BIOL 3320 Lab 2
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What is cytology?
The study of cells
Cell
The smallest unit of the life
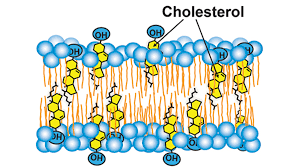
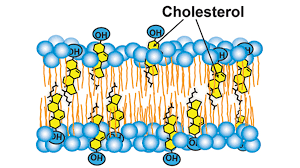
Cholesterol
A steroid that stabilizes the membrane’s structure in the face of changing temperatures cell recognized by glycoproteins and glycolipids.
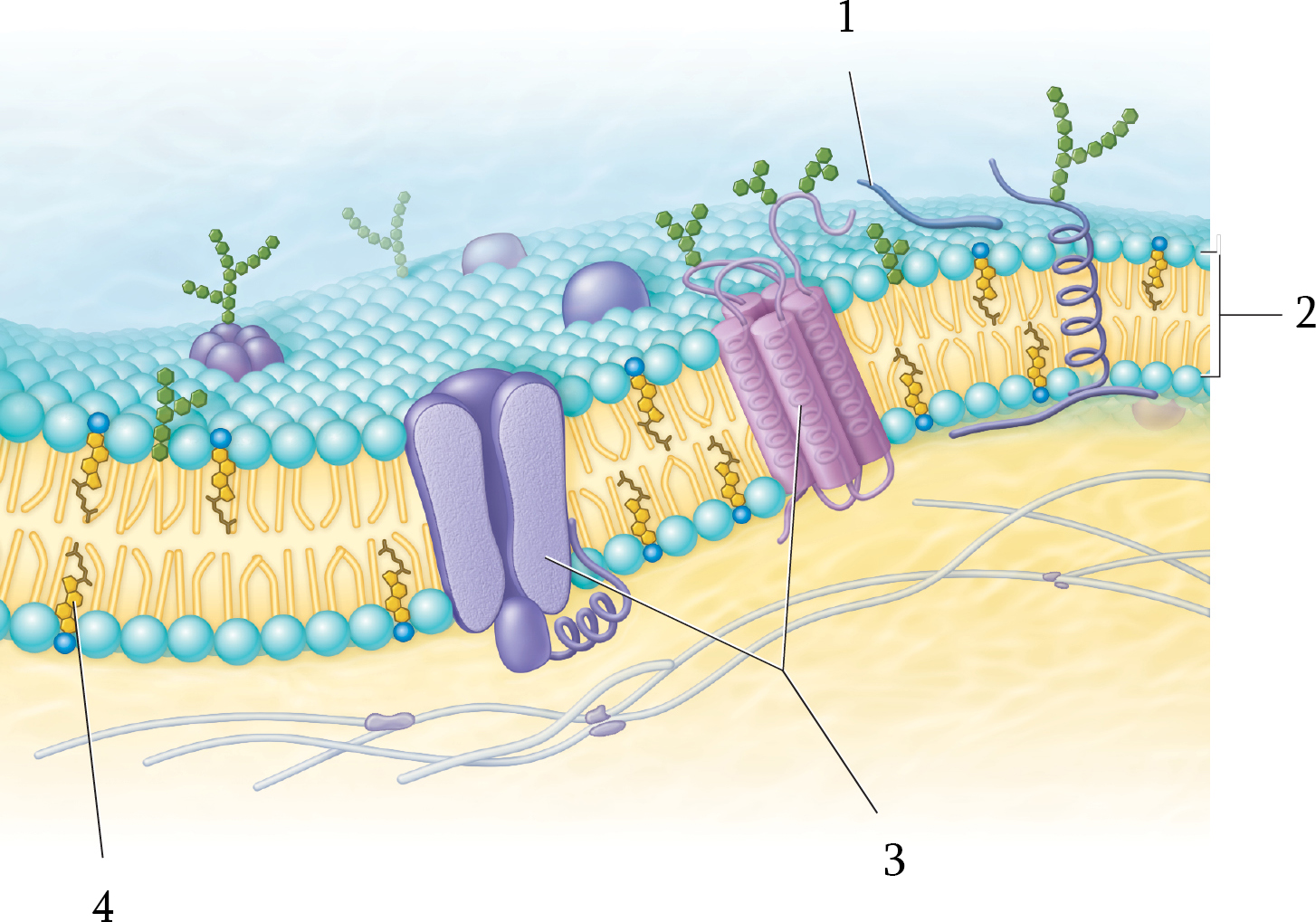
Where is the peripheral proteins in the plasma membrane?
1; located only on one face of the membrane.
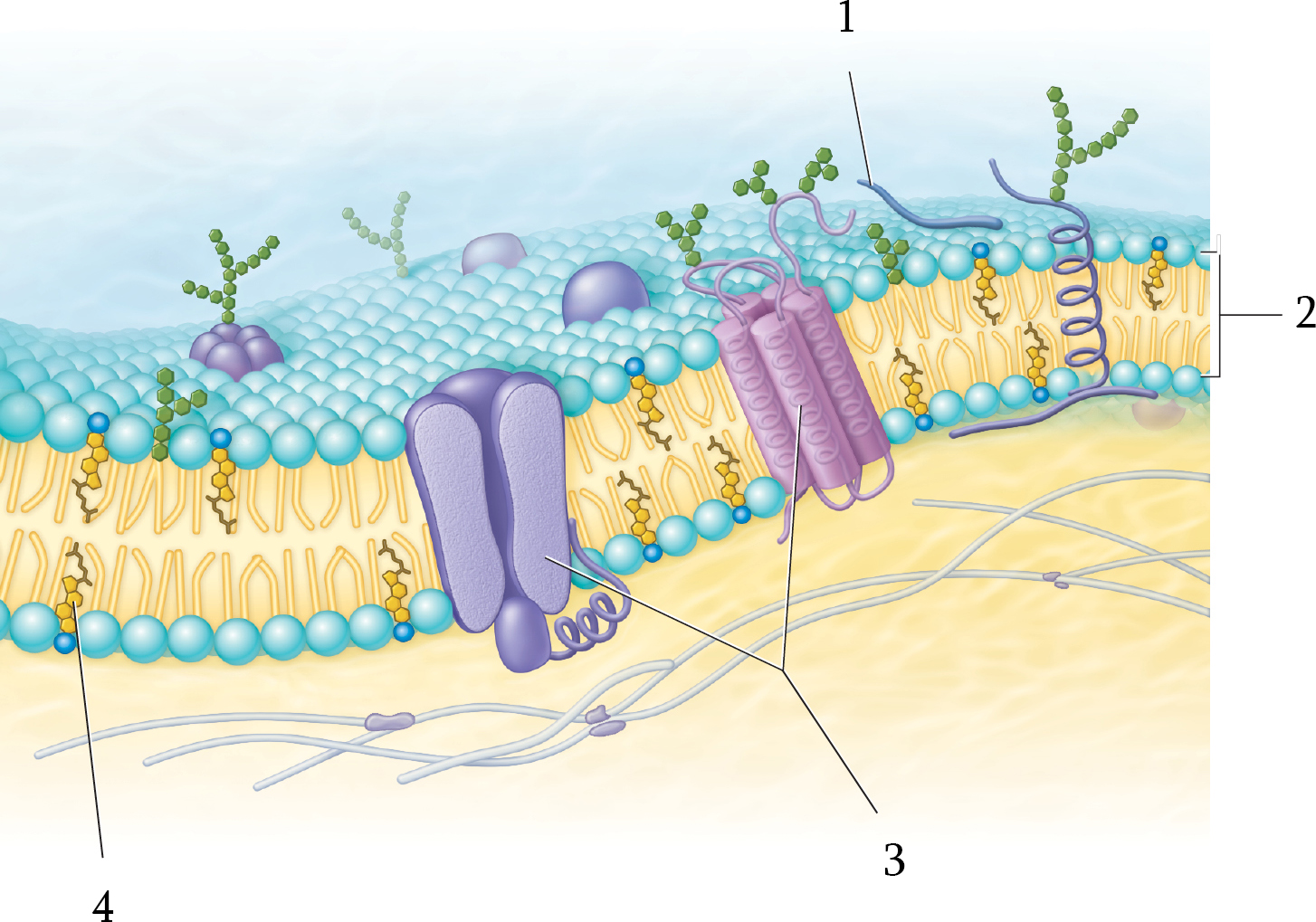
Phospholipid layer
2
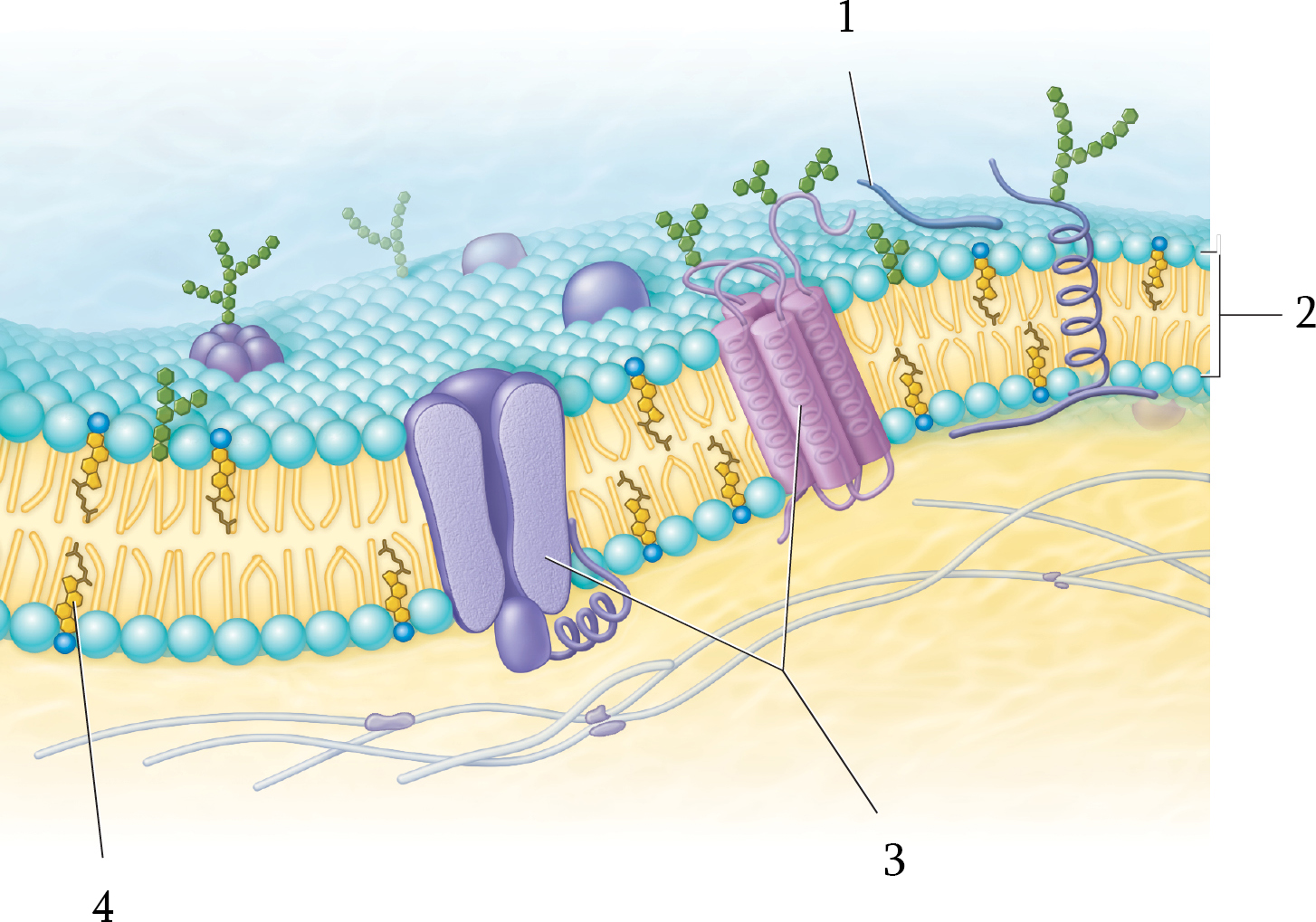
Where is the integral proteins in the plasma membrane?
3; spans the width of the membrane
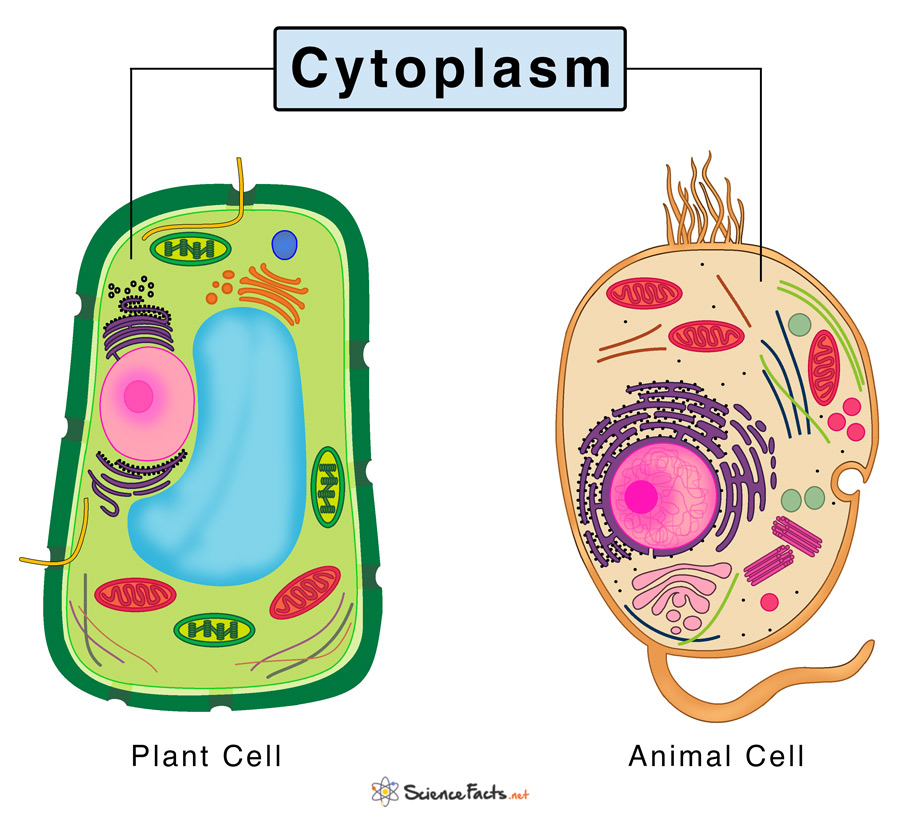
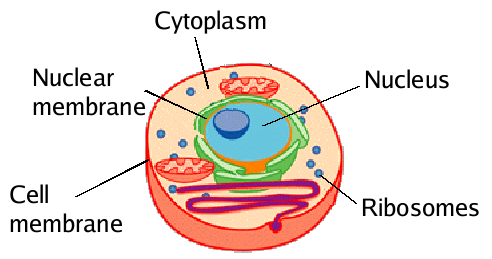
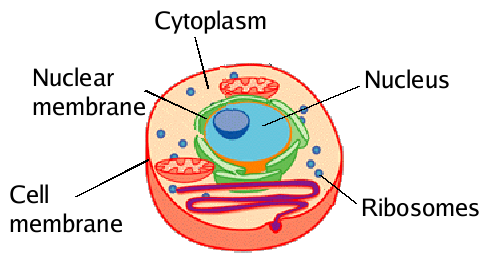
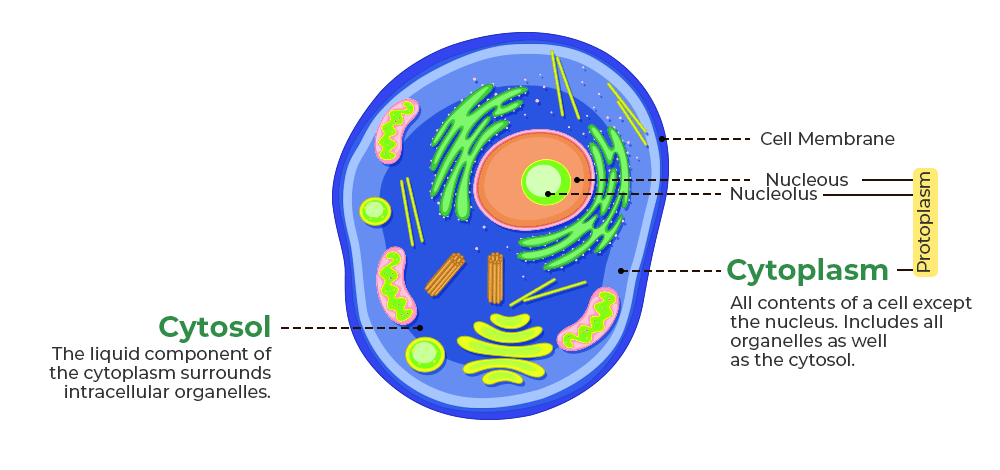
Cytoplasm
The material inside the cell consists of cytosol, cytoskeleton, and organelles.
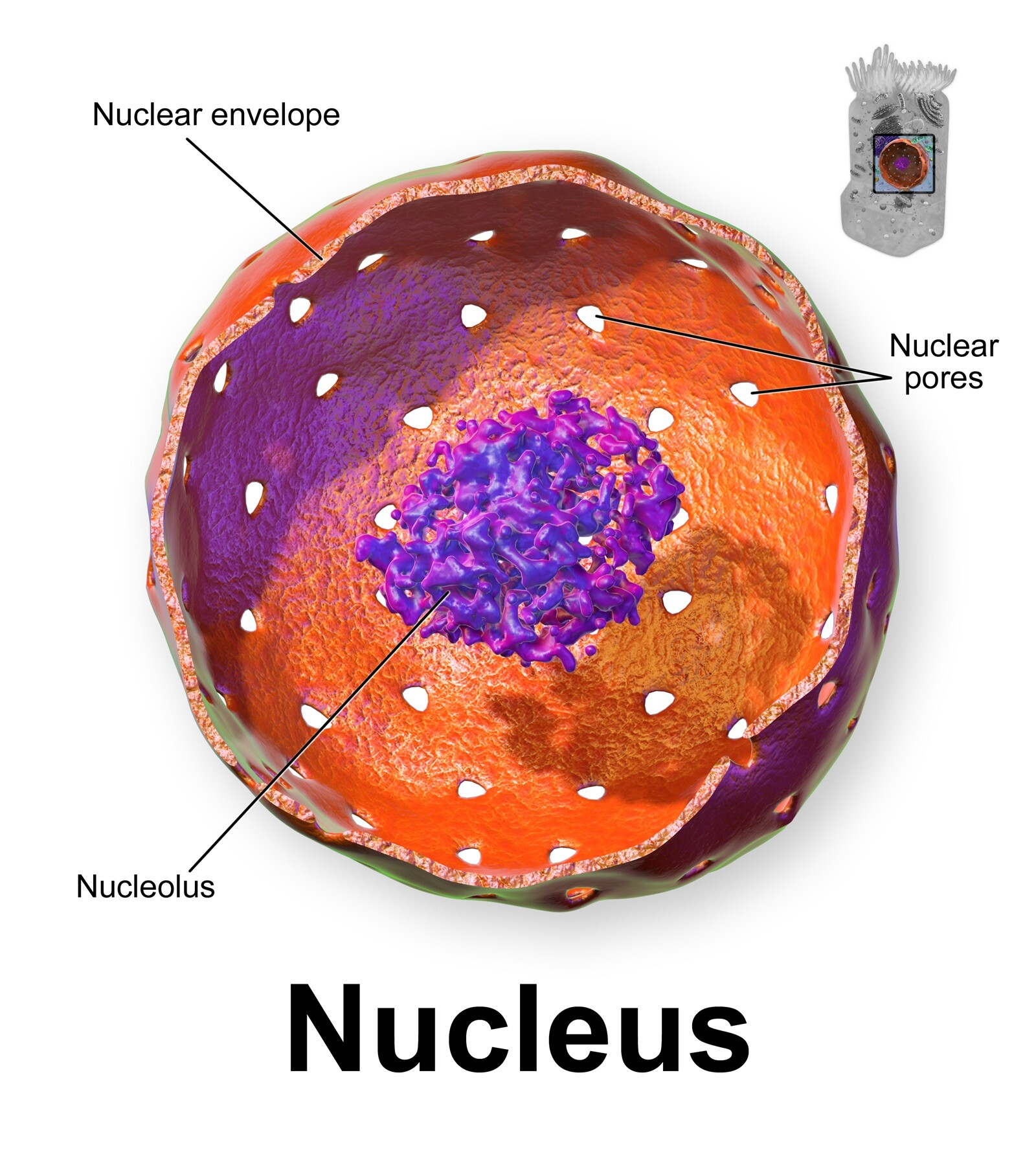
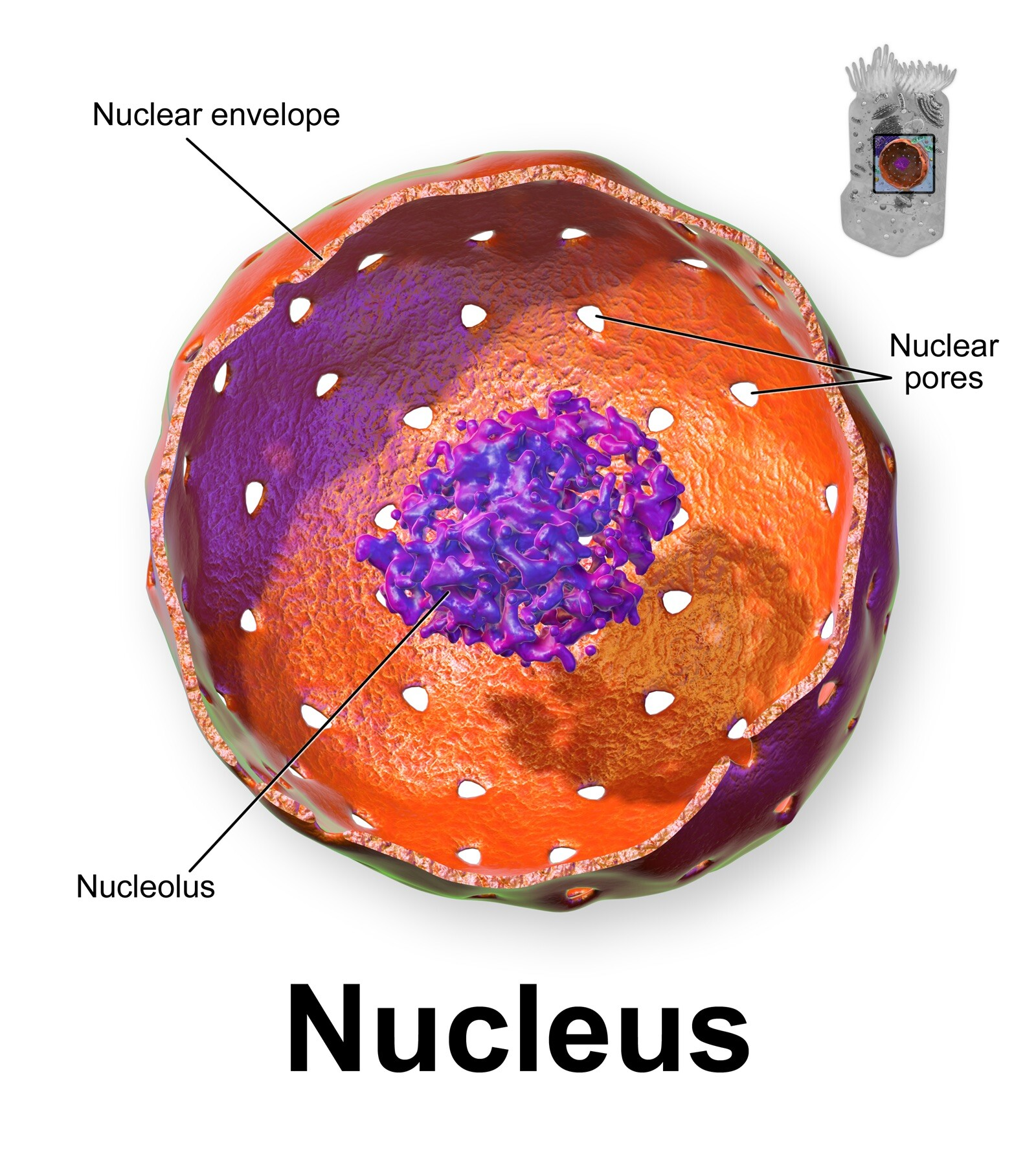
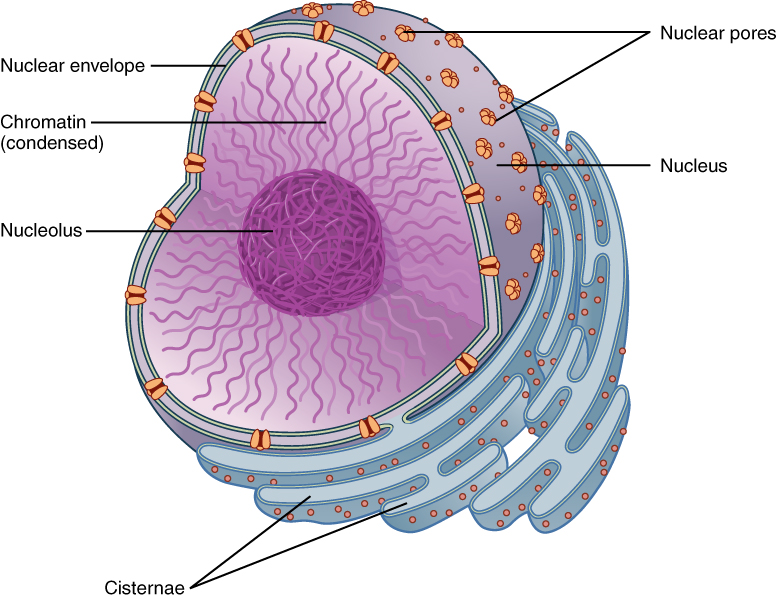
Nucleus
The center of the cell’s biosynthetic center that directs the synthesis of almost all proteins and certain nucleic acids.
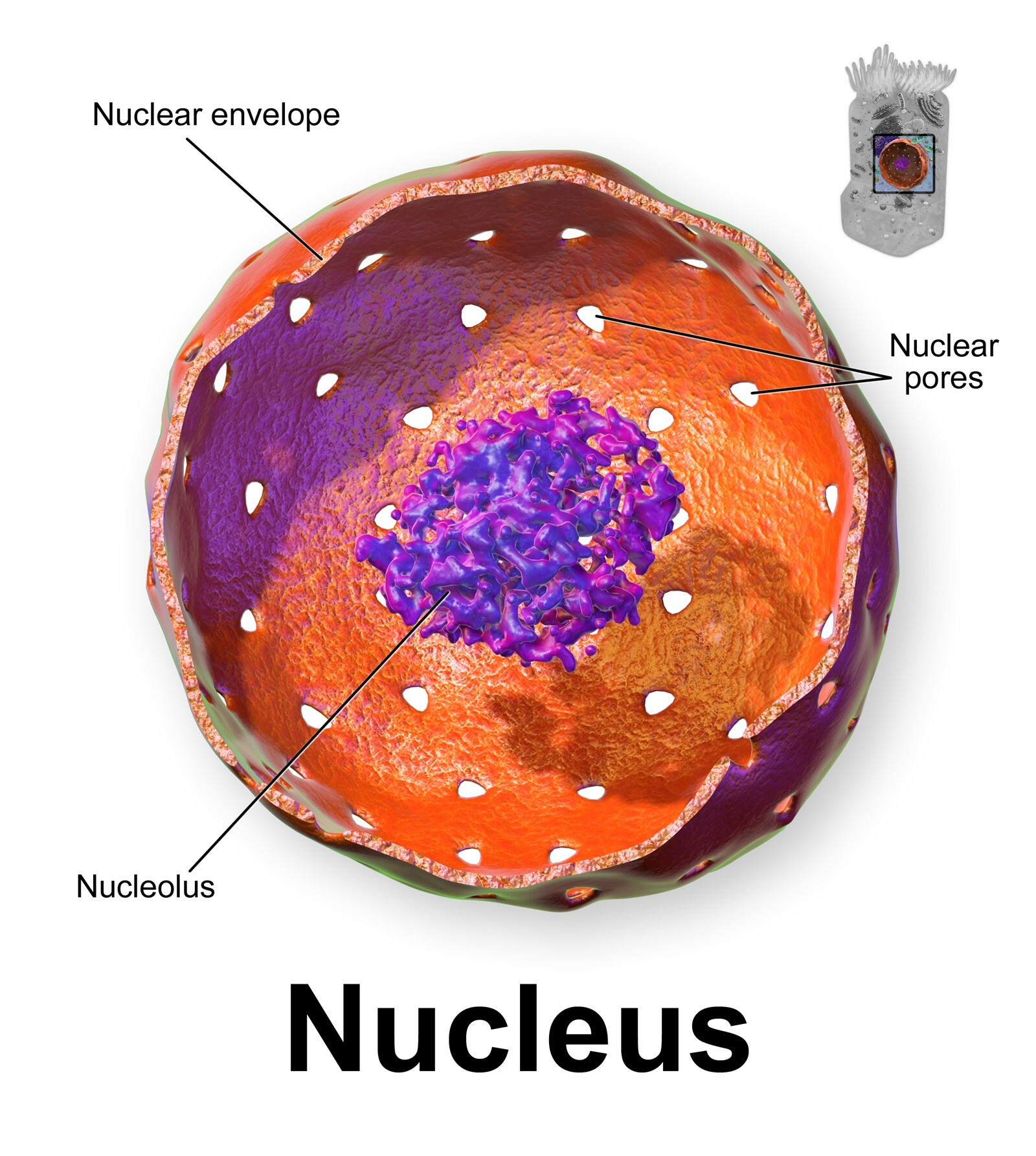
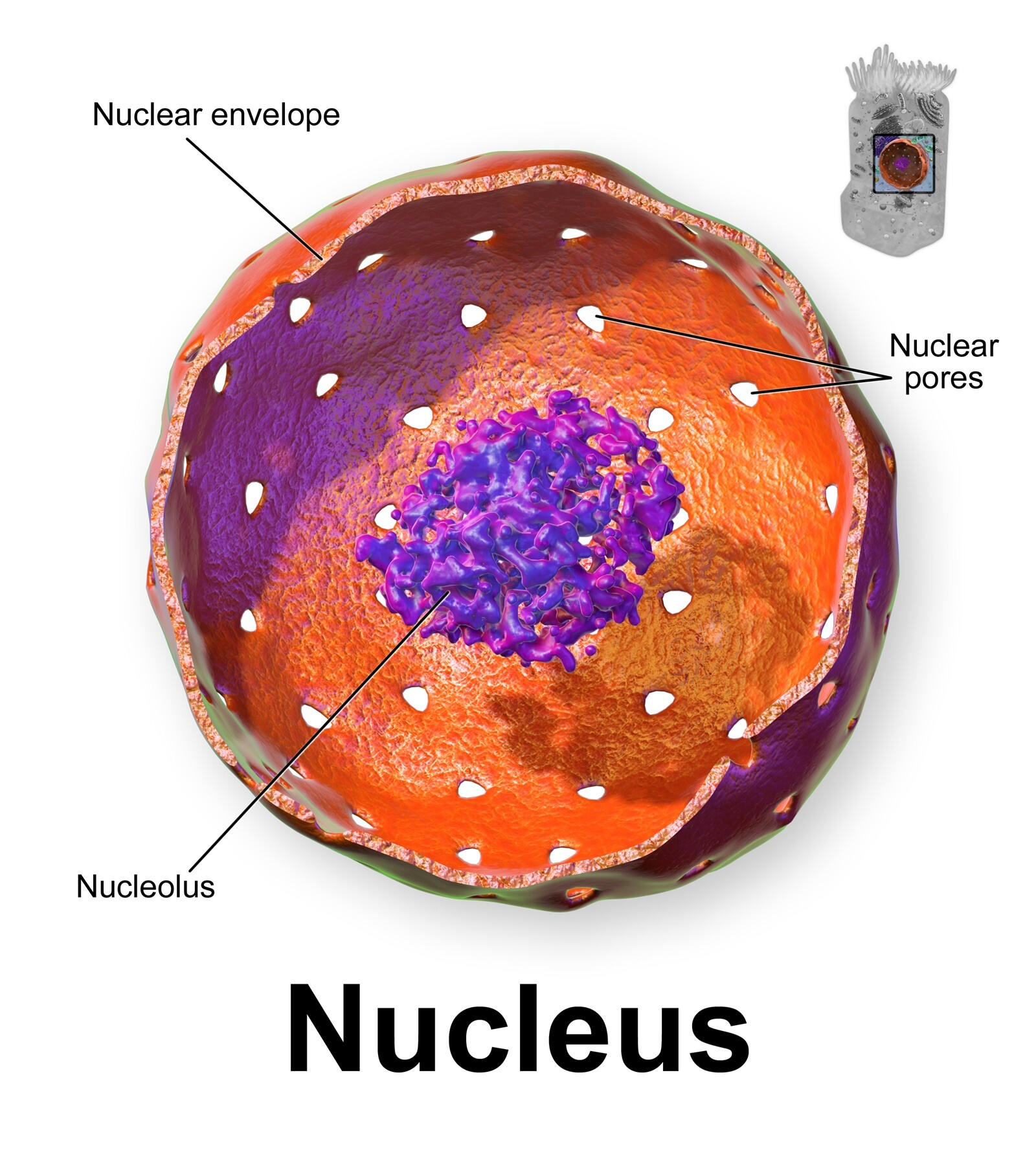
Nucleolus
The dark-staining region is also known as the birthplace of ribosomes.
