INTECH 2100 - Introduction to Multimedia
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
1
New cards
Multi (many);
Media (tools used as the medium of communication)
Media (tools used as the medium of communication)
Multimedia can split up into two words: ______ and ______ .
2
New cards
Interactivity
fundamental feature of multimedia, which gives user some control over the content
3
New cards
Multimedia Application
**application** which uses a collection of multiple media sources e.g. text, graphics, images, sound/audio, animation and/or video.
4
New cards
Digitized
Media elements have been **captured in a code** that the computer can understand.
5
New cards
Multimedia
It is a combination of text, art, sound, animation, and video. It is the use of multiple forms of media to present information.
6
New cards
electronic or digitally
Multimedia is delivered to the user by ________ manipulated means.
7
New cards
Multimedia Project
Its **development** requires creative, technical, organizational, and business skills.
8
New cards
Web-based multimedia
It is defined as an **online, interactive experience that incorporates two or more media elements** including text, graphics, sound, animation and video.
9
New cards
Media
It refers to the **communication channels** through which news, entertainment, education, data, or promotional messages are disseminated.
10
New cards
Print media (newspapers, magazines)
Broadcast media (tv, radio, billboards)
Digital or New Media (mail, telephone, fax, and Internet)
Broadcast media (tv, radio, billboards)
Digital or New Media (mail, telephone, fax, and Internet)
Types of Media
11
New cards
Text
Images
Video
Audio
Animation
Images
Video
Audio
Animation
Common Types of Multimedia used in Web Design
12
New cards
Text
A type of multimedia that is the **most basic form of multimedia** and is used to convey information.
13
New cards
Images
A type of multimedia that can be used to **illustrate concepts** or to make a website more visually appealing.
14
New cards
Video
A type of multimedia that can be used to **tell stories, demonstrate products, or provide educational content.**
15
New cards
Audio
A type of multimedia that can be used to add **sound effects, music, or narration to a website.**
16
New cards
Animation
A type of multimedia that can **create interactive elements** or make a website more visually stimulating.
17
New cards
Increase User Engagement
Improve Communication
Enhance the User Experience
Improve Communication
Enhance the User Experience
When used effectively, multimedia can help to:
18
New cards
Use high-quality media
Make sure the media is relevant
Use multimedia sparingly
Test your website on different devices
Make sure the media is relevant
Use multimedia sparingly
Test your website on different devices
Tips for using Multimedia in Web Design
19
New cards
Multimedia Design Principles
**guidelines** that help educators and instructional designers create effective and engaging learning materials using various media formats.
20
New cards
The Coherence Principle
__**Principle**__**: Cut out the extras.** Remove all the fluff. Use only the information that the learner needs. **Use simple text and simple visuals** that directly relate to the topic.
21
New cards
The Signaling Principle
__**Principle**__**:** Show the learner what to **pay attention to on the screen**. Highlight and put emphasis on the important words.
22
New cards
The Redundancy Principle
__**Principle**__**: With a narration voiceover, don’t use graphics and text.** Use only graphics on the screen.
23
New cards
The Spatial Contiguity Principle
__**Principle**__**:** Keep all related **text and graphics** **physically close together** in your frame.
24
New cards
The Temporal Contiguity Principle
__**Principle**__**:** Make sure the **visuals and audio occur at the same time**, instead of audio playing before or after.
25
New cards
The Segmenting Principle
__**Principle**__**:** Provide learners with control over thier learning. Make sure learning is **segmented into small chunks,** instead of long stream.
26
New cards
The Pre-training Principle
__**Principle**__**: Create an introductory guide** that teachers the basic definitions, terms, and concepts before beginning the course right away.
27
New cards
The Modality Principle
__**Principle**__**:** In **voiceover** supported learning, **limit the amount of text used**. **Rely on visuals** instead. Text should be used only for key definitions, list, and directions.
