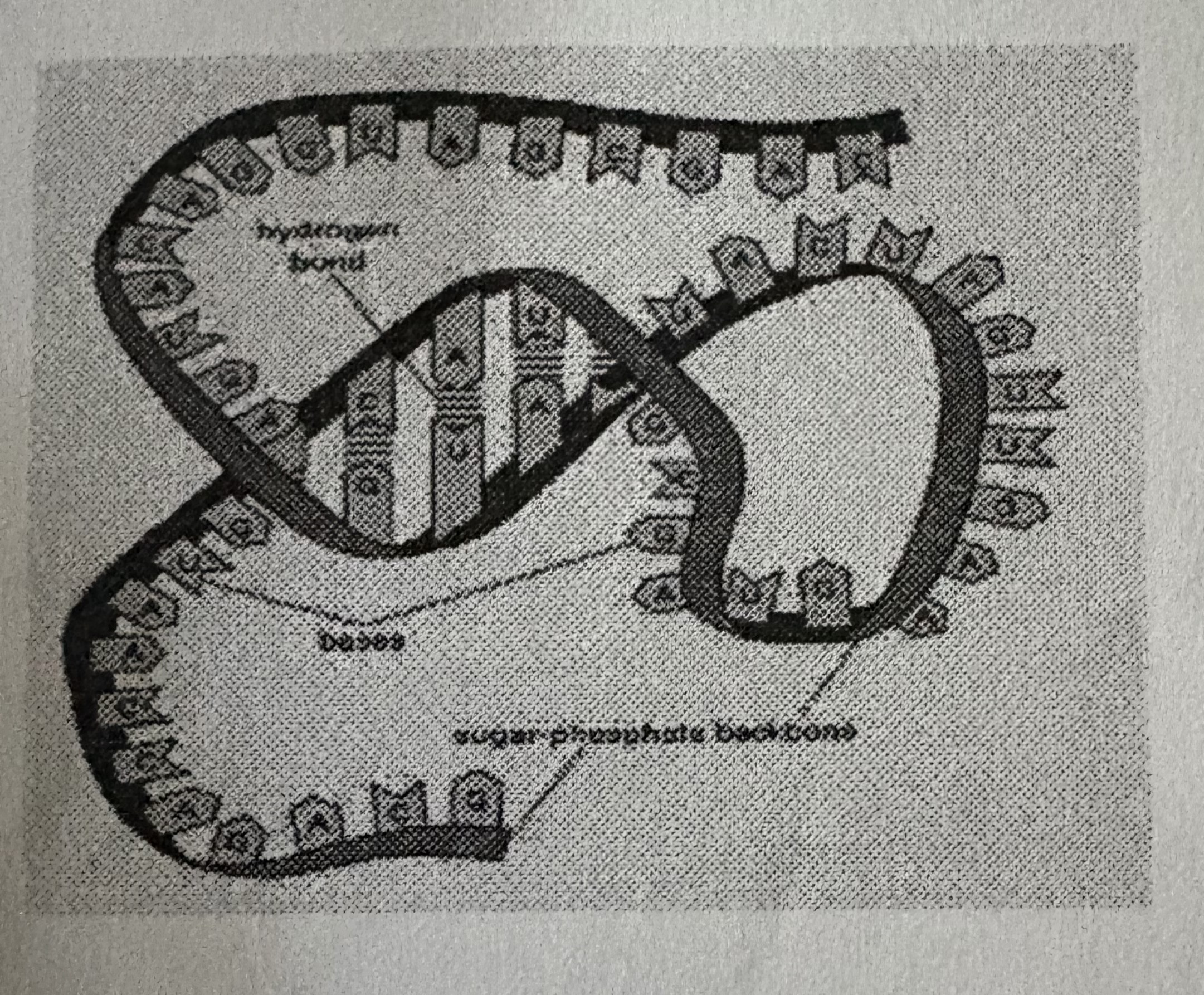
RNA can…
store and transfer info from DNA, ESSENTIAL IN THE MAKING OF PROTEINS
RNA can also…
act as an enzyme
Both DNA and RNA are…
POLYMERS
Nucleotides are the ____ that make up ____and ____
monomers . DNA. RNA.
