unit 3: national income and price determination
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bruh
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
RGDP and unemployment
higher levels of RGDP → unemployment ↓
lower levels of RGDP → unemployment ↑
aggregate demand
demand for all g/s in economy
point on curve: RGDP for given PL
inverse relationship
wealth effect, interest rate effect, Xn effect
wealth effect
when PL ↑, wealth buys fewer g/s → RGDP ↓
when PL ↓, wealth buy more g/s → RGDP ↑
interest rate effect
at higher PL, nominal interest rates ↑ → investment ↓
at lower PL, nominal interest rates ↓ → investment ↑
net exports effect
at higher PL, foreign consumers purchase less of US goods → Xn ↓
at lower PL, foreign consumers purchase more of US goods → Xn ↑
shift of AD
caused by change in components of GDP
C+I+G+Xn
disposable income
$ that consumers have available to spend on g/s
personal income - taxes = DI
spending’s + savings = DI
either spend or save
MPC
marginal propensity (tendency) to consume
∆ consumption / ∆ disposable income
MPC + MPS = 1
MPS
marginal propensity (tendency) to save
∆ savings / ∆ disposable income
MPC + MPS = 1
spending multiplier
1 / MPS
initial change * multiplier = total change in GDP
tax multiplier
-MPC / MPS
| tax multiplier | = spending multiplier - 1
1 less bc impact of tax on economy is indirect
use tax multiplier with transfer payments
short-run aggregate supply
supply for all g/s in economy
direct relationship
wages and prices do not change quickly in response to changes in PL (sticky)
SRAS shifters (supply shocks)
resource prices (wages)
productivity (capital stock)
future inflation expectations
resource prices
decrease wages → ↑ SRAS
increase wages → ↓ SRAS
productivity
increase productivity → ↑ SRAS
decrease productivity→ ↓ SRAS
inflation expectations
lower prices: businesses lower prices (due to less profit expectations), workers lower wage expectations
higher prices: businesses increase prices, workers demand higher wages
long run aggregate supply
vertical at full employment output
wages flexible in long run
RGDP = YF
short-run equliibrium
at intersection of AD and SRAS
RGDP = Y1
PL * RGDP = nominal GDP
inflationary gap
current output > long-run full employment output
unhealthy: operating above full employment, overworking
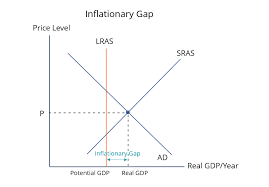
recessionary gap
current output < long-run full employment output
unhealthy: high unemployment > natural rate
long-run equilibrium
current output = long run full employment output
unemployment = natural rate
cyclical unemployment = 0
long-run self adjustment
no gov. action
recessionary gap
lower prices: businesses lower prices (due to less profit expectations), workers lower wage expectations
inflationary gap
higher prices: businesses increase prices, workers demand higher wages
fiscal policy
gov tools used to combat inflation / unemployment
change in taxes and gov spending
fiscal policy - taxes
increase taxes → decrease disposable income → decrease consumer spending
fiscal policy - gov spending
gov purchases
transfer payments
increase → increase consumer spending, decrease → decrease consumer spending
expansionary fiscal policy
fight unemployment
increase gov spending/decrease taxes
contractionary fiscal policy
fight inflation
decrease gov spending / increase taxes
automatic stabilizers
limit fluctuations of business cycle
taxes
increase during expansions
decrease during contractions
transfer payments
decrease during expansions
increase during contractions