28
New cards
The Multimedia Principle
__**Principle**__**: Avoid using text on screen, use relevant visuals instead**. Be thoughtful about the visuals, make sure they enhance or clarify the information.
29
New cards
The Personalization Principle
__**Principle**__**: Keep your message simple and casual.** Avoid using overly professional sounding text, or long, complex words.
30
New cards
The Voice Principle
__**Principle**__**:** Use audio that was recorded by a **human**, instead of an automated robotic voice.
31
New cards
The Image Principle
__**Principle**__**:** Use relevant animations and visuals. **Limit the amount of talking head screen time** by the instruction.
32
New cards
Hypertext
It is a text which contains **links** to other **texts**.
\
It is non-linear documents. By clicking on the hot spots in the text, the reader is immediately transported to related material in the document.
\
It is non-linear documents. By clicking on the hot spots in the text, the reader is immediately transported to related material in the document.
33
New cards
Hot Sports or Overview Mechanisms
In hypertext, the navigation in the document is by _________.
34
New cards
Ted Nelson
Hypertext was invented by _________ around 1965,
35
New cards
Hypertext
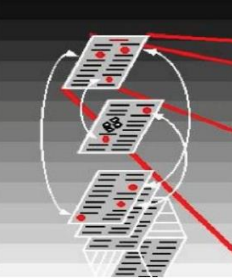
36
New cards
Hypermedia
It is not constrained to be text- based. It can include **other media**, e.g., graphics, images, and especially the continuous media – sound and video.
37
New cards
Hypermedia
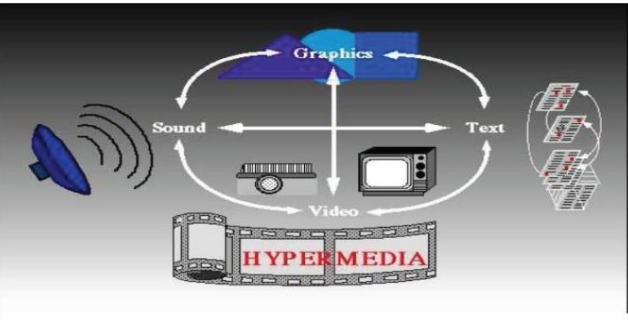
38
New cards
The World Wide Web (WWW)
PowerPoint Application
Adobe Acrobat (or other PDF software)
Adobe Products
PowerPoint Application
Adobe Acrobat (or other PDF software)
Adobe Products
Examples of Hypermedia Applications
39
New cards
World Wide Web (WWW)
It is the best example of a hypermedia application.
40
New cards
Linear
A multimedia website can be ___________, which users start at the beginning and progress through a set sequence of events until they reach the end.
41
New cards
Non-linear
Most websites use a _________ approach to navigation, which users have more control over what they are interested in pursuing.
42
New cards
Book
Film
Film
Examples of Linear Multimedia
43
New cards
Interactive Multimedia
It enables the user to **directly respond to** and control any or **all of the media elements**. Hence, these users become active participants instead of the passive recipients of information.
44
New cards
1) MM refers to the integration of multiple forms of expression. HM is a more diverse form of term used in non-linear data representation.
\
2) MM requires multimedia delviery systems. with audio, video, and display output. HM uses clickable links on web browsers to access media.
\
3) MM comes in two formats: Linear and Non-Linear. HM is a non-linear representation of interactive multimedia information.
\
4) MM uses variety of output devices. HM uses computer display as output device.
\
5) MM model is based on integration and interactivity. HM model is based on interconnectivity and cross-referencing.
\
2) MM requires multimedia delviery systems. with audio, video, and display output. HM uses clickable links on web browsers to access media.
\
3) MM comes in two formats: Linear and Non-Linear. HM is a non-linear representation of interactive multimedia information.
\
4) MM uses variety of output devices. HM uses computer display as output device.
\
5) MM model is based on integration and interactivity. HM model is based on interconnectivity and cross-referencing.