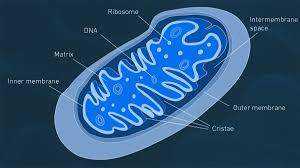
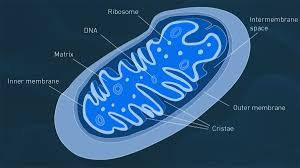
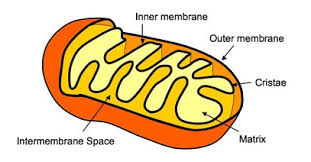
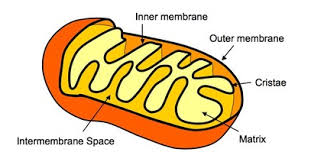
Mitochondrion
Bean-shaped and produces the bulk of the cell’s ATP (energy) through the breakdown of glucose and fatty acids. The double surrounding membrane is the matrix.
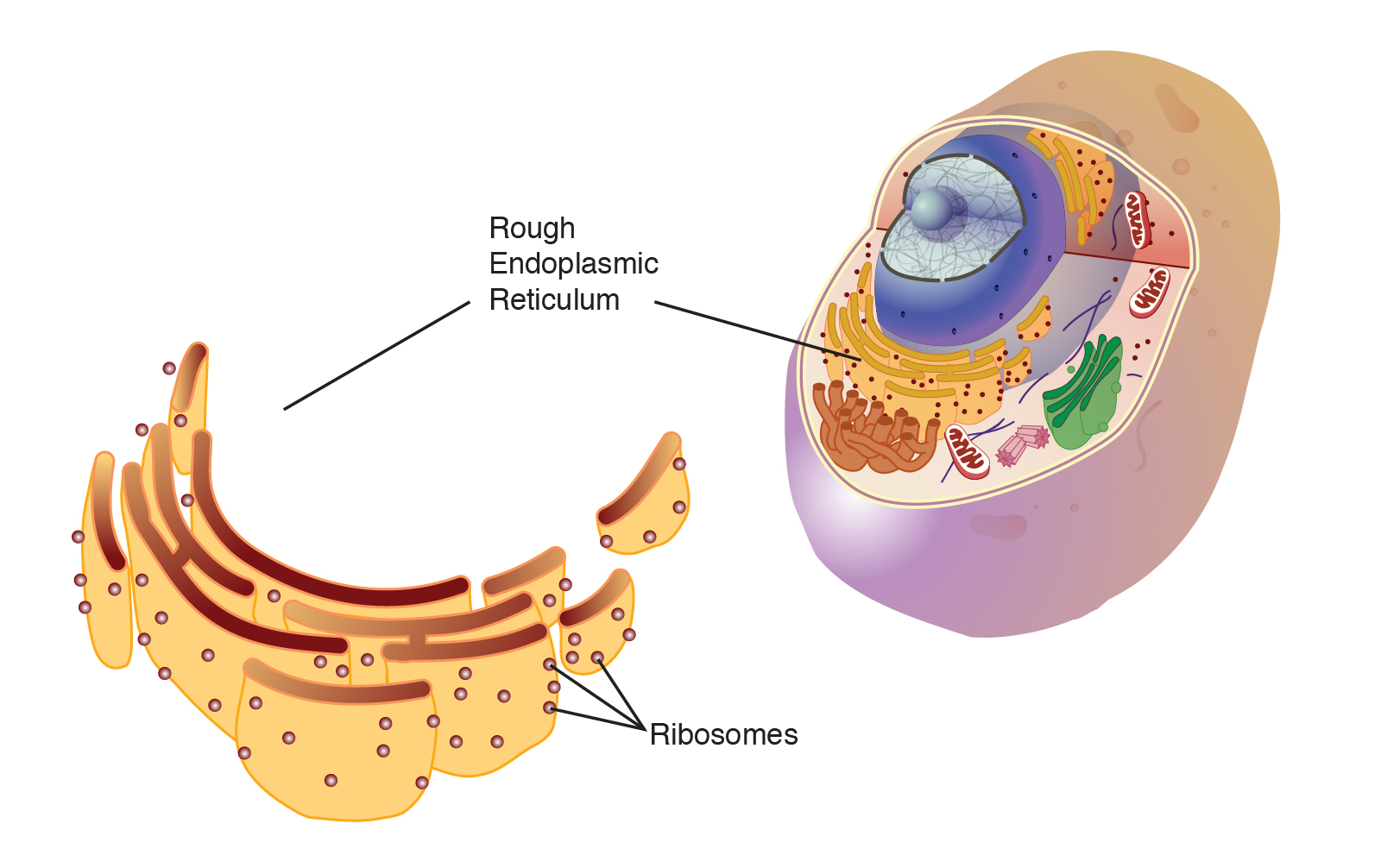
Ribosomes
The small, granular ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis in the cell, which are composed of subunits and RNA.
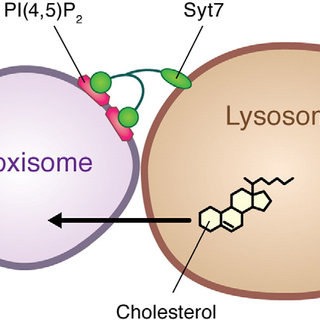
Peroxisomes
The small, membrane-enclosed organelles contain enzymes that catalyze reactions that metabolize certain types of fatty acids.
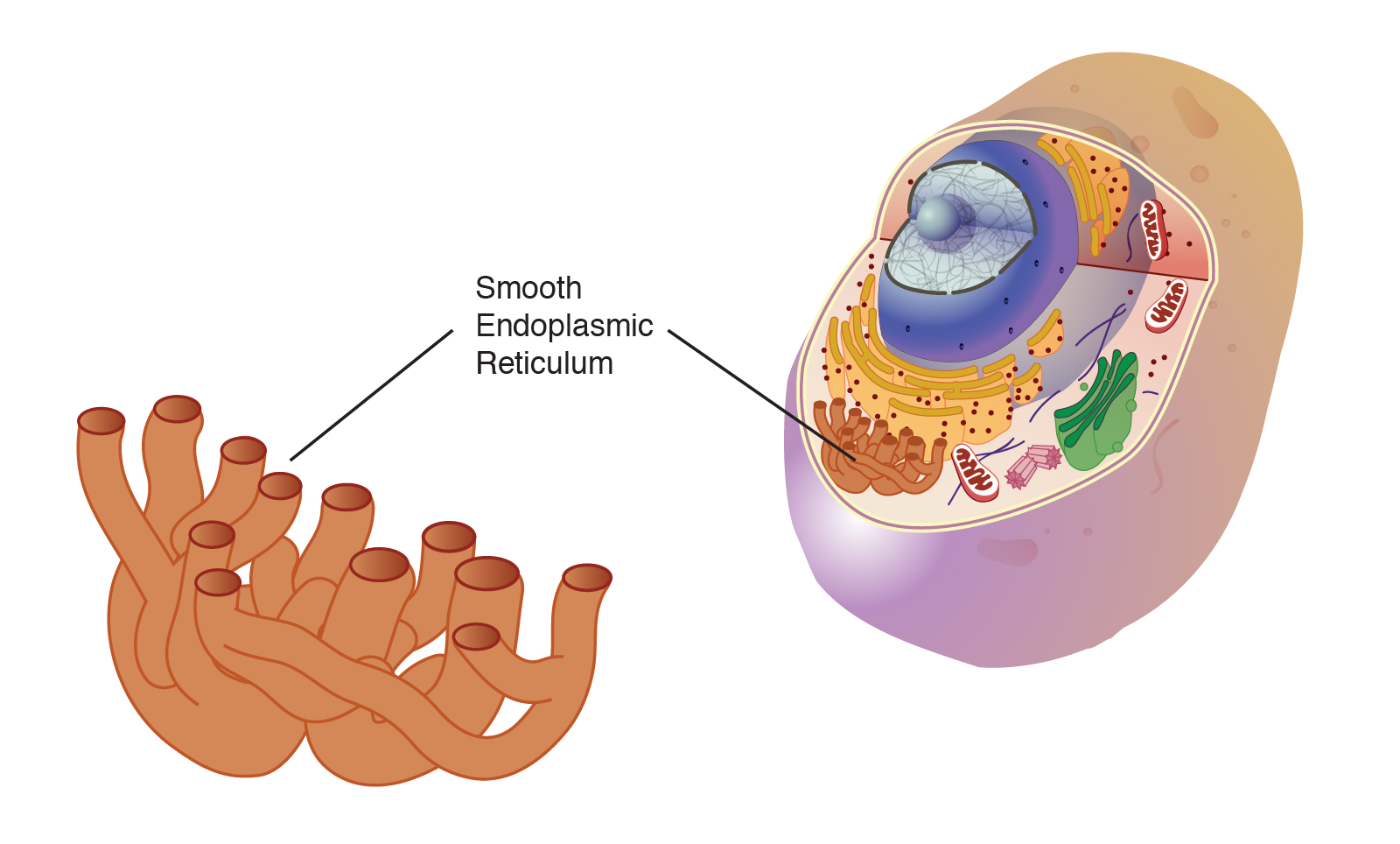
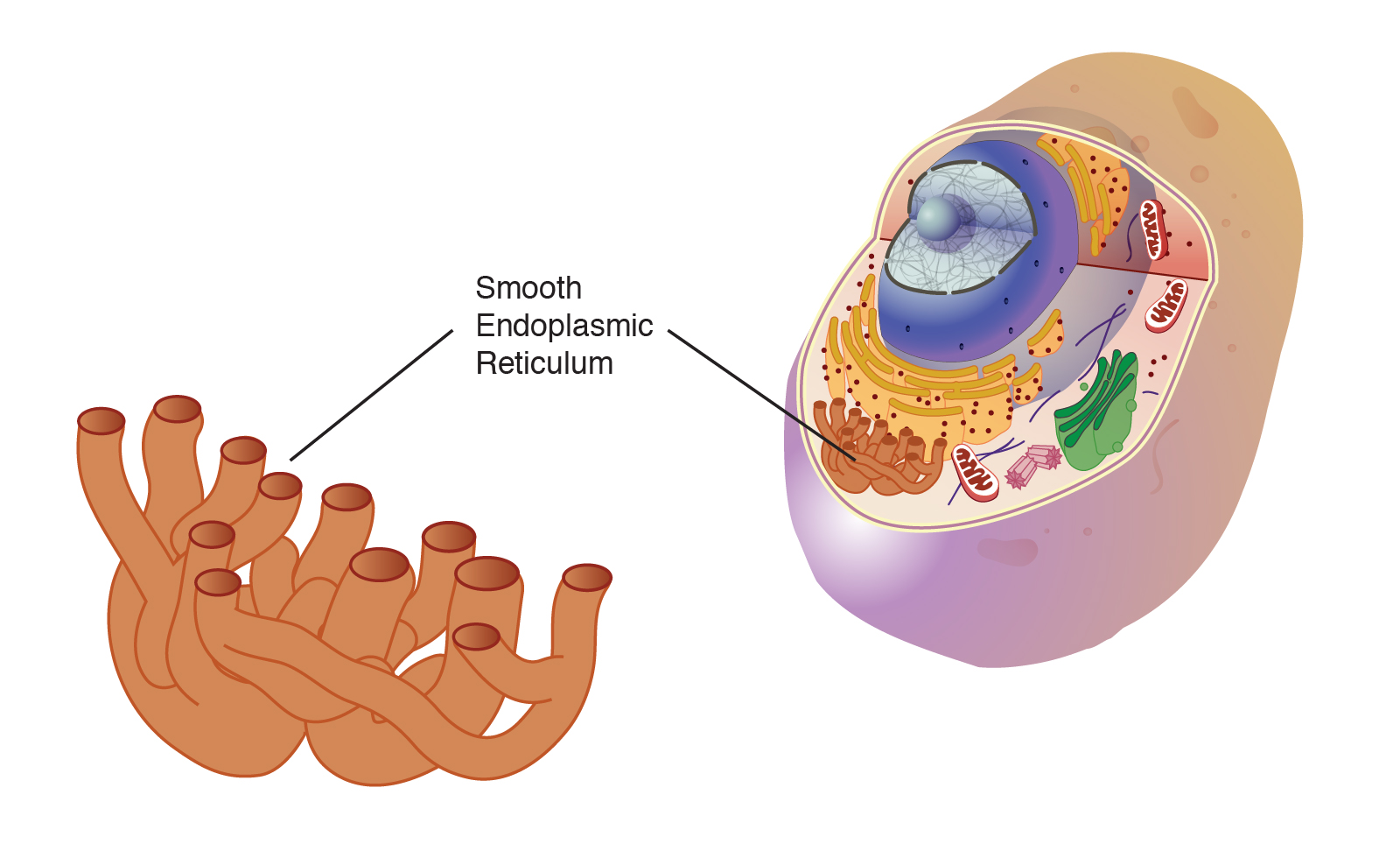
Smooth ER
Lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification processes.
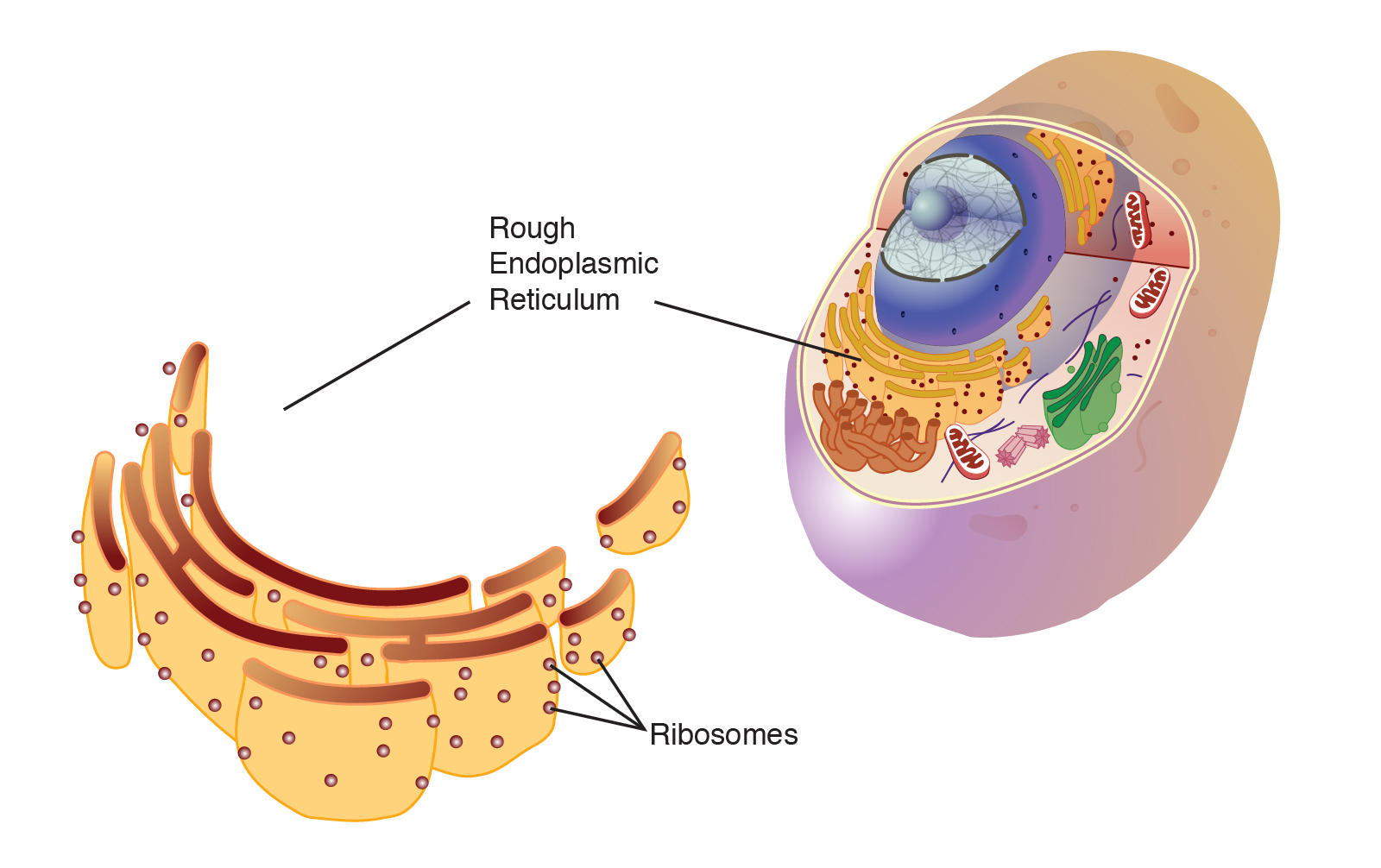
Rough ER
Has ribosomes on its surface and is responsible for protein synthesis and modification.
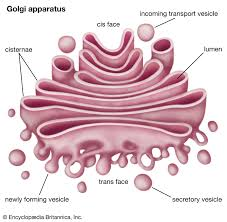
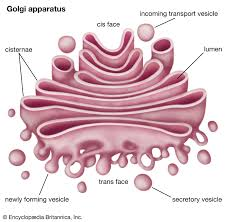
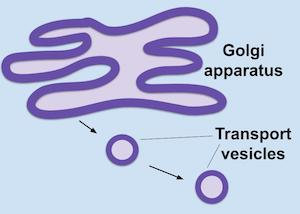
Golgi Apparatus
Stack of flattened sacs near the RER. Its membrane-enclosed sacs receive vesicles from the RER and modify, sort, and package proteins for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Lysosomes
membrane-enclosed vesicular organelles filled with digestive enzymes that catalyze reactions.
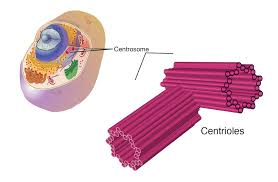
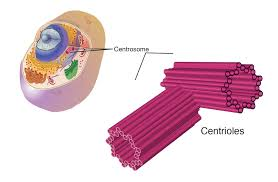
Centrioles
Paired organelles composed of microtubules that are centered in the cell, called the centrosome, appear to be microtubule-organizing centers and assembling/disassemble microtubules.
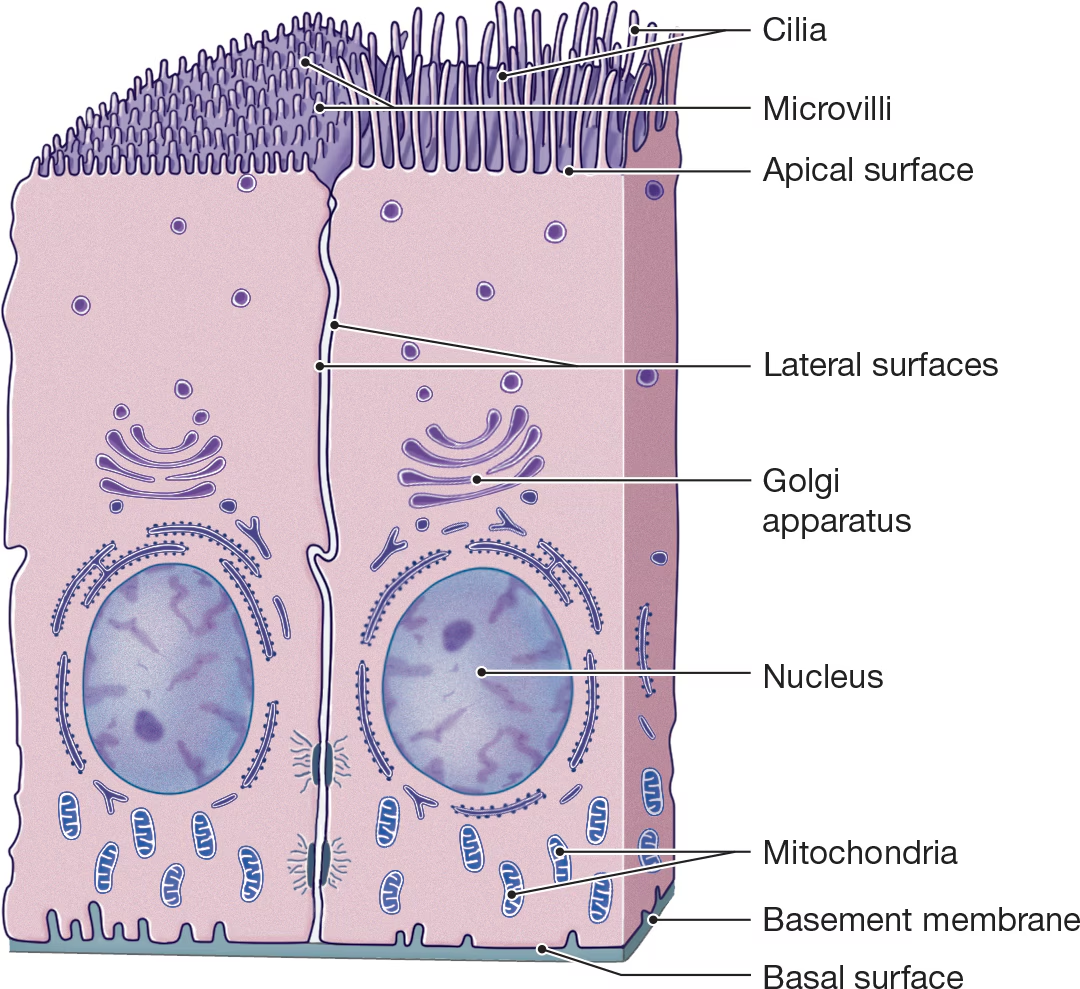
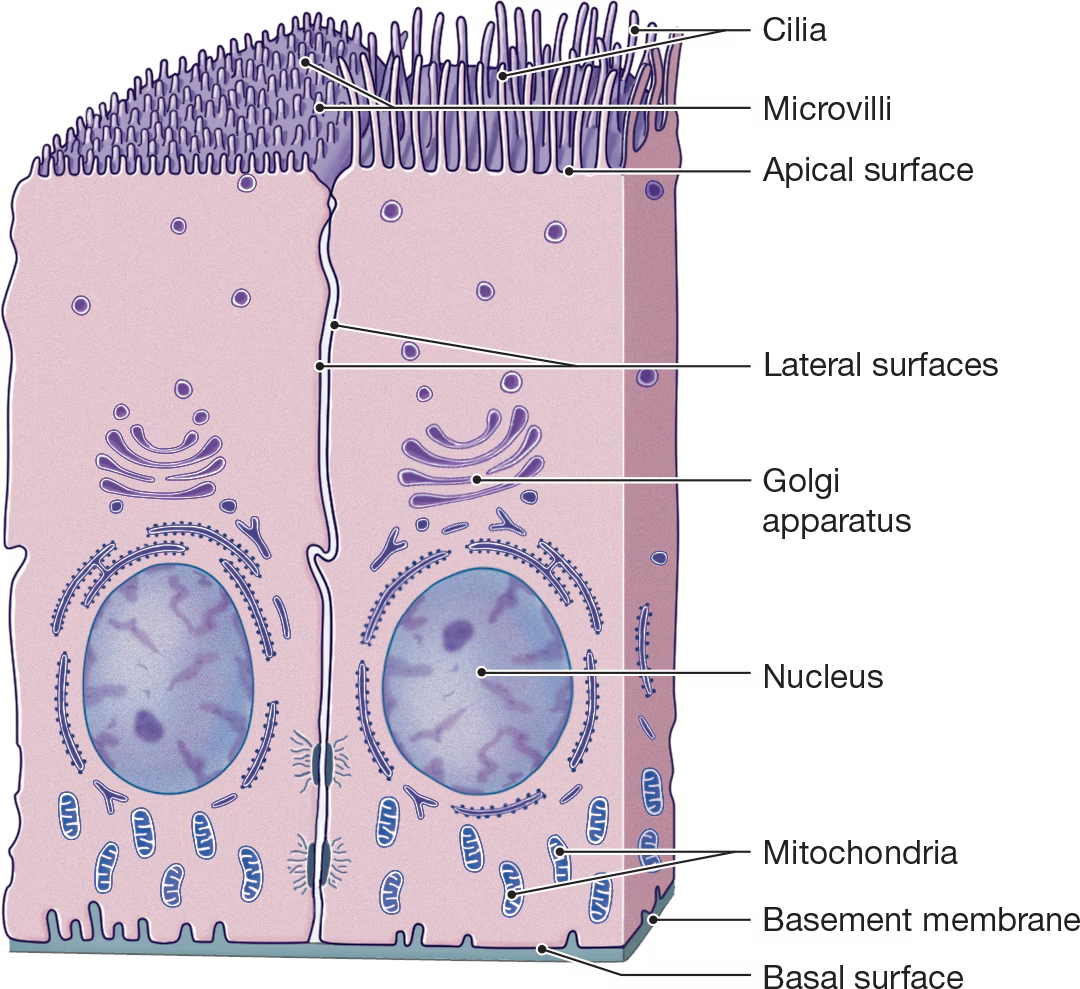
Cillia
Small hair-like extensions that beat rhythmically together and propel substances past the cell and are abundant in the respiratory tract. (Acts like tiny brooms)

Flagella
Single extensions that propel the cell itself (only found in sperm cells)

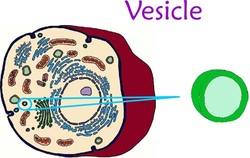
Vesicle
act as the cell's transport, storage, and waste disposal system, moving substances like proteins and lipids between organelles, out of the cell (secretion), or bringing things in (uptake)
Plasma Membrane
The outer boundary of the cell
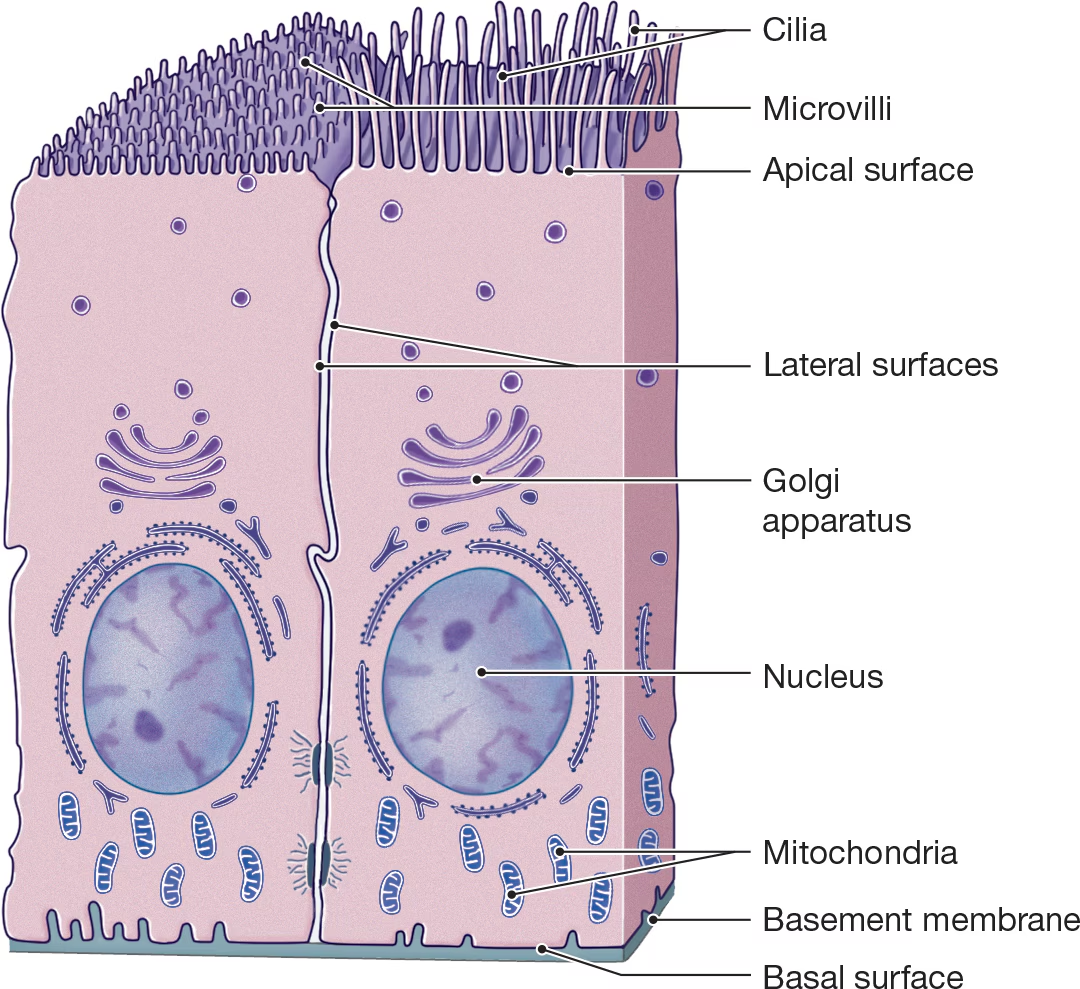
Microvilli
Folded into projections where rapid absorption is needed to increase its surface area.