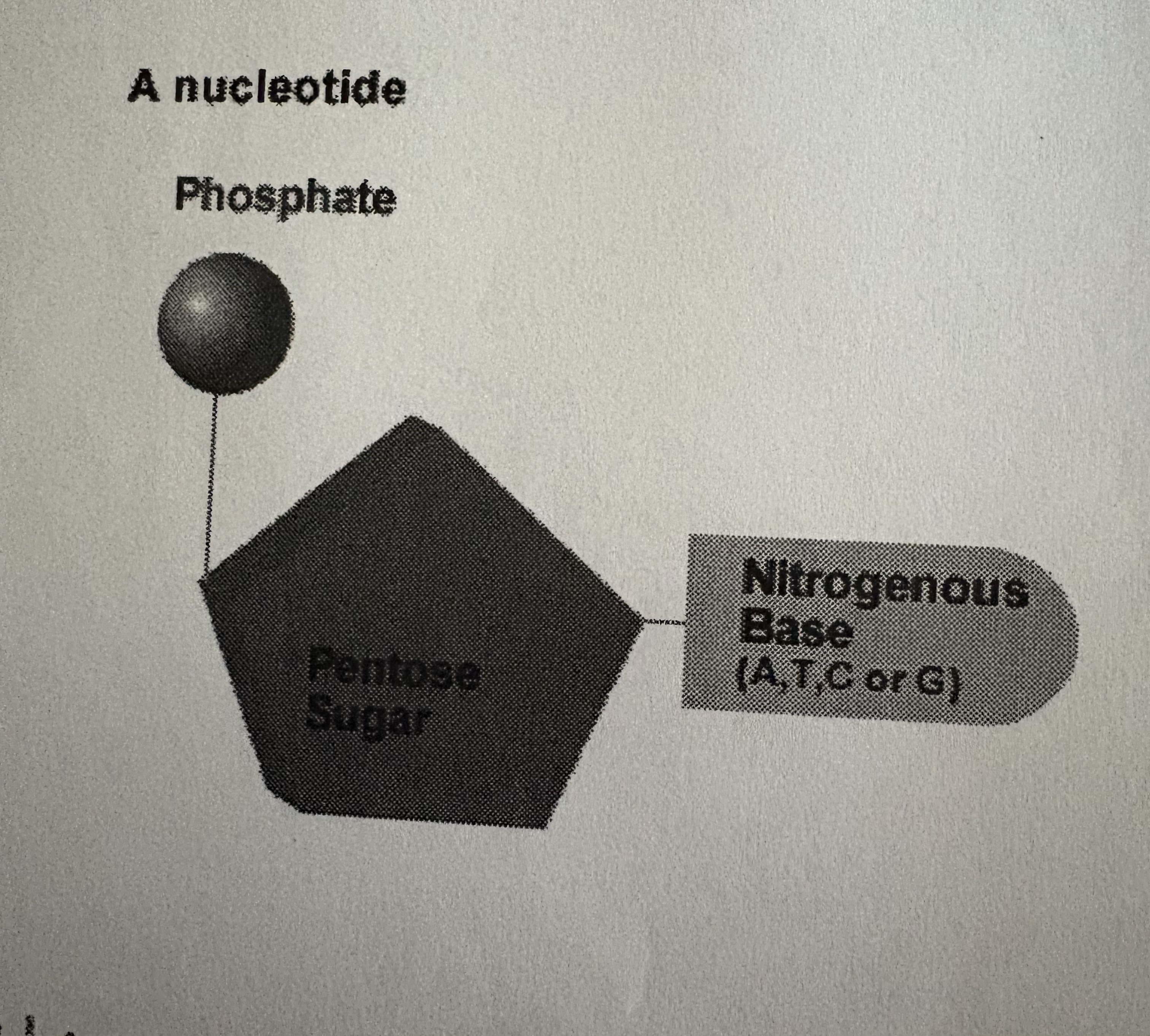
what are Nucleotides made up of?
PHOSPHATE GROUP , FIVE CARBON SUGAR , NITROGENOUS BASE.
a nucleotide is one part of the ladder u see
hydrogen bond -
a weak attraction between one HYDROGEN ATOM in one molecule and a HIGHLY electronegative atom (oxygen) in another molecule
mixture -
physical combination of two or more substances where each substance have it’s own properties and is not chemically bonded to others
solution -
a homogeneous mixture of one/more solutes dissolved in a solvent
solute-
the substance that gets dissolved in a solvent to form a solution
solvent -
a substance that can dissolve another substance, called a solute, to form a solution
suspension -
a heterogeneous mixture where solid particles are dispersed in a liquid OR gas, but they are large enough to eventually settle over time when the mixture is undisturbed