Differences of Multimedia and Hypermedia
45
New cards
Integration and Interactivity
Multimedia model is based on _______.
46
New cards
Interconnectivity and Cross-referencing
Hypermedia model is based on __________.
47
New cards
ASCII
Most text files store their text using the _______ coding scheme.
48
New cards
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
ASCII stands for __________.
49
New cards
7
Each character is translated into how many bits.
50
New cards
Typography
It is the art and technique of **arranging type** to make written language legible, readable, and appealing when displayed.
51
New cards
Typeface
Typeface style, width and height.
Typeface style, width and height.
The Basic Elements of Text
52
New cards
X-Height
The height of every individual character is called _______.
53
New cards
similar
When pairing fonts together, most graphic designers usually pick a typeface with _________ (similar/different) x-height.
54
New cards
set width
It refers to the area of the body of the letter and the buffering space that follows.
55
New cards
point system.
In text, the most popular way to measure type is called the _________.
56
New cards
Typeface
It is the name of the design in full-style or family of styles. It is the collective name of a family of related fonts.
57
New cards
Font
In text, it refers to the format or storage mechanism. It is the **variation in weight and size** of a typeface.
58
New cards
1 Ascender Line
2 Base Line
3 Descender Line
4 X-Height
5 Upper Case Character
6 Lower Case Character
2 Base Line
3 Descender Line
4 X-Height
5 Upper Case Character
6 Lower Case Character
The Anatomy of Type (1 - 6)

59
New cards
Tracking
Kerning
Leading
Kerning
Leading
The Advanced Elements of Text
60
New cards

Tracking
It is the space between text characters.
61
New cards
Letter spacing.
Tracking is also referred to as _________.
62
New cards
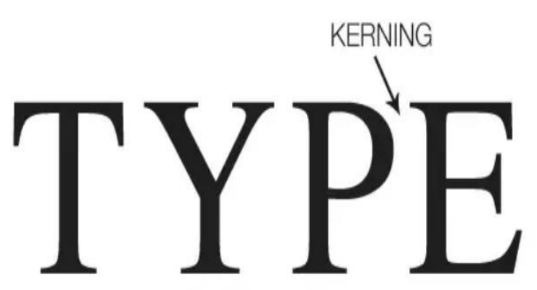
Kerning
It only refers to the space in between letters and characters.

63
New cards

Leading
It addresses the **vertical gaps** between lines of text - often crucial in the creation of magazine articles, blog pages, and other pieces of written work.
64
New cards
Pixels
Graphics on a screen are made up of tiny blocks called __________.
65
New cards
Picture Elements
‘Pixels’ is short for _____.
66
New cards
Higher
__**Higher/Lower.**__ The more pixels on the screen, the ________ the resolution and the ________ the quality of the picture will be.
67
New cards
More
__**More/Less**__. The higher the image resolution, the ____ memory is needed to store the graphic.
68
New cards
Raster/Bitmap Image
Vector Graphics
Vector Graphics
Types of Image
69
New cards
Raster/Bitmap
This type of image is organized as a grid of colored squares called pixels.
70
New cards
.jpeg
.png
.gif
.png
.gif
File Format of Raster/Bitmap Images
71
New cards
binary number
Each color of a raster/bitmap image is stored as a _________.
72
New cards
Vector graphics
This type of image is computer images created using a **sequence of commands or mathematical statements** that place lines and shapes in a two-dimensional or three-dimensional space.
73
New cards
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG)
One of the most common vector file formats __________. It is an open standard for vector graphics.
74
New cards
CAD packages
AutoShapes in Microsoft Office
animated movies
Encapsulated PostScript (EPS)
Animation programs such as Blender and Adobe After Effects
Image manipulation programs such as Adobe Photoshop and GIMP
Portable Document Format (PDF)
Windows Meta-File (WMF)
AutoShapes in Microsoft Office
animated movies
Encapsulated PostScript (EPS)
Animation programs such as Blender and Adobe After Effects
Image manipulation programs such as Adobe Photoshop and GIMP
Portable Document Format (PDF)
Windows Meta-File (WMF)
Vector graphics are used in:
75
New cards
Joint Photographer’s Expert Group
Meaning of JPEG
76
New cards
JPEG/JPG
It is the **most popular lossy** image format. It allows the users to **specify what level of compression** they desire.