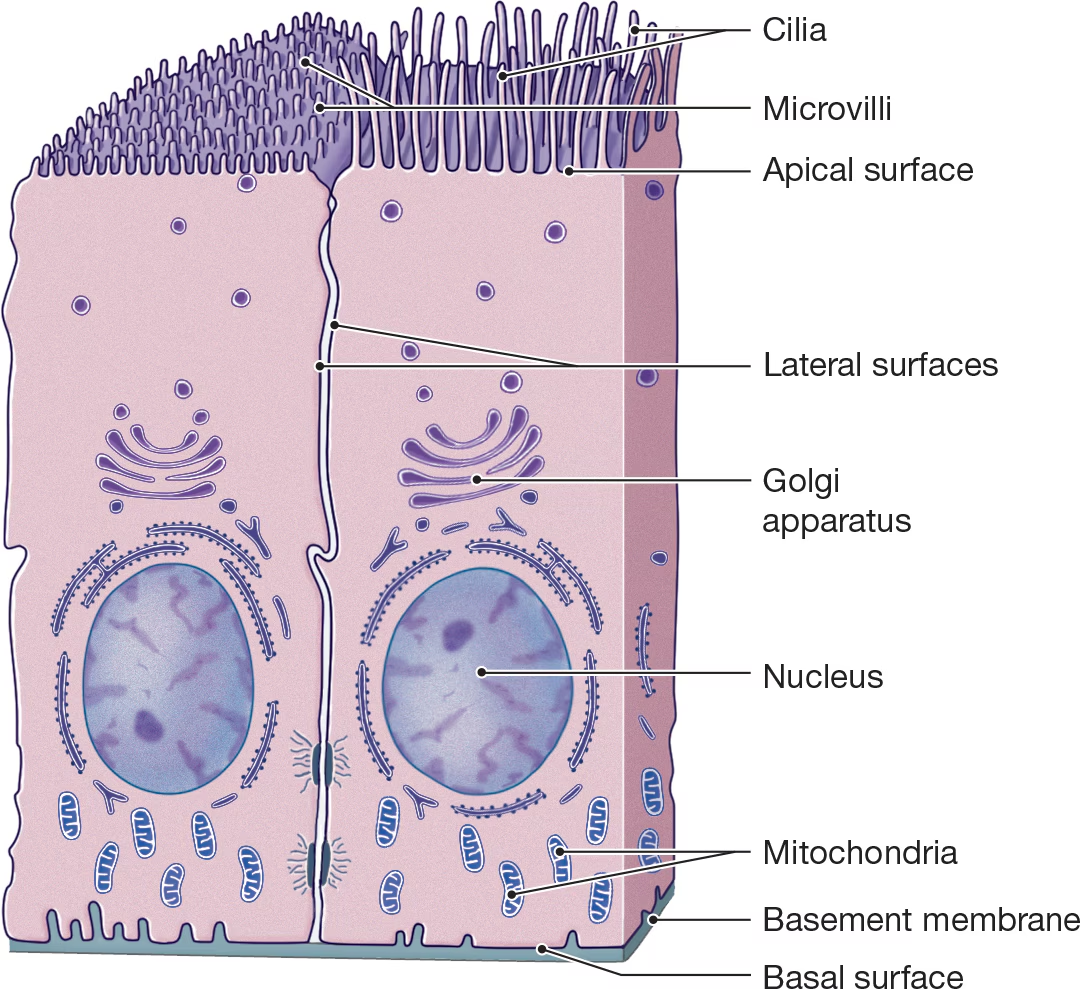
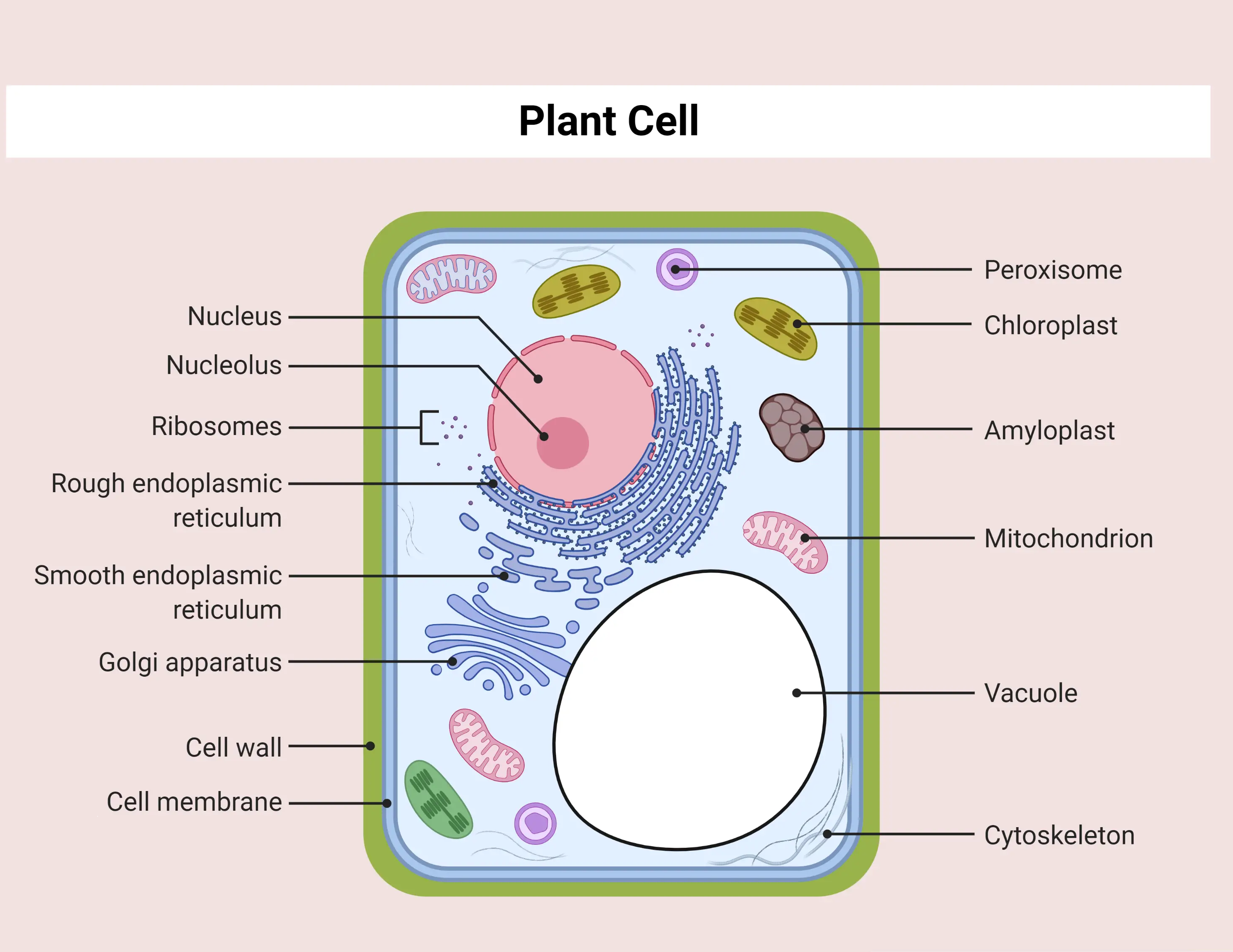
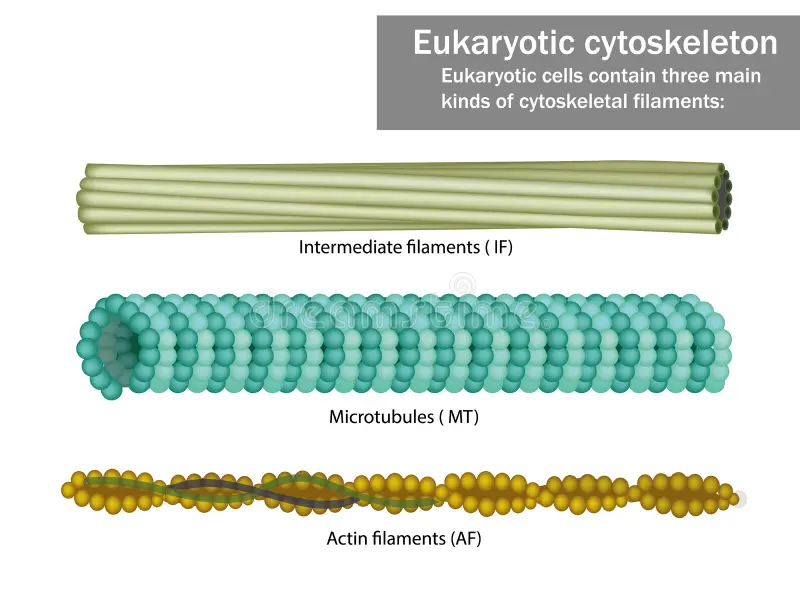
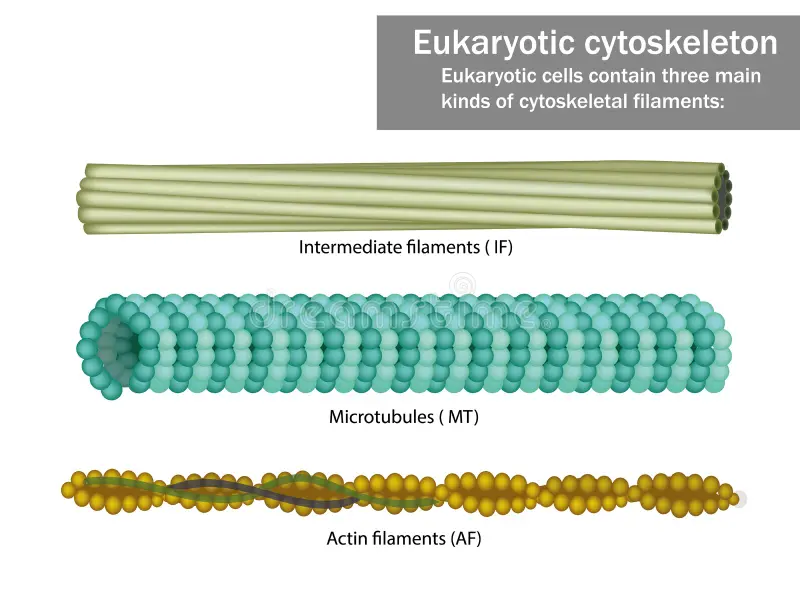
Cytoskeleton
A collection of protein filaments, including actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules.
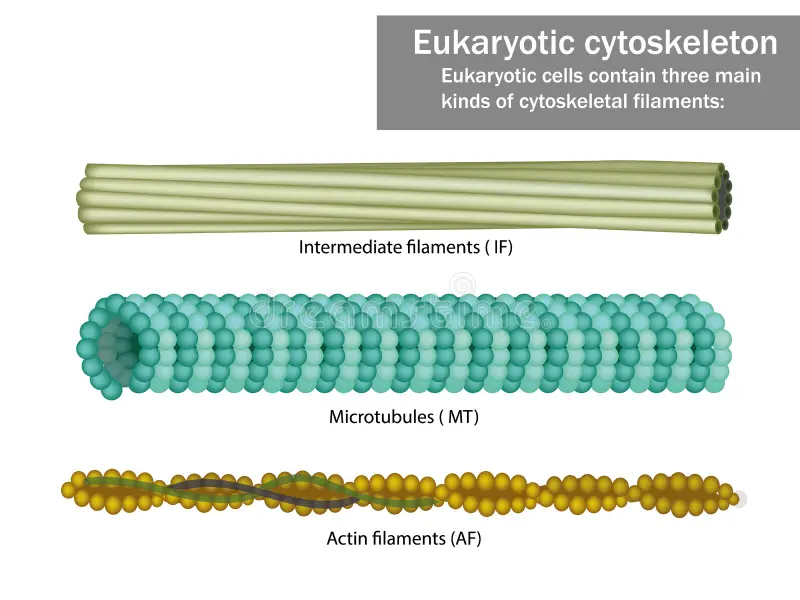
Actin Filaments
Small filaments are located along the plasma membrane and in the core of the microvilli.
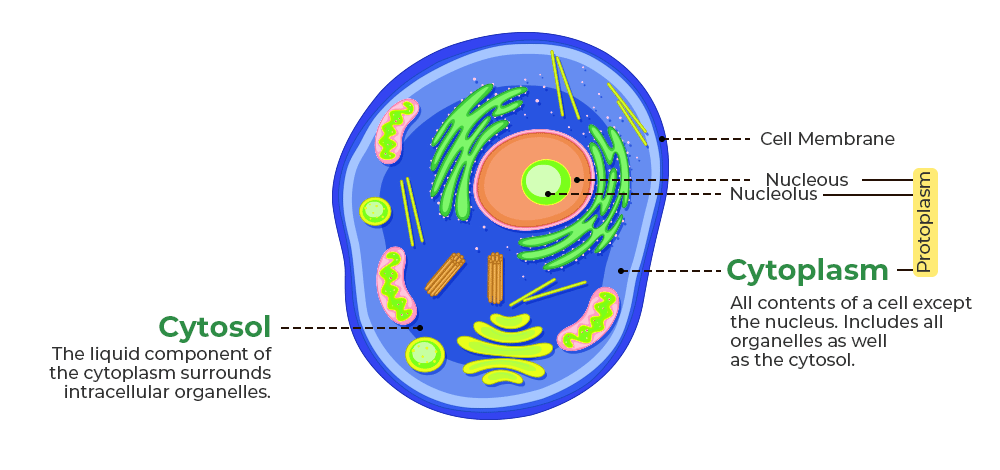
Cystol
The fluid portion of the cytoplasm contains water, solutes, RNA, enzymes, and other proteins.
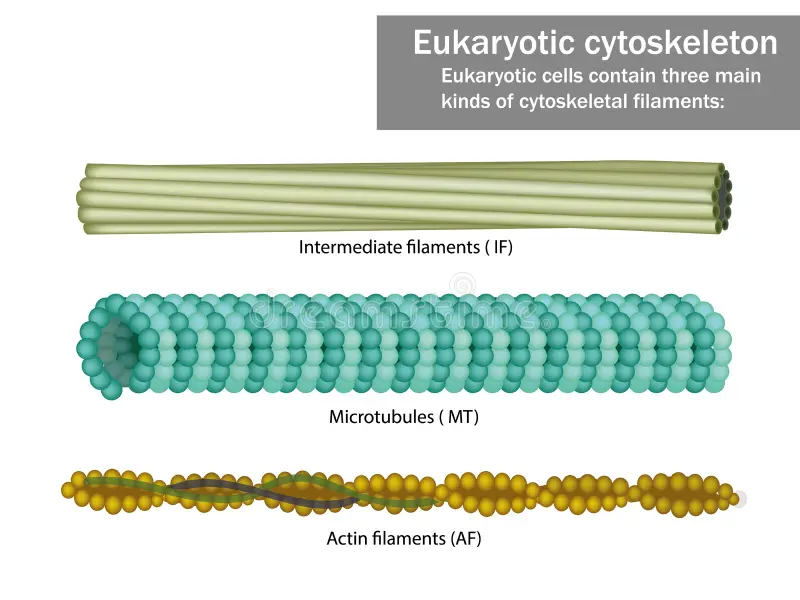
Intermediate Filaments
Rope-like structures that maintain the shape of organelles and the nucleus, and give the cell its strength.
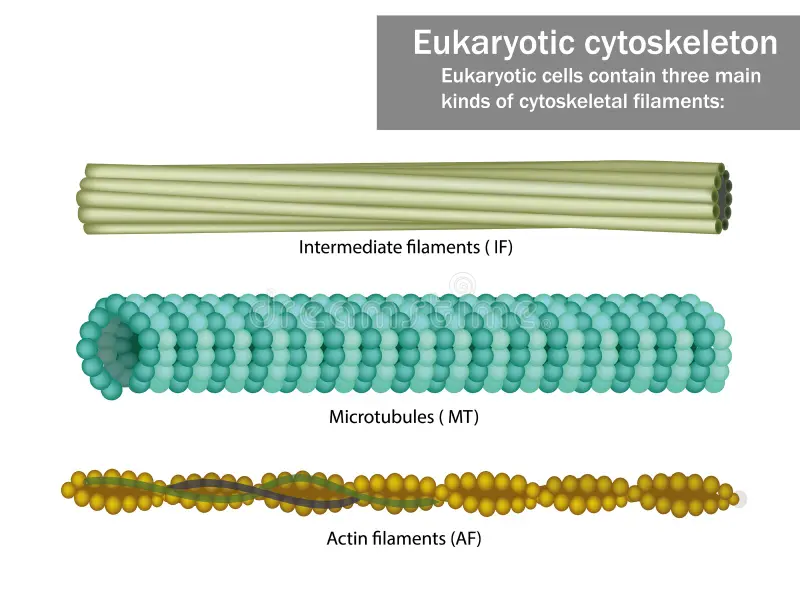
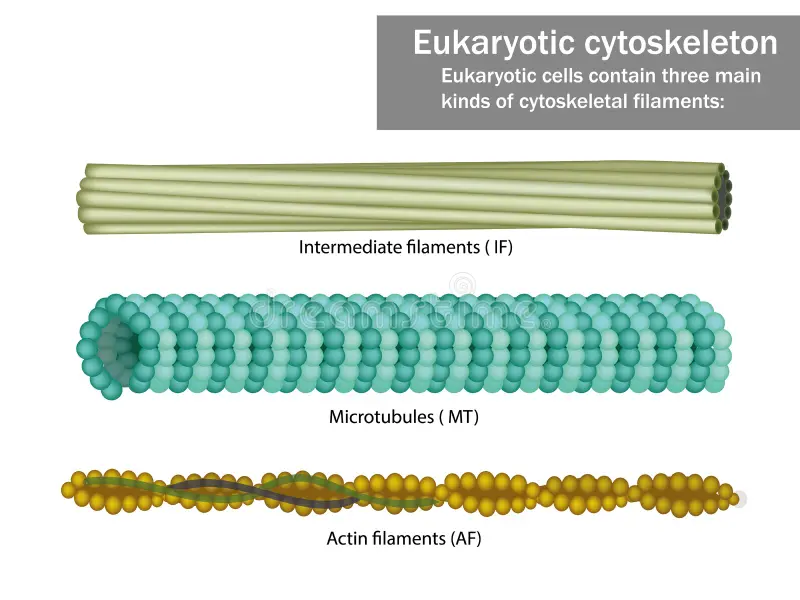
Microtubules
The largest filaments are hollow tubes that maintain the shape of the cell, hold organelles in place, move substances within the cell, and function in cell division. They also form cilia and flagella.
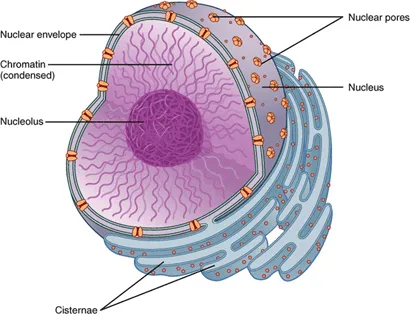
Chromatin
A ball-like mass of tightly coiled DNA and proteins
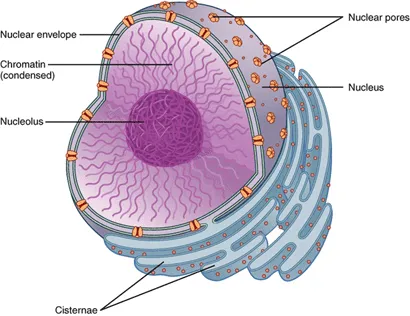
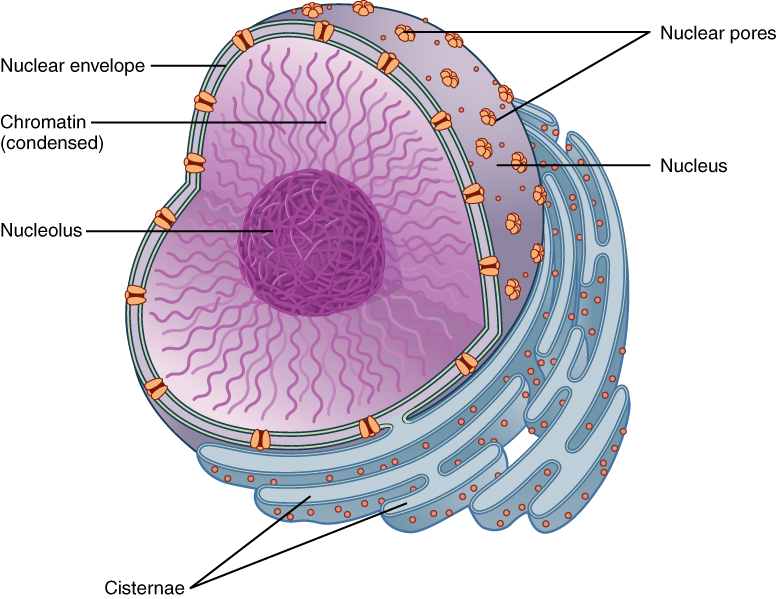
Nuclear pores
The holes in the nucleus
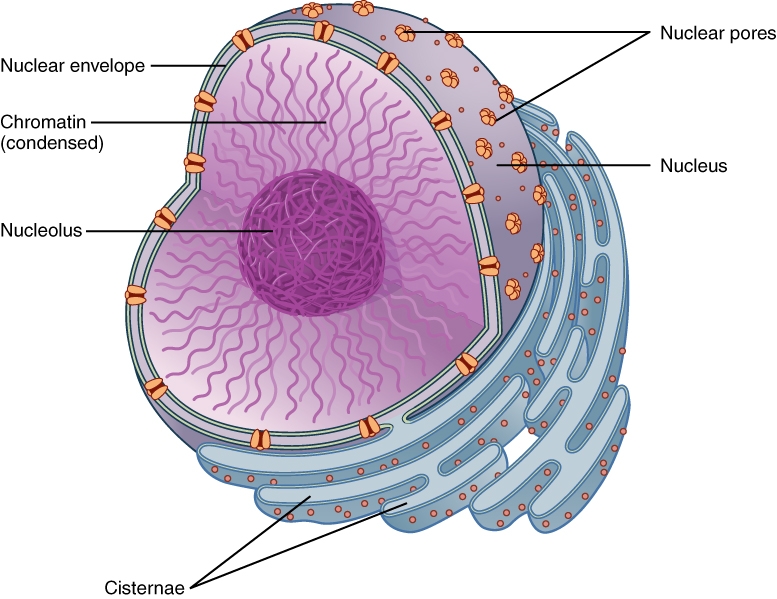
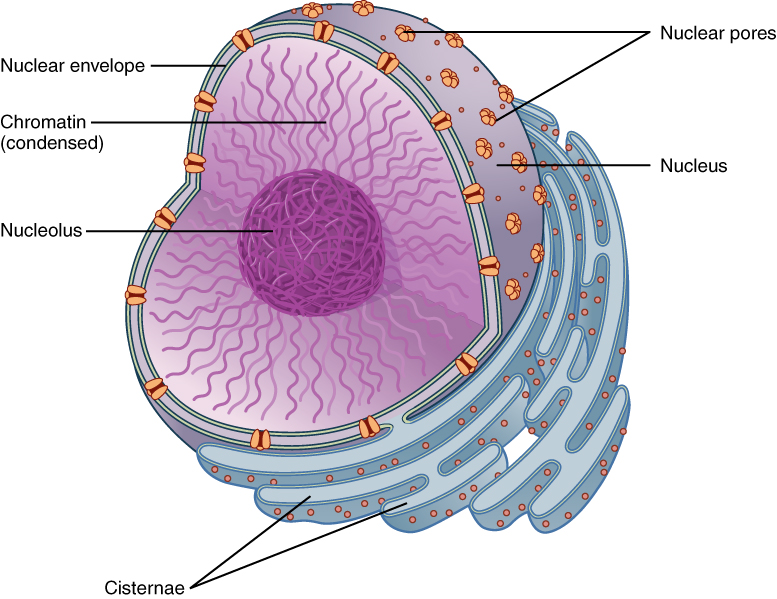
Nuclear Envelope
The double membrane that surrounds the nucleus
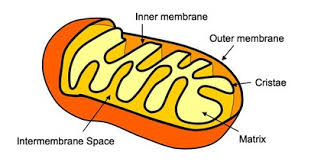
Matrix
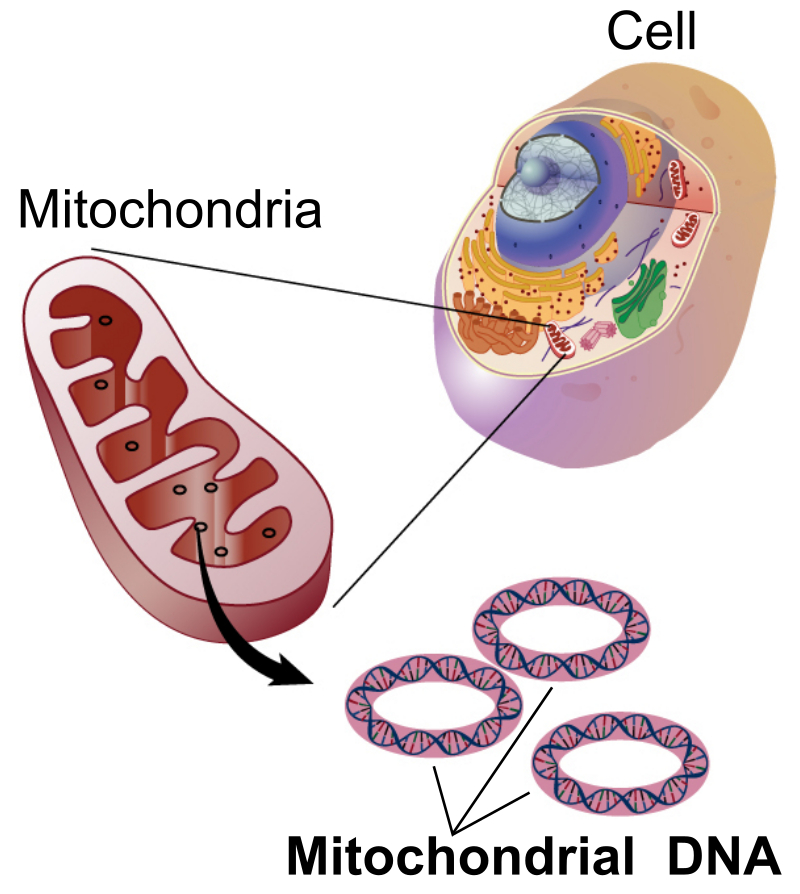
Mitochondrial DNA
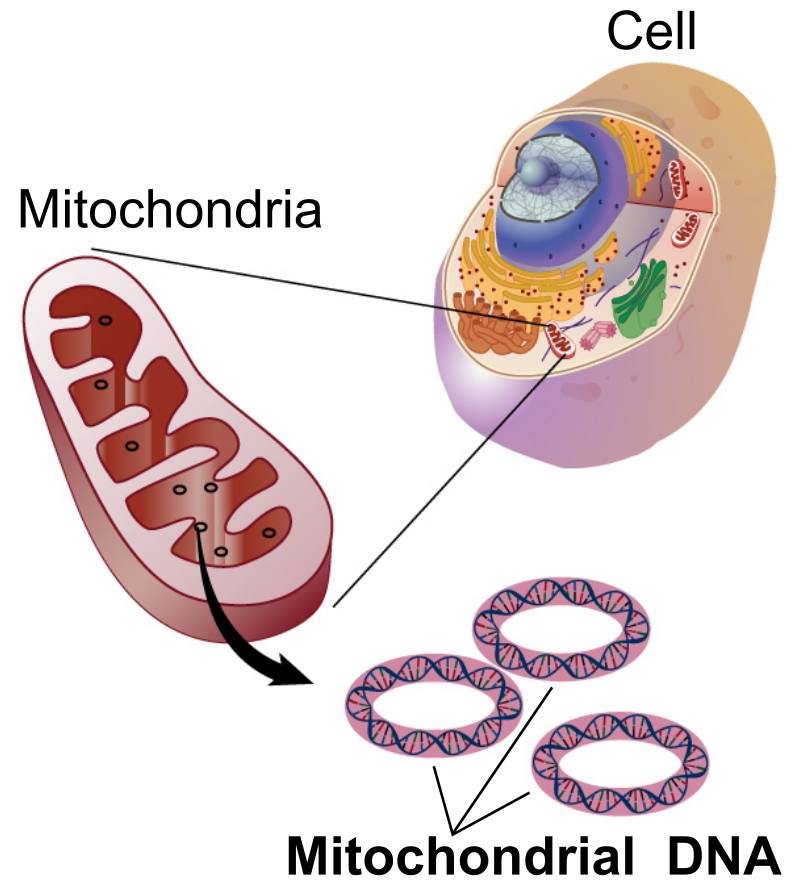
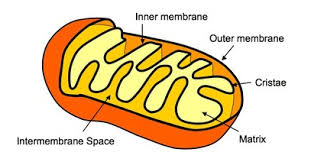
Inner membrane
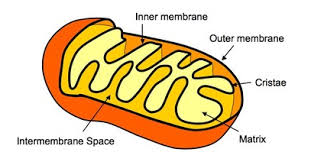
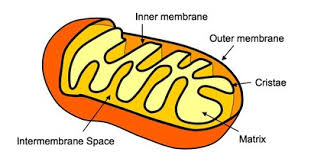
Inter-membrane Space
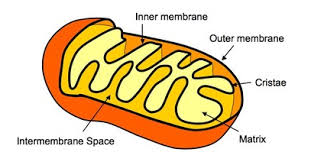
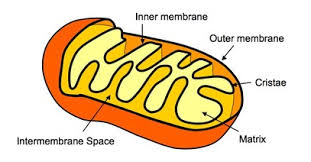
Outer mitochondrial membrane
Phagocytes
Cells that are immune to lysosomes that ingest and digest damaged cells, foreign cells like bacteria, and are infected with viruses that have a large number of lysosomes.
Name the five components of the plasma membrane
Phospholipid layer
Integral Proteins
Peripheral Proteins
Carbohydrates
Microvilli
Name the 5 components of the cytoskeleton
Actin Filaments
Intermediate Filaments
Microtubules
Cilia
Flagella
Name the 8 components of the cytoplasmic organelles
Ribosomes
Peroxisomes
Mitochondria
Smooth ER
Rough ER
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes
Centrioles
Name the 4 components of the nucleus
Nuclear Envelope
Nuclear Pores
Chromatin
Nucleolus
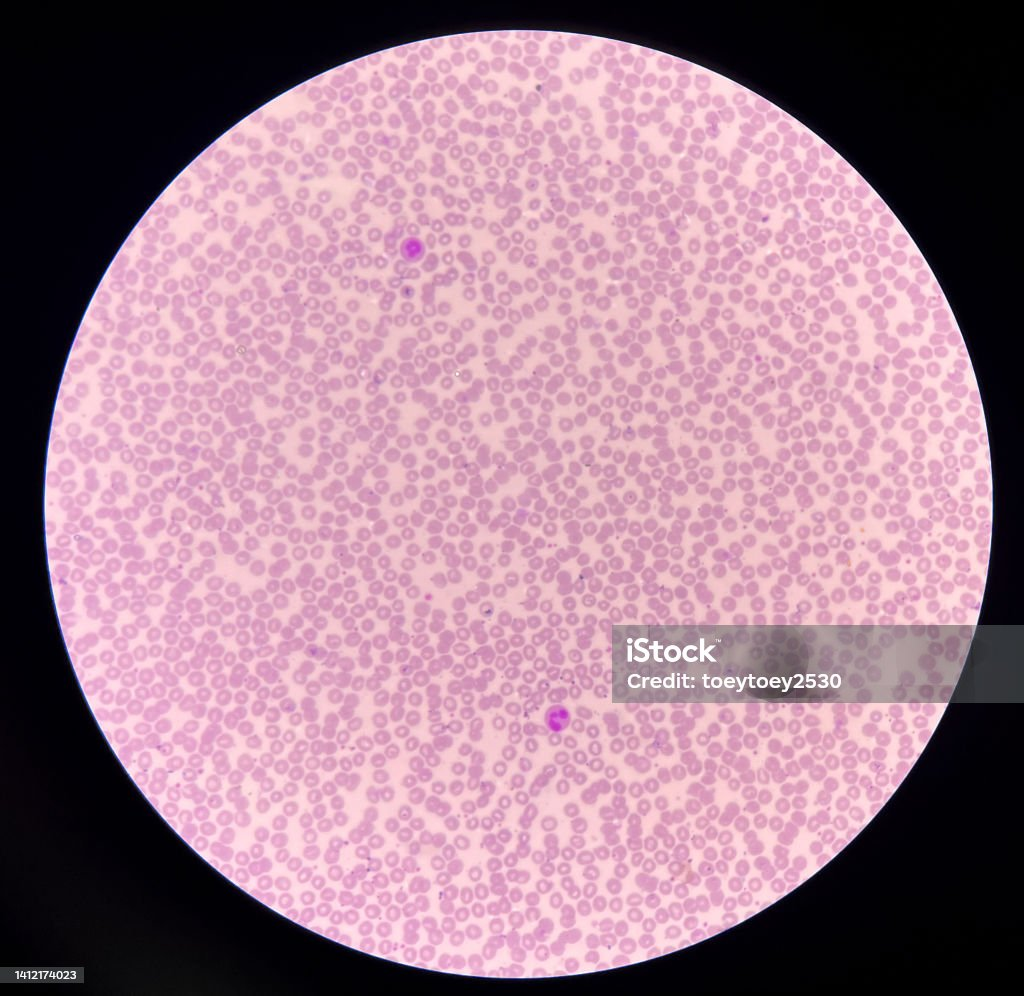
What magnification level are the Red Blood Cells?
4x
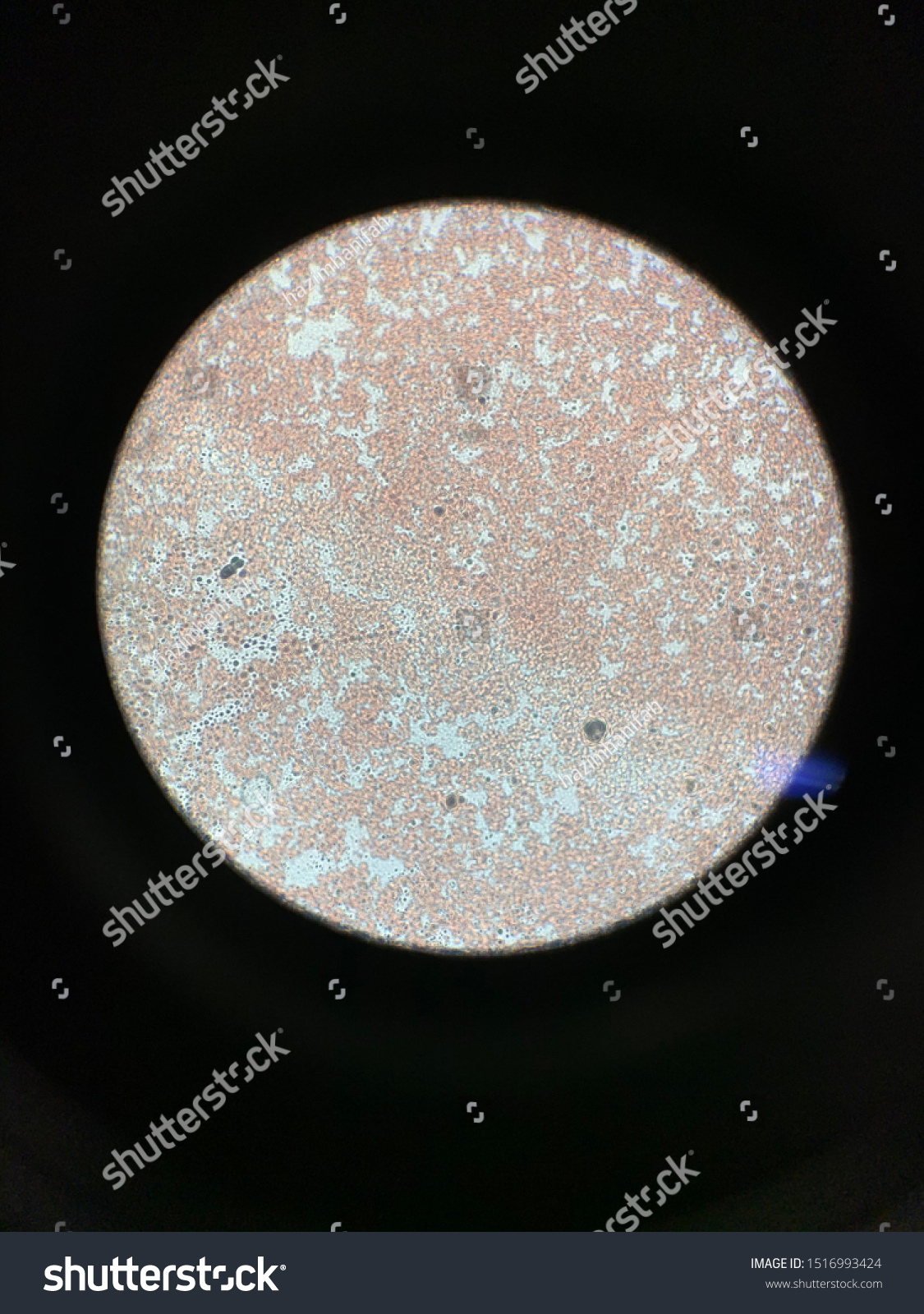
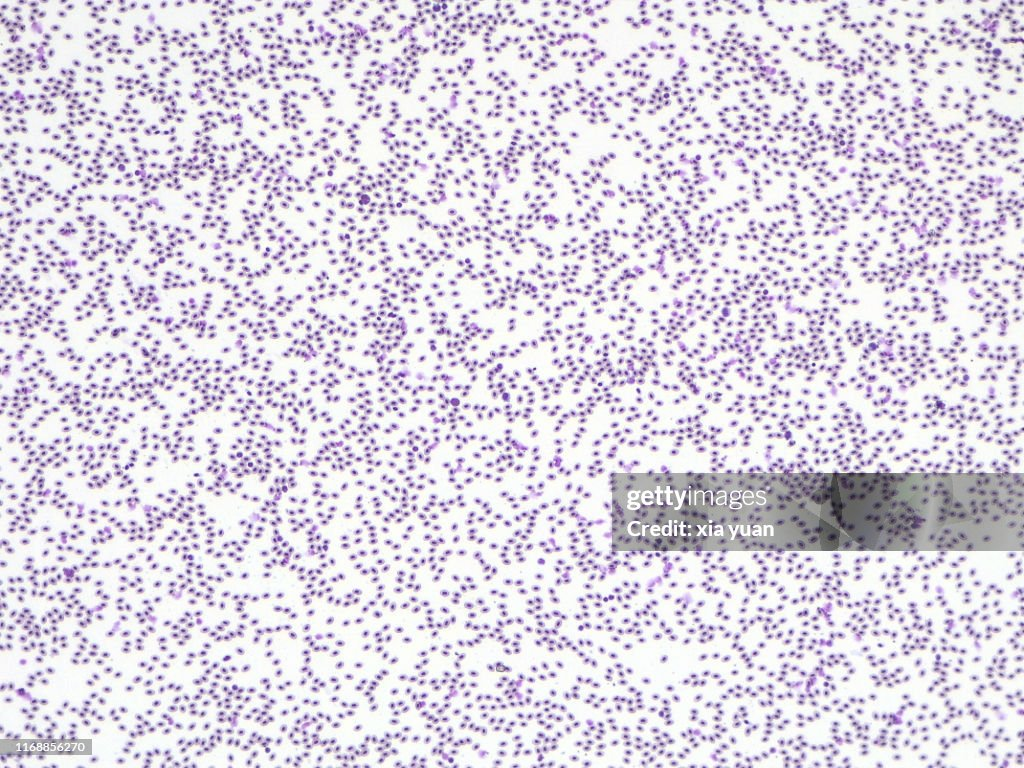
What magnification level are the Red Blood Cells?
10x
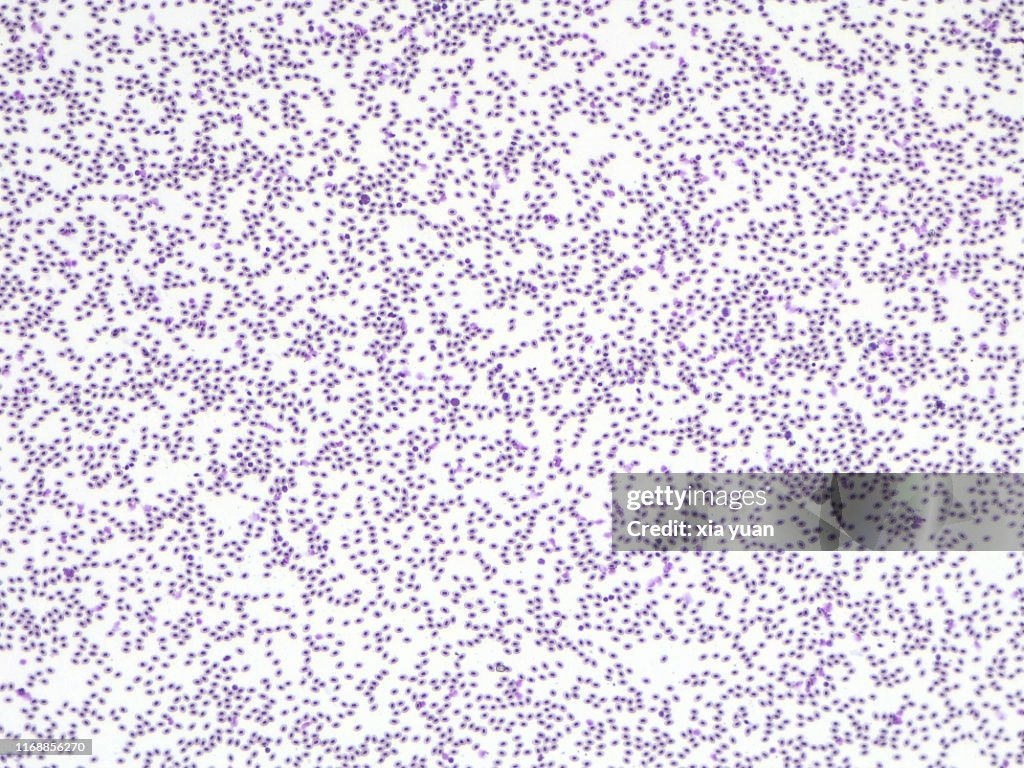
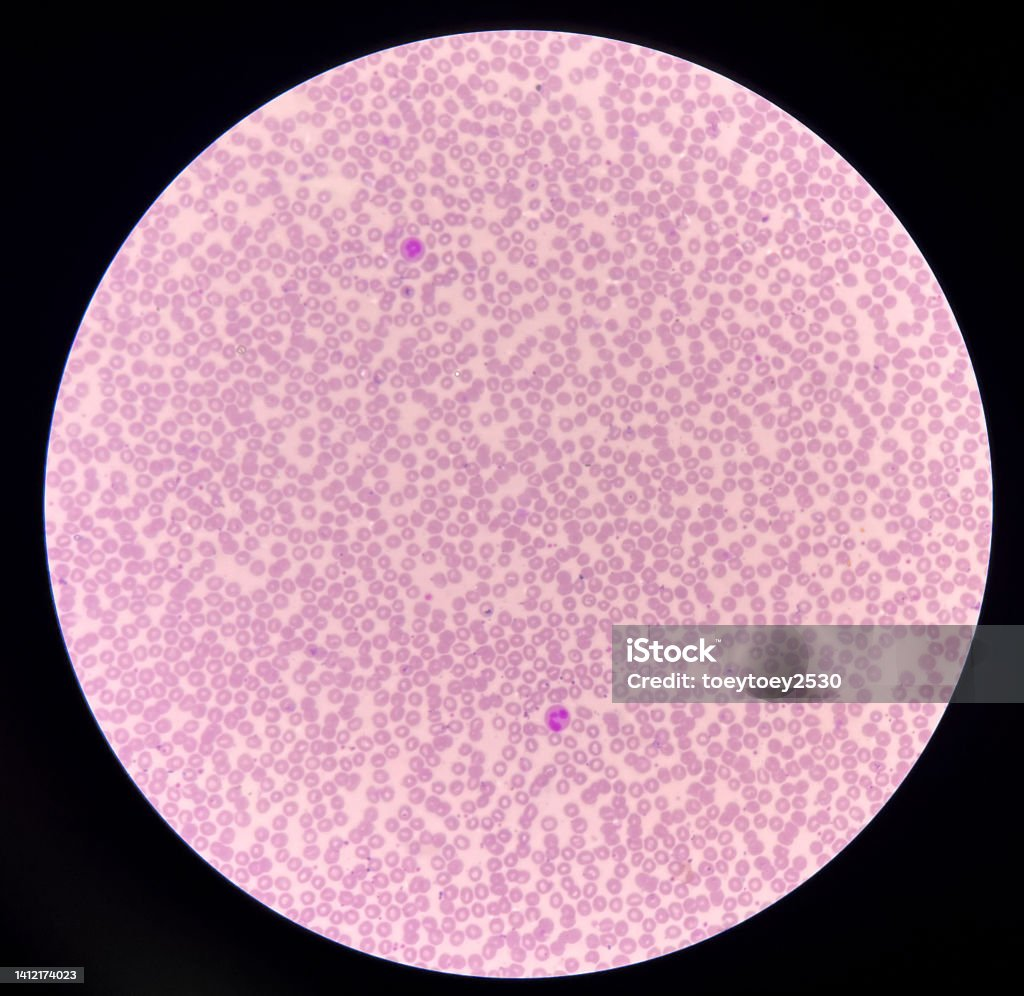
What magnification level are the Red Blood Cells?
40x
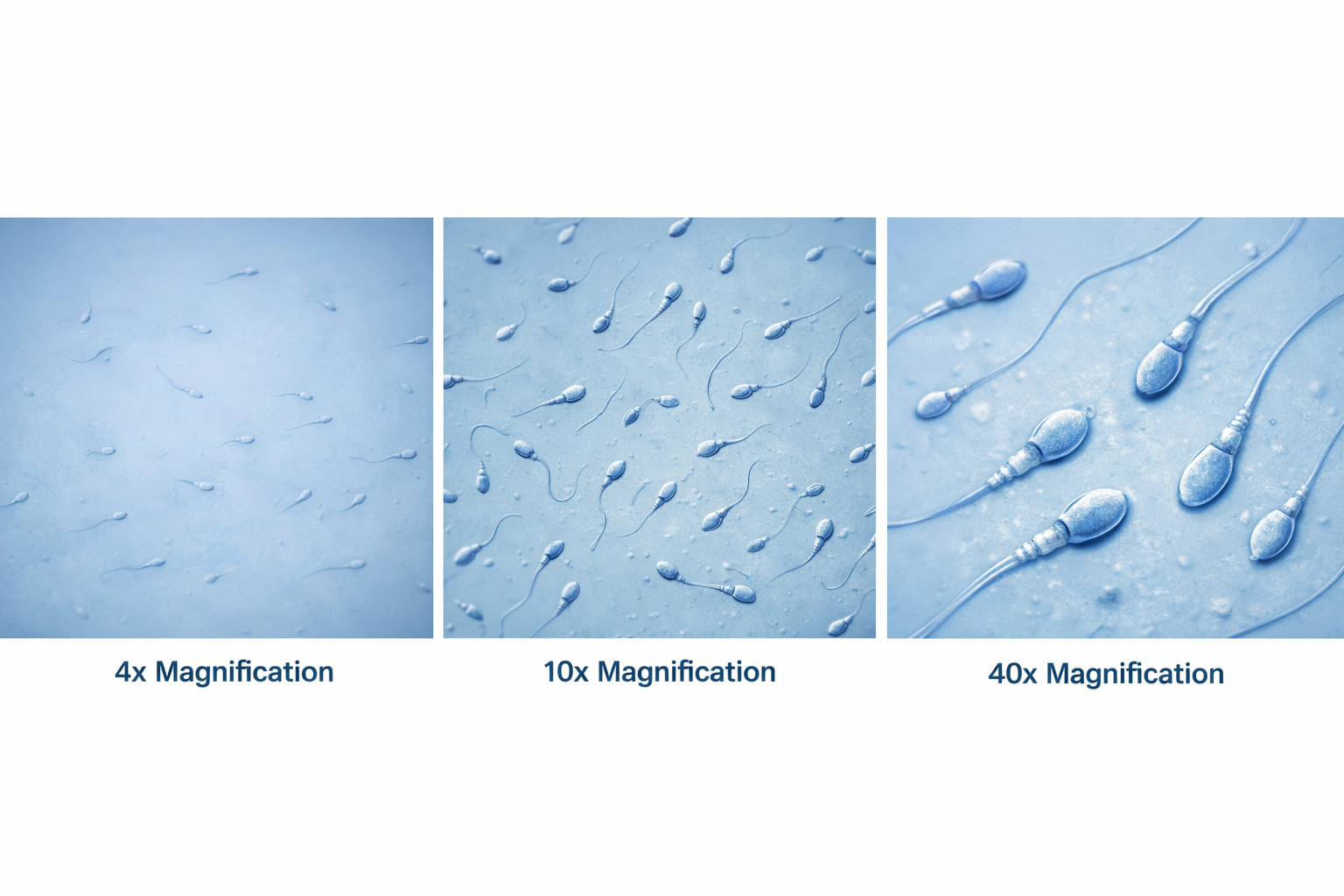
What magnification level are the Sperm Cells?
4x
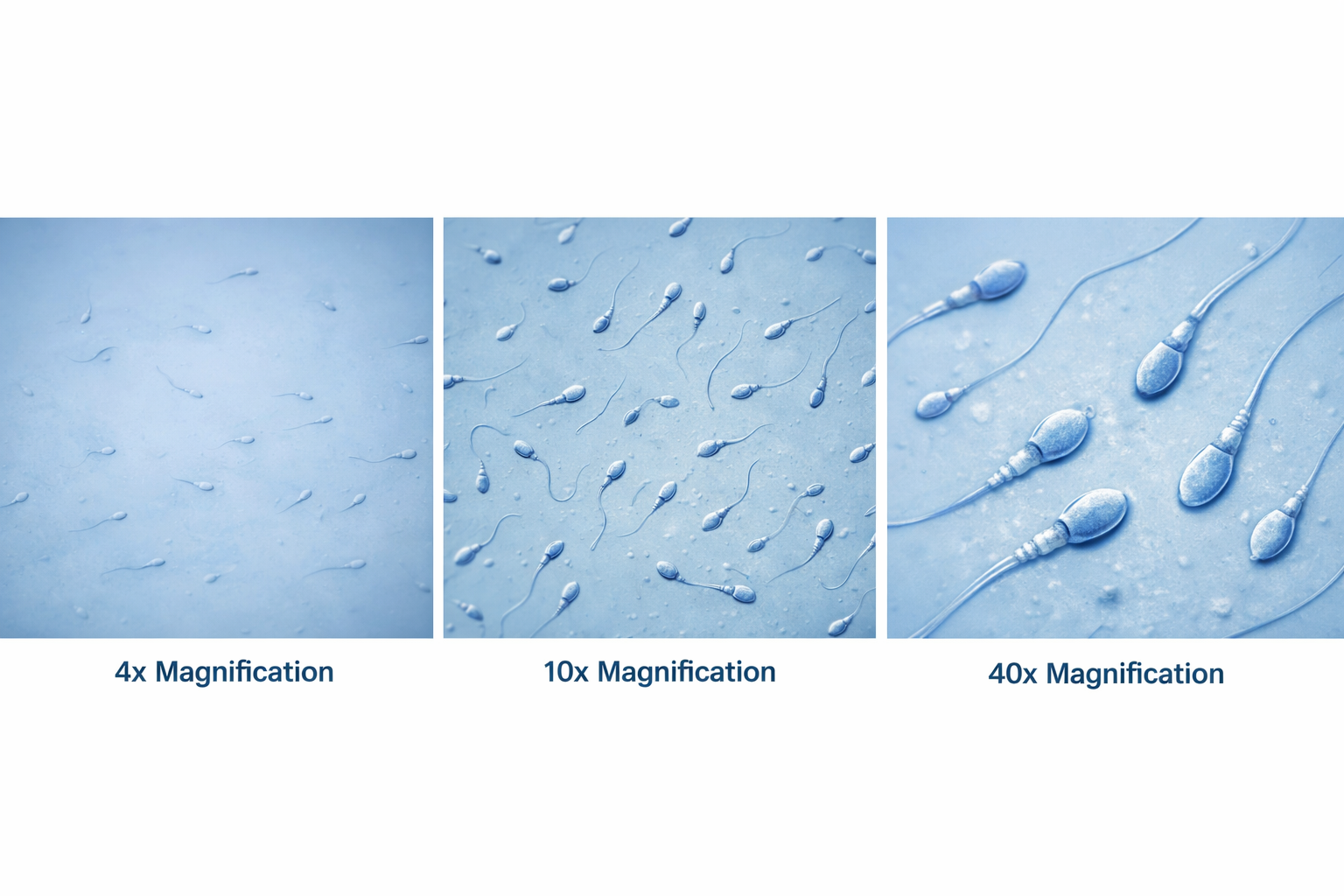
What magnification level are the Sperm Cells?
10x
What magnification level are the Sperm Cells?
40x
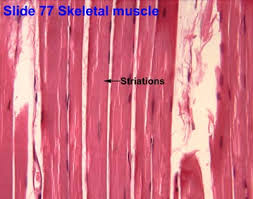
What magnification level are the Skeletal Muscle Cells?
4x

What magnification level are the Skeletal Muscles?
10x

What magnification level are the Skeletal Muscle Cells?
40x
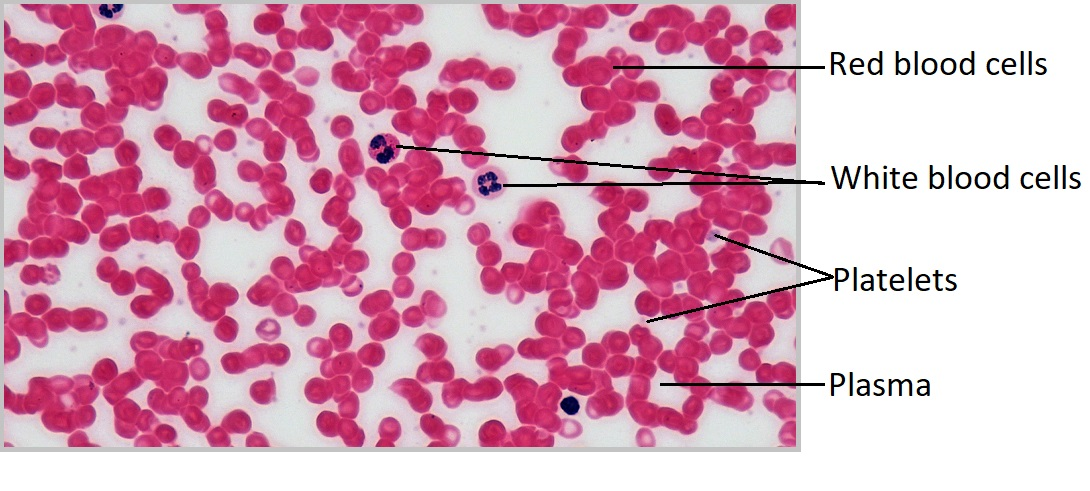
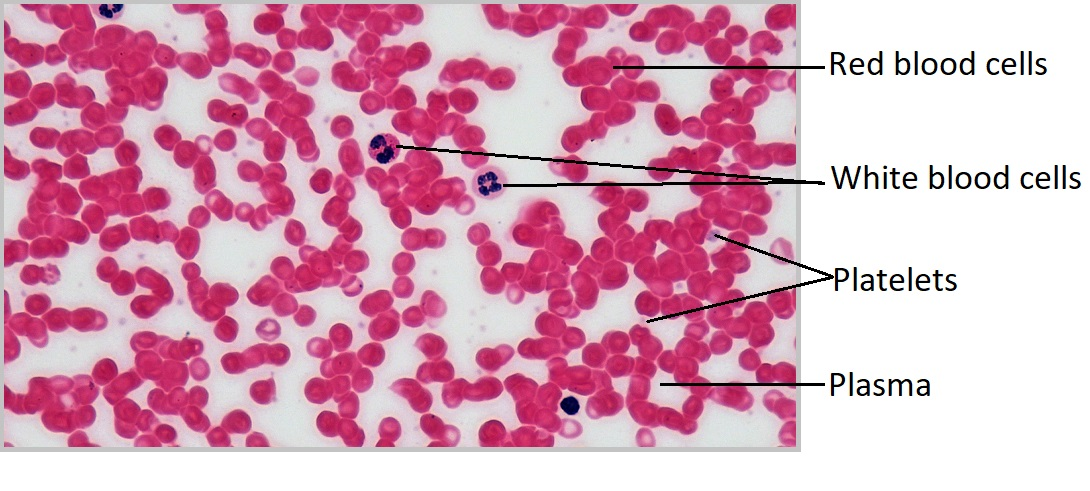
Where are the platelets?
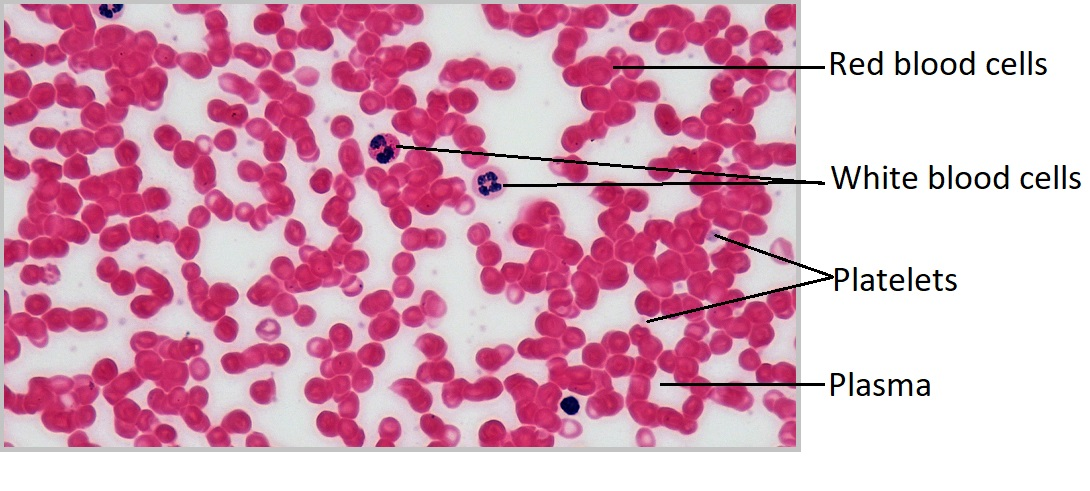
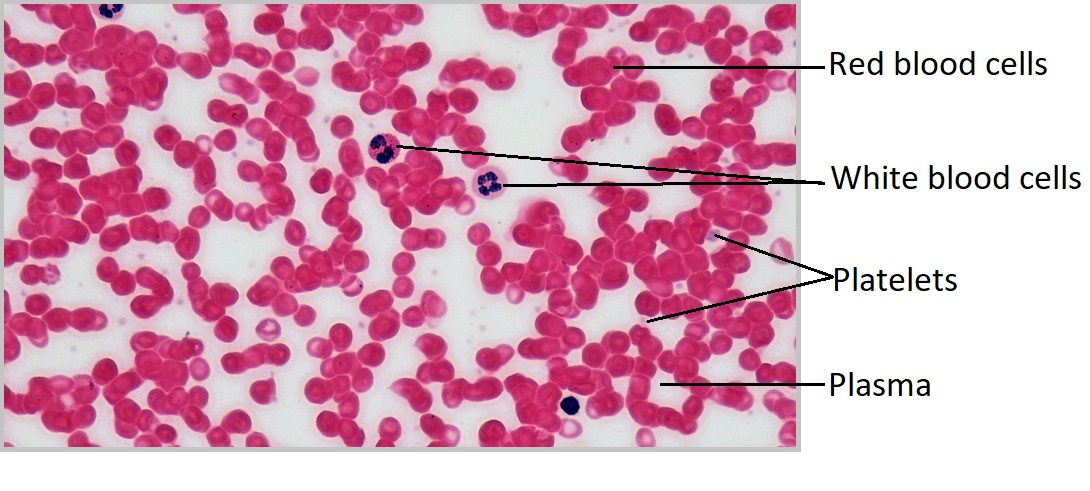
Where are the Leukocytes (white blood cells)?
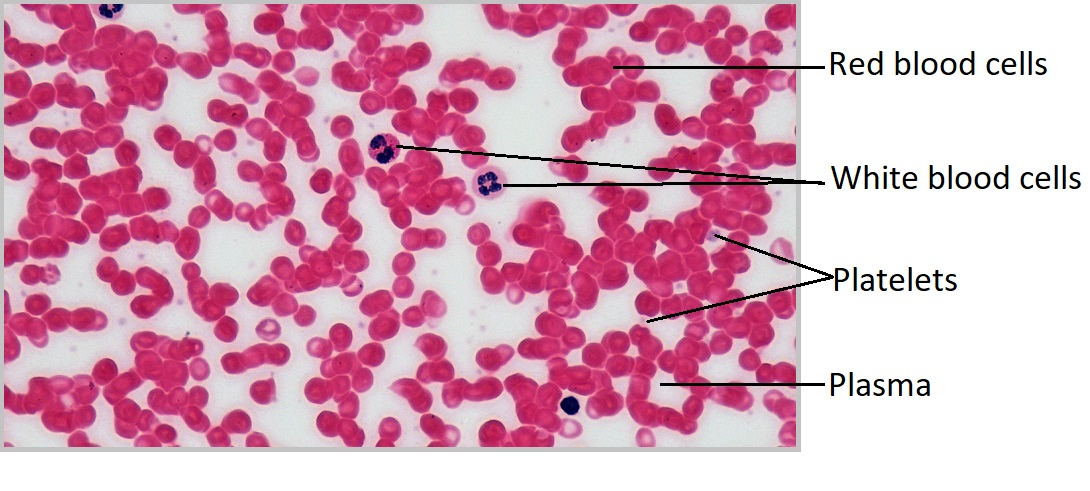
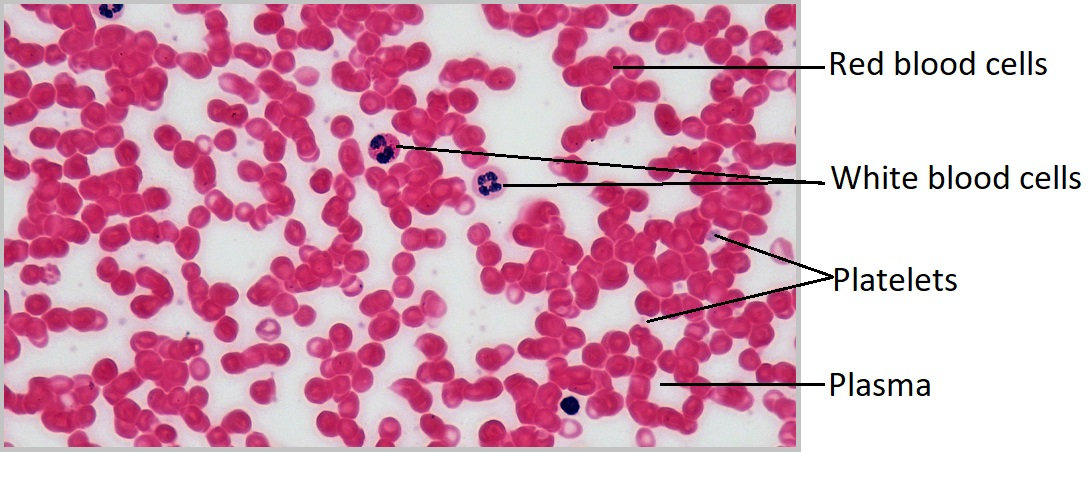
Where are the Erythrocytes (red blood cells)?
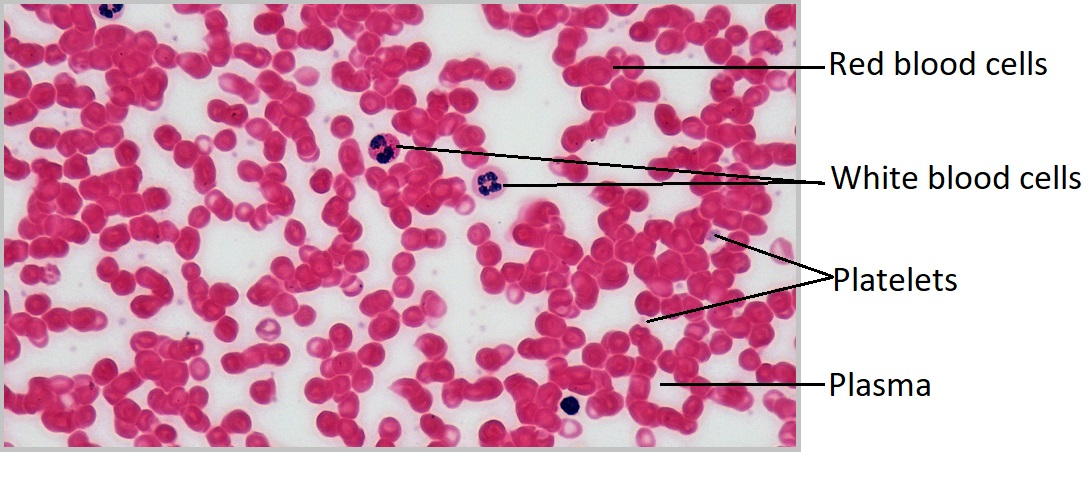
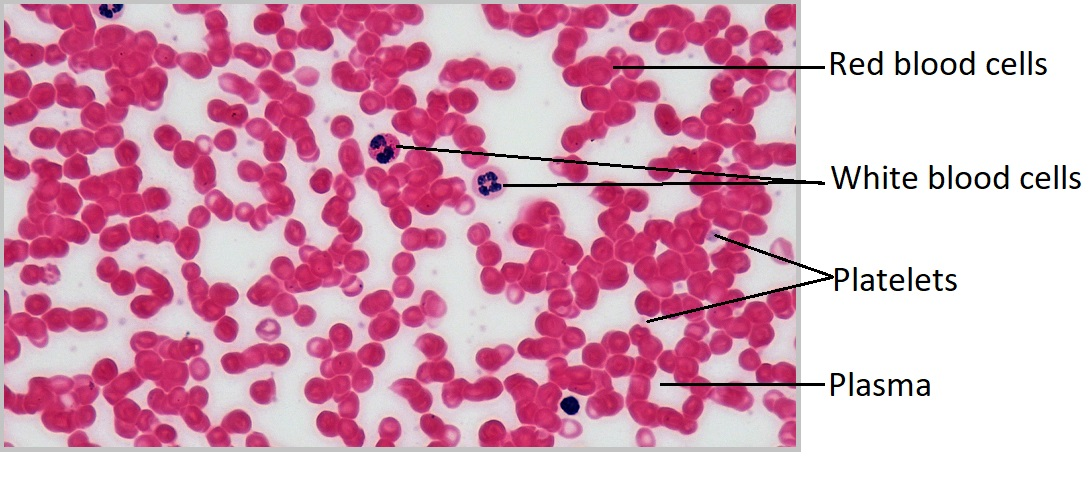
Where is the plasma (liquid extracellular matrix) in the red blood cell?