\
It is often used for **digital camera images** because it has a fairly small file size for the quality that it displays.
\
It is often used for **digital camera images** because it has a fairly small file size for the quality that it displays.
77
New cards
Portable Network Graphics
Meaning of PNG
78
New cards
PNG
It is the **best of lossless image formats**. It is widely supported across web. It allows you to include an alpha channel within file.
\
It is often used where the **graphic might be changed by another person** or where the **image contains layers of graphics that need to be kept separate** from each other. It is high quality.
\
It is often used where the **graphic might be changed by another person** or where the **image contains layers of graphics that need to be kept separate** from each other. It is high quality.
79
New cards
BitMaP
Meaning of BMP
80
New cards
BMP
Image format that needs to be **avoid if possible**. They offer **little to no compression** which results in large files.
81
New cards
Tagged Image File Format
Meaning of TIFF/TIF
82
New cards
TIFF/TIF
This image format offers **both compressed and uncompressed** version. Compressed are similar to PNG, and uncompressed is similar to BMP.
83
New cards
Portable Document Format
Meaning of PDF
84
New cards
PDF
It is the **most widely used document format**. It is a great vector image format. It is created by Adobe.
85
New cards
Encapsulated PostScript
Meaning of EPS
86
New cards
EPS
It is the most common vector image format that is also the standard format for print industry.
87
New cards
Graphics Integrated Format
Meaning of GIF
88
New cards
GIF
It is a lossless format that supports both **animated and static images**. It is great for webpage banner ads.
\
It compresses images to a **maximum 8-bit colour depth**, making it unsuitable for high-quality photographs. It is often used where **transparency is needed** on the graphic.
\
It compresses images to a **maximum 8-bit colour depth**, making it unsuitable for high-quality photographs. It is often used where **transparency is needed** on the graphic.
89
New cards
1 bit
Color depth of Black and White Image
90
New cards
24-bit
Most computer systems and digital cameras use ______ images.
91
New cards
Metadata
It means ‘data about data’ and provides information about the image..
92
New cards
filename
file format - eg JPEG, GIF or PNG
dimensions
resolution
colour depth
time and date the image was last changed
camera settings when the photo was taken
GPS
file format - eg JPEG, GIF or PNG
dimensions
resolution
colour depth
time and date the image was last changed
camera settings when the photo was taken
GPS
Metadata includes:
93
New cards
Compression
It is used to reduce file sizes and change various attributes of an image file.
94
New cards
file type
resolution
dimensions
bit depth
resolution
dimensions
bit depth
Compression change various attributes of an image files which include:
95
New cards
Lossy Compression Algorithm
Lossless Compression Algorithm
Lossless Compression Algorithm
Types of Compression
96
New cards
Lossless Compression Algorithm
It reduces the size of files **without losing any information or quality** in the file, which means that we can **reconstruct the original data** from the compressed file.
\
It saves less space, but won’t usually impact your image quality.
\
It saves less space, but won’t usually impact your image quality.
97
New cards
Lossy Compression Algorithm
It reduces the size of files by **discarding the less important information in a file**, which can significantly **reduce file size but also affect file quality.**
\
It will save you the most space, but can affect your image quality.
\
It will save you the most space, but can affect your image quality.
98
New cards
JPEG
Image Format/s that Use/s Lossy Compression Algorithm
99
New cards
RAW, BMP, PNG, GIF
Image Format/s that Use/s Lossless Compression Algorithm
100
New cards
Magenta
Cyan
Yellow
Cyan
Yellow
Three Base Colors