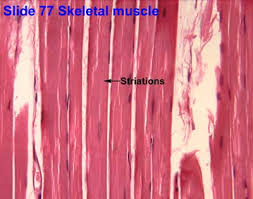
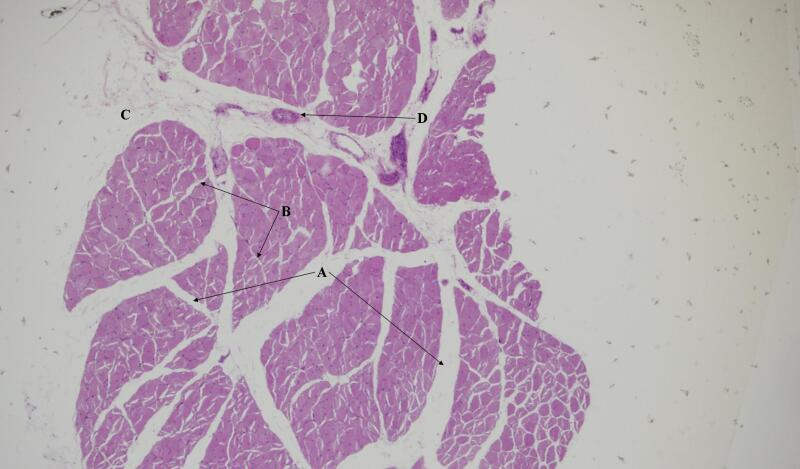
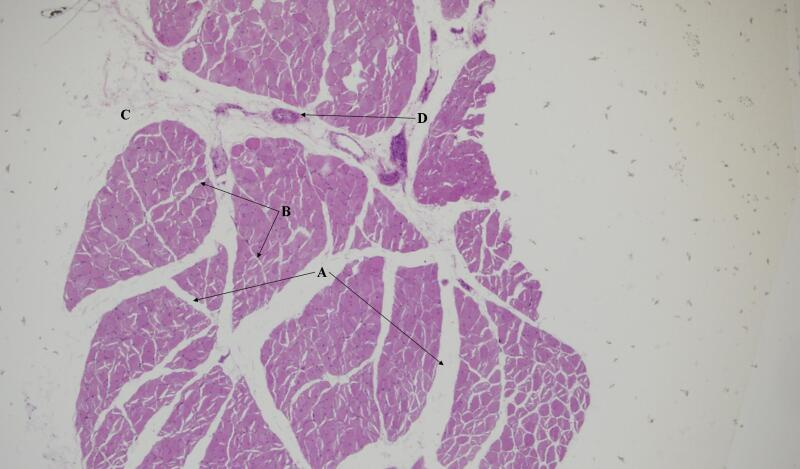
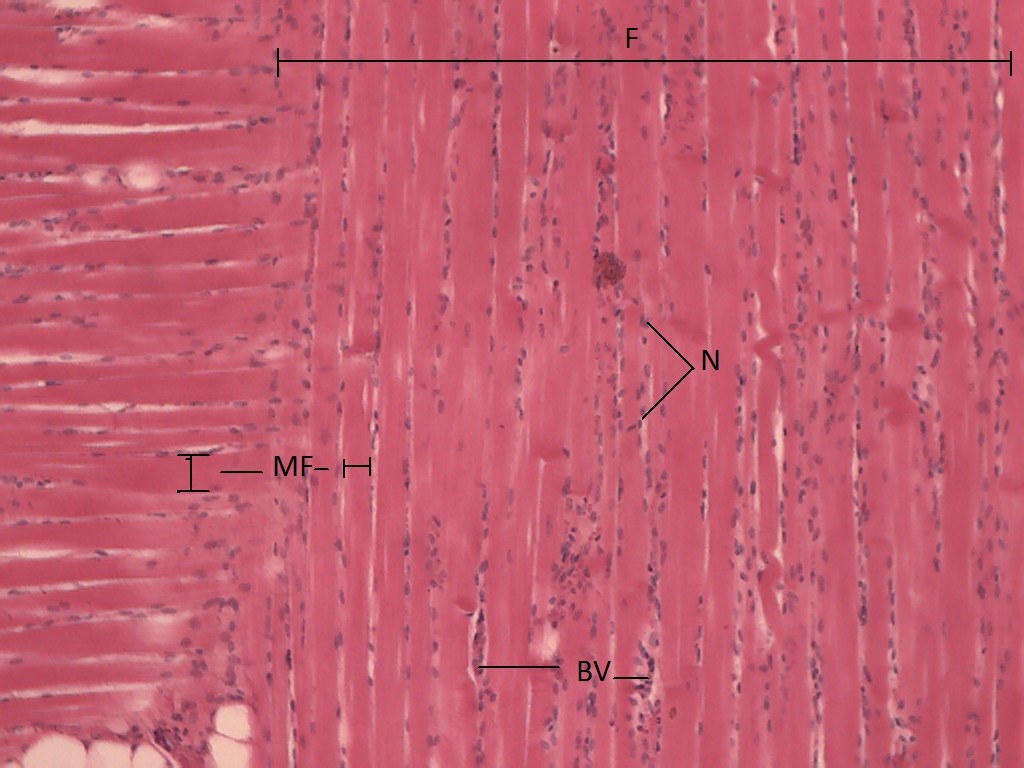
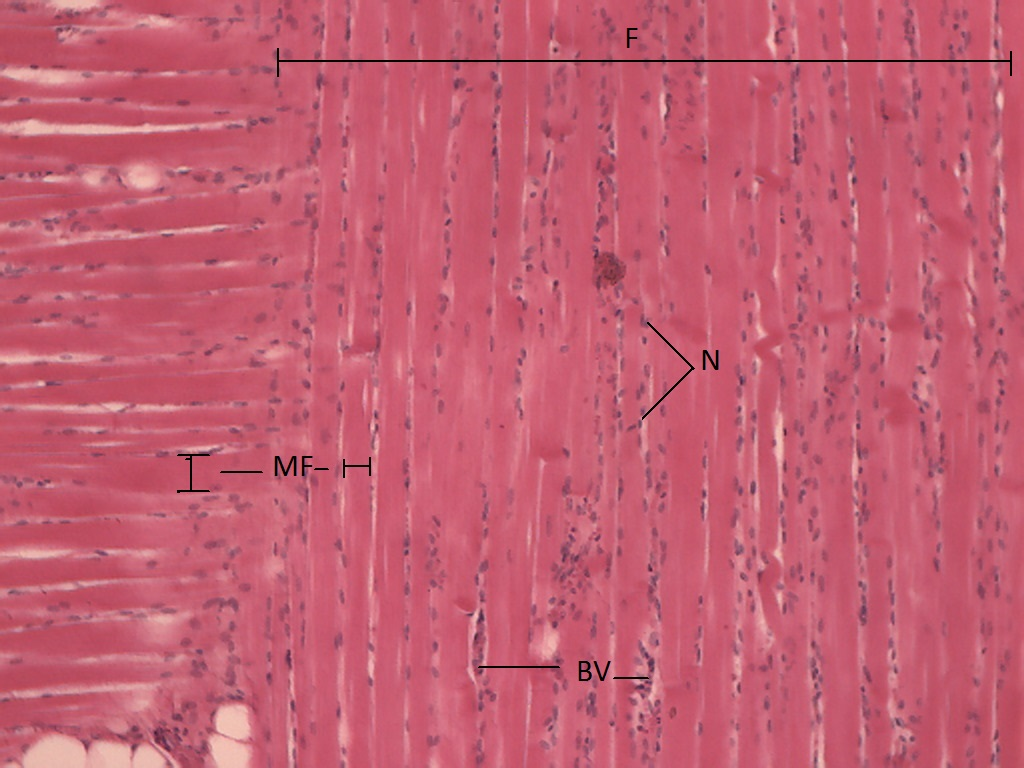
Where are the striations in the skeletal tissue?
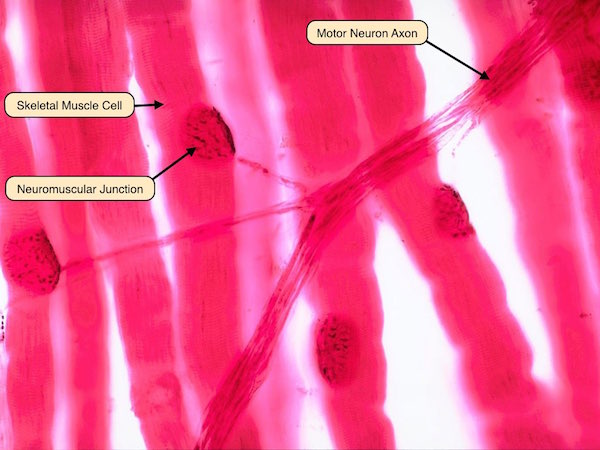
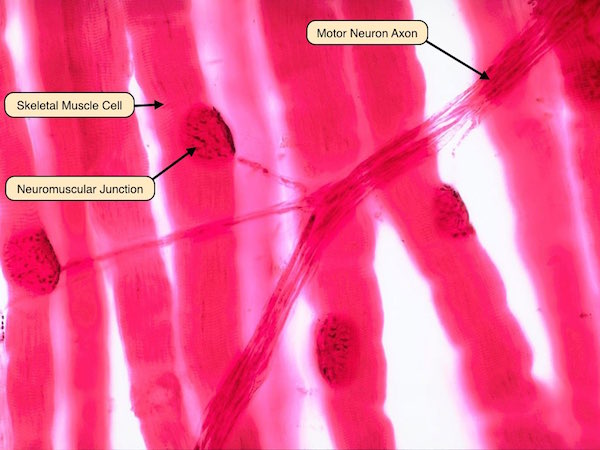
Where are the skeletal muscles?
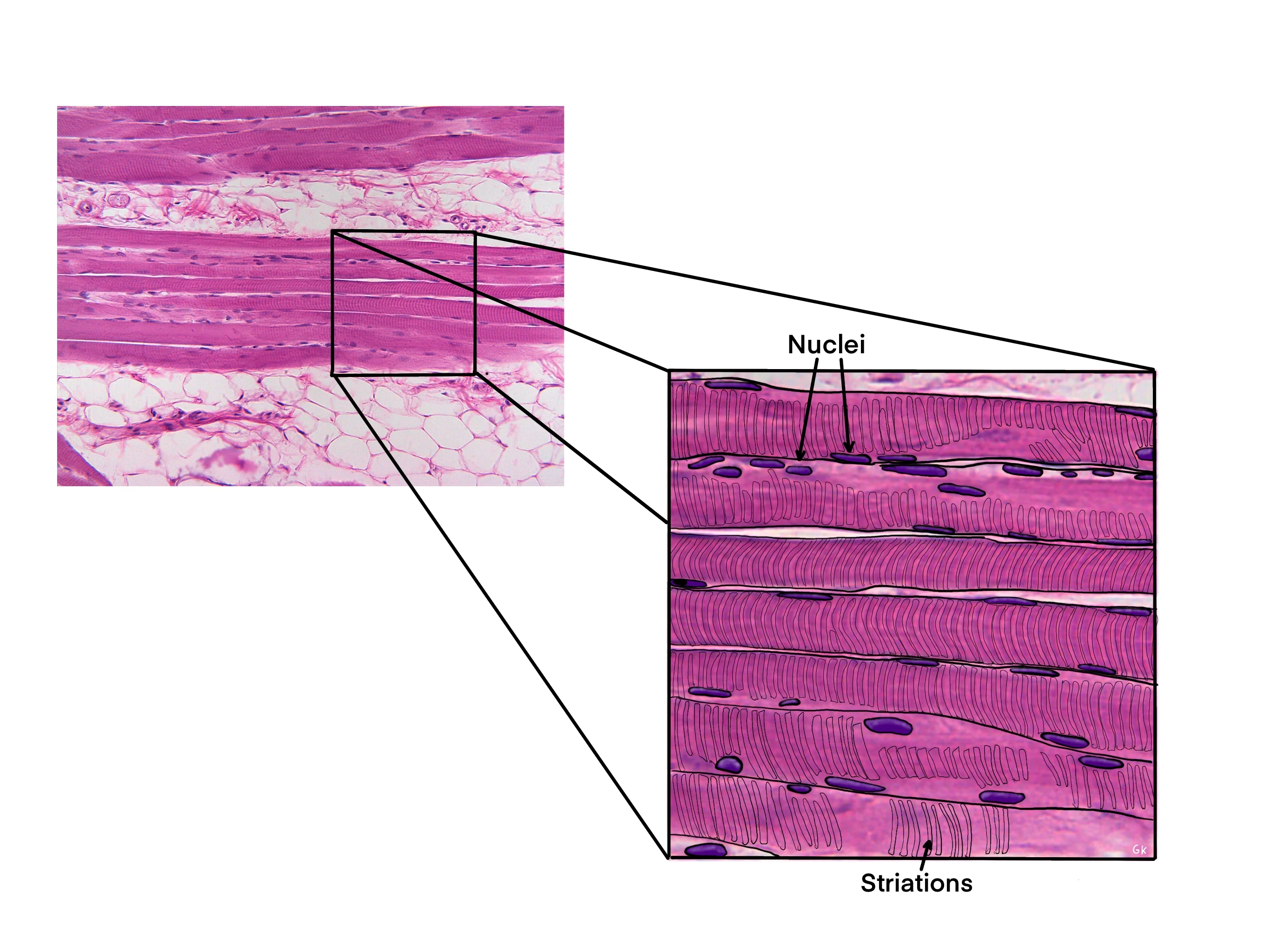
Where are nuclei in the skeletal muscle cell?
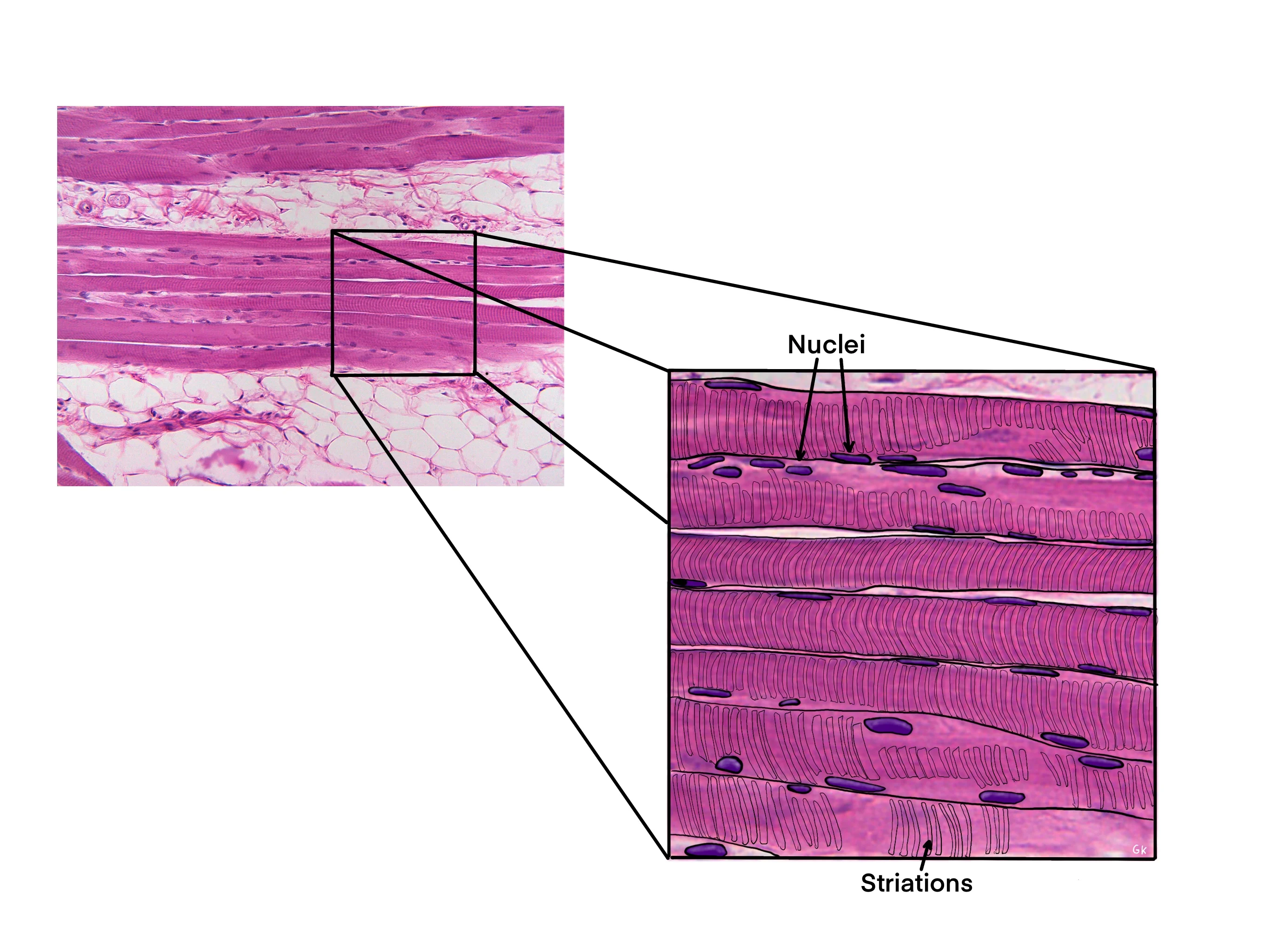
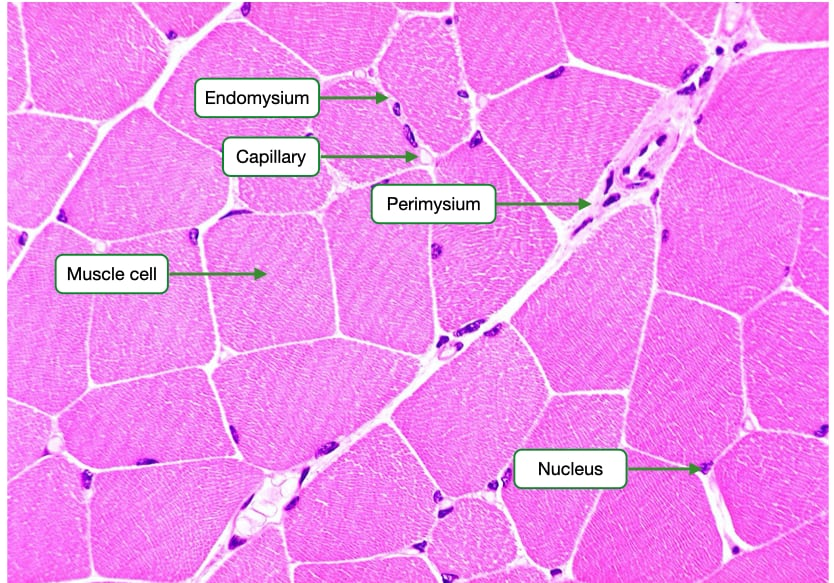
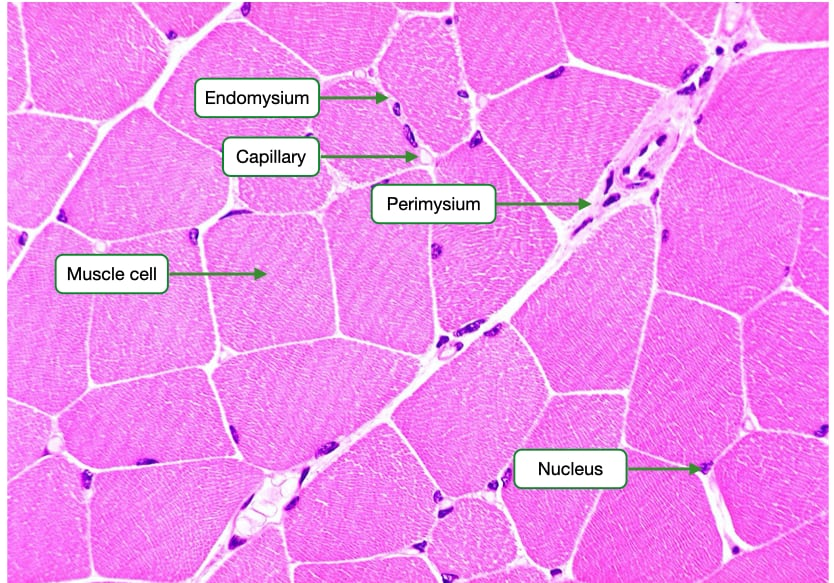
Where is the endomysium in the skeletal muscle cell?
Osmosis
Refers to the movement of the solvent from a low to high solute concentration across a semipermeable membrane.
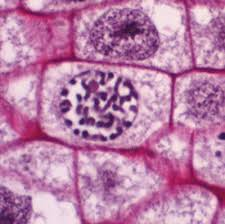
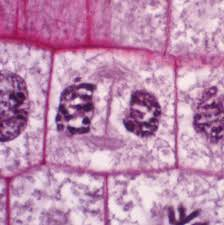
Prophase
The first stage of cell division, before metaphase, during which the chromosomes become visible as paired chromatids and the nuclear envelope disappears. The first prophase of meiosis includes the reduction division.
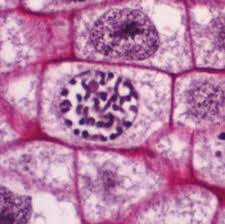
Metaphase
The stage of cell division in which chromosomes line up along the cell’s equator (metaphase plate) before being separated.
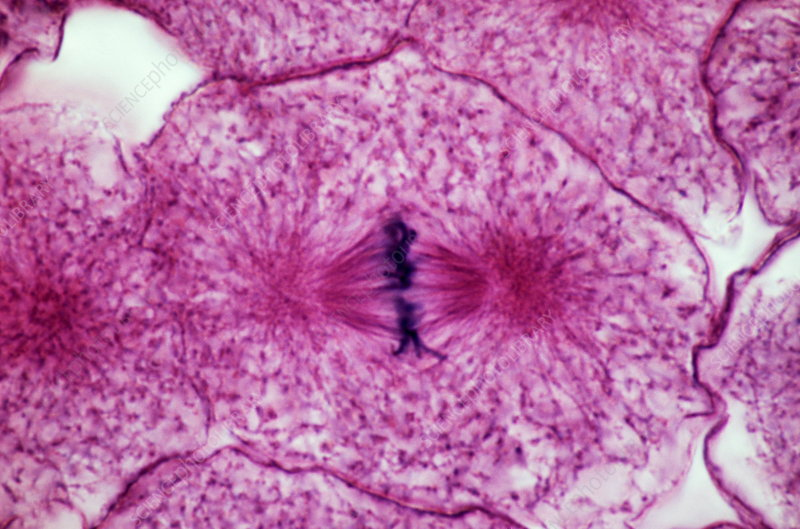
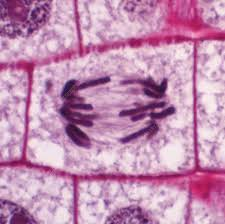
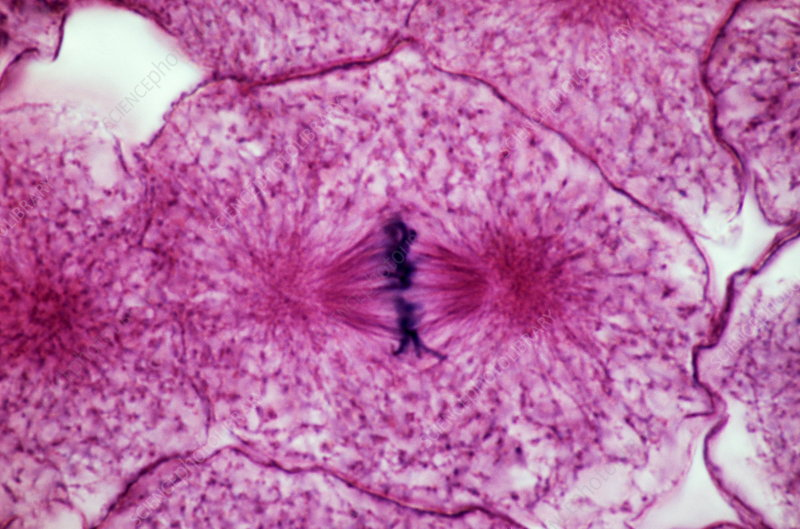
Anaphase
the stage of cell division in which sister chromatids separate and are pulled toward opposite poles of the cell.
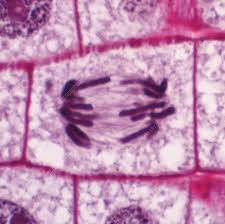
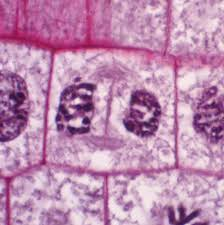
Telophase
The stage of cell division in which chromosomes reach opposite poles, nuclear membranes reform, and the cell begins to divide. Cleavage furrow forms
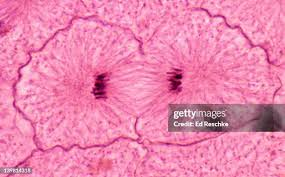
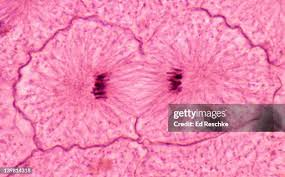
Cytokinesis
The final stage of cell division in which the cytoplasm divides, producing two separate daughter cells.

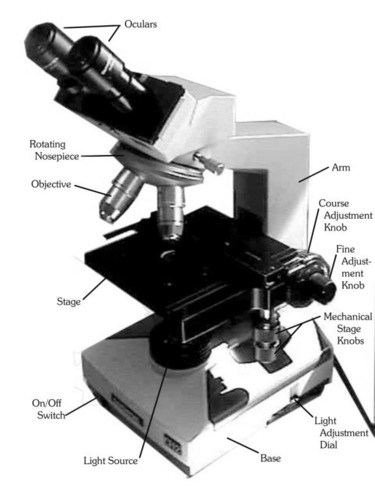
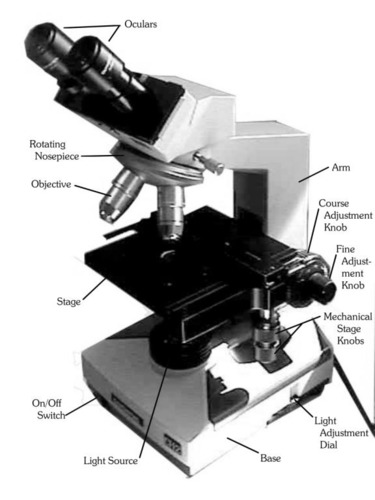
Ocular Lens
The lens through which you examine the slide (10x power)


Objective Lenses
lenses with various powers of magnification. Note that 10x is called the low-power objective, and 4x is referred to as the scan objective.


Nosepiece
Allows the user to switch between objectives
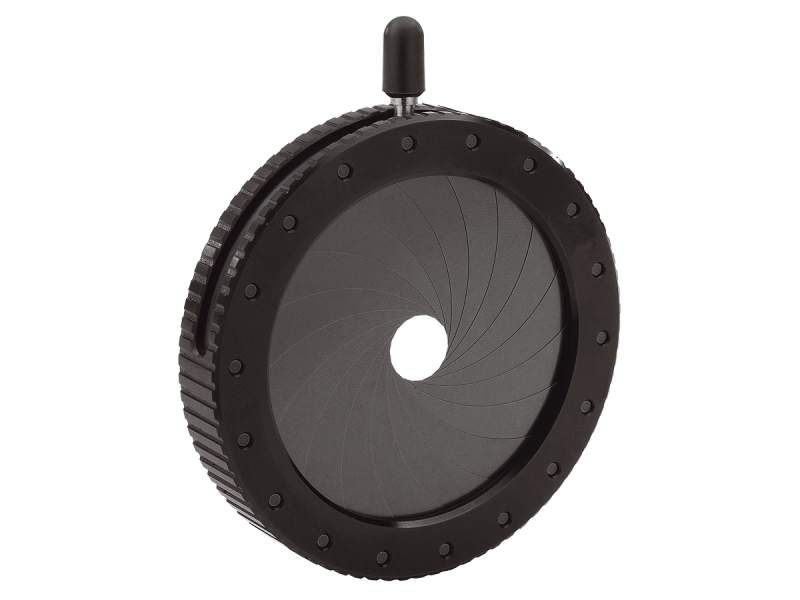


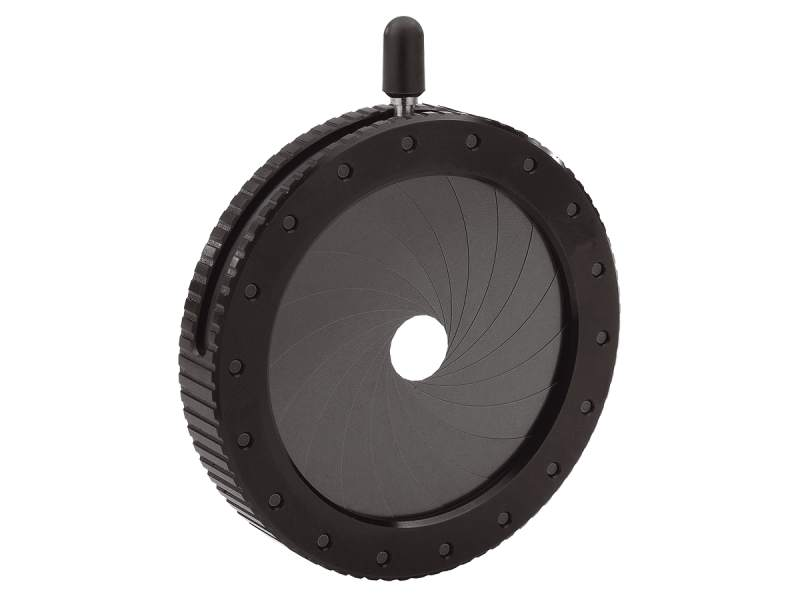
Iris Diaphragm
The underside of the stage that controls the amount of light entering the microscope.
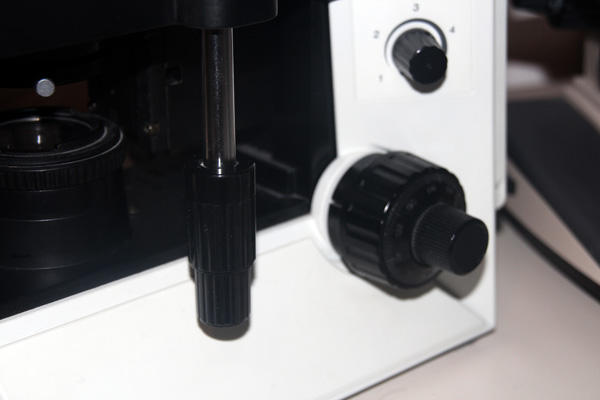


Mechanical Stage adjustment knob
Ability to move the slide by turning the knob
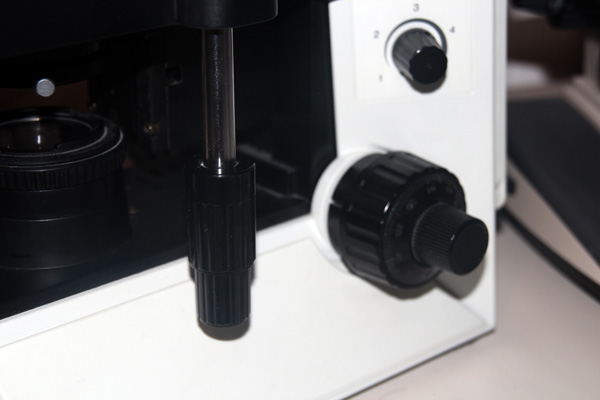

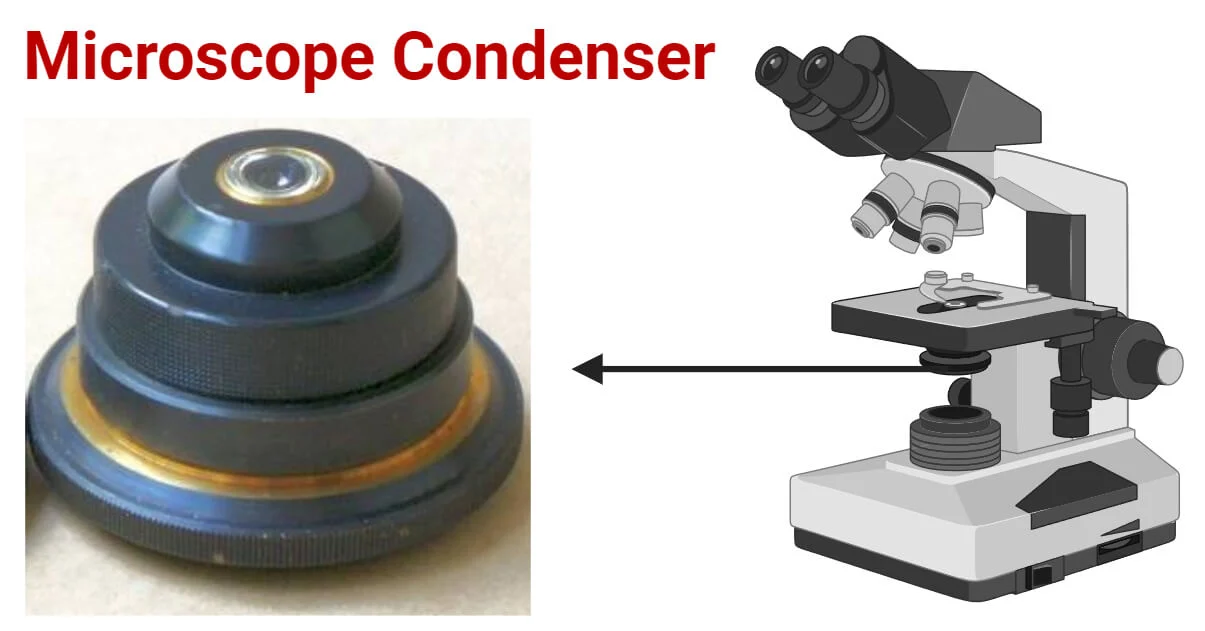
Condenser
The lens that sits under the stage
Light adjustment dial
Adjust the amount of light coming into the image
How is the “e” oriented on the slide? Is it right side up, upside down, backward, and etc?
Upside Down
Diffusion
The movement of solute particles from a high concentration to a low solute concentration
Tonicity
One solution’s ability to cause osmosis relative to another
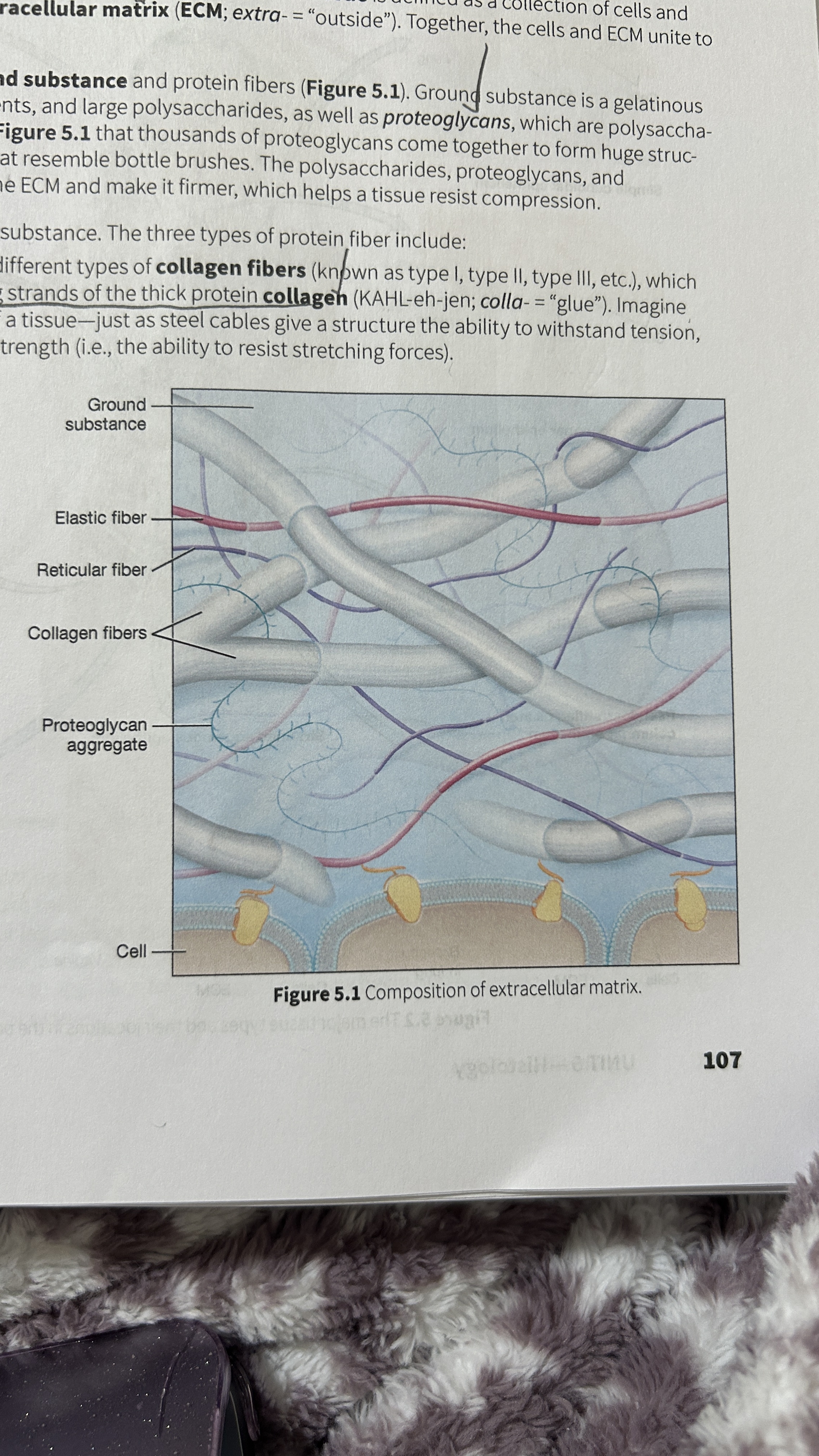
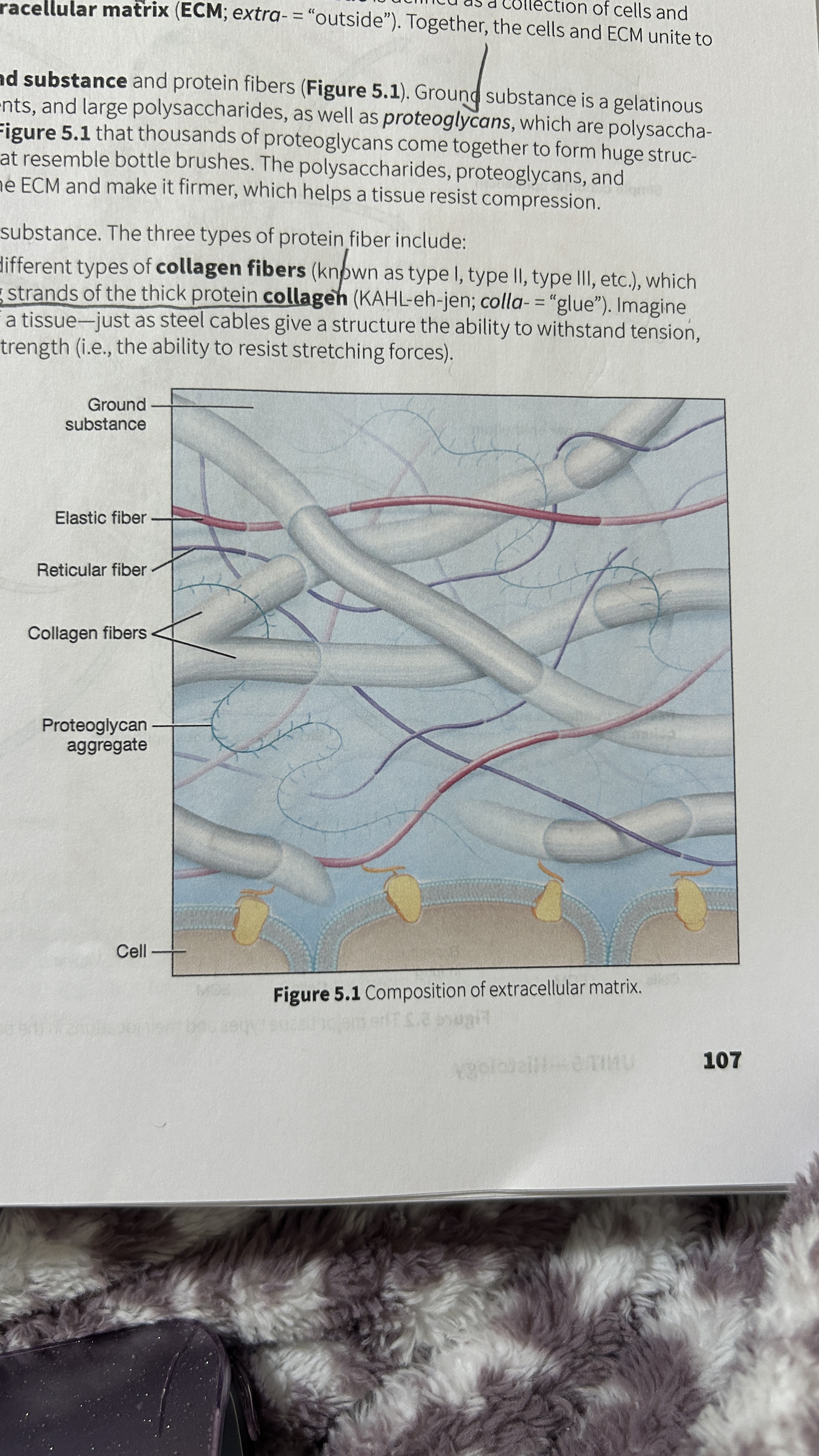
Tissue
A collection of cells and ECM
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
The surrounding material that makes up tissue
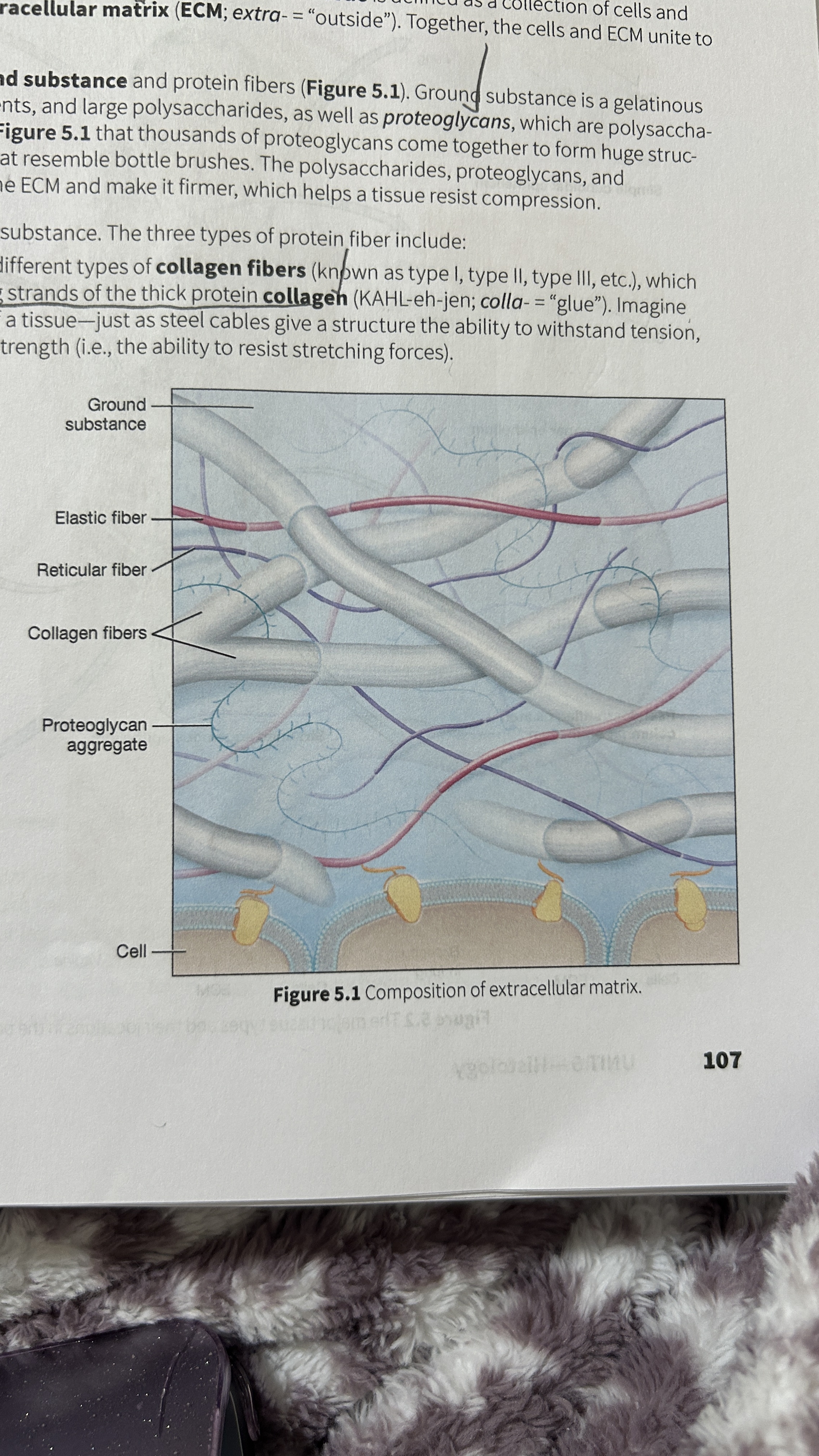
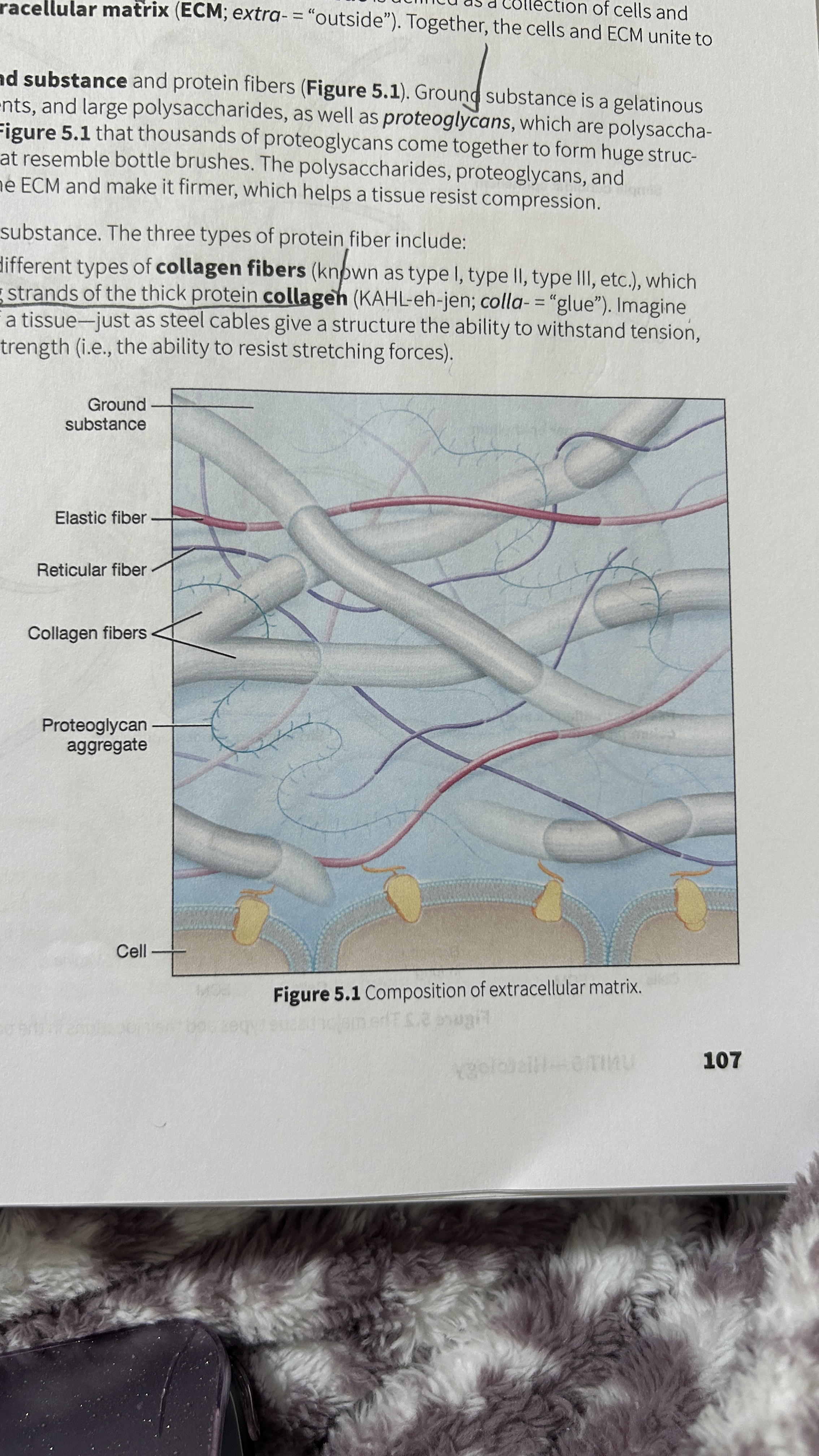
Ground Substance
Gelatinous material that contains water, ions, nutrients, large polysaccharides, and proteoglycans.
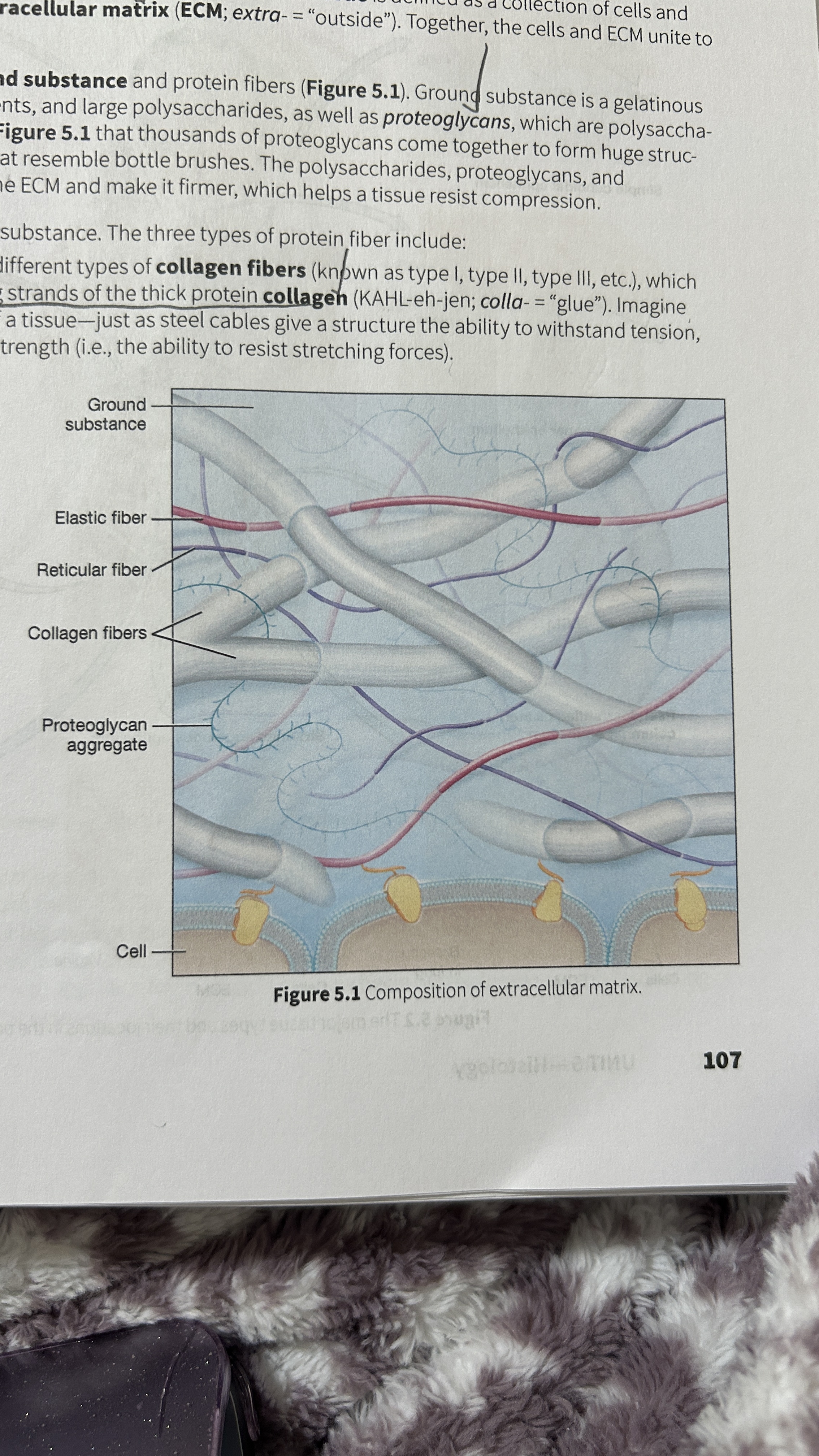
Proteoglycan
polysaccharide bound to a protein core
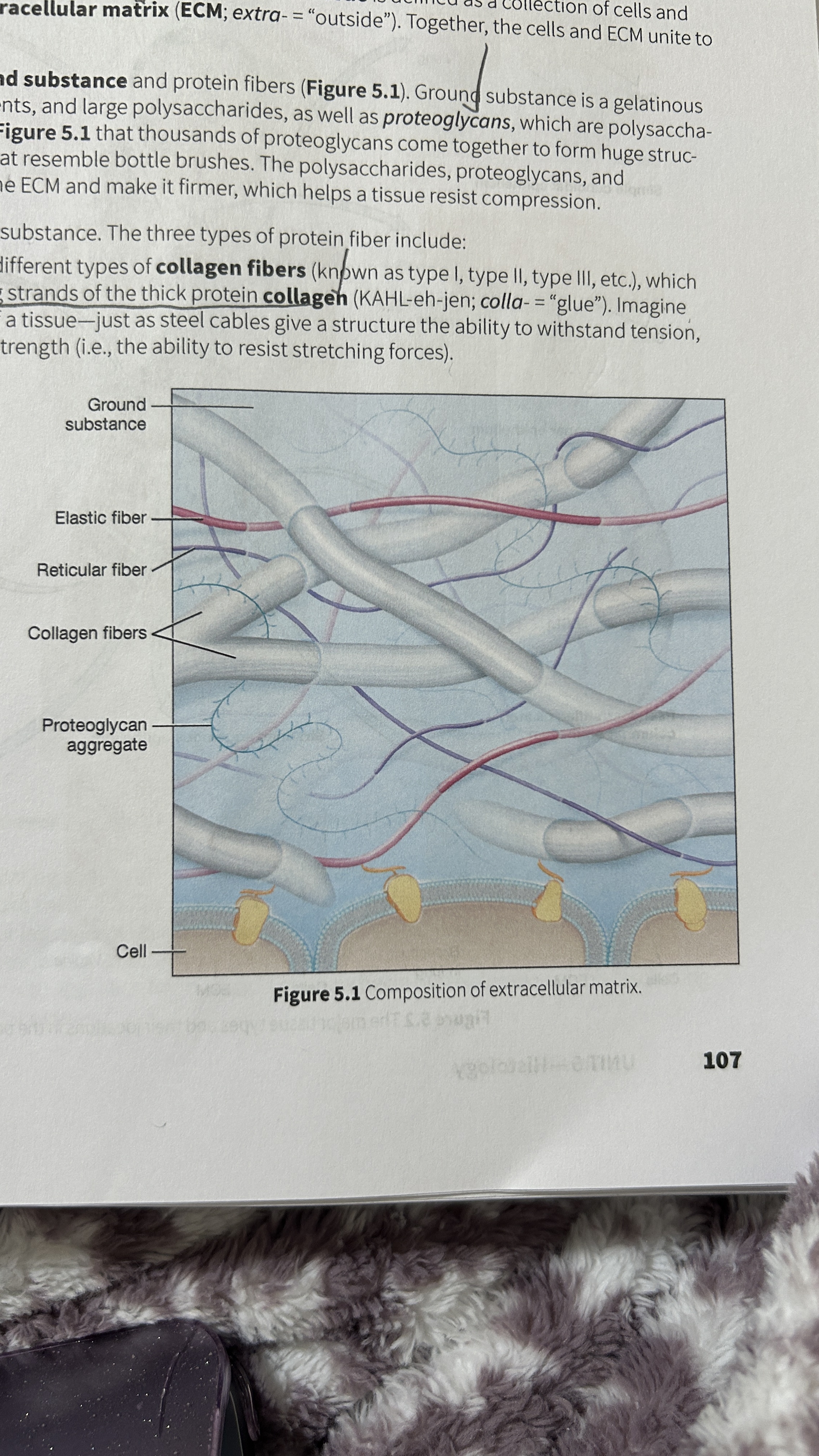
Proteoglycan Aggregates
Thousands of proteoglycans that resemble bottle brushes
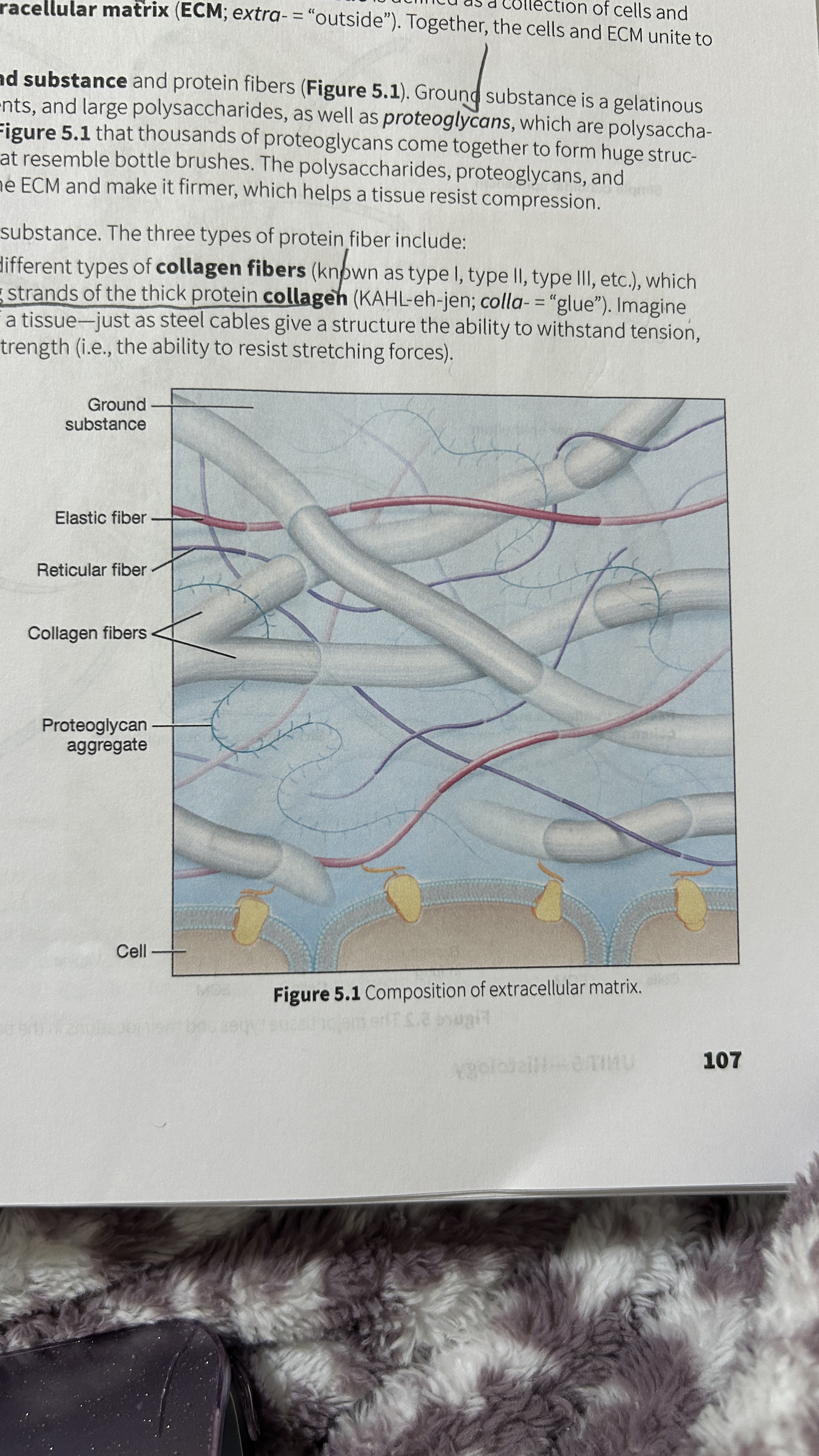
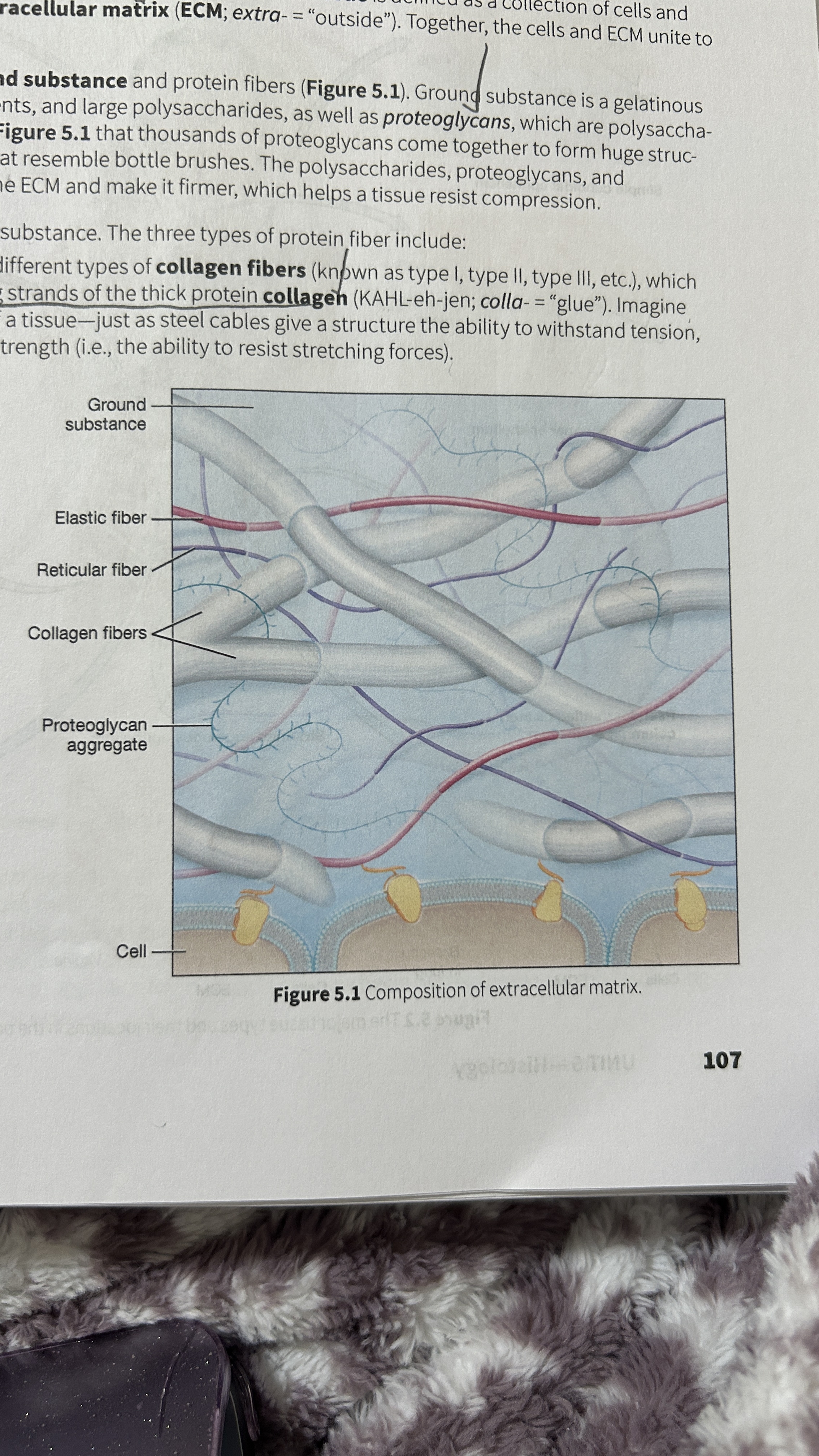
Collagen Fibers
composed of multiple entwining strands of the thick protein collagen (glue) and resist stretch in one way. Tendons and ligaments
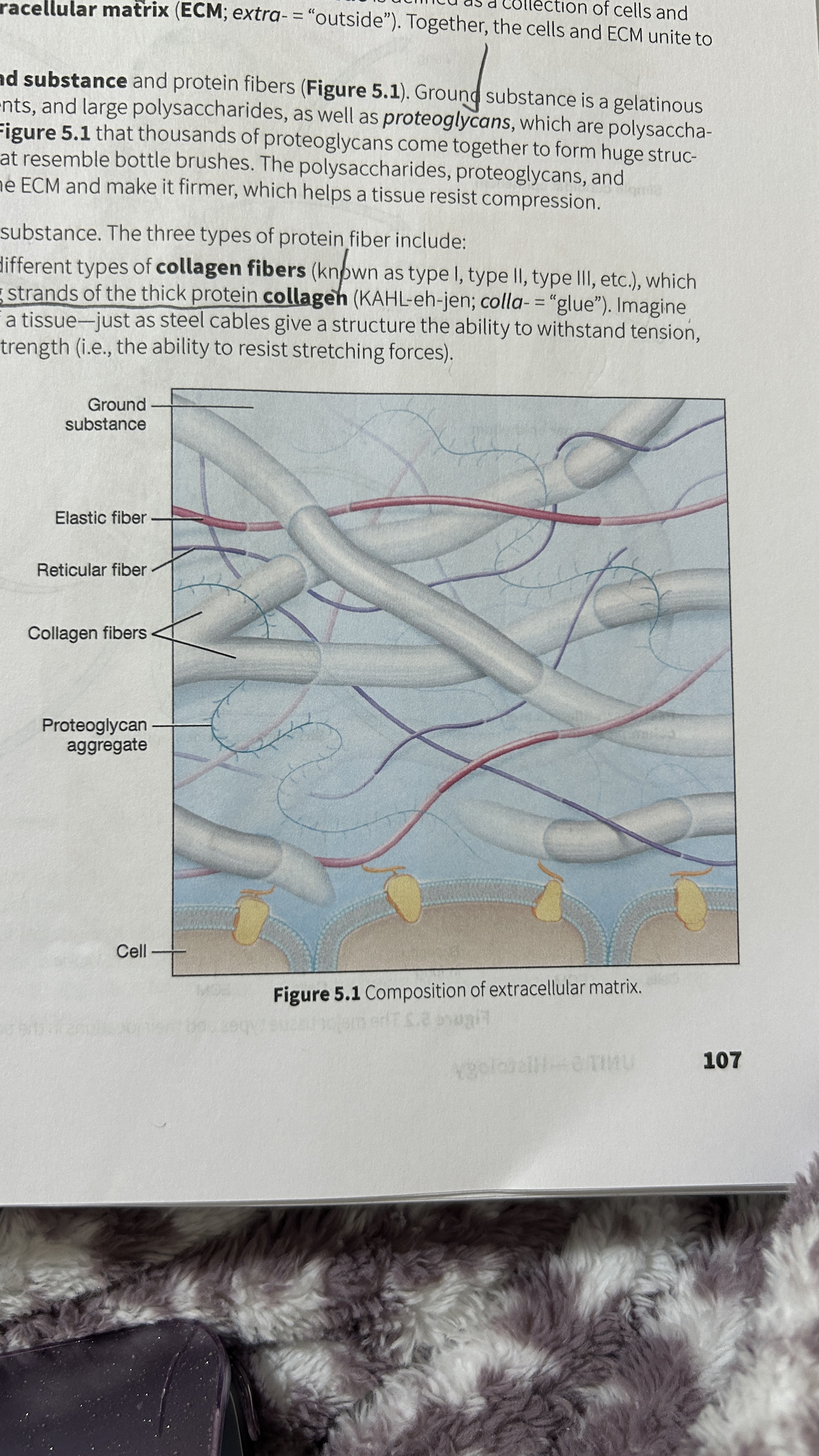
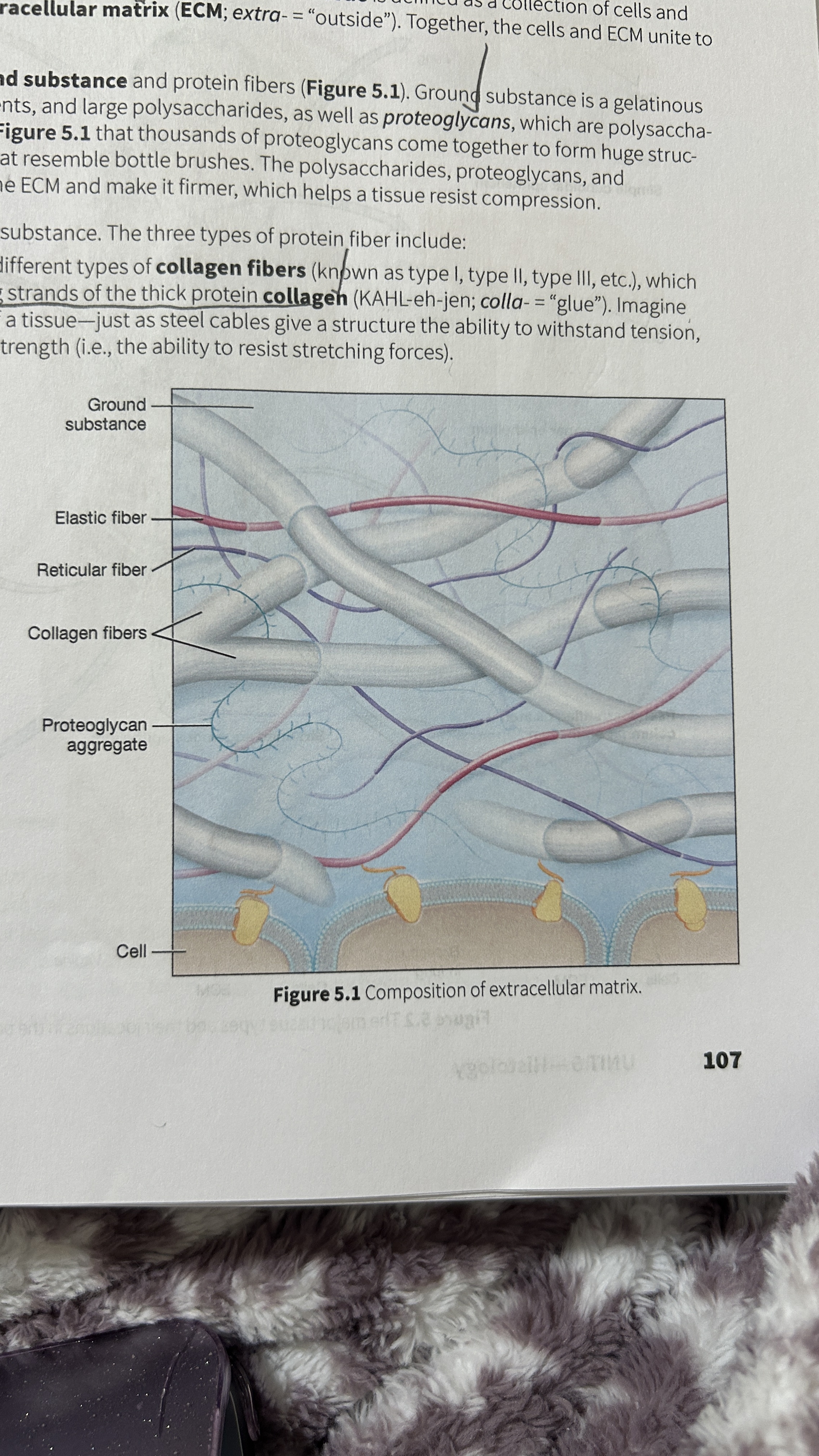
Elastic Fibers
Fibers composed of elastin proteins allow tissue to stretch, a property known as distensibility, and return to their original form, a property known as elasticity like elastic ligaments of the vertebrae
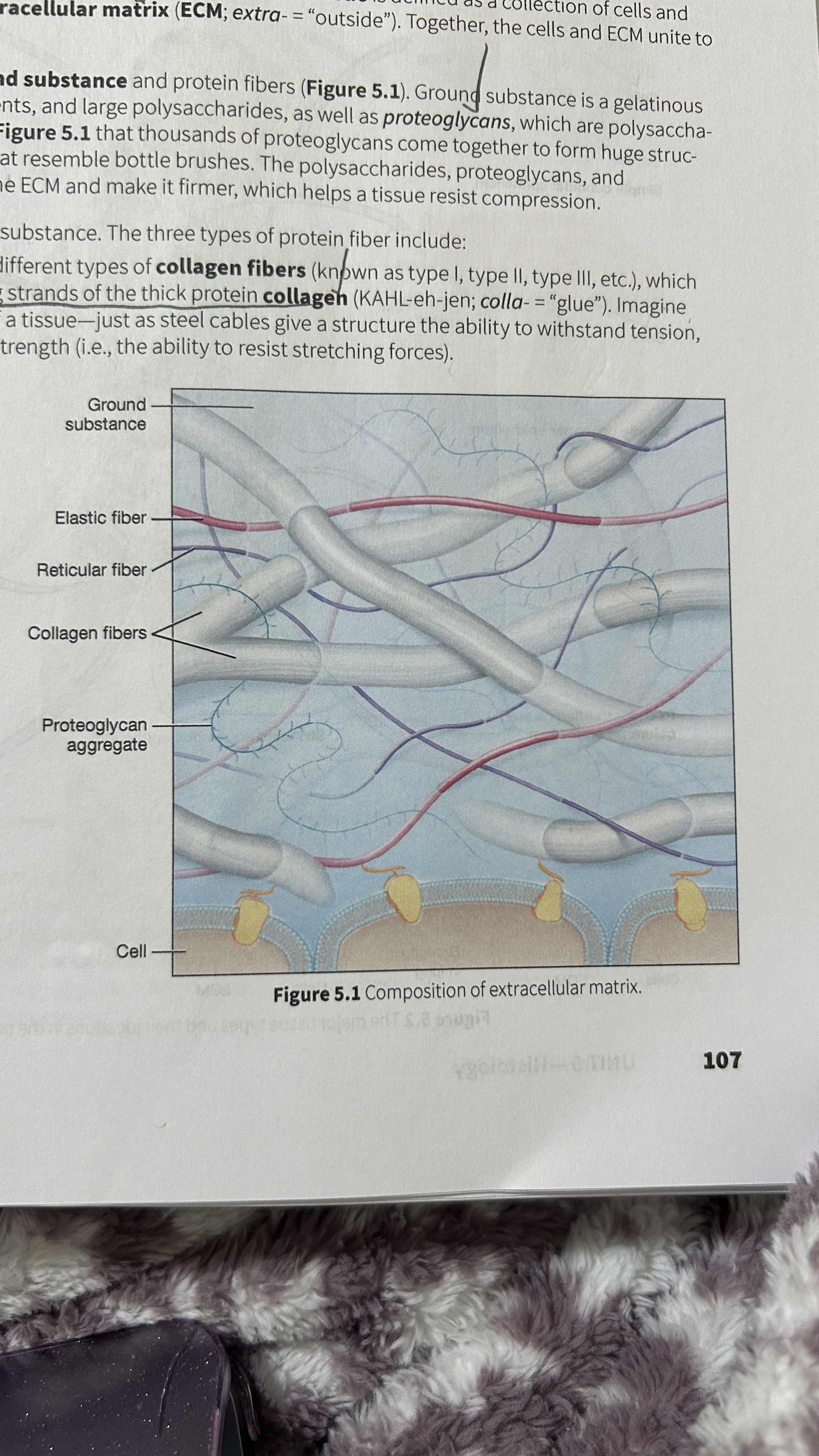
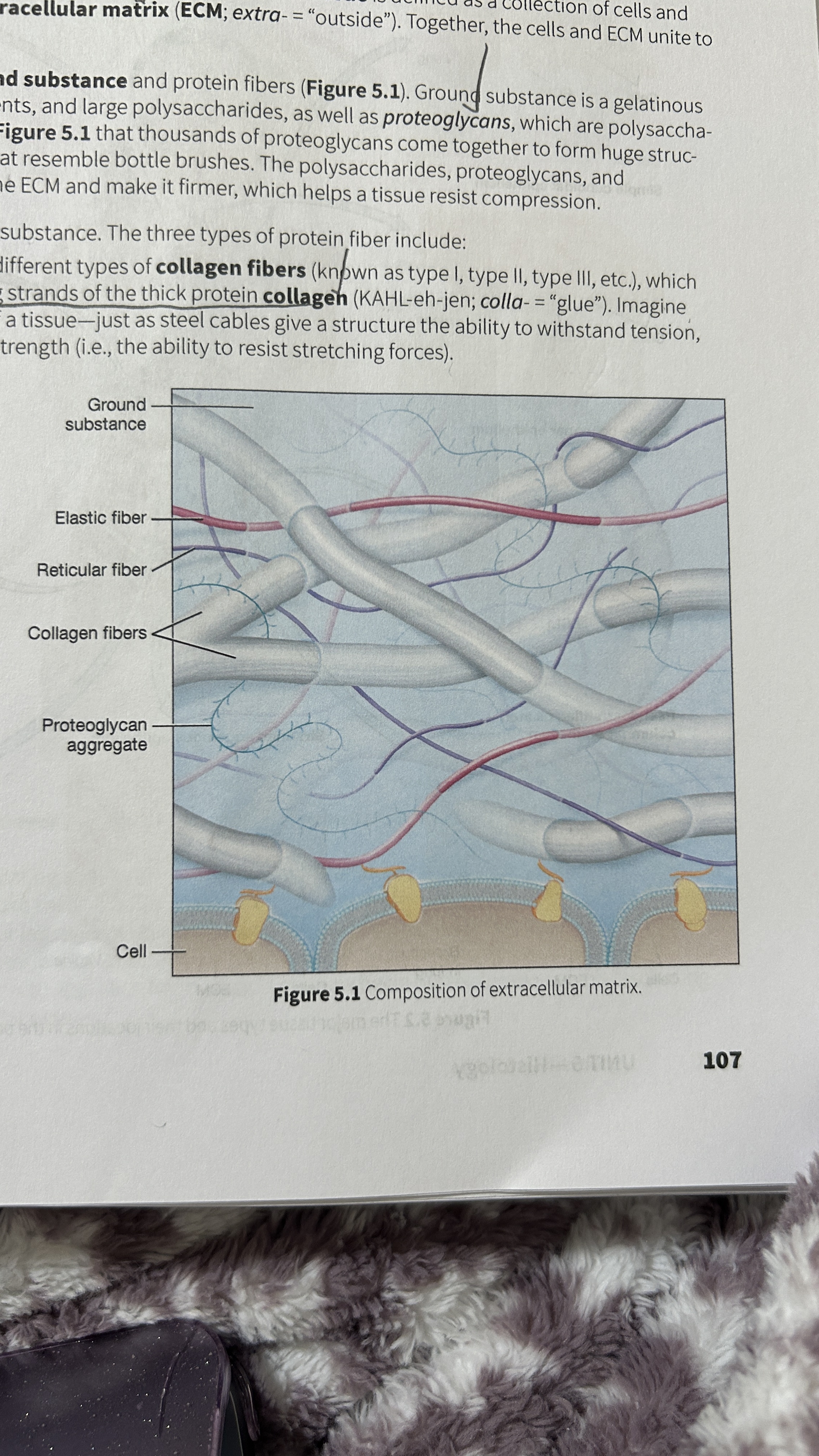
Reticular Fibers
Made by thin cells which is a special type of collagen fibers. Network of interwoven fibers (stroma), resists force in many directions, stabilized functional cells (parenchyma) and structures like sheaths around organs

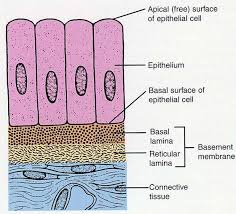
Epithelial Tissue
our covering and lining tissues. Provides protection, secretion, and absorption. sheet-like, connected by tight junctions, with little ECM between cells, and includes endothelial cells.

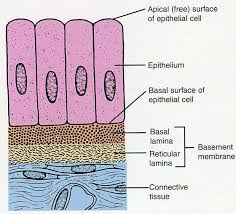
Basal Lamina
holds ECM underneath the cells, which effectively glues the epithelium in place.
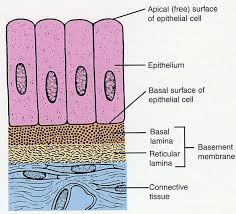
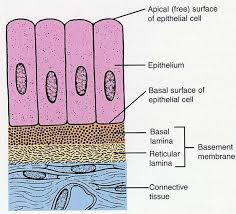
Lamina Reticularis
Another layer that anchors collagen fibers to the ECM is produced by connective tissue deep to the epithelium.
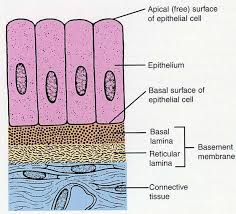
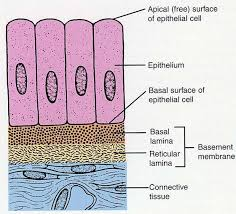
Basement Membrane
Basal lamina and Lamina reticulars
Avascular
Have no blood vessels like epithelia cells
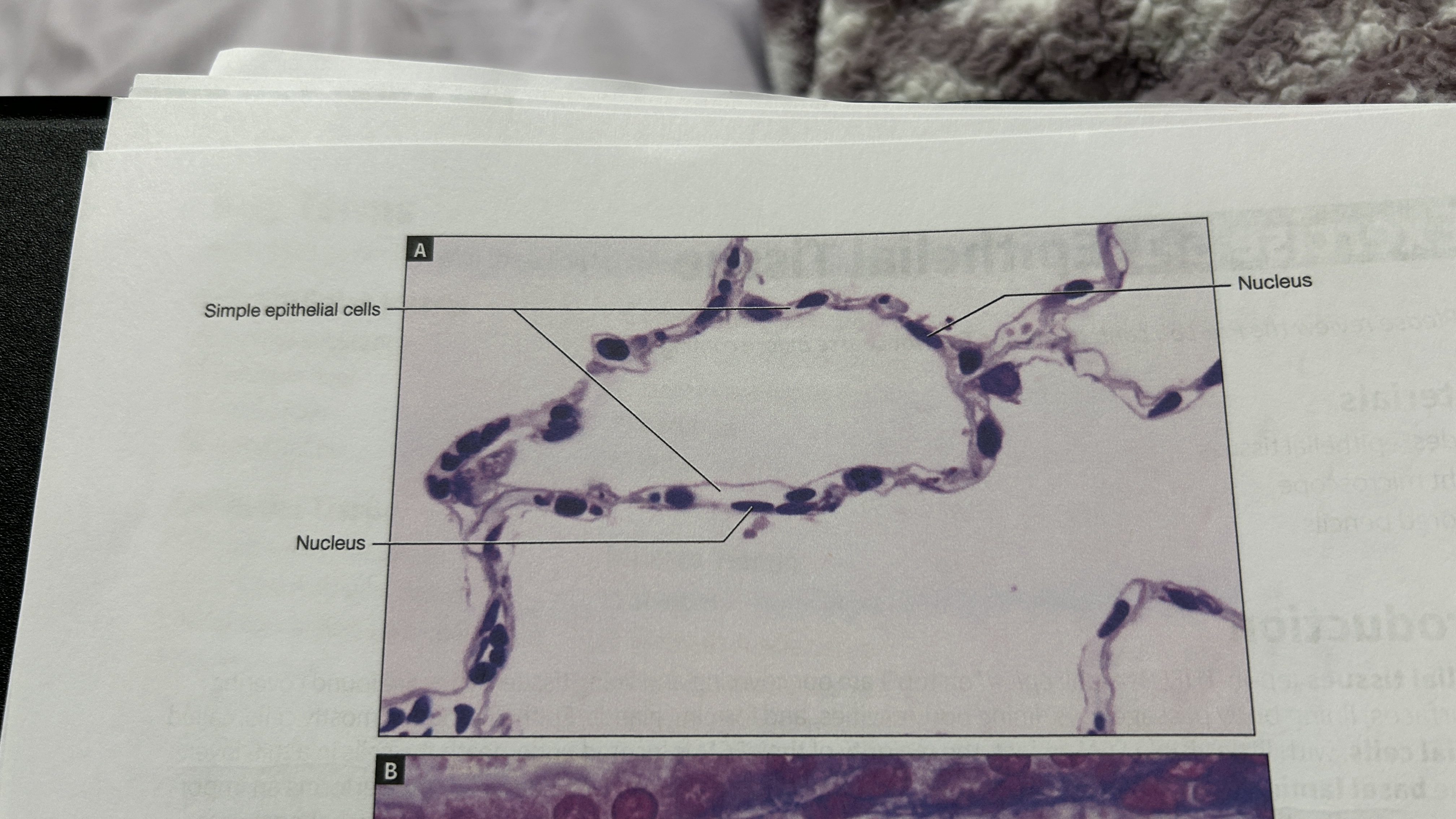
Simple epithelia
One layer of cells
Stratified epithelia
Two or more layers of cells
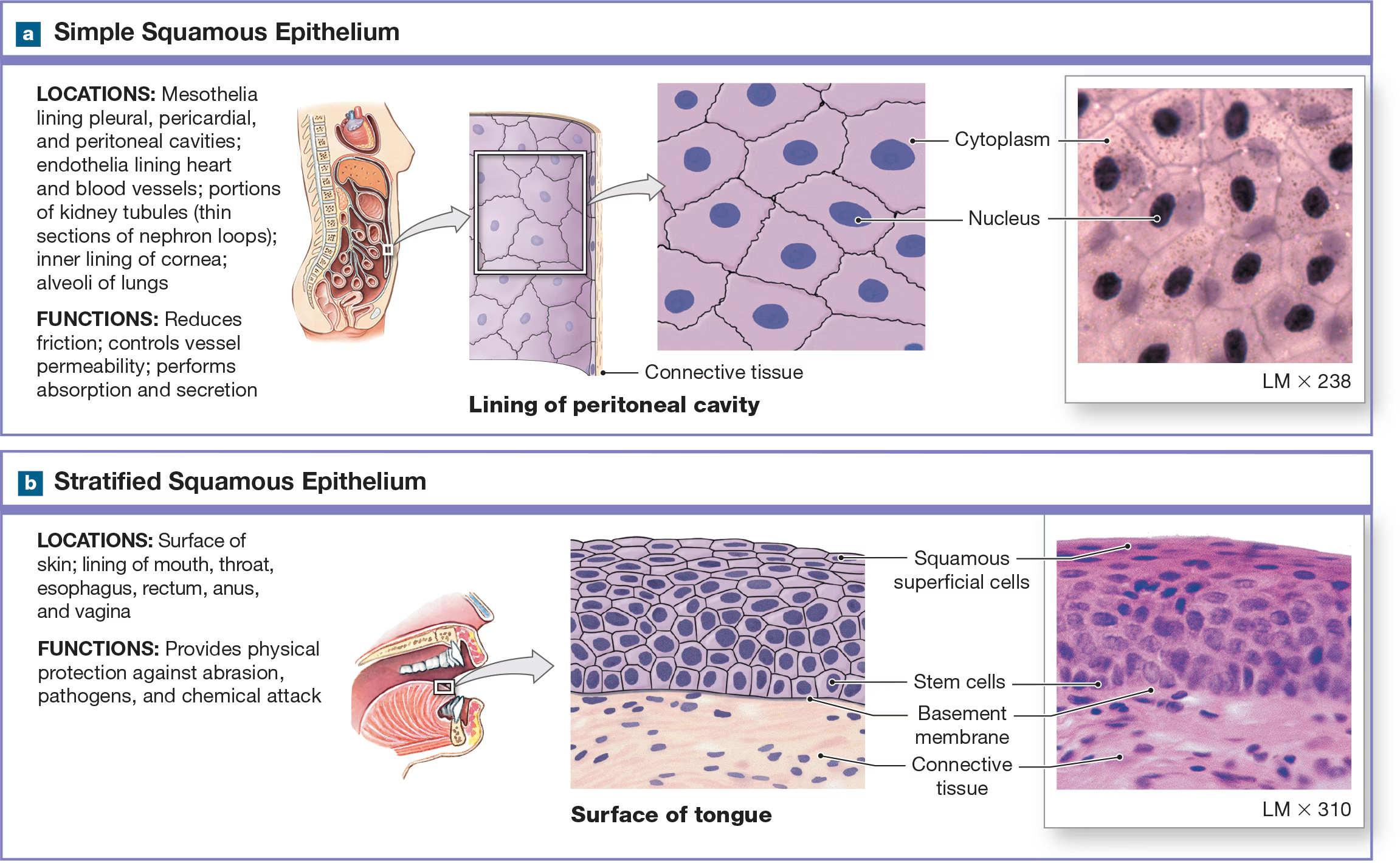
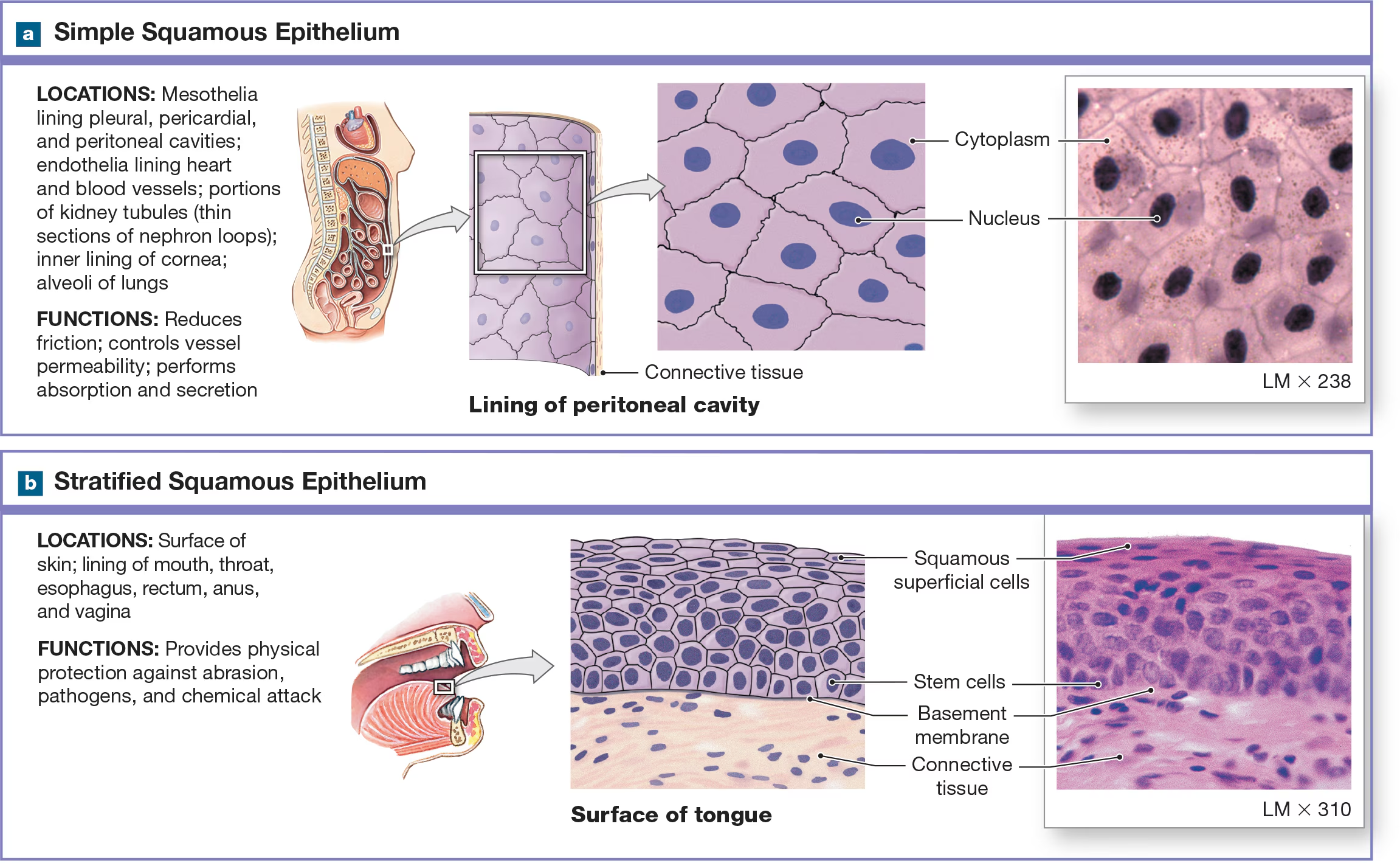
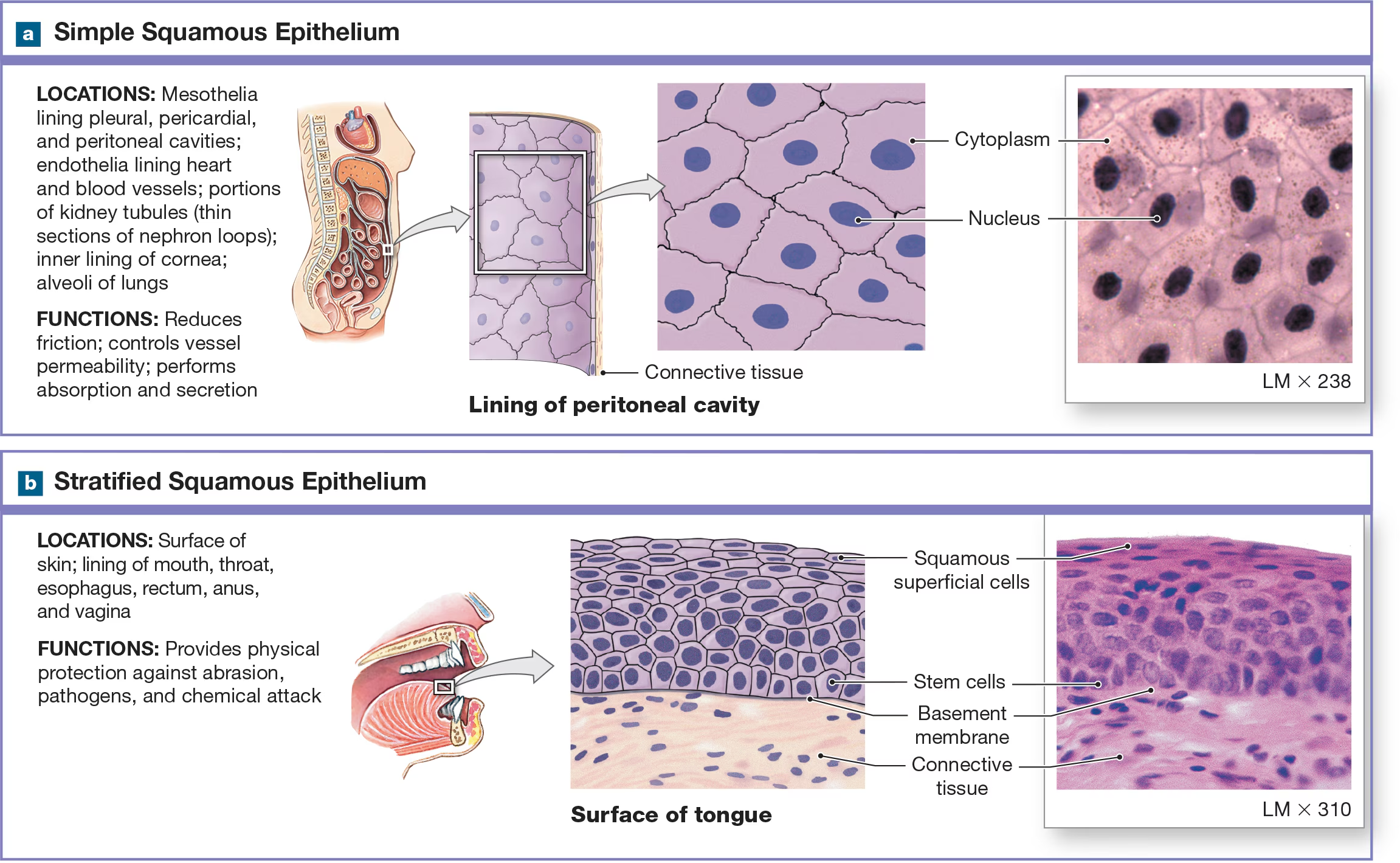
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Single layer of flat cells with a centrally located nucleus found in air sacs of the lungs.
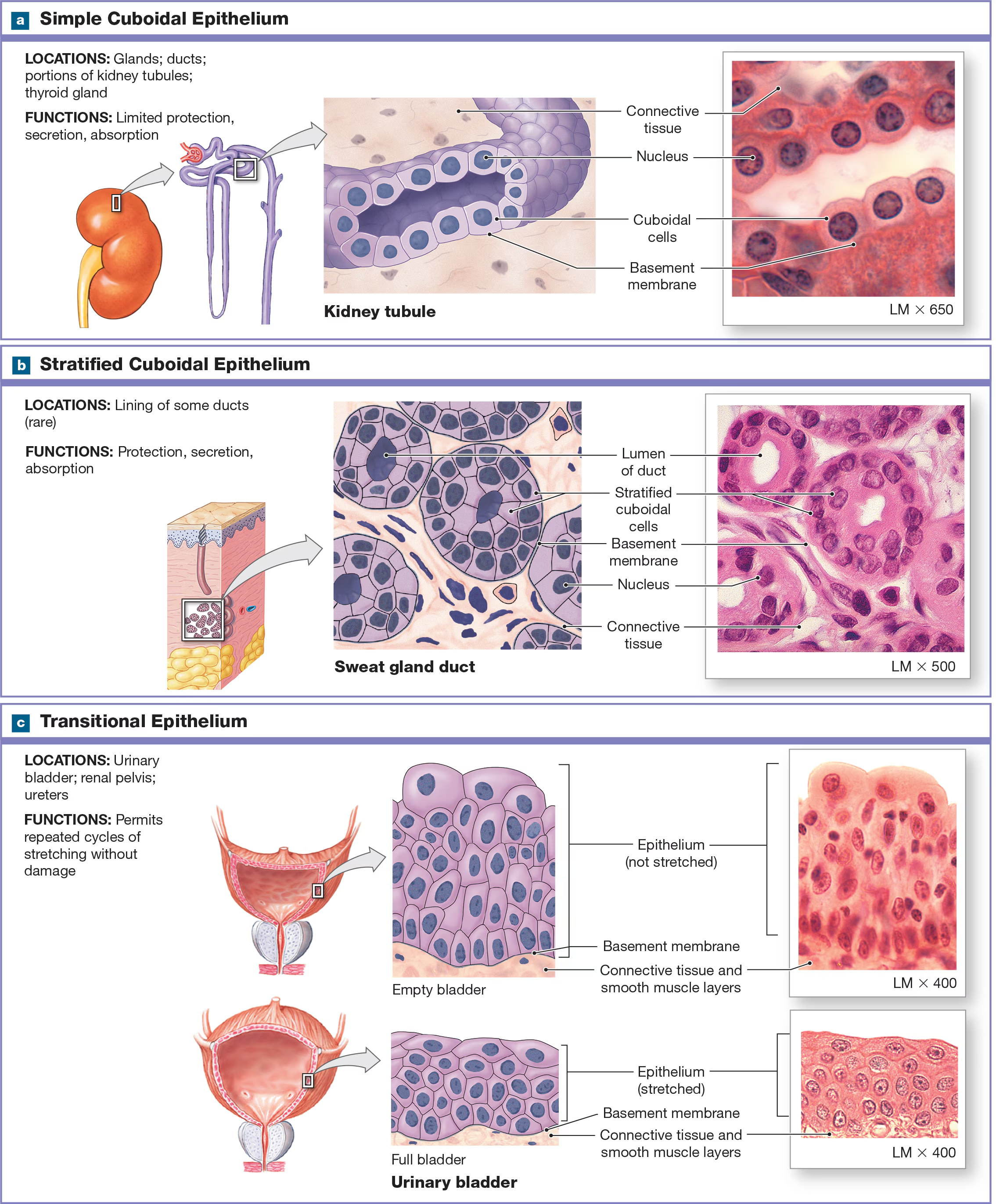
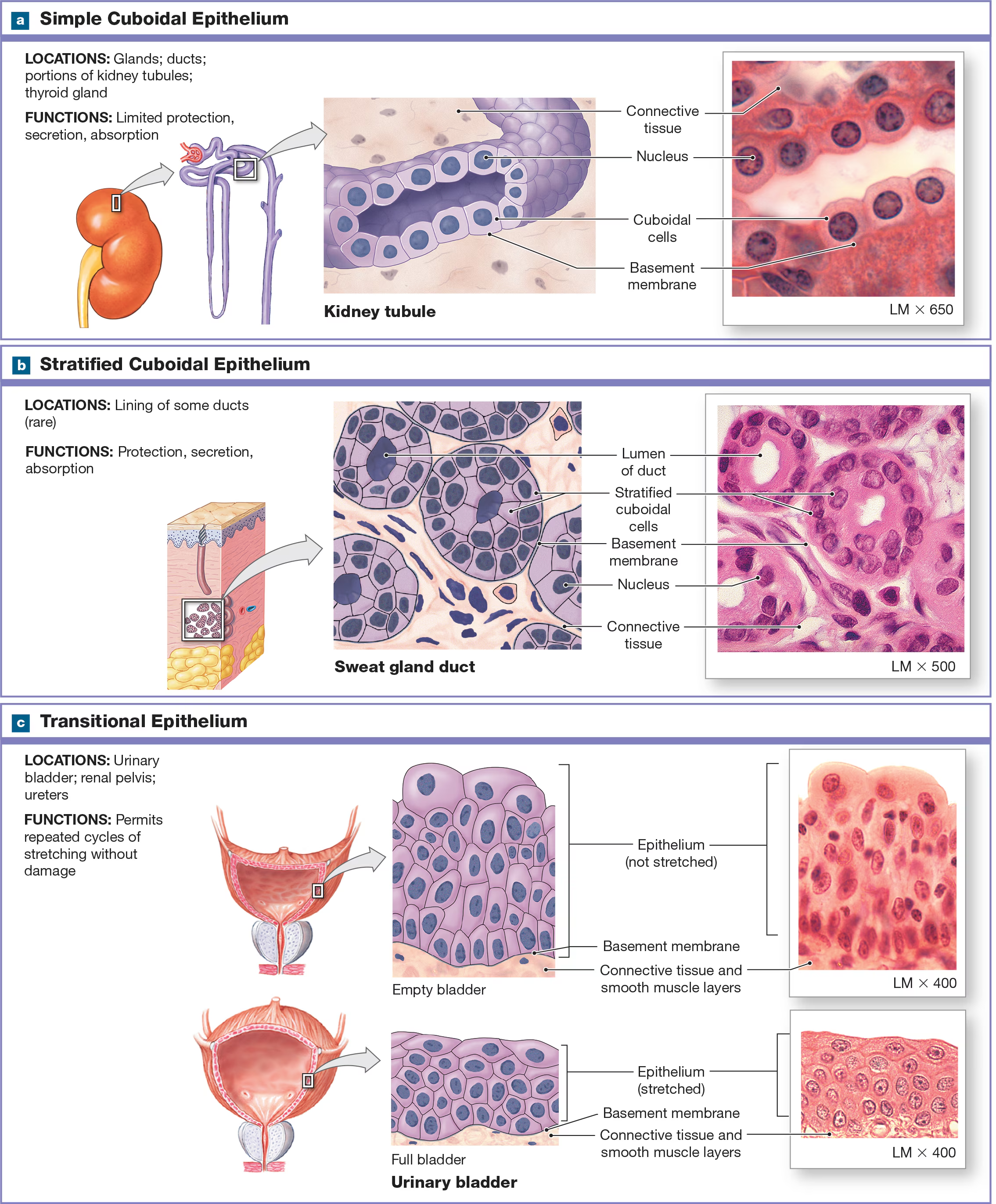
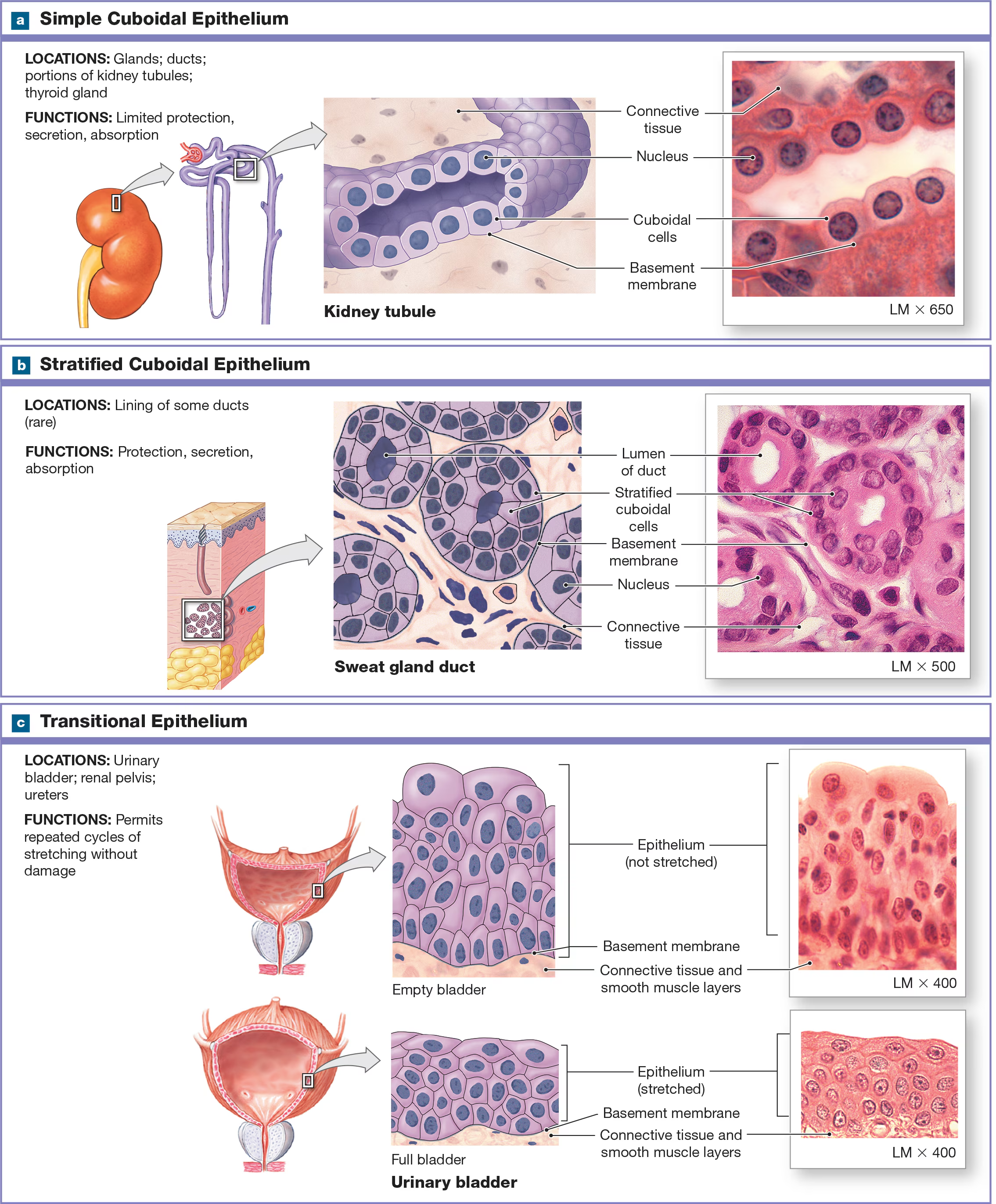
Simple Cuboidal epithelium
Short and have a spherical, central nucleus and are found near the kidneys, the lining of respiratory passageways, and thyroid glands.
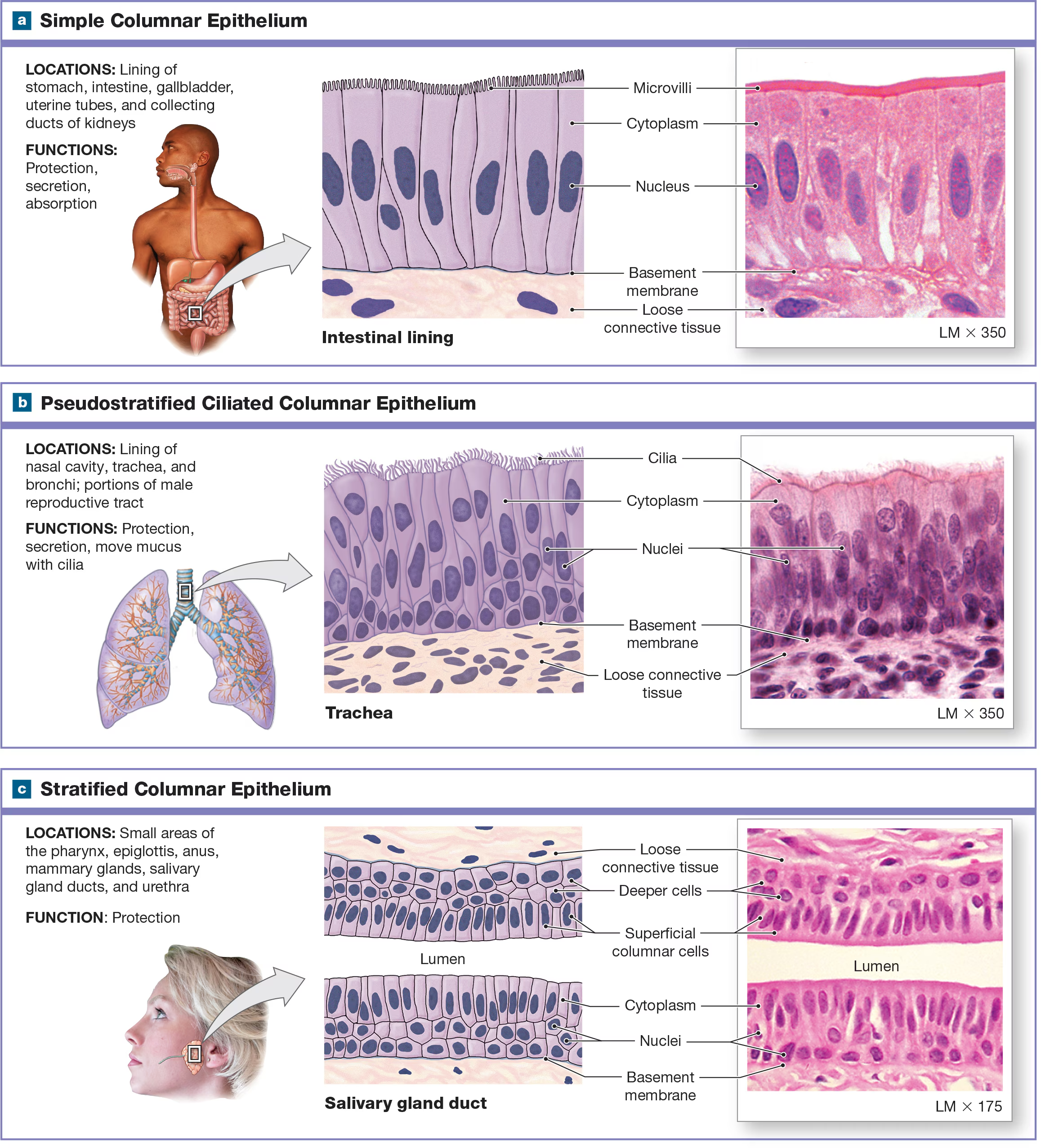
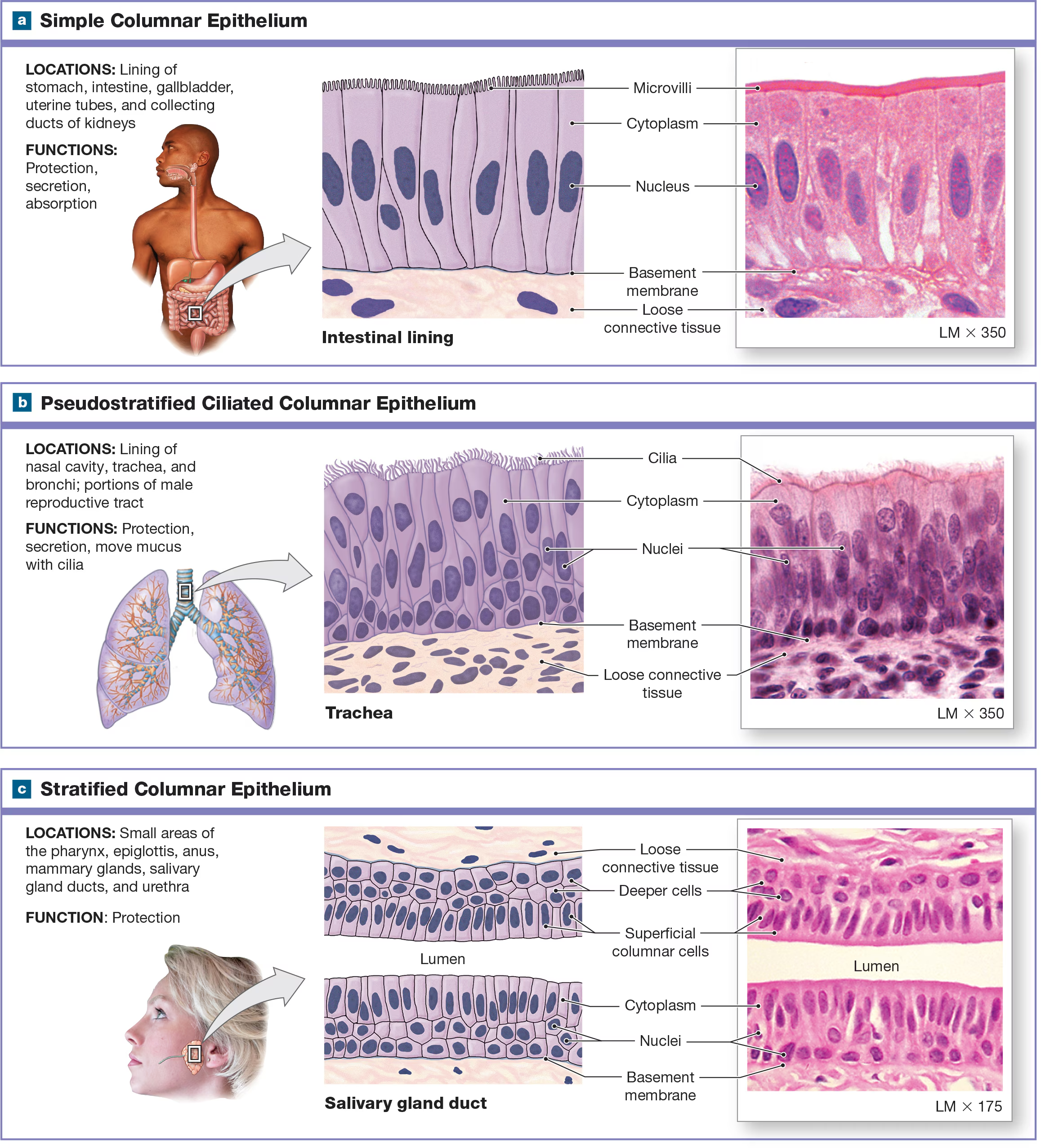
Simple Columnar Epithelium
spherical nuclei near the base of the cell and line respiratory passageways and digestive tract the cilia are folded into microvilli
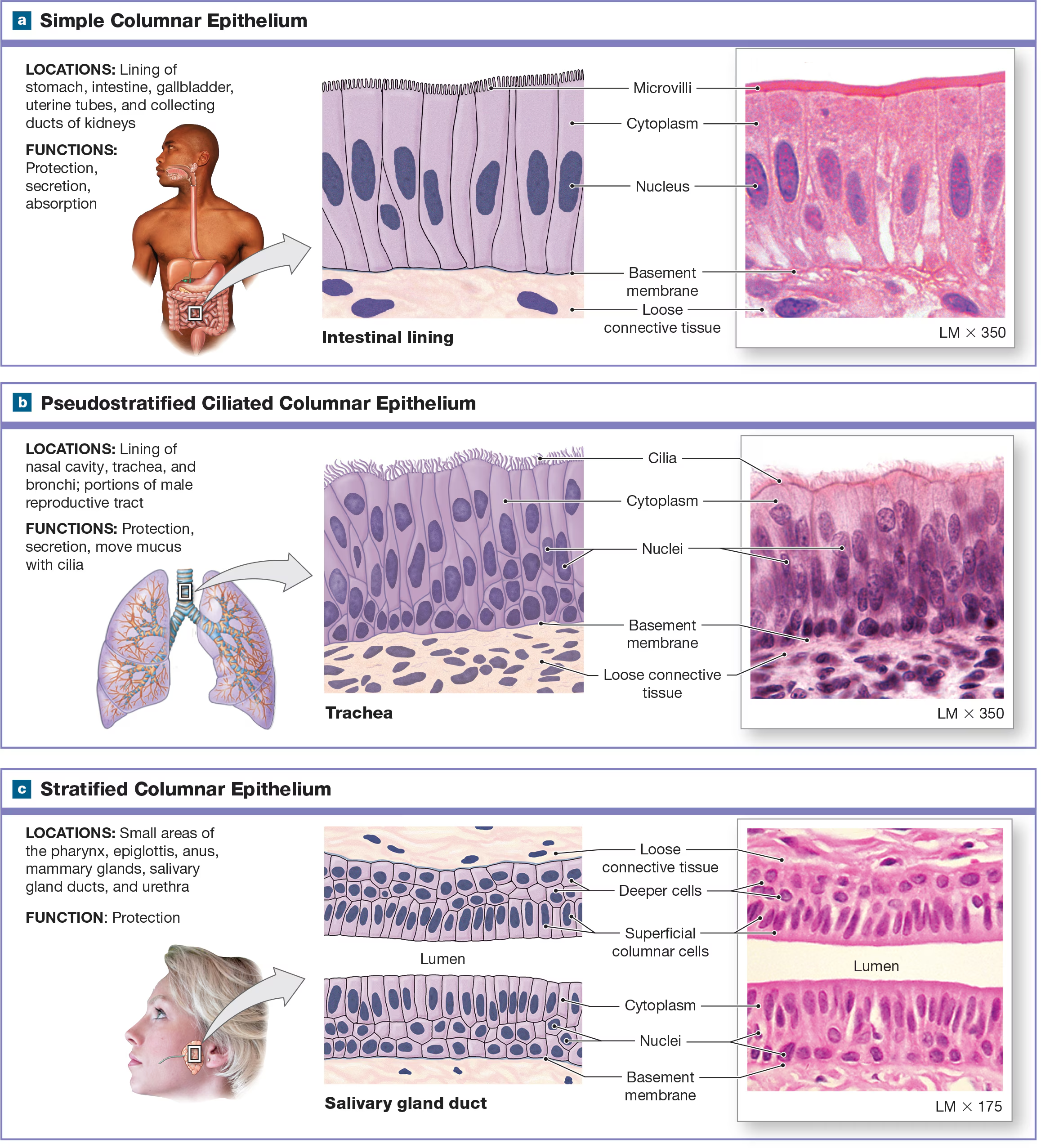
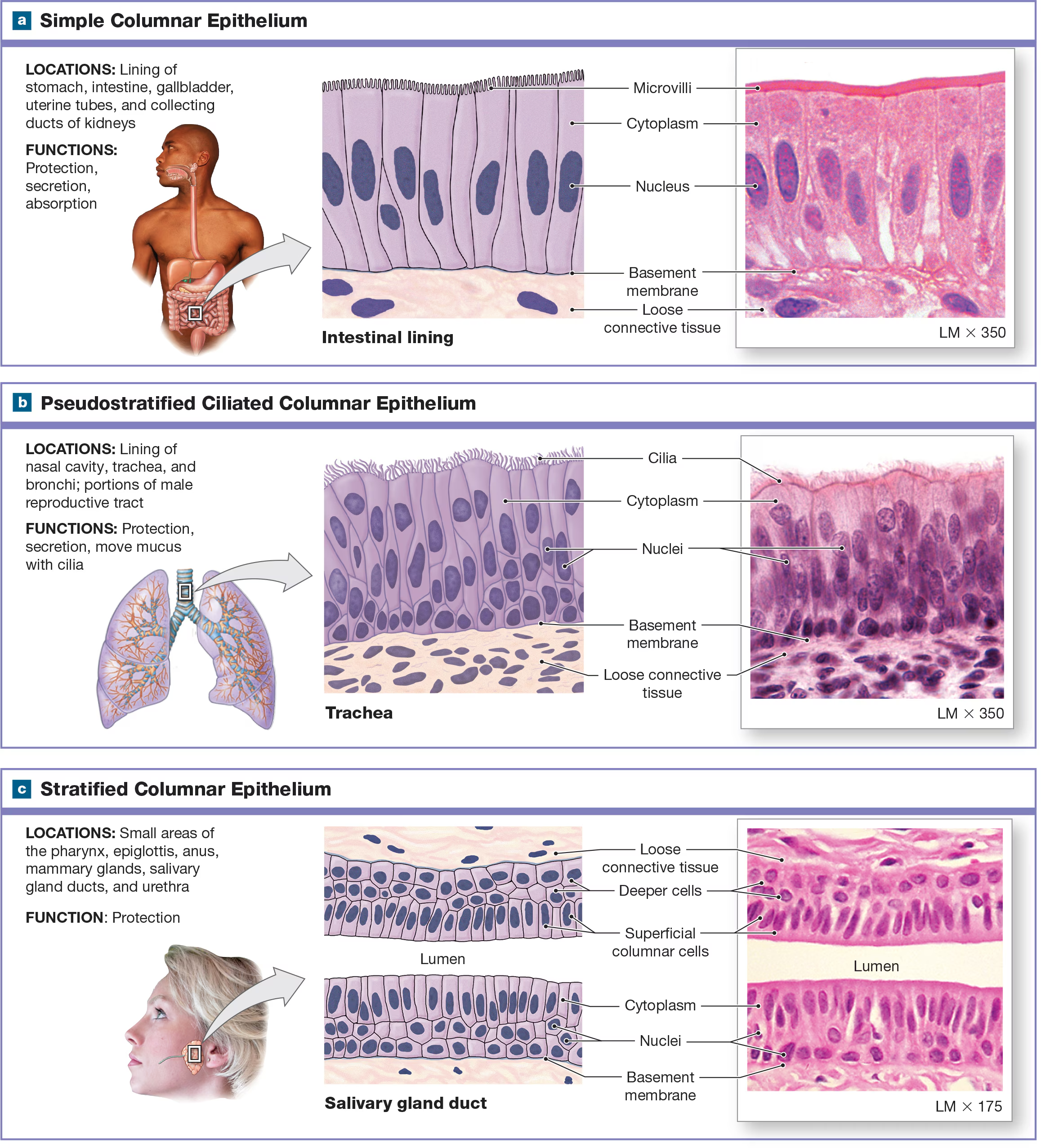
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium/ Respiratory Epithelium
It appears to have several layers, but it only has one layer of cells at different heights, all of which are attached to the same basal lamina. Usually has cilia and is shaped like a columnar found in the nasal cavity and respiratory tract.
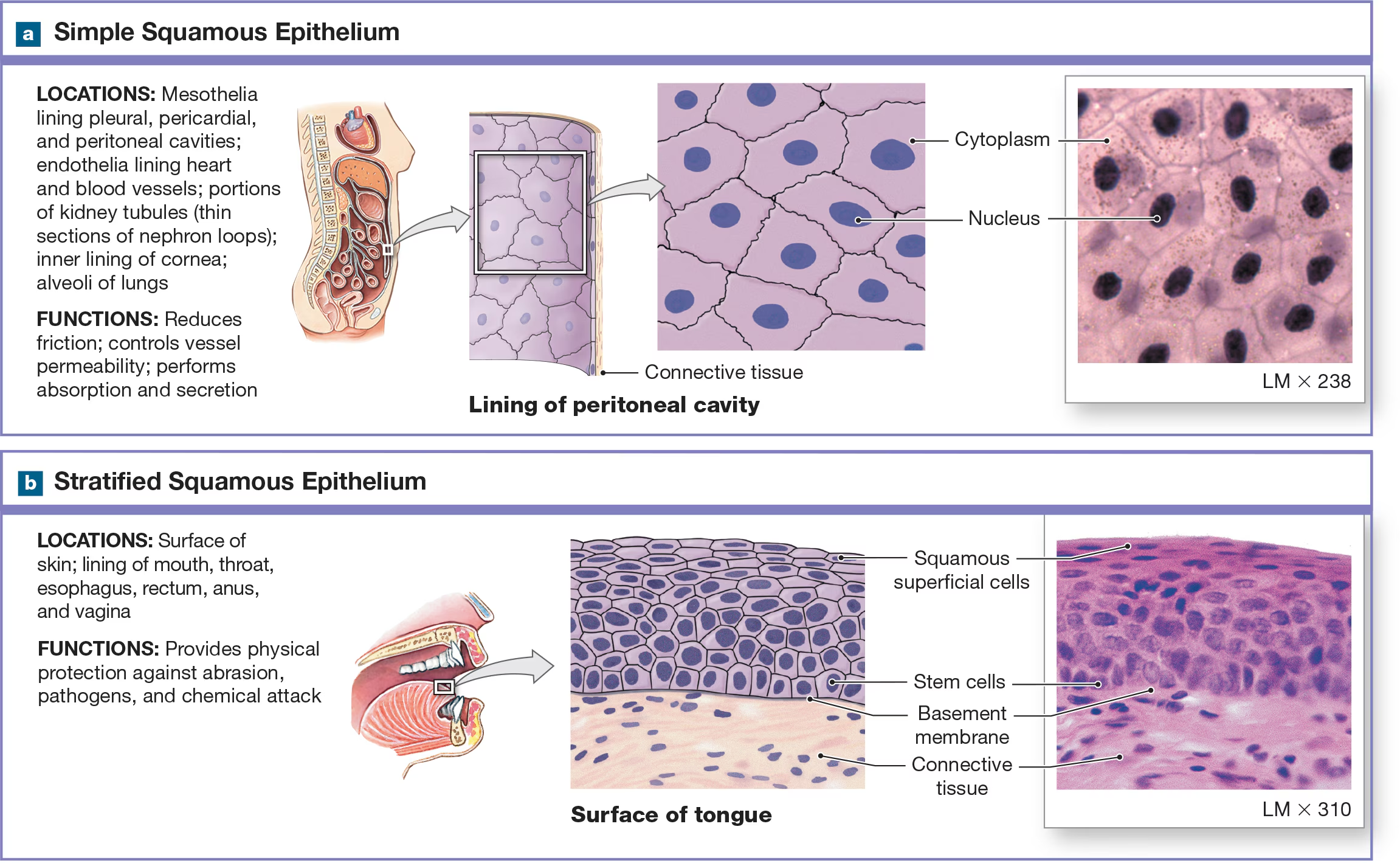
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
many layers of flattened and has two variants: keratinized and non-keratinized
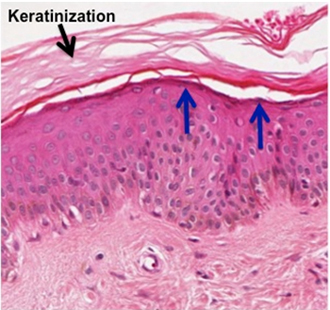
Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium
keratinocytes epithelial cells; super dry/flaky cells are dead because there too far away from the blood supply located in deeper tissue; therefore, these cells are found in superficial layers of the skin unprotected.
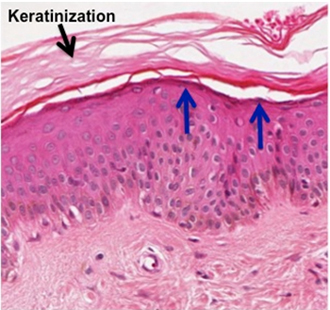
Keratinocytes
epithelial cells that produce keratin proteins
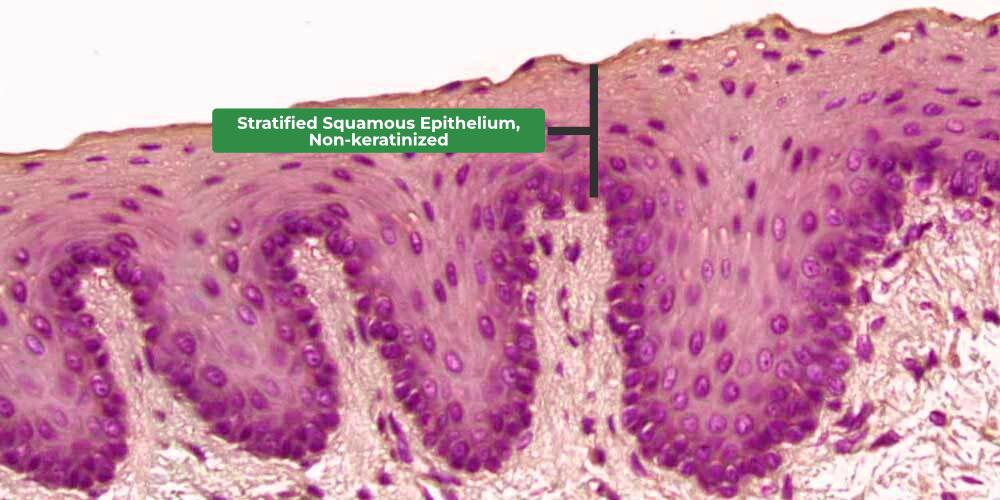
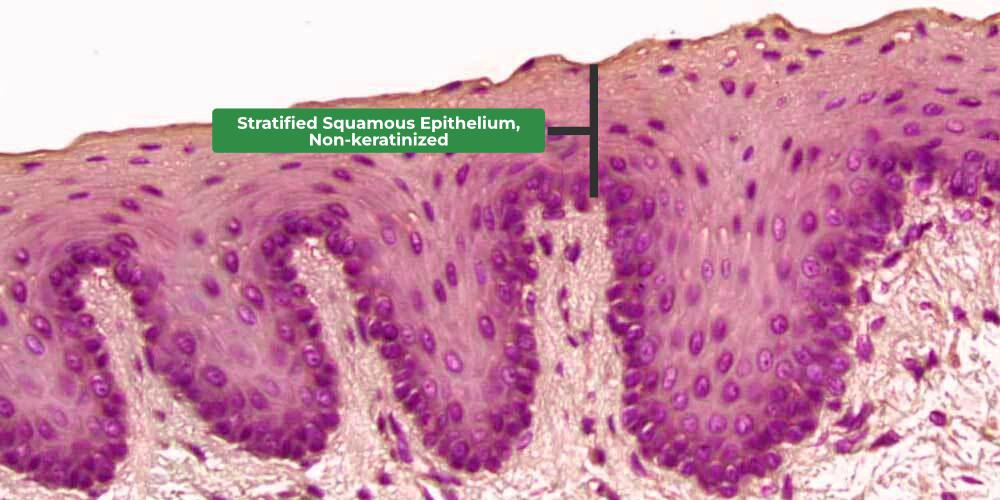
Stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium
No keratin and is found in more protective layers like the oral cavity, the pharynx (throat), the anus, and the vagina. Superficial cells survive because they're not as thick.
Which types of epithelium are rare?
stratified cuboidal and columnar epithelium, and they are found in the lining of ducts in certain glands like salivary.
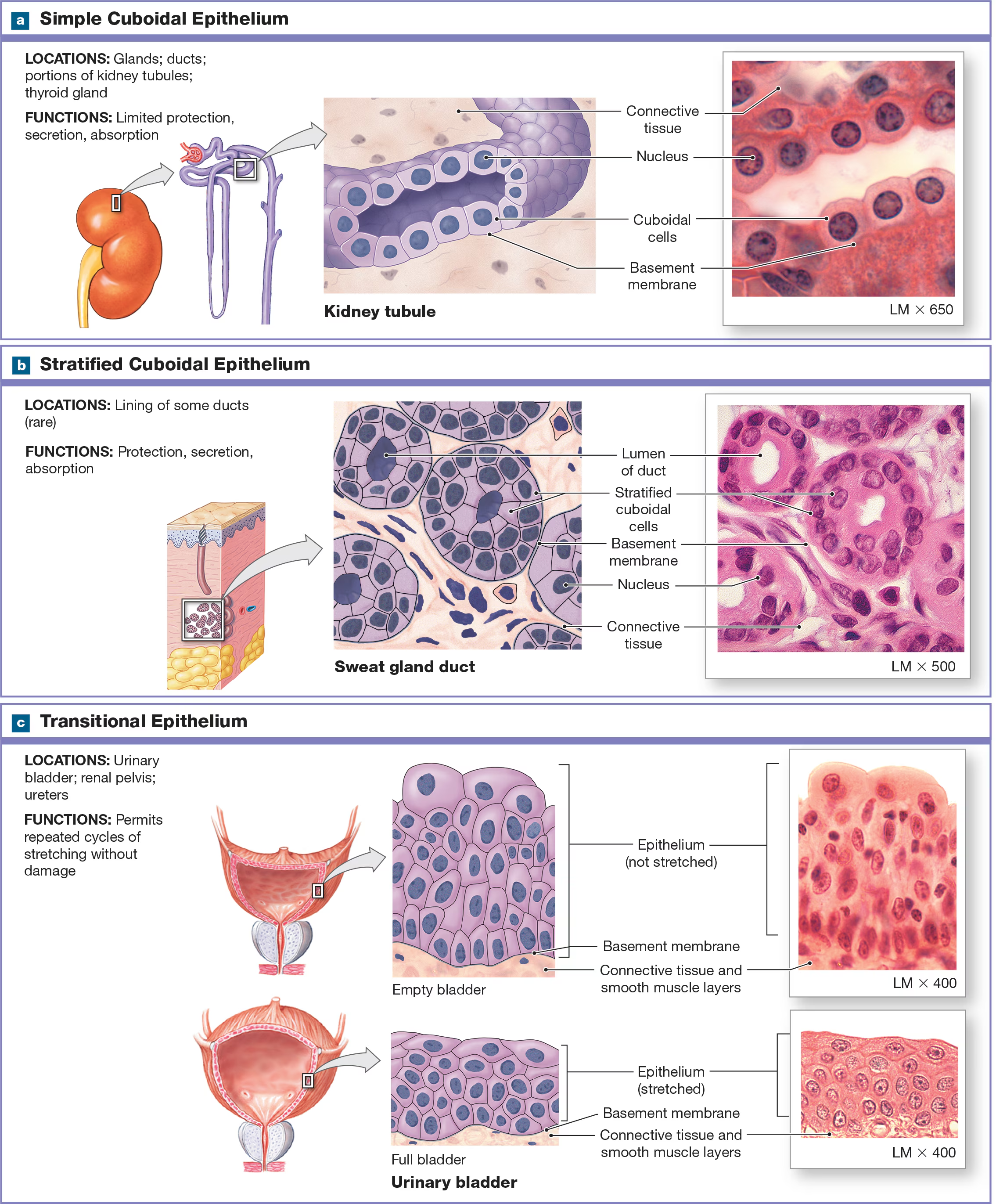
Transitional Epithelium/ urinary epithelium
Stratified but not classified by shape because its cells can change shape (apical = dome-shaped, but when stretched its flattened and appear squamous). Found in the urinary bladder and